- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Routing
- Re: NO LSA Type 2 For Stubs Links
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-13-2020 03:12 PM - edited 07-13-2020 03:18 PM
hey guys, i hope you all are doing well. just have a quick one. total noob here btw so my apologies if this seems dumb.
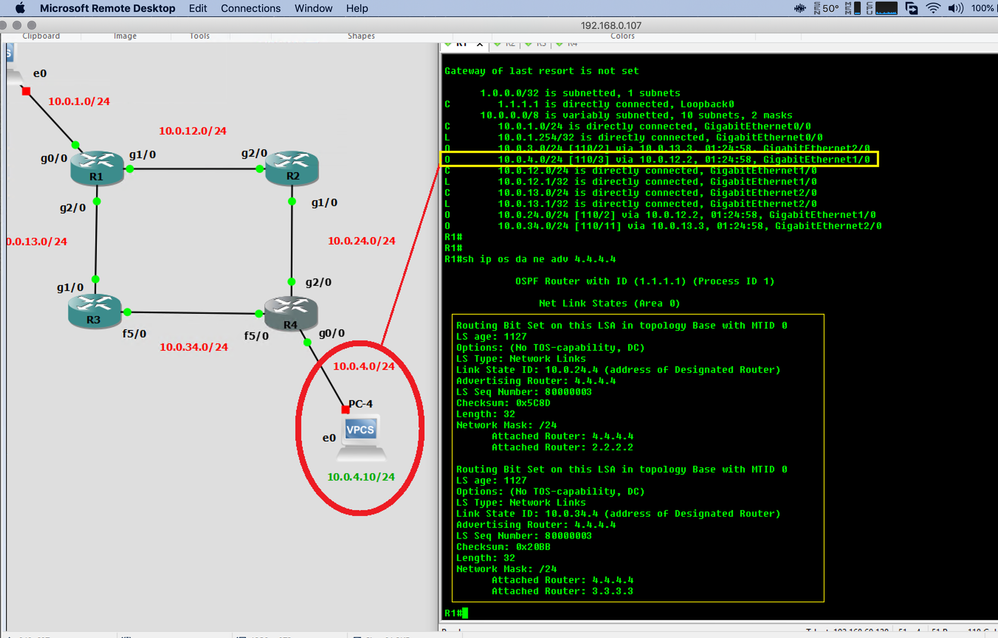
on my lab, as i follow one of Keith Barker's video (screenshot), upon verification on R1, i noticed that R4's network 10.0.4.0/24 (supposedly a LAN of its own) isn't included in R4's LSA Type2. Only networks directly connected to its interfaces fa5/0 (to R3) & gi2/0 (to R2) are created. i would expect stubs are included in "Network LSAs" considering they're technically "networks", are they not?
nonetheless, they're learned as "OSPF" routes most probably through LSA Type 1. i'm definitely missing something here.
enlighten me, oh wise ones! :(
- jiro
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
Routing Protocols
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-15-2020 02:19 AM
Hello @sujirou ,
@Martin L is right there is no real advantage for OSPF to create an LSA type 2 for stub networks because there are no OSPF neighbours out there and no election of DR/BDR takes place.
The network LSA is needed if two or more OSPF routers share a common segment the OSPF network type is broadcast (the default for LAN interfaces) and the network LSA describes from the point of view of the DR and using as link-id the DR LAN ip address all the nodes connected to the common segment.
Just to be clear in modern networks in point to point links to avoid DR/BDR election and the creation of an unnecessary LSA type 2 is best practice to use ip ospf network point-to-point (only two neighbors on the link).
So the expectation to see a stub network to generate its own network LSA is not correct. OSPF attempts to minimize and optimize the number of LSAs in the database and the network LSA for a stub network is useless as it provides no additional info as the list of nodes on segment is empty.
Stub networks are listed and advertised in router LSA, this is correct and sufficient to describe the topology within the area.
Hope to help
Giuseppe
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-13-2020 03:59 PM - edited 07-14-2020 06:25 PM
I think show ip ospf database router x.x.x.x will show you what you looking for. try , let me know
Regards, ML
**Please Rate All Helpful Responses **
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-14-2020 01:58 PM - edited 07-14-2020 01:59 PM
my example:
R1#sh ip ospf database router 3.3.3.3
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.0.41) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 547
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 3.3.3.3
Advertising Router: 3.3.3.3
LS Seq Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0xB5C3
Length: 60
Number of Links: 3
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 3.3.3.3
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.255
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 10.0.34.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 10
Link connected to: a Transit Network
(Link ID) Designated Router address: 10.0.13.3
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 10.0.13.3
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 10
but if you do network adv-router R3 does not show whole story
R1#sh ip os da ne adv-router 3.3.3.3
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.0.41) (Process ID 1)
Net Link States (Area 0)
Routing Bit Set on this LSA
LS age: 536
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Network Links
Link State ID: 10.0.13.3 (address of Designated Router)
Advertising Router: 3.3.3.3
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0xEB89
Length: 32
Network Mask: /24
Attached Router: 3.3.3.3
Attached Router: 192.168.0.41
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-14-2020 02:17 PM
but if you do network adv-router R3 does not show whole story
R1#sh ip os da ne adv-router 3.3.3.3
this is precisely what i was looking for --> a stub link's entry in the LSA Type 2 data when you type that command. i would expect a stub to turn up along with transits since it's still a network :(
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-14-2020 02:04 PM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-14-2020 06:21 AM
Hello
Could you try the following:
sh ip ospf database router | in Stub|(Link ID)
Please rate and mark as an accepted solution if you have found any of the information provided useful.
