Introduction
Baseboard Management Controller (BMC), also called as Service processor, resides on each blade for OS independent/pre-OS management. The BMC's focus is to monitor/manage a single blade in the UCS chassis. The UCS manager talks to the BMC and configures the blade. BMC controls things like BIOS (upgrade/downgrade), assigning MAC addresses, assigning WWNs, etc.
BMC Overview
BMC runs independent of the processor on the blade and hence in any event of processor, memory or any other hardware failure, BMC will still provide the services. The BMC starts running as soon as the blade is inserted into the chassis. The power button on the front side of the blade does not turns on/off the BMC. The management connectivity to BMC is through two 100BASE-T interfaces on the blade to the chassis internal management, these connections are not via the NIC's or the Mezz cards used by the blade to send traffic. However at any given instance the connectivity to BMC is only via one of the two 100BASE-T interfaces, the other one being redundant.
The BMC maintains two IP instances per 100BASE-T ethernet interface, one IP instance connects to the "chassis left/right infrastructure VLAN" for communication to CMC (Chassis Management Controller) and the other IP instance connects to the "fabric A/B infrastructure VLAN" for communication to endpoints external to the chassis. Hence the BMC has a total of four IP addresses on two physical ethernet interfaces. The BMC firmware is stored on separate flash chips and multiple versions of firmware can reside on the flash at a time. BMC gets an external IP address from a pool created in the UCS manager; this IP is then used to access BMC services like KVM. The BMC communicates with BIOS running on the blade using IPMI.
Integration with UCS
BMC for Cisco Unified Computing System is tightly integrated with the Cisco UCS Manager and uses a policy-based approach to configure, patch, and update its associated storage, network, and server resources. BMC communicates with the Cisco UCS Manager through a granular set of XML interfaces that directly expose the hardware service profiles from the Cisco UCS Manager. It integrates with and builds on the Cisco UCS Manager to automate the full server stack provisioning of the Cisco Unified Computing System, including the virtual hardware and network resources, base OS, drivers, disk layouts, system software, application middleware, and custom code and content at the business-application layer. Supporting configurations specific to Cisco Unified Computing System as well as any user-defined custom configurations.
Tasks performed by BMC
Tasks that the BMC perform includes:
a) Blade inventory
b) Monitor sensors (blade voltages, temp, fans, etc.)
c) Log events for failure analysis.
d) LED guided diagnostics
e) Power management
f) Provide remote management capabilities (IPMI, KVM, vMedia (using USB) and SOL(Serial over LAN))
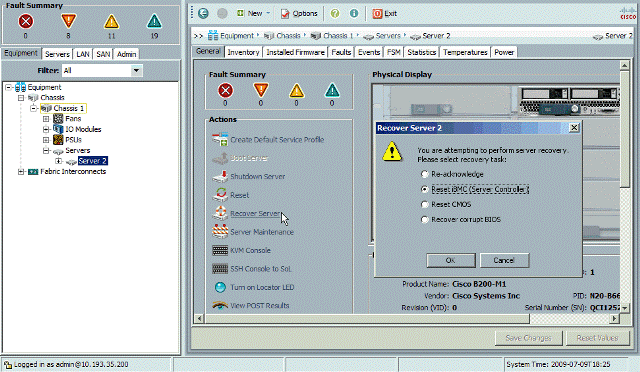
In case you are not able to access the services provided by the BMC; you will need to reboot the BMC. This can be done using UCS manager and navigating to Equipment tab > Chassis {no.} > Server {no.} and clicking on Recover Server in the General tab on the work pane. Then select Reset iBMC and click OK. You can also directly telnet to the BMC's IP address and give a reboot command. Any of these methods do not affect any OS running on the blade.