- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Service Providers
- Service Providers Knowledge Base
- L2VPN using BGP for Auto Discovery & Signaling
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on 06-23-2013 08:38 AM
1. L2VPN Overview
Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) emulates the behavior of a LAN across an L2 switched, IP or MPLS-enabled IP network, allowing Ethernet devices to communicate with each other as they would when connected to a common LAN segment. Point-to-point L2 connections are vital when creating L2VPNs.
As Internet service providers (ISPs) look to replace their Frame Relay or Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) infrastructures with an IP infrastructure, there is a need to provide standard methods of using an L2 switched, IP or MPLS-enabled IP infrastructure. These methods provide a serviceable L2 interface to customers; specifically, to provide virtual circuits between pairs of customer sites.
Building a L2VPN system requires coordination between the ISP and the customer. The ISP provides L2 connectivity; the customer builds a network using data link resources obtained from the ISP. In an L2VPN service, the ISP does not require information about the customer's network topology, policies, routing information, point-to-point links, or network point-to-point links from other ISPs.
There are two fundamentally different kinds of Layer 2 VPN service that a service provider could offer to a customer: Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) and Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS). There is also the possibility of an IP-only LAN-like Service (IPLS).
A VPWS is a VPN service that supplies an L2 point-to-point service. As this is a point-to-point service, there are very few scaling issues with the service as such. Scaling issues might arise from the number of end-points that can be supported on a particular PE.
A VPLS is an L2 service that emulates LAN service across a Wide Area Network (WAN). With regard to the amount of state information that must be kept at the edges in order to support the forwarding function, it has the scaling characteristics of a LAN. Other scaling issues might arise from the number of end-points that can be supported on a particular PE.
2. Why L2VPN Auto Discovery?
Discovery refers to the process of finding all the PEs that participates in a given VPLS/VPWS instance. A PE either can be configured with the identities of all the other PEs in a given L2VPN service or can use some protocol to discover the other PEs. The later is called auto-discovery.
The former approach is fairly configuration-intensive, especially since it is required that the PEs participating in a given VPLS is fully meshed (i.e., that every PE in a given VPLS establish pseudowires to every other PE in that VPLS). Furthermore, when the topology of a VPLS changes (i.e., a PE is added to, or removed from, the VPLS), the VPLS configuration on all PEs in that VPLS must be changed.
In the auto-discovery approach, each PE "discovers" which other PEs are part of a given VPLS/VPWS by means of some protocol, in this case BGP. This allows each PE's configuration to consist only of the identity of the VPLS/VPWS instance established on this PE, not the identity of every other PE in that VPLS/VPWS instance -- that is auto-discovered. Moreover, when the topology changes, only the affected PE's configuration changes; other PEs automatically find out about the change and adapt.
2.1 VPLS auto-discovery
Conventional VPLS implementation requires manual configuration of each neighbor (VPLS PE) in the VPLS domain. When a new PE is added or removed from the VPLS domain, manual configuration of each PE in the VPLS domain is required.
Manual configuration changes add operational costs and increase the chance of network mis-configuration.
VPLS Auto Discovery eliminates the need to manually provision a VPLS neighbor. VPLS auto discovery automatically detects when new PEs are added or removed from the VPLS domain.
Auto-discovery by nature requires the information to be distributed to all members of a VPN - multipoint mechanism - which BGP is well suited for.
BGP is also used for signaling to exchange label bindings and signal MTU and state changes. Although LDP is better suited for signaling between two endpoints, it is needed for interoperability with other vendors.
2.2 VPWS auto-discovery
There is no true auto-discovery in VPWS as it is in VPLS. In VPWS, to connect CEs, user has to explicitly configure at each PE. All what is discovered in VPWS is the existence of other PEs.
3. VPLS Operation with BGP Auto-Discovery and Signaling
There are two primary functions of the VPLS control plane: auto-discovery, and setup and teardown of the pseudowires that constitute the VPLS, often called signaling. Both of these functions are accomplished with a single BGP Update advertisement.
When the L2VPN address-family (AF) and VPLS/VPWS subsequent address-family (SAF) are configured, BGP will connect to L2VPN to receive configured VPLS bridge domains. In the case of distributed BGP and the presence of multiple BGP speakers, L2VPN still communicates with one active BGP instance only. Therefore, BGP distribution is completely hidden from L2VPN.
When a VPLS Bridge domain is configured with BGP auto-discovery and signaling enabled, BGP needs to distribute NLRI for the VPLS bridge domain with the PE as the BGP next-hop and appropriate VE-ID. Additionally, the VPLS is associated with one or more BGP export Route Targets (RTs) that are also distributed (along with NLRI). VPLS SAFI NLRI uses AFI = 25 and SAFI = 65. The keywords "l2vpn" and "vpls-vpws" will be introduced to represent AF and SAF respectively in the BGP configuration.
If a PE receiving VPLS NLRIs is configured with the VPLS associated with a particular import RT, it can then import all the NLRIs tagged with the same RT. Generic BGP RPL policies for RT filtering will be supported for the VPLS/VPWS SAFI. No specific NLRI policy will be added for VPLS/VPWS SAFIs.
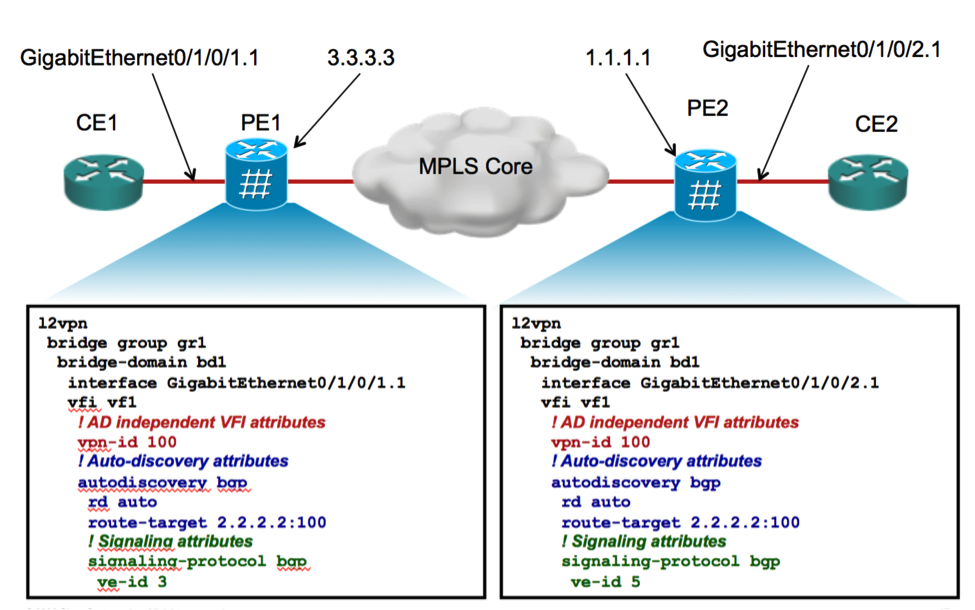
The NLRI format for VPLS BGP-AD & BGP Signaling is shown in the diagram below:
Length (2 octets) |
Route Distinguisher (8 octets) |
VE ID (2 octets) |
VE Block Offset (2 octets) |
VE Block Size (2 octets) |
Label Base (3 octets) |
Figure 1: NLRI format for VPLS with BGP Auto-discovery and Signaling
3.1 Responsibilities of BGP & L2VPN
3.1.1. BGP
- Advertise LRI, RTs, VE-IDs and label blocks using AFI = 25 SAFI = 65.