This then could assist others on these forums to find a valuable answer and broadens the community’s global network.
Kind Regards
Paul
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-14-2020 02:09 PM
hi Paul, thank you for responding. i did that. it shows up (as expected) but only as Type1 LSA - coming from the "router" part of the command.
what i'm looking for is type2 when you issue a "sh ip ospf database network" command.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-14-2020 02:33 PM - edited 07-14-2020 02:36 PM
Hello
@sujirou wrote:
hi Paul, thank you for responding. i did that. it shows up (as expected) but only as Type1 LSA - coming from the "router" part of the command.
what i'm looking for is type2 when you issue a "sh ip ospf database network" command.
Why would you expect it to be a type2 LSA these LSA's are only shown for designated routers for the ospf area's
So a type 1 LSA would be for that network say in the bacbone area 0 (as shown in your OP) and if it was in a different area than the backbone the LSA for that networkwould become a type 3 summary or type 5 if redistibuted into ospf.
Please rate and mark as an accepted solution if you have found any of the information provided useful.
This then could assist others on these forums to find a valuable answer and broadens the community’s global network.
Kind Regards
Paul
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-14-2020 06:57 PM - edited 07-14-2020 09:07 PM
are you looking for specific format of output of database; looking for this Net Link States (highlight below)?
R1#sh ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 5 0x80000002 0x0020B9 1
3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 11 0x80000002 0x00B5C3 3
Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
10.0.13.3 3.3.3.3 11 0x80000001 0x00AD56
if so, you can only get it from sh ip ospf database - straight command on router, not from "remote" router. Getting info from perspective of R1 while R3 is DR, you need to do following:
step 1 show ip os databse to see Net type 2 and get Router ID that create it (DR), then , step 2, use sh ip ospf database router 3.3.3.3 to get more detailed info. Link called Transit Network is LSA type 2 you looking for. sh ip ospf database network output shows all attached routers to Type 2 LSA.
R3 is DR and connects to R1 ( BDR) on 10.0.13.0/24; R1 shows 1 link count in Router Link States section.
Regards, ML
**Please Rate All Helpful Responses **
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-14-2020 09:57 PM - edited 07-14-2020 10:12 PM
R3 is DR and connects to R1 ( BDR) on 10.0.13.0/24; R1 shows 1 link count in Router Link States section. --let me clarify this just in case there is a confusion. OSPF has 11 LSA types; Router LSA type 1 has 4 link types: p2p, transit network, stub network, and virtual link. Type 2 Network LSA is listed by R1 as 1 link count in Router Link States section and then as Type 2 right after. This is called Transit Network - refers as pseudonode - as OSPF cannot show 2 and more routers connected to shared medium where election is held.
to see what links are under Link count (details); use sh ip ospf database router 1.1.1.1. In my case of R1 has 1 link which is LSA type 2 listed as Transit network and connecting to R3
in case of R3, it has 2 stub networks (loopbacks) and Transit network connecting to R1.
Command sh ip os database network is used to show attached routers to type 2 , aka pseudonode
So, no, there is no LSA type 2 for stub links as stub is defined as dead-link which only has 1 router by osfp (no neighbors) and virtual link is special case.
Regards, ML
**Please Rate All Helpful Responses **
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-15-2020 02:19 AM
Hello @sujirou ,
@Martin L is right there is no real advantage for OSPF to create an LSA type 2 for stub networks because there are no OSPF neighbours out there and no election of DR/BDR takes place.
The network LSA is needed if two or more OSPF routers share a common segment the OSPF network type is broadcast (the default for LAN interfaces) and the network LSA describes from the point of view of the DR and using as link-id the DR LAN ip address all the nodes connected to the common segment.
Just to be clear in modern networks in point to point links to avoid DR/BDR election and the creation of an unnecessary LSA type 2 is best practice to use ip ospf network point-to-point (only two neighbors on the link).
So the expectation to see a stub network to generate its own network LSA is not correct. OSPF attempts to minimize and optimize the number of LSAs in the database and the network LSA for a stub network is useless as it provides no additional info as the list of nodes on segment is empty.
Stub networks are listed and advertised in router LSA, this is correct and sufficient to describe the topology within the area.
Hope to help
Giuseppe
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-18-2020 11:28 PM
Thank you, Sirs! all your responses are very well understood and very much appreciated! i know there was something i'm missing - that was to minimize data transfer across links as much as possible. perhaps additional overhead for router resources to have to sift through when in fact they offer little or no advantage to the overall performance as they would have when they were created. i just wanted to know the reason, and i think i got it. still a long way to go for me, but i'm getting there. thanks to you, Good Sirs! hope y'all are safe and sound always.
warm regards and deepest respect!
jiro
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: