ARP or Address Resolution Protocol helps mapping IP to a mac address , used when a host is trying to reach another host in the same VLAN/Subnet
What problems can someone cause using ARP ? You can bring down the entire services in that VLAN with ARP
How can you do that. Assume a host PCA has MACA and another PCB sends out ARP request for any host or sends out a GARP using PCA's MAC as the source mac address. This causes other hosts in that VLAN to update their ARP cache and send the packet destined to PCA IP to PCB. This is one of the ways you can cause service interruption. For details refer the following link on ARP spoofing
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARP_spoofing
In 3 years that I have spent in LAN Switching TAC, I have not come across such issues often. Whenever I have, it was sometimes very easy to track down the rouge device but at times it turned out to be a PIA.
This blog is to provide a way to help narrow down the rogue host in a huge network
In simple attcks where the rouge host was sending ARP request sourced from a different host MAC address, what we do is to identify the port on which the MAC address is learnt, backtrack till you either reach the legitimate host and on multiple tries you will also be able to track down the rouge host.
Switch# show mac address-table address xxxx.xxxx.xxxx
Simple right. Well, if it is the scenario I mentioned above, it will be simple.
However, consider the following scenario. What if the rouge host send out ARP request or GARP with IP address of the legitimate host but uses source MAC address as a bogus multicast MAC address. This will cause a few hosts to update their ARP cache with the wrong multicast MAC for unicast IP (Cisco devices do not update their ARP cache when they receive such ARP request/GARP with multicast MAC as source MAC)
So say users may lose access to an important server in the same VLAN - HOW WILL YOU DETECT THE ROGUE DEVICE NOW??
Note: Switches do not dynamically learn multicast MAC address, so you cannot backtrack they was we did in the case of unicast.
To make things worse, imagine you have a huge network !!!
Lets assume we have a network as shown below
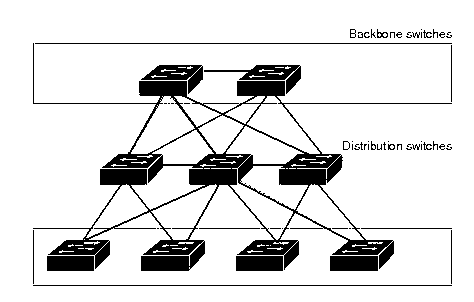
This may still look simple. Imagine an enterprise network with 20 switches and hundred's of hosts connected.
WHERE DO WE START?
WHAT DO WE DO?
First of all , lets create a SPANNING TREE loop free topology, after identifying blocked ports you will end up with the following topology

I always prefer to start from the root bridge and go down the tree - or you can start in the middle and move down or up (like binary search)
SPAN each active link (spanning tree forwarding), one at a time, ingress direction, to see from where the ARP request are coming - with this you can move from one switch to another and finally track the Switch which has the Rouge Host connected.
If you have a switch like the Catalyst 6500 all over the network , you can use an internal tool called ELAM . With ELAM we can track the incoming interface on which ARP was received - but you would need to call TAC for help on this one :-)
The above said procedure needs a lot of patience, you will be able to narrow down to the Rouge host, even if it takes some time.
How can one be proactive in avoiding such attacks ?? - using DHCP snooping with Dynamic ARP inspection. For details, refer the following
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12.2SX/configuration/guide/dynarp.html
Hope you guys enjoyed this one.
Please do not get any idea of becoming the rouge device, you will definitely be tracked (and there is a high probability you will be fired )
If you have liked this one, you will definately like my previous blog on VTP pruning
https://supportforums.cisco.com/community/netpro/network-infrastructure/switching/blog/2011/08/05/troubleshoot-l2-connectivty-issue-vtp-pruning