- Learn VE-ID, range, as well as the RD/RT configured under a VPLS bridge domain. <ve-id, range, rd> along with RT.
- Import NLRIs based on RT(s) and passes {VFI_ID, local label, remote-label and next-hop, layer2info} to L2VPN_MGR.
- Replay the necessary information for the imported VFIs on the request of L2VPN_MGR.
- Provide an API for L2VPN to retrieve AS number.
3.1.2. L2VPN
- Learns the configured VFIs from Sysdb.
- Obtains the configured data such as RT, VPLS-ID, VPN-ID, VE-ID, VE-ID range, CE-ID and CE-ID from Sysdb.
- Obtains label block from LSD and maps the local label range (block size, label base, offset) per VFI.
- Notifies BGP of the configured parameters such RT, etc. Also, L2VPN_MGR shall replay this information upon request from BGP.
- Receives information such as local label, remote label, etc., pertaining to the PWs from BGP, creates appropriate entries in the bridge database, and notifies L2FIB to setup forwarding plane.
- Display auto-discovered data via show output.
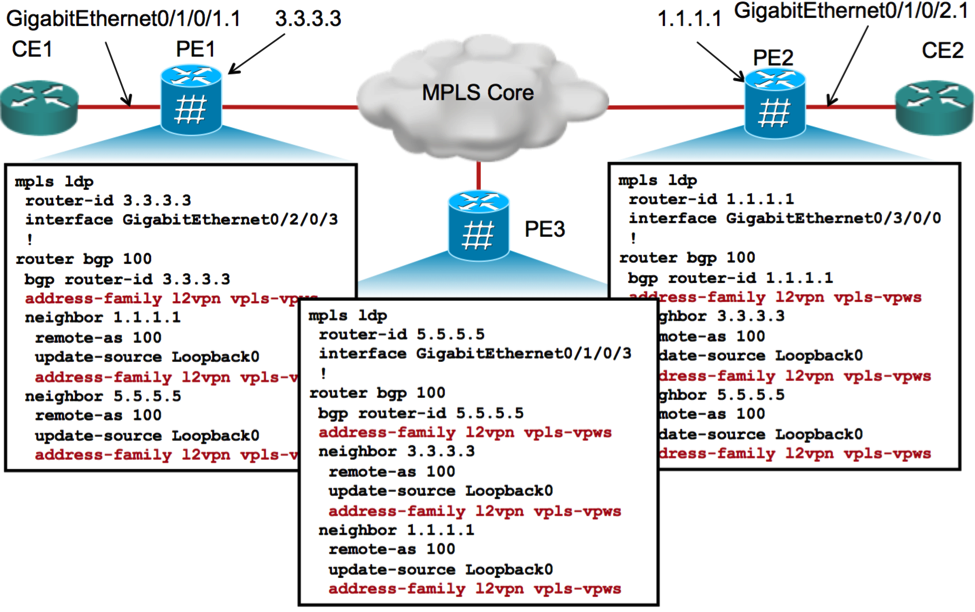
3.2 Configuring VPLS with BGP AD & Signaling
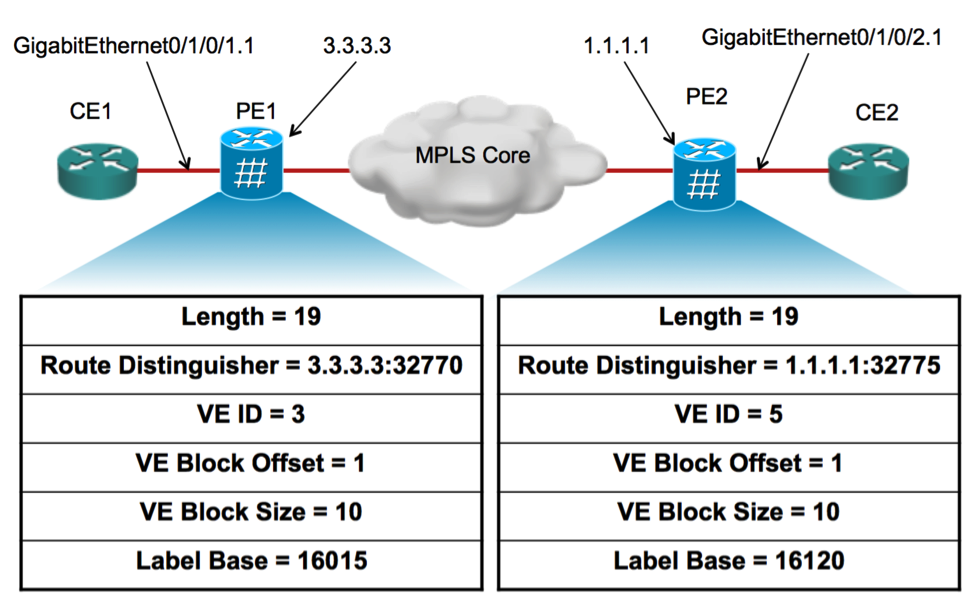
3.3 Example of NLRI for VPLS with BGP-AD & Signaling
3.4 Verification of VPLS with BGP-AD & Signaling
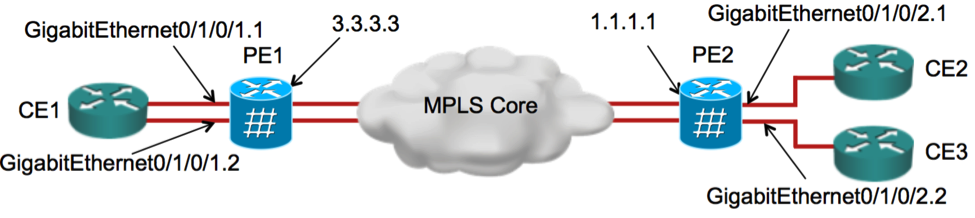
PE1:
PE1# show l2vpn discovery bridge-domain
Service Type: VPLS, Connected
List of VPNs (1 VPNs):
Bridge group: bg1, bridge-domain: bd1, id: 0
List of Local Edges (1 Edges):
Local Edge ID: 3, Label Blocks (1 Blocks)
Label base Offset Size Time Created
---------- ------ ---- -------------------
16015 1 10 01/24/2009 16:23:27
List of Remote Edges (1 Edges):
Remote Edge ID: 5, NLRIs (1 NLRIs)
Label base Offset Size Peer ID Time Created
---------- ------ ---- --------------- -------------------
16120 1 10 1.1.1.1 01/24/2009 16:23:46
PE1# show l2vpn bridge-domain detail
VFI vf1
VPN-ID: 100, Auto Discovery: BGP, state is Provisioned (Service Connected)
Route Distinguisher: (auto) 3.3.3.3:32770
Import Route Targets:
2.2.2.2:100
Export Route Targets:
2.2.2.2:100
Signaling protocol: BGP
Local VE-ID: 3 , Advertised Local VE-ID : 3
VE-Range: 10
PW: neighbor 1.1.1.1, PW ID 100, state is up (established)
Encapsulation MPLS, Auto-discovered (BGP), protocol BGP
MPLS Local Remote
------------ ------------------------------ -------------------------
Label 16019 16122
MTU 1500 1500
Control word disabled disabled
PW type VPLS VPLS
VE-ID 3 5
PE1# show bgp l2vpn vpls
BGP router identifier 3.3.3.3, local AS number 100
BGP generic scan interval 60 secs
BGP table state: Active
Table ID: 0x0
BGP main routing table version 898
BGP NSR converge version 3
BGP NSR converged
BGP scan interval 60 secs
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best
i - internal, S stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Rcvd Label Local Label
Route Distinguisher: 1.1.1.1:32775
*>i5:1/32 1.1.1.1 16120 nolabel
Route Distinguisher: 3.3.3.3:32770 (default for vrf bg1:bd1)
*> 3:1/32 0.0.0.0 nolabel 16015
*>i5:1/32 1.1.1.1 16120 nolabel
Processed 3 prefixes, 3 paths
PE2:
PE2# show l2vpn discovery bridge-domain
Service Type: VPLS, Connected
List of VPNs (1 VPNs):
Bridge group: bg1, bridge-domain: bd1, id: 0
List of Local Edges (1 Edges):
Local Edge ID: 5, Label Blocks (1 Blocks)
Label base Offset Size Time Created
---------- ------ ---- -------------------
16120 1 10 01/24/2009 16:03:26
List of Remote Edges (1 Edges):
Remote Edge ID: 3, NLRIs (1 NLRIs)
Label base Offset Size Peer ID Time Created
---------- ------ ---- --------------- -------------------
16015 1 10 3.3.3.3 01/24/2009 16:03:26
PE2# show l2vpn bridge-domain detail
VFI vf1
VPN-ID: 100, Auto Discovery: BGP, state is Provisioned (Service Connected)
Route Distinguisher: (auto) 1.1.1.1:32775
Import Route Targets:
2.2.2.2:100
Export Route Targets:
2.2.2.2:100
Signaling protocol: BGP
Local VE-ID: 5 , Advertised Local VE-ID : 5
VE-Range: 10
PW: neighbor 3.3.3.3, PW ID 100, state is up ( established )
Encapsulation MPLS, Auto-discovered (BGP), protocol BGP
MPLS Local Remote
------------ ------------------------------ -------------------------
Label 16122 16019
MTU 1500 1500
Control word disabled disabled
PW type VPLS VPLS
VE-ID 5 3
------------ ------------------------------ -------------------------
PE2# show bgp l2vpn vpls
BGP router identifier 1.1.1.1, local AS number 100
BGP generic scan interval 60 secs
BGP table state: Active
Table ID: 0x0
BGP main routing table version 802
BGP NSR converge version 7
BGP NSR converged
BGP scan interval 60 secs
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best
i - internal, S stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Rcvd Label Local Label
Route Distinguisher: 1.1.1.1:32775 (default for vrf bg1:bd1)
*>i3:1/32 3.3.3.3 16015 nolabel
*> 5:1/32 0.0.0.0 nolabel 16120
Route Distinguisher: 3.3.3.3:32770
*>i3:1/32 3.3.3.3 16015 nolabel
Processed 3 prefixes, 3 paths
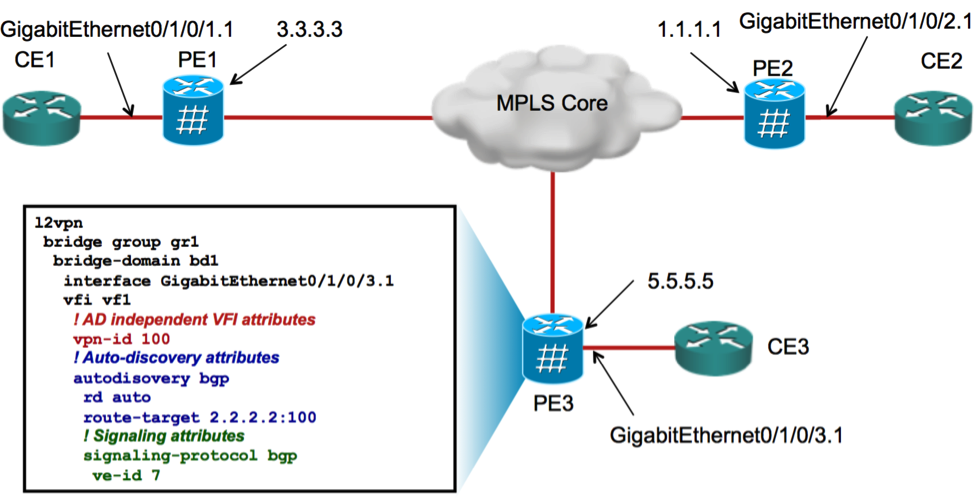
3.5 Adding a third PE (PE3)
A third PE (PE3) is added to the same VPLS domain with BGP AD & signaling.
3.5.1. L2VPN config for PE3
Following is the L2VPN config for PE3:
3.5.2. Verification of PE3
PE1# show l2vpn discovery bridge-domain
Service Type: VPLS, Connected
List of VPNs (1 VPNs):
Bridge group: bg1, bridge-domain: bd1, id: 0
List of Local Edges (1 Edges):
Local Edge ID: 3, Label Blocks (1 Blocks)
Label base Offset Size Time Created
---------- ------ ---- -------------------
16015 1 10 01/24/2009 16:23:27
List of Remote Edges (2 Edges):
Remote Edge ID: 5, NLRIs (1 NLRIs)
Label base Offset Size Peer ID Time Created
---------- ------ ---- --------------- -------------------
16120 1 10 1.1.1.1 01/24/2009 16:23:46
Remote Edge ID: 7, NLRIs (1 NLRIs)
Label base Offset Size Peer ID Time Created
---------- ------ ---- --------------- -------------------
16145 1 10 5.5.5.5 01/24/2009 16:40:32
PE1# show l2vpn bridge-domain detail
VFI vf1
VPN-ID: 100, Auto Discovery: BGP, state is Provisioned (Service Connected)
Route Distinguisher: (auto) 3.3.3.3:32770
Import Route Targets:
2.2.2.2:100
Export Route Targets:
2.2.2.2:100
Signaling protocol: BGP
Local VE-ID: 3 , Advertised Local VE-ID : 3
VE-Range: 10
PW: neighbor 1.1.1.1, PW ID 100, state is up ( established )
Encapsulation MPLS, Auto-discovered (BGP), protocol BGP
MPLS Local Remote
------------ ------------------------------ -------------------------
Label 16019 16122
MTU 1500 1500
Control word disabled disabled
PW type VPLS VPLS
VE-ID 3 5
------------ ------------------------------ -------------------------
PW: neighbor 5.5.5.5, PW ID 100, state is up ( established )
Encapsulation MPLS, Auto-discovered (BGP), protocol BGP
MPLS Local Remote
------------ ------------------------------ -------------------------
Label 16021 16147
MTU 1500 1500
Control word disabled disabled
PW type VPLS VPLS
VE-ID 3 7
------------ ------------------------------ -------------------------
PE1# show bgp l2vpn vpls
BGP router identifier 3.3.3.3, local AS number 100
BGP generic scan interval 60 secs
BGP table state: Active
Table ID: 0x0
BGP main routing table version 898
BGP NSR converge version 3
BGP NSR converged
BGP scan interval 60 secs
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best
i - internal, S stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Rcvd Label Local Label
Route Distinguisher: 1.1.1.1:32775
*>i5:1/32 1.1.1.1 16120 nolabel
Route Distinguisher: 3.3.3.3:32770 (default for vrf bg1:bd1)
*> 3:1/32 0.0.0.0 nolabel 16015
*>i5:1/32 1.1.1.1 16120 nolabel
*>i7:1/32 7.7.7.7 16145 nolabel
Route Distinguisher: 5.5.5.5:32780
*>i7:1/32 7.7.7.7 16145 nolabel
Processed 5 prefixes, 5 paths
4. VPWS Operation with BGP Auto-Discovery and Signaling
Similar to VPLS, two primary functions of the VPWS control plane is: auto-discovery, and setup and teardown of the pseudowires that constitute the VPWS to build a full mesh of CEs, often called signaling. Both of these functions are accomplished with a single BGP Update advertisement.
When a VPWS cross-connect is configured with BGP auto-discovery and signaling enabled, BGP needs to distribute NLRI for the xconnect with the PE as the BGP next-hop and appropriate CE-ID. Additionally, the cross-connect is associated with one or more BGP export Route Targets (RTs) that are also distributed (along with NLRI). VPLS SAFI NLRI uses AFI = 25 and SAFI = 25 [5]. The keywords "l2vpn" and "vpls-vpws" will be introduced to represent AF and SAF respectively in the BGP configuration.
The configured attributes are similar to VPLS with the following differences:
• CE-IDs instead of VE-IDs
• ce-id-range instead of ve-id-range.
• ACs are configured with remote CE-IDs. This association is save in L2VPN database and used to establish P2P xconnects.
If a PE receiving VPWS NLRIs is configured with the cross-connect associated with a particular import RT, it can then import all the NLRIs tagged with the same RT.
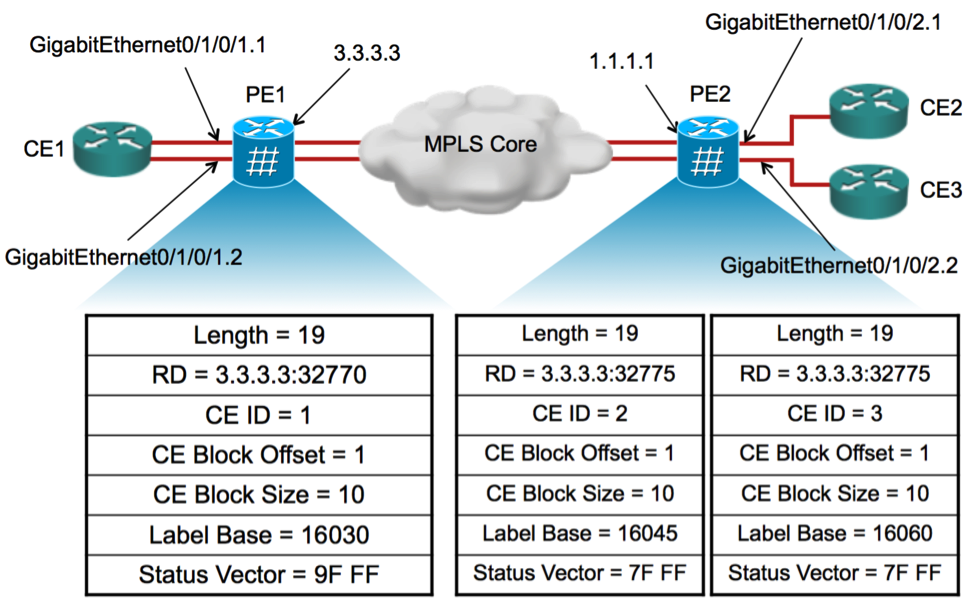
The NLRI is in the format shown in diagram below:
Length (2 octets) |
Route Distinguisher (8 octets) |
CE ID (2 octets) |
CE Block Offset (2 octets) |
CE Block Size (2 octets) |
Label Base (3 octets) |
Status Vector (SubTLV) |
Figure 2: NLRI format for VPWS BGP Auto-discovery and Signaling
4.1 Responsibilities of BGP & L2VPN
4.1.1. BGP
- Advertising NLRI, RTs, CE-IDs and labelblocks using AFI = 25 SAFI = VPWS.
- Learns CE-IDs, range, as well as the RD/RT configured under a vpls domain. <MP2MP_ID, ce-id, range, rd> along with RT for ce-id locally configured (rd and RT remain the same for a VPLS)
- Obtains label block from LSD and maps the local label range (block size, label base, offset) per MP2MP_ID (xconnect group)
- Imports NLRIs based on RT(s) and passes {MP2MP_ID, local label, remote-label and nexthop, remote CE-ID, l2info} to L2VPN_MGR for each local CE_ID
- Replay the necessary information for the imported VFIs on the request of L2VPN_MGR.
4.1.2. L2VPN
- Learns the configured Xconnect from Sysdb.
- Obtains the configured data such as RT, VPLS-ID, VPN-ID, VE-ID, VE-ID range, CE-ID and CE-ID from Sysdb.
- Notifies BGP of the configured parameters such RT, etc. Also, L2VPN_MGR shall replay this information upon request from BGP.
- Receives information such as local label, remote label, etc., pertaining to the PWs from BGP, update xconnect database entry, and notifies L2FIB to setup forwarding plane.
- Display auto-discovered data via show output.
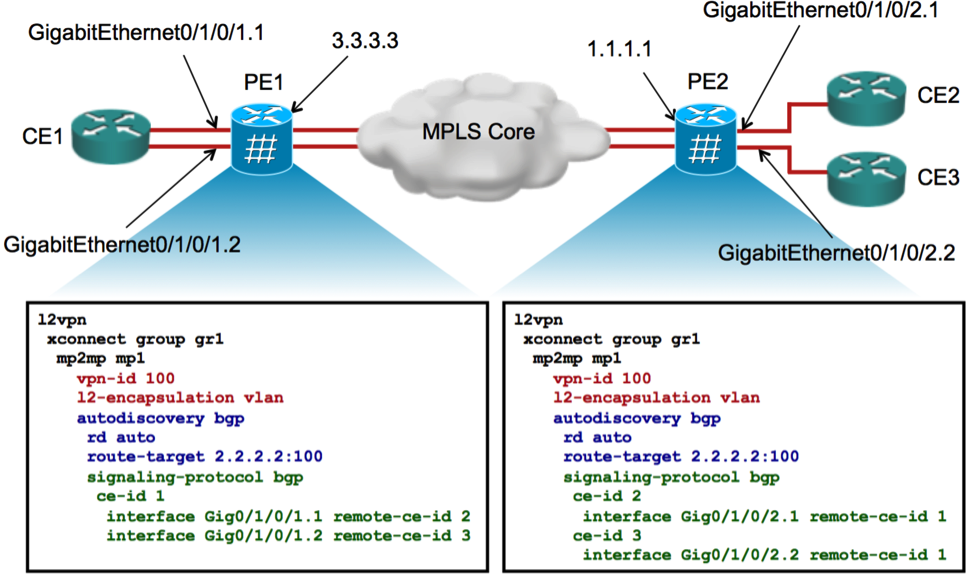
4.2 Configuring VPWS with BGP AD & Signaling
4.3 Example of NLRIs of VPWS with BGP AD & Signaling
4.4 Verification of VPWS with BGP-AD & Signaling
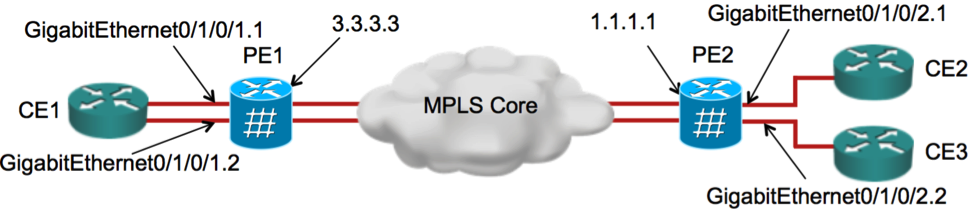
PE1:
PE1# show l2vpn discovery xconnect
Service Type: VPWS, Connected
List of VPNs (1 VPNs):
XC Group: gr1, MP2MP mp1
List of Local Edges (1 Edges):
Local Edge ID: 1, Label Blocks (1 Blocks)
Label base Offset Size Time Created
---------- ------ ---- -------------------
16030 1 10 01/24/2009 21:23:04
Status Vector: 9f ff
List of Remote Edges (2 Edges):
Remote Edge ID: 2, NLRIs (1 NLRIs)
Label base Offset Size Peer ID Time Created
---------- ------ ---- --------------- -------------------
16045 1 10 1.1.1.1 01/24/2009 21:29:35
Status Vector: 7f ff
Remote Edge ID: 3, NLRIs (1 NLRIs)
Label base Offset Size Peer ID Time Created
---------- ------ ---- --------------- -------------------
16060 1 10 1.1.1.1 01/24/2009 21:29:35
Status Vector: 7f ff
PE1# show l2vpn xconnect mp2mp detail
Group gr1, MP2MP mp1, state: up
VPN ID: 100
VPN MTU: 1500
L2 Encapsulation: VLAN
Auto Discovery: BGP, state is Advertised (Service Connected)
Route Distinguisher: (auto) 3.3.3.3:32770
Import Route Targets:
2.2.2.2:100
Export Route Targets:
2.2.2.2:100
Signaling protocol:BGP
CE Range:10
….
Group gr1, XC mp1.1:2, state is up; Interworking none
Local CE ID: 1, Remote CE ID: 2, Discovery State: Advertised
AC: GigabitEthernet0/1/0/1.1, state is up
Type VLAN; Num Ranges: 1
VLAN ranges: [1, 1]
MTU 1500; XC ID 0x2000013; interworking none
PW: neighbor 1.1.1.1, PW ID 65538, state is up ( established )
PW class not set, XC ID 0x2000013
Encapsulation MPLS, Auto-discovered (BGP), protocol BGP
MPLS Local Remote
------------ ------------------------------ -----------------------------
Label 16031 16045
MTU 1500 1500
Control word enabled enabled
PW type Ethernet VLAN Ethernet VLAN
CE-ID 1 2
------------ ------------------------------ -----------------------------
...
Group gr1, XC mp1.1:3, state is up; Interworking none
Local CE ID: 1, Remote CE ID: 3, Discovery State: Advertised
AC: GigabitEthernet0/1/0/1.2, state is up
Type VLAN; Num Ranges: 1
VLAN ranges: [2, 2]
MTU 1500; XC ID 0x2000014; interworking none
PW: neighbor 1.1.1.1, PW ID 65539, state is up ( established )
PW class not set, XC ID 0x2000014
Encapsulation MPLS, Auto-discovered (BGP), protocol BGP
MPLS Local Remote
------------ ------------------------------ -----------------------------
Label 16032 16060
MTU 1500 1500
Control word enabled enabled
PW type Ethernet VLAN Ethernet VLAN
CE-ID 1 3
------------ ------------------------------ -----------------------------
PE1# show bgp l2vpn vpws
BGP router identifier 3.3.3.3, local AS number 100
BGP generic scan interval 60 secs
BGP table state: Active
Table ID: 0x0
BGP main routing table version 913
BGP NSR converge version 3
BGP NSR converged
BGP scan interval 60 secs
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best
i - internal, S stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Rcvd Label Local Label
Route Distinguisher: 1.1.1.1:32775
*>i2:1/32 1.1.1.1 16045 nolabel
*>i3:1/32 1.1.1.1 16060 nolabel
Route Distinguisher: 3.3.3.3:32770 (default for vrf gr1:mp1)
*> 1:1/32 0.0.0.0 nolabel 16030
*>i2:1/32 1.1.1.1 16045 nolabel
*>i3:1/32 1.1.1.1 16060 nolabel
Processed 5 prefixes, 5 paths
PE2:
PE2# show l2vpn discovery xconnect
Service Type: VPWS, Connected
List of VPNs (1 VPNs):
XC Group: gr1, MP2MP mp1
List of Local Edges (2 Edges):
Local Edge ID: 2, Label Blocks (1 Blocks)
Label base Offset Size Time Created
---------- ------ ---- -------------------
16045 1 10 01/24/2009 21:09:14
Status Vector: 7f ff
Local Edge ID: 3, Label Blocks (1 Blocks)
Label base Offset Size Time Created
---------- ------ ---- -------------------
16060 1 10 01/24/2009 21:09:14
Status Vector: 7f ff
List of Remote Edges (1 Edges):
Remote Edge ID: 1, NLRIs (1 NLRIs)
Label base Offset Size Peer ID Time Created
---------- ------ ---- --------------- -------------------
16030 1 10 3.3.3.3 01/24/2009 21:09:16
Status Vector: 9f ff
PE2# show l2vpn xconnect mp2mp detail
Group gr1, MP2MP mp1, state: up
VPN ID: 100
VPN MTU: 1500
L2 Encapsulation: VLAN
Auto Discovery: BGP, state is Advertised (Service Connected)
Route Distinguisher: (auto) 1.1.1.1:32775
Import Route Targets:
2.2.2.2:100
Export Route Targets:
2.2.2.2:100
Signaling protocol:BGP
CE Range:10
...
Group gr1, XC mp1.2:1, state is up; Interworking none
Local CE ID: 2, Remote CE ID: 1, Discovery State: Advertised
AC: GigabitEthernet0/1/0/2.1, state is up
Type VLAN; Num Ranges: 1
VLAN ranges: [1, 1]
MTU 1500; XC ID 0x2000008; interworking none
PW: neighbor 3.3.3.3, PW ID 131073, state is up ( established )
PW class not set, XC ID 0x2000008
Encapsulation MPLS, Auto-discovered (BGP), protocol BGP
MPLS Local Remote
------------ ------------------------------ -----------------------------
Label 16045 16031
MTU 1500 1500
Control word enabled enabled
PW type Ethernet VLAN Ethernet VLAN
CE-ID 2 1
------------ ------------------------------ -----------------------------
...
PE2# show bgp l2vpn vpws
BGP router identifier 1.1.1.1, local AS number 100
BGP generic scan interval 60 secs
BGP table state: Active
Table ID: 0x0
BGP main routing table version 819
BGP NSR converge version 7
BGP NSR converged
BGP scan interval 60 secs
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best
i - internal, S stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Rcvd Label Local Label
Route Distinguisher: 1.1.1.1:32775 (default for vrf gr1:mp1)
*>i1:1/32 3.3.3.3 16030 nolabel
*> 2:1/32 0.0.0.0 nolabel 16045
*> 3:1/32 0.0.0.0 nolabel 16060
Route Distinguisher: 3.3.3.3:32770
*>i1:1/32 3.3.3.3 16030 nolabel
Processed 4 prefixes, 4 paths
5. Troubleshooting
L2VPN discovery not working
Check the router bgp configs, as sample configs shown below:
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#show run router bgp
router bgp 100
nsr
bgp router-id 2.2.2.2
bgp graceful-restart
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
neighbor 3.3.3.3
remote-as 100
update-source Loopback0
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
!
!
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:PE2#show run router bgp
router bgp 100
nsr
bgp router-id 3.3.3.3
bgp graceful-restart
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
neighbor 2.2.2.2
remote-as 100
update-source Loopback0
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
!
!
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:PE2#
Check the configs for BGP AD under l2vpn BD :
-> Check the VPN-ID matches with the other side PE
-> Check the ve-id is different from the other side PE
-> Check the rd, generally it will be auto
-> Check the signalling protocol configured the same correctly on both the ends
Sample Cfgs :
On PE1 :
l2vpn
bridge group bg1
bridge-domain bg1_bd1
interface PW-Ether2.1
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1/10.1
!
vfi bgp_ad1
vpn-id 1001
autodiscovery bgp
rd auto
route-target 10.1.1.1:1
signaling-protocol bgp
ve-id 1001
!
!
On PE2 :
l2vpn
bridge group bg1
bridge-domain bg1_bd1
interface GigabitEthernet0/2/1/11.101
!
vfi bgp_ad1
vpn-id 1001
autodiscovery bgp
rd auto
route-target 10.1.1.1:1
signaling-protocol bgp
ve-id 2001
!
!
!
If still the VFI is down
--> Start from IGP Neighborship
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#show ospf neighbor
* Indicates MADJ interface
Neighbors for OSPF 100
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
3.3.3.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:35 30.2.1.2 Bundle-Ether3
Neighbor is up for 23:38:15
3.3.3.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:38 30.1.1.2 TenGigE0/1/0/1
Neighbor is up for 1d22h
4.4.4.4 1 FULL/DR 00:00:35 60.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/1/9
Neighbor is up for 1d22h
Total neighbor count: 3
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#
--> Then check the BGP l2vpn Neighbors
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#show bgp l2vpn vpls summary
BGP router identifier 2.2.2.2, local AS number 100
BGP generic scan interval 60 secs
Non-stop routing is enabled
BGP table state: Active
Table ID: 0x0 RD version: 0
BGP main routing table version 1
BGP NSR Initial initsync version 1 (Reached)
BGP scan interval 60 secs
BGP is operating in STANDALONE mode.
Process RcvTblVer bRIB/RIB LabelVer ImportVer SendTblVer StandbyVer
Speaker 1 1 1 1 1 1
Neighbor Spk AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down St/PfxRcd
3.3.3.3 0 100 4 4 1 0 0 00:01:21 0
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#
--> Check the BD Detail for more details when the PW is down.
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#show l2vpn bridge-domain bd-name bg1_bd1
Legend: pp = Partially Programmed.
Bridge group: bg1, bridge-domain: bg1_bd1, id: 20, state: up, ShgId: 0, MSTi: 0
Aging: 300 s, MAC limit: 4000, Action: none, Notification: syslog
Filter MAC addresses: 0
ACs: 2 (2 up), VFIs: 1, PWs: 1 (1 up), PBBs: 0 (0 up)
List of ACs:
Gi0/1/1/10.1, state: up, Static MAC addresses: 0
PE2.1, state: up, Static MAC addresses: 0
List of Access PWs:
List of VFIs:
VFI bgp_ad1 (up)
Neighbor 3.3.3.3 pw-id 1001, state: up, Static MAC addresses: 0
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#show l2vpn bridge-domain bd-name bg1_bd1
Legend: pp = Partially Programmed.
Bridge group: bg1, bridge-domain: bg1_bd1, id: 20, state: up, ShgId: 0, MSTi: 0
Aging: 300 s, MAC limit: 4000, Action: none, Notification: syslog
Filter MAC addresses: 0
ACs: 2 (2 up), VFIs: 1, PWs: 1 (1 up), PBBs: 0 (0 up)
List of ACs:
Gi0/1/1/10.1, state: up, Static MAC addresses: 0
PE2.1, state: up, Static MAC addresses: 0
List of Access PWs:
List of VFIs:
VFI bgp_ad1 (up)
Neighbor 3.3.3.3 pw-id 1001, state: up, Static MAC addresses: 0
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#show l2vpn bridge-domain autodiscovery bgp detail
Legend: pp = Partially Programmed.
Bridge group: bg1, bridge-domain: bg1_bd1, id: 20, state: up, ShgId: 0, MSTi: 0
Coupled state: disabled
MAC learning: enabled
MAC withdraw: enabled
MAC withdraw for Access PW: enabled
MAC withdraw sent on: bridge port up
MAC withdraw relaying (access to access): disabled
Flooding:
Broadcast & Multicast: enabled
Unknown unicast: enabled
MAC aging time: 300 s, Type: inactivity
MAC limit: 4000, Action: none, Notification: syslog
MAC limit reached: no
MAC port down flush: enabled
MAC Secure: disabled, Logging: disabled
Split Horizon Group: none
Dynamic ARP Inspection: disabled, Logging: disabled
IP Source Guard: disabled, Logging: disabled
DHCPv4 snooping: disabled
IGMP Snooping: enabled
IGMP Snooping profile: none
MLD Snooping profile: none
Storm Control: disabled
Bridge MTU: 1500
MIB cvplsConfigIndex: 21
Filter MAC addresses:
Create time: 26/06/2013 12:36:30 (00:14:13 ago)
No status change since creation
ACs: 2 (2 up), VFIs: 1, PWs: 1 (1 up), PBBs: 0 (0 up)
List of VFIs:
VFI bgp_ad1 (up)
VPN-ID: 1001, Auto Discovery: BGP, state is Provisioned (Service Connected) Route Distinguisher: (auto) 2.2.2.2:32768
Import Route Targets:
10.1.1.1:1
Export Route Targets:
10.1.1.1:1
Signaling protocol: BGP
Local VE-ID: 1001 , Advertised Local VE-ID : 1001
VE-Range: 10
PW: neighbor 3.3.3.3, PW ID 1001, state is up ( established )
PW class not set, XC ID 0xc0000414
Encapsulation MPLS, Auto-discovered (BGP), protocol BGP
Source address 2.2.2.2
PW type VPLS, control word disabled, interworking none
Sequencing not set
MPLS Local Remote
------------ ------------------------------ -------------------------
Label 289975 16046
MTU 1500 1500
Control word disabled disabled
PW type VPLS VPLS
VE-ID 1001 2001
------------ ------------------------------ -------------------------
MIB cpwVcIndex: 3221226516
Create time: 26/06/2013 12:37:26 (00:13:18 ago)
Last time status changed: 26/06/2013 12:37:26 (00:13:18 ago)
MAC withdraw messages: sent 0, received 0
Static MAC addresses:
Statistics:
packets: received 0, sent 0
bytes: received 0, sent 0
DHCPv4 snooping: disabled
IGMP Snooping profile: none
MLD Snooping profile: none
VFI Statistics:
drops: illegal VLAN 0, illegal length 0
RP/0/RSP1/CPU0:PE1#
6. Glossary
- PSN (Packet Switched Network): a network using IP or MPLS as the mechanism for packet forwarding
- PE (Provider Edge): a device connected to customer devices through virtual circuits and providing L2VPN service
- VE (VPLS Edge): a PE participating in VPLS
- CE (Customer Edge): a customer device connected to the PE.
- AC (Attachment Circuit): the connection between the CE and the PE. It is either a port interface or a sub-interface (VLAN, ATM VPI/VCI, Frame Relay)
- PW (Pseudo Wire): an emulated circuit between two PE’s through a PSN.
- XC (Cross-Connect): a configured connection between two segments in a PE. A segment can be either an AC or a PW.
- VFI (Virtual Forwarding Instance): the set of Pseudowires facing the core network
- NLRI (Network Layer Reachability Information): VPN information exchanged between PEs for auto-discovery and signaling.
- RD (Route Distinguisher): is an address qualifier used only within a single VPN. It is used to distinguish the distinct VPN routes of separate customers who connect to the provider.
- BGP extended community: an 8 byte encoded value used to provide extra functionality and avoid routing loops.
- RT (Route Target): a BGP extended community to tag VPN routes with unique values in order to determine which routes belong to particular VPN.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
great document!
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, reranti:
If I have a deployment that implements the traditional L3VPN and also L2VPN with BGP-AD/LDP signaling: do I have to consider completely different route-targets for each L3 and L2 VPN?
That is: since the AFI is different for each service, can I repeat RTs for a specific L2 and L3 environment? It's not a requirement, but I'd like to to know if it's possible.
Thanks,
c.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, reranti:
Another question if you find the time. What would be your considerations when trying to put a limit on a VPLS endpoint number? I mean, AFAIC, L3VPN you can handle 1000 termination points (customer CE) without much of a problem. What would be a reasonable number when talking L2VPN?
Thanks,
c.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Within MPLS domain, could I use the same vpn-id more than 1 PE?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
that's the way some docs suggest and the way i've implemented it in the field. only thing is it has to be unique within the PE. all PEs that terminate the same VPLS should can use same vpn-id.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/crs/software/crs_r4-1/lxvpn/configuration/guide/vc41crs/vc41vpls.html
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi reranti,
Can you add route-reflector requirements, configs and toubleshooting?
Thanks!
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Created 3 years ago and it's still giving off fruit. Great document.Thank you very much.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hello,
First of all, Great Document. Now, i've been trying enable VPLS with BGP autodiscovery and BGP signalling between an ASR920 and an ASR9010 (as Route Reflector), i see the BGP l2vpn vpls information being shared between them. I have another ASR9010, the VPLS service work great between these two XRs, but not towards the ASR920 XE router.
When validating the bridge-domain in the ASR920, i can only see information coming from the service-instance, but not from the VFI.
Any Suggestions?
This is the config so far:
ASR9010
bridge group VPLS4761
bridge-domain 2705
interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0/1.2705
!
vfi VFI2705
vpn-id 2705
autodiscovery bgp
rd 127:2705
route-target 127:2705
signaling-protocol bgp
ve-id 104
router bgp xxxx
neighbor-group iBGP
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
route-reflector-client
next-hop-self
ASR920
l2vpn vfi context VFI2705
vpn id 2705
autodiscovery bgp signaling bgp
ve id 113
ve range 100
rd 127:2705
route-target export 127:2705
route-target import 127:2705
route-target export 23456:2705
bridge-domain 2705
member GigabitEthernet0/0/0 service-instance 2705
member vfi VFI2705
router bgp xxxx
!
address-family l2vpn vpls
neighbor 10.19.0.4 activate
neighbor 10.19.0.4 send-community both
neighbor 10.19.0.4 prefix-length-size 2
neighbor 10.19.0.4 suppress-signaling-protocol ldp
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Good Day
Can you explain me when do I use rewrite ingress tag pop 2 symmetric ?
Regards
Wilson
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
Well, this has not really something to do with BGP autodiscovery, the "rewrite ingress tag pop 2 symmetric" is more an option, which you can use in vlan manipulation in terms of flexible matching and rewrite options.
Have a look at the following document, this gives some insights about the possibilities:
https://supportforums.cisco.com/document/85231/understanding-ethernet-virtual-circuits-evc
EVC Options
Flexible Matching
One of the things that make EVCs so powerful is their flexible matching criteria. EVCs allow us to classify inbound frames in a highly flexible manner based on 1 or more VLAN tags or CoS values. Here are some examples
| Configuration | Effect |
|---|---|
| encapsulation dot1q 10 | Match the single VLAN tag 10 |
|
encapsulation dot1q 25 second-dot1q 13 |
Match first VLAN tag 25 and second tag 13 |
| encapsulation dot1q any second-dot1q 22 | Match any double tagged frame with a second tag of 22 |
|
encapsulation dot1q 16 cos 4 |
Match a single tag 16 when it has CoS value 4 |
| encapsulation dot1q untagged | Match the native (untagged) VLAN |
| encapsulation dot1q default | The catch all class for all traffic not previously classified |
The options here are not exhaustive but just some examples. The other thing to remember about tag matching is that we follow a longest match criteria.
Rewrite Options
Along with a number of flexible matching options we have numerous tag rewrite options.
| Configuration | Effect |
|---|---|
| rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric | remove the top 802.1q tag |
| rewrite ingress tag pop 2 symmetric | remove the top two 802.1q tags |
|
rewrite ingress tag translate 1-to-1 dot1q 28 symmetric |
remove the top tag and replace it with 28 |
|
rewrite ingress tag translate 2-to-2 dot1 22 second-dot1q 23 |
remove the top two tags and replace them with 22 and 23 (23 will be the inner tag) |
| rewrite ingress tag push dot1q 56 second-dot1q 55 | push two new tags on top of the existing frame. The top tag will be 56; inner tag of 55 |
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
hi
Its a very good document. Thanks for sharing.
I just wanted to understand how does the MTU propagate with BGP AD implementation of VPLS and VPWS because i dont find any field in the NLRI which could do this. In case of LDP it used to be part of the label mapping message ( PW ID FEC TLV has interface parameters ) between the targeted peers .
Thanks
regards
Aseem.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
thanks for that article. Helped a lot in understanding L2PVN mechanics.
VPLS is clear to me. For VPLS I know of:
RFC 4761 --> defines VPLS with BGP-AD and BGP-SIG
RFC 4762 --> defines VPLS with LDP-SIG
RFC 6074 --> defines (among other stuff) BGP-AD extension for RFC 4762, so it becomes
VPLS with BGP-AD and LDP-SIG
However, if it comes to VPWS things get a little more obscure. I am missing such clear definitions for VPWS as there are for VPLS. When it comes to VPWS people normally do:
Manual Provisioning of LDP-FEC128 Services.
Manual Provisioning of LDP-FEC129 Services.
... but there are extensions to provide BGP-AD for PWE3 --> RFC 6074
Q1: RFC 6074 defines (along with VPLS-AD) VPWS BGP-AD for LDP FEC129 as well.
Is this also supported in IOS-XR, or is the occurence of bgp l2vpn vpls-vpws only for RRF- purposes in terms of VPWS.
Q2: The same mechanism from RFC 4761 is used for VPWS in this article. In which RFC is that documented?
Many Thanks,
Rene
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
for BGP-signaled L2VPNs this is cover by
Layer2 Info Extended Community
The up to date form can be found here:
https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-bess-fat-pw-bgp-01
This should look like L2VPN:19:e:8000 attached to a VPLS Prefix.
| | MTU (dec)
| -> CW+FlowLabel RX/TX (hex)
----> 19 = Encaps VPLS (dec)
Cheers
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Why is it giving
AC: GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1, state is unresolved
and the VPLS isn't working
RP/0/0/CPU0:XRV29#show l2vpn bridge-domain detail
Mon Nov 28 15:22:26.468 UTC
Legend: pp = Partially Programmed.
Bridge group: 1, bridge-domain: 1, id: 0, state: up, ShgId: 0, MSTi: 0
Coupled state: disabled
MAC learning: enabled
MAC withdraw: enabled
MAC withdraw for Access PW: enabled
MAC withdraw sent on: bridge port up
MAC withdraw relaying (access to access): disabled
Flooding:
Broadcast & Multicast: enabled
Unknown unicast: enabled
MAC aging time: 300 s, Type: inactivity
MAC limit: 4000, Action: none, Notification: syslog
MAC limit reached: no
MAC port down flush: enabled
MAC Secure: disabled, Logging: disabled
Split Horizon Group: none
Dynamic ARP Inspection: disabled, Logging: disabled
IP Source Guard: disabled, Logging: disabled
DHCPv4 snooping: disabled
IGMP Snooping: enabled
IGMP Snooping profile: none
MLD Snooping profile: none
Storm Control: disabled
Bridge MTU: 1500
MIB cvplsConfigIndex: 1
Filter MAC addresses:
P2MP PW: disabled
Create time: 28/11/2016 12:32:26 (02:50:00 ago)
No status change since creation
ACs: 1 (0 up), VFIs: 1, PWs: 1 (1 up), PBBs: 0 (0 up)
List of ACs:
AC: GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1, state is unresolved
XRV30 running config
router bgp 1
address-family vpnv4 unicast
!
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
neighbor 29.29.29.29
remote-as 1
update-source Loopback0
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
!
neighbor 31.31.31.31
remote-as 1
update-source Loopback0
address-family vpnv4 unicast
!
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
!
!
l2vpn
bridge group 1
bridge-domain 1
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
!
vfi 1
vpn-id 1
autodiscovery bgp
rd auto
route-target 1:1
signaling-protocol bgp
ve-id 1
XRV31 running configuration
router bgp 1
address-family vpnv4 unicast
!
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
neighbor 29.29.29.29
remote-as 1
update-source Loopback0
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
route-reflector-client
!
!
neighbor 30.30.30.30
remote-as 1
update-source Loopback0
address-family vpnv4 unicast
route-reflector-client
!
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
route-reflector-client
!
!
!
mpls ldp
XRV29 running configuration
router bgp 1
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
neighbor 30.30.30.30
remote-as 1
update-source Loopback0
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
!
neighbor 31.31.31.31
remote-as 1
update-source Loopback0
address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws
!
!
!
l2vpn
bridge group 1
bridge-domain 1
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1
!
vfi 1
vpn-id 1
autodiscovery bgp
rd auto
route-target 1:1
signaling-protocol bgp
ve-id 5
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Have you configured GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 as l2transport?
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: