- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Data Center and Cloud
- Data Center and Cloud Knowledge Base
- Understanding and Deploying UCS B-Series Storage Area Networking
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on
10-15-2009
03:43 PM
- edited on
03-25-2019
01:23 PM
by
ciscomoderator
![]()
This document focuses on connecting UCS 6120XP Fabric Interconnect Switch to uplink SAN storage array using fibre channel via Cisco MDS-9124 SAN Switch
Before you begin, make sure you are familiar with the concepts discussed in the previous chapters of this document
Unified Communications Virtualization Deployment Guide On UCS B-Series Blade Servers
VMWare ESXi 4.0 Installation on UCS Blade Server with UCS Manager KVM
Understanding and Deploying UCS B-Series LAN Networking
Introduction
In Data Centers, there are about four different options available for storing and running virtual machines
Local Storage (DAS)
iSCSI
NFS
Fibre Channel
The local storage or DAS (Direct Attached Storage) is an option where virtual machines are stored on the local hard drives attached in the rack mount servers (like Cisco UCS C210M1 rack mount servers).
Then we have iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface) option. As the name suggest it a mechanism to transport SCSI data over IP based networks. With this option the storage array (or hard disk) is not directly attached to the server machine rather it is connected to the server machine (which some times also referred to as word "compute" meaning CPU, Memory, I/O) via iSCSI protocol.
NFS (Network File System) in the past mainly used for file sharing purposes. But the simplicity of NFS protocol and 10GiG Ethernet availability in the data centers making it a strong choice to run virtual machines as well. It is basically a shared folder on the IP network. It allows a user on a client computer to access files over a network in a manner similar to how local storage is accessed.
Fiber Channel is widely accepted protocol used for SAN (Storage Area Networking). It has substantially lower CPU cost than iSCSI and NFS. And this is discussed in this document.
SAN Protocol Choices
There are multiple choices available in order to connect to the SAN storage. The decision is mainly based on the storage area networking you have in place in your Data Center and the type of SAN connectivity you are using or going to use. The most popular choices, in order to transport the storage data over the network, available today are
Fiber Channel Protocol and
iSCSI
Cisco's current recommendation is to use the Fiber Channel to run Virtual Unified Communications applications on UCS platform. But as the data center are evolving and 10GE fabric is becoming more popular in data centers, the iSCSI and NFS offer compelling reasons to go with as well.
For the purpose of this document we are going to discuss the Fiber Channel as our main SAN connectivity/networking protocol.
Physical Wiring Options
From the physical wire connectivity following option is available in UCS Architecture
Connect the Fabric Interconnect switch to another SAN switch (could be MDS or Nexus switch for instance) and eventually to the rest of SAN network including SAN-storage arrays.
NOTE: For Virtual UC deployments, Cisco's recommendation is to use the multi tier model to avoid single point of failure. Also it is not a supported configuration to directly connect UCS Fabric Interconnect switch to the SAN storage array.
Following network diagram illustrates a typical UC on UCS B-Series Architecture in Data Center.
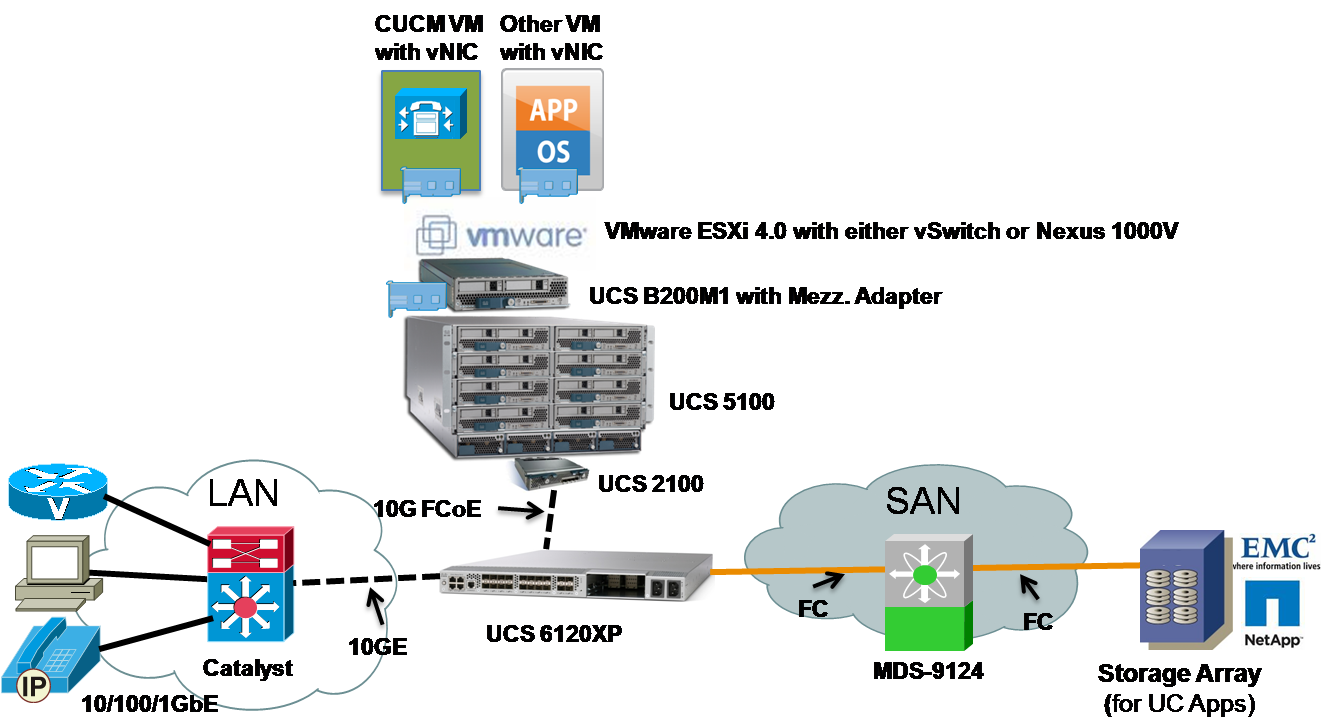
The terms “storage server” and “storage array” will be used interchangeably in this document
N-Port Virtualization (NPV) Mode
The fabric interconnect operates in N-Port Virtualization (NPV) mode and not as a FC switch in the fabric. This means that it does not require a FC domain ID to keep the number of domain IDs in the SAN fabric the same. The fabric interconnect joins the fabric through a normal FLOGI. The FLOGIs that comes from the server blade adapters is translated by the NPV process into FDISC into the fabric.
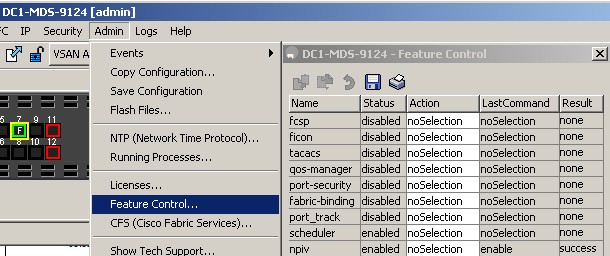
Make sure that upstream MDS switches are NPIV enabled, and assign the selected interface to the Cisco UCS with the appropriate VSAN number.
Configuring N Port Virtualization
N Port virtualization (NPV) reduces the number of Fibre Channel domain IDs in SANs. Switches operating in the NPV mode do not join a fabric; rather, they pass traffic between NPV core switch links and end devices, which eliminates the domain IDs for these edge switches.
NPV is supported by the following Cisco MDS 9000 switches only:
- Cisco MDS 9124 Multilayer Fabric Switch
- Cisco MDS 9134 Fabric Switch
- Cisco Fabric Switch for HP C-Class BladeSystem
- Cisco Fabric Switch for IBM BladeCenter
Configuration Screen Shots
Enable npvi via CLI (if you are unable to enable it via GUI)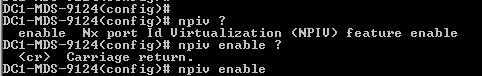
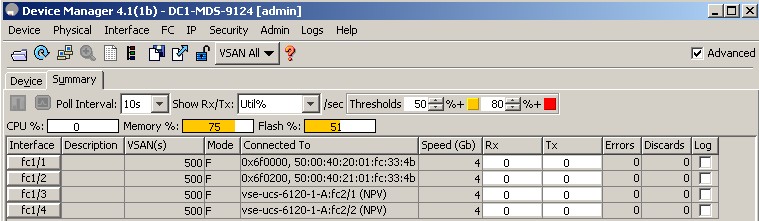
MDS Switch should show that npiv is enabled as shown in the following screen
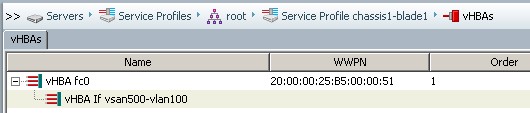
Following screen shows the virtual HBA (vHBA) configuration on the UCS B-Series service profile
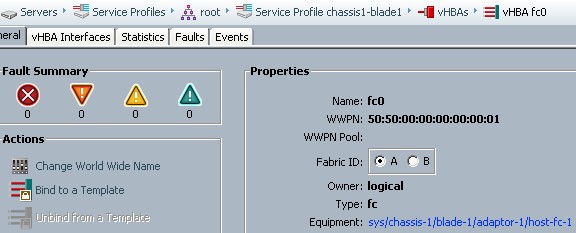
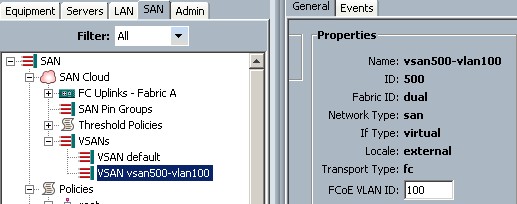
Make sure VSAN configuration is done and the VLAN is id is assigned within the VSAN (VSAN ID is 500 in the following example)
Troubleshooting
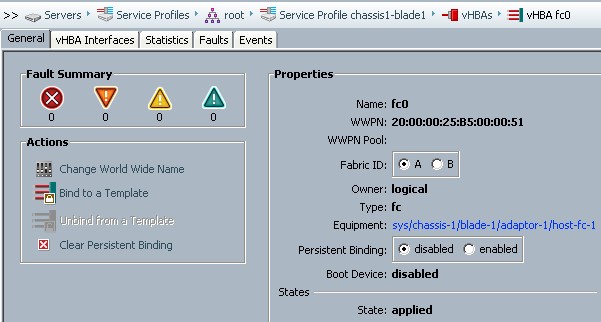
WWPN should be set to correct value otherwise MDS won't perform switching
Hint:
In UCS Service Profile
- WWPN is assigned to vHBA
- WWNN is assgined to Server
In order to make it work with UCS B-Series, make sure that the minimum MDS software version is 3.3 (1c) or above.
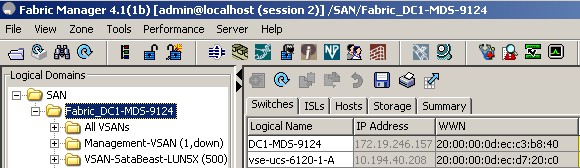
If "show flogi database" shows the UCS WWPNs' then it means the MDS SAN switch is successfully
connected to UCS.
DC1-MDS-9124# show flogi database
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
INTERFACE VSAN FCID PORT NAME NODE NAME
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
fc1/1 500 0x6f0000 50:00:40:20:01:fc:33:4b 20:01:00:04:02:fc:33:4b
fc1/2 500 0x6f0200 50:00:40:21:01:fc:33:4b 20:01:00:04:02:fc:33:4b
fc1/3 500 0x6f0300 20:41:00:0d:ec:d7:20:c0 21:f4:00:0d:ec:d7:20:c1
fc1/4 500 0x6f0400 20:42:00:0d:ec:d7:20:c0 21:f4:00:0d:ec:d7:20:c1
fc1/7 500 0x6f0100 21:00:00:1b:32:8a:eb:e7 20:00:00:1b:32:8a:eb:e7
Total number of flogi = 5.
DC1-MDS-9124#
Run following command on the UCS Fabric Interconnect switch
vse-ucs-6120-1-A(nxos)# show npv flogi-table
No flogi sessions found.
If UCS Fabric Interconnect Switch returns no flogi session, then it means it is not connect to MDS and further config review and troubleshooting is required. This command should show some entries
Following screen shows some important (but not all) config. verification steps
References:
- Comparison of Storage Protocol Performance in VMware vSphere™ 4
http://www.vmware.com/files/pdf/perf_vsphere_storage_protocols.pdf
- Iometer is a free storage performance testing tool that can be configured to measure throughput and latency under a wide variety of access profiles.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I started here, but ended up here.
I was evaluating a design of UCS B series, and have either 9124 or 9148 as upstream FC switches. 9124 is the least expensive, but, in its data sheet, it doesn't say it supports NPIV (or NPV core): "NPVmode with F-Port trunking and channeling (edge switch deployment only)"
NPV is the FC mode in which the FI's run. And, in that case, you need NPIV in the upstream switch. So, that's a bit confusing here, though the configuration shown must be valid, because I suppose you tested it.
Also, take a look at the thread above, as I was pointed at some limitations of the 9124 if run in NPIV.
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: