Introduction
Clients cannot associate to the AP if it is configured as a WDS device.
Resolution
Ensure that the mobility network-id command is not enabled on the Cisco Access Point (AP) if it serves as the Wireless Domain Services (WDS) device. The mobility network-id command is used for Layer 3 (L3) mobility, and the AP configured as a WDS cannot provide L3 mobility. This command must only be enabled when a Wireless LAN Services Module (WLSM) is used to provide WDS. A WLSM must be the WDS device to properly configure L3 mobility.
Understanding Layer 3 Mobility
When you use a WLSM as the WDS device on your network, you can install access points anywhere in a large Layer 3 network without configuring one specific subnet or VLAN throughout the wired switch infrastructure. Client devices use multipoint GRE (mGRE) tunnels to roam to access points that reside on different Layer 3 subnets. The roaming clients stay connected to your network without changing IP addresses.
For instructions on configuring WDS on a switch's Wireless LAN Services Module (WLSM), refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless LAN Services Module Installation and Configuration Note.
The Layer 3 mobility wireless LAN solution consists of these hardware and software components:
•1100 or 1200 series access points participating in WDS
•Catalyst 6500 switch with Supervisor Module and WLSM configured as the WDS device
Note
You must use a WLSM as your WDS device to properly configure Layer 3 mobility. Layer 3 mobility is not supported when you use an access point as your WDS device.
•Cisco (or Cisco compatible) client devices
Figure shows the components that interact to perform Layer 3 mobility.

For more information about the L3 mobility, check "Layer 3 Mobility Architecture"

Layer 3 Mobility Control Protocol
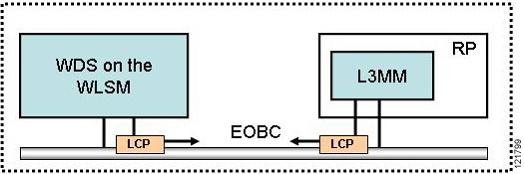
WLSM Operational Overview
The WLSM works with the Supervisor Engine 720 and with Cisco Aironet 1100 and 1200 series access points to provide a logical network over an existing network infrastructure. Within this network, a mobile user can roam and remain within the same Layer 3 broadcast domain. Layer 3 roaming is accomplished using an FSRT for each active roaming subnet (mobility group), terminated at one end on the Supervisor Engine 720 and at the other end on the Cisco Aironet access point.
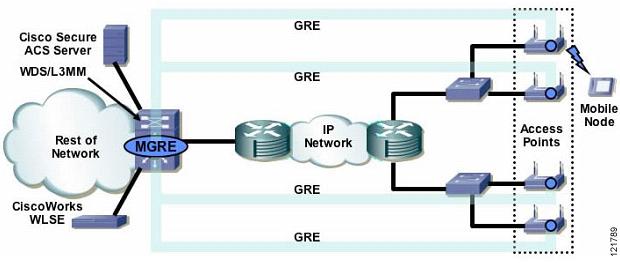
For detailed information, please refer WLSM Operational Overview.
Advantages of using WDS on WLSM
The introduction of switch-based WDS and the WLSM facilitates Layer 3 (L3) fast secure roaming (FSR) and provides a highly scalable solution for L3 mobility in the campus. Switch-based WDS centralizes the functionality of WDS in the WLSM blade in a central switch and provides these benefits:
- Increased WDS scalability—The scalability increases to 300 APs and 6000 users across a campus wireless LAN (WLAN) network.
- Simplified design and implementation—No VLANs span the campus network. With the use of multipoint generic routing encapsulation (mGRE) architecture, no changes to the current network wired infrastructure are necessary.
- Manageability for a large WLAN deployment—This solution provides a single point of ingress for both WLAN control and user data into the wired network for which to apply security and quality of service (QoS) policies.
- L3 mobility between floors and across multiple buildings
- The ability to use advanced features on the Cisco Catalyst 6500, which includes other Catalyst 6500 service modules
- Enhanced end-to-end security and QoS by integration with the Catalyst 6500 platform
Reference