- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Switching
- Re: vPC and peer link does it forward traffic or only state
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
vPC and peer link does it forward traffic or only state
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-20-2020 10:36 AM
I am new to Nexus and vPC peer links concept, and due to the latter I am reading the following:
However, what I do not understand if the link (east-west) forwards traffic or just keep alive, and link state. I have read the link numerous times, but if they are answering my question - i am just not getting it.
So, does the East-West peer link forward layer 2 traffic or is it just management traffic? Would traffic ever take this path to forward frames or packets over if routing?
Thank you
RR
- Labels:
-
LAN Switching
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-20-2020 10:41 AM - edited 04-20-2020 10:45 AM
Hi,
The east-west traffic using the vPC peer link is just layer-2 data traffic (not management) with all vlans included. For management, all Cisco Nexus devices come with an out-of-band management port that can be used to manage the device. It can also be used for vPC peer-keep-alive.
figure-3 in this link:
HTH
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-21-2020 09:44 AM
When you say 'layer 2' does that mean STP will making blocking or change the path that frames can take? I thinking I am confusing myself, because the figures show traffic going up and down the leaf/spine but not the cross-link between the two switches. So is there ever a case that traffic user/production traffic will take the peer link that is connected between the two switches?
Thank you
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-20-2020 11:45 AM
Hi @romanroma
vPC peer-link will transfer two type of traffics:
- vPC control-plane traffic using Cisco Fabric Services over Ethernet (CFSoE). This includs:
- Configuration validation and comparison (consistency check)
- Synchronization of MAC addresses for vPC member ports
- vPC member port status advertisement
- Spanning Tree Protocol management
- Synchronization of HSRP and IGMP snooping
- and few more
- user traffic. This will include:
- traffic destined to servers connected on orphan port on the vPC peer
- BUM traffic - this is mandatory to be sent over vPC peer-link in case there are orphan ports on vPC peer. This traffic will not be sent out of vPC enabled port-channels (this is where loop avoidance mechanism kicks in)
If you want to learn vPC, I strongly recommend you to read the vPC design guide:
It is written for Nexus 7000, but the information and details from the doc, applies on all Nexus platforms.
Cheers,
Sergiu
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-21-2020 09:49 AM
"
- user traffic. This will include:
- traffic destined to servers connected on orphan port on the vPC peer
- BUM traffic - this is mandatory to be sent over vPC peer-link in case there are orphan ports on vPC peer. This traffic will not be sent out of vPC enabled port-channels (this is where loop avoidance mechanism kicks i
Does this link only get used during an orphaned situation? I am still trying to understand if traditional STP methods keeps this link in block state, and only the leaf/spin links are used, and only opens the link when the vPC is in a bad health state.
Reading all I can since got moved to Nexus switches due to low man power and resources.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-21-2020 10:47 AM
Hi @romanroma
The unicast traffic destined to servers connected on orphan ports and all BUM (Broadcast, Unknown unicast and Multicast) traffic is being sent over Peer-Link.
The vPC Peer-link interface is always* in STP forwarding state.
*Note: the vpc peer-link is by default configured as STP port type network, meaning if one of the peers is not sending STP BPDUs to the other one, the port goes into BA_inc (bridge assurance inconsistency).
Regards,
Sergiu
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-24-2020 06:47 AM
Another confusion,
I am reading the following docs:
And is says:
"• vPC peer link: The vPC peer link is the link used to synchronize states between the vPC peer devices. The vPC peer link carries control traffic between two vPC switches and also multicast, broadcast data traffic. In some link failure scenarios, it also carries unicast traffic. You should have at least two 10 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces for peer links. "
So how do you know or when are the "some link failures" when the peer link will allow unicast traffic? I am just not getting the concept when the vPC link, which usually carries: keep alive, multicast, broadcast and control traffic.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-24-2020 07:30 AM
Hi @romanroma
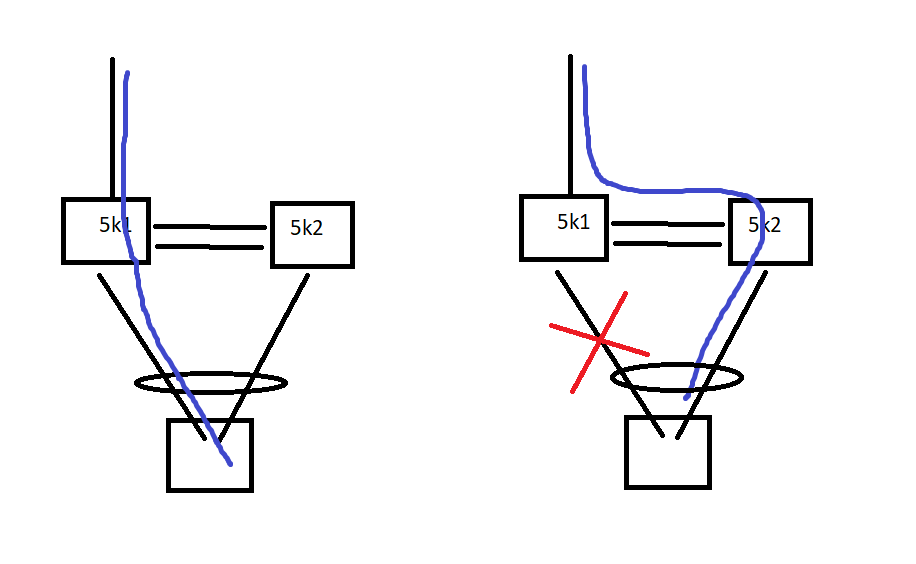
The failure scenario where unicast traffic is being forwarded over the peer-link, is when one link from the vPC port-channel goes down, and unicast traffic is received on the peer where the link is down. Here is a graphical view of the scenario:
left - working scenario ; right - failure scenario
Cheers,
Sergiu
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-27-2020 09:43 AM
That is very helpful thank you...
One last question - So I am trying to find the path of a remote interface and port, which I have already found by using 'sh fabricpath route switchid' and the 'sh fabricpath switch-id'; however, if I have more then one path in the spine-leaf model - how do I find out what path is being taken? I am using vPC and fabricpath, but does the STP and root/bridge switch concept still apply to the vlans and topology path?
Thank you so much... much appreciated.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-27-2020 10:12 AM
Hello,
The FP will load-balance the unicast traffic over equal cost routes.
You can try the following to find the egress interface:
show fabricpath load-balance unicast forwarding-path ftag ftag-id switchid switch-id flow-type {l2 {{dst-mac dst-mac | source-mac src-mac} ether-type ether-type}} | {l3 {dst-ip dst-ip | src-ip src-ip | dst-ipv6 dst-ipv6 | srcipv6 src-ipv6}} | {l4 {l4-src-port l4-src-port | l4-dst-port l4-dst-port | dst-ip dst-ip | src-ip src-ip | dst-ipv6 dst-ipv6 | srcipv6 src-ipv6}}} {vlan vlan-id} {module mod-no}
Example:
switch# show fabricpath load-balance unicast forwarding-path ftag 1 switchid 200 src-mac 00:10:20:30:40:50 dst-mac 00:30:40:50:60:70 vlan 200 Missing params will be substituted by 0's. crc8_hash: 229 This flow selects interface Po400
Cheers,
Sergiu
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-29-2020 07:50 AM
Do you recommend using src-mac as one of the local interfaces of the switch or possibly use the mac address of a network device?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-29-2020 08:23 AM
source and destination of the user traffic
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-24-2020 07:54 AM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-27-2020 09:45 AM
I appreciate your help... I believe that is what is taking place, I am not seeing traffic go over my East-West link, so I think there is a mesh switch that is in leaf-spine topology that is being used. I am very new to vPC and Fabricpath.
Much appreciated... I will keep this in mind.
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide