- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Networking Knowledge Base
- How to Onboard a Remote Router into an Existing SD-WAN Fabric
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on
11-21-2019
11:13 AM
- edited on
08-13-2020
03:27 PM
by
Anna Komarovska
![]()
- Benefits
- Documentation
- Prerequisites
- Limitations
- Supported Platforms
- Step-By-Step Configuration
- Verify Device Requirements
- Option 1: Onboard Device via ZTP
- Option 2: Onboard a Device via PnP Portal
- Option 3: Onboard Device via Manual CLI Configuration
- Verification
Benefits
Cisco’s software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) solution, powered by Viptela, allows user to quickly and seamlessly establish an overlay fabric to connect an enterprise’s data centers, branch and campus locations, as well as colocation facilities in order to improve the network’s speed, security, and efficiency.
Documentation
This upgrade guide is designed to be used as a detailed example of onboarding a remote device and adding it to your existing SD-WAN fabric. This guide should be used in conjunction with the complete “SD-WAN End-to-End Deployment Guide.”
Prerequisites
This configuration guide assumes that an SD-WAN fabric consisting of at least one vManage, one vSmart, and one vBond instance has already been setup and at least one SD-WAN compatible platform (see Supported Platforms below) has been physically connected, is powered on, and is reachable from a remote workstation. The guide also assumes that the remote routing device that’s being added to the fabric has a version of the SD-WAN image installed that is compatible with the hardware platform, as well as the version of vManage installed on the vManage controller.
Limitations
This guide will cover the process for adding a remote vEdge or cEdge router to an existing SD-WAN fabric. Router configurations beyond those necessary for connectivity to the SD-WAN controllers are not covered by this guide. Router software upgrades are also not covered by this guide.
Supported Platforms
The IOS XE SD-WAN software can be installed on the following hardware platforms:
- Cisco ASR 1000 series aggregation services routers
- Cisco ISR 1000 series integrated services routers
- Cisco ISR 4000 series integrated services routers
- Cisco/Viptela vEdge routers
- ENCS 5100
- ISRv
- ENCS 5406
- ISRv
- T1, E1, and 4G NIMs
- ENCS 5408
- ISRv
- T1, E1, and 4G NIMs
- ENCS 5412
- ISRv
- T1, E1, and 4G NIMs
The following interface modules are supported for the ISR 4000 series routers:
- NIM-1GE-CU-SFP
- NIM-2GE-CU-SFP
- NIM-1MFT-T1/E1
- NIM-2MFT-T1/E1
- NIM-4MFT-T1/E1
- NIM-8MFT-T1/E1
- NIM-ES2-4
- NIM-ES2-8
- NIM-LTEA-EA
- NIM-LTEA-LA
- NIM-VAB-A
- NIM-VAB-M
- SM-X-4X1G-1X10G
- SM-X-6X1G
The following crypto modules are required for the ASR 1000 series routers:
- ASR1001HX-IPSECHW for the ASR 1001-HX
- ASR1002HX-IPSECHW for the ASR 1002-HX
Step-By-Step Configuration
Verify Device Requirements
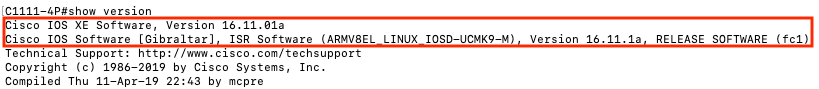
Before a remote router can be added to an SD-WAN fabric, the router needs to be running the Cisco IOS-XE SD-WAN image that is compatible with it. The router’s software image version can be checked by issuing the “show version” command on the router’s CLI.
If your remote router is not running an appropriate version of IOS-XE SD-WAN, the software can be downloaded and installed using the guide located at this page, and following the sections “Download the XE SD-WAN Software” and “Install the XE SD-WAN Software.”
After ensuring that the remote router is running the correct XE SD-WAN software version, and that the device is physically powered on and remotely reachable, follow one of the available options for onboarding the device into your SD-WAN fabric.
Option 1: Onboard Device via ZTP
The first option for onboarding a remote device into an SD-WAN fabric, is to use Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP). This approach requires the least hands-on configuration from a user, however, it relies on the GigabitEthernet0/0 interface on the remote router to be configured for DHCP, and physically connected to an internet gateway in order to receive an IP address and locate its vBond IP address to begin the authentication process with the controllers.
Assuming that the remote router is physically connected and configured to receive its IP address from a DHCP server, these simple steps can be followed to check the code version for the remote router and ensure ZTP is enabled for your SD-WAN fabric.
- Login to the vManage web console. Use the sidebar on the left to navigate to Administration > Settings.
- Click “Edit” next to “Enforce Software Version (ZTP)”
- Click the toggle next to the respective hardware platform that is being onboarded, then use the drop-down menu to the right of the toggle to select a software version to upgrade the remote router to. Ensure that the version selected matches, or is newer than the version of the XE SD-WAN software that’s installed on the hardware platform. Click “Save” to enforce changes.
- After enabling ZTP and selecting a software upgrade version, power-on or reboot the router that is being onboarded. The router will contact the ZTP server and authenticate itself with vBond to be added to the SD-WAN edge device list for the fabric. The router software version is then upgraded to match the version selected in vManage in Step 3.
- After the router’s software is upgraded, the full configuration defined in vManage (not covered by this guide) is pushed to the remote router, which then becomes in sync with vManage.
Option 2: Onboard a Device via PnP Portal
The second option for onboarding a remote device into a SD-WAN fabric is to use the “Plug and Play Device Portal” or “PnP Portal,” for short. The PnP Portal is accessible through software.cisco.com using a Cisco Smart Account.
Similarly to onboarding using ZTP, onboarding through the PnP Portal requires the remote router to already be physically connected, using interface GigabitEthernet0/0, to a DHCP server and configured to receive an IP address from that server.
Once the remote router has received an IP address, following these steps will ensure that the PnP server is ready to receive onboarding requests for your device(s) and redirect the remote devices to vBond for authentication.
- Log into the Cisco Smart Account corresponding to the existing SD-WAN controllers at software.cisco.com
- Navigate to the Plug and Play Connect portal
- Ensure that the existing SD-WAN controllers are listed and configured under the “Controller Profiles” tab.
- Under the “Devices” tab, ensure that the remote router is listed, with the appropriate Serial Number and Base PID.
- Power on/reboot the remote router. The router will communicate with the PnP server, which will subsequently redirect the onboarding request to vBond to authenticate the hardware device with vBond and the other two SD-WAN controllers and adding it to the fabric.
- Any additional software upgrades or device configuration for the remote router can now be done through vManage.
Option 3: Onboard Device via Manual CLI Configuration
Lastly, a remote router can be onboarded, and brought into the rest of the SD-WAN fabric by logging into the router via SSH or Telnet and configuring the vBond IP address, as well as a few other configurations specific to the SD-WAN fabric. This will enable the remote router to communicate with vBond, and subsequently, the other SD-WAN controllers. The following steps assume that the remote router is physically connected to an internet gateway using interface GigabitEthernet 0/0.
To begin, connect to the router’s console via SSH or Telnet using an admin account, then enter configuration mode by entering “config-t” and enter the following configuration/commands to establish basic connectivity to vBond:
ip domain lookup
ip name-server <DNS Server IP Address>
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <Gateway IP Address>
interface GigabitEthernet1
ip address <IPv4 Address being assigned to this Device/Interface> <Subnet Mask>
no shutdown
commit
end
An example of a complete configuration following these steps would look like:
ip domain lookup ip name-server 128.0.0.125 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 128.0.0.1 interface GigabitEthernet1 ip address 128.0.0.24 255.255.255.240 no shutdown commit end
Once basic connectivity to vBond has been established, the following configuration/commands will need to be entered in order to establish control connections with the SD-WAN controllers:
config-t
system
hostname <Desired Hostname of this Remote Router>
system
system-ip <Private IPv4 Address to be Used as a Router ID for this Device>
site-id <Site ID Number for the Site this Remote Router will be in>
organization-name <Organization Name as Defined in vManage Admin Settings>
vbond <IP Address of vBond Instance>
interface Tunnel 0
ip unnumbered GigabitEthernet1
tunnel source GigabitEthernet1
tunnel mode sdwan
sdwan
interface GigabitEthernet1
tunnel-interface
color <Tunnel Color>
encapsulation <Encapsulation type> (gre | ipsec)
commit
end
An example of a complete configuration following these steps would look like:
config-t system host-name Site-Edge-1 system-ip 4.4.4.4 site-id 102 organization-name “Enterprise Network - 102" vbond 128.100.100.102 interface Tunnel 0 ip unnumbered GigabitEthernet1 tunnel source GigabitEthernet1 tunnel mode sdwan sdwan interface GigabitEthernet1 tunnel-interface color biz-internet encapsulation ipsec commit end
After entering these commands and establishing basic connectivity to the SD-WAN controllers, ensure that the Root Certificate (which is already installed on the controllers) file has been copied from one of the controllers to the bootflash of the router that is being configured/onboarded. Then, issue the command "request platform software sdwan root-cert-chain install bootflash: <Root Certificate Filename e.g. root.crt>" to install the root certificate on the edge router.
In order for the edge router to appear in the devices list on the vManage web GUI, a valid WAN edge device list (in .csv format) will need to be signed and uploaded to vManage. By issuing the command "show sdwan certificate serial" the serial number and device PID for this edge router will be displayed in the following format. Copy the serial number and PID generated by this command to make the WAN edge serial file.
This information is necessary for generating the valid WAN edge device list file, however, this file can only be used if using vManage version 16.9.x or older. On vManage 17.x and newer, the WAN edge serial file is a signed, binary file that can only be obtained through Cisco, and only for the edge devices for which a license has been purchased. For vManage 17.x and newer, these WAN edge serial files can be downloaded from a the Network Plug and Play Connect portal, using a valid Cisco Smart Account. For vManage 16.9.x and older, the WAN edge serial file can be generated using the output copied from the "show sdwan certificate serial" command. On a local PC, create a new file titled "vedges.csv" and paste the output copied from the previous command. This file can contain the serial number and PIDs for more than one edge router being onboarded, with each device beginning on a new line, as such:
ab1cde23-4567-8f89-01fd-gh2i3j44k5l6,F1AB23CD4E5678F9, mn7opq89-0123-4r45-67st-uv8w9x01y2z3,F1AB23CD4E5678F9, ab4cde56-7890-1f23-45gh-ij6k7l89m0n1,F1AB23CD4E5678F9
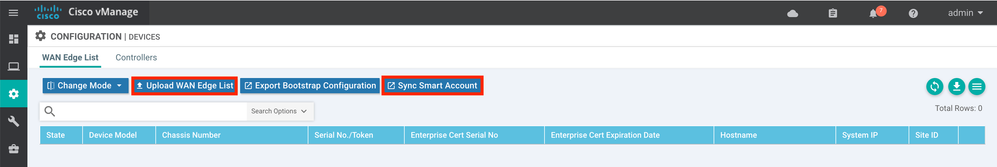
After this file is generated, navigate to the vManage web GUI, then go to the Configuration tab and select "Devices" to go the devices page. Click on "Upload WAN Edge List" to upload the .csv file.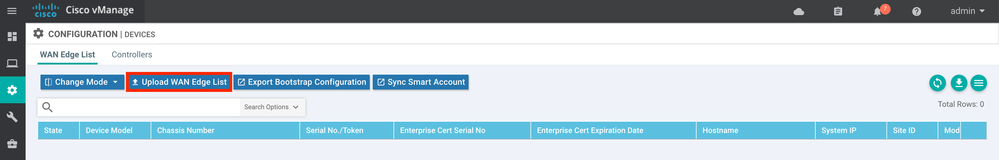
Verification
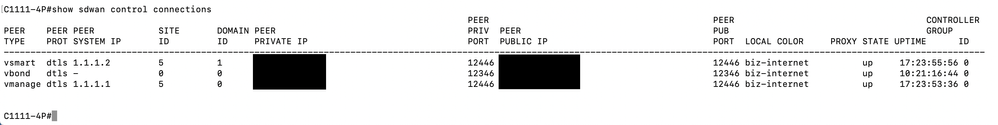
Control connections can be verified by entering the commands “show sdwan control summary” and “show sdwan control connections” on the remote device, through the CLI.
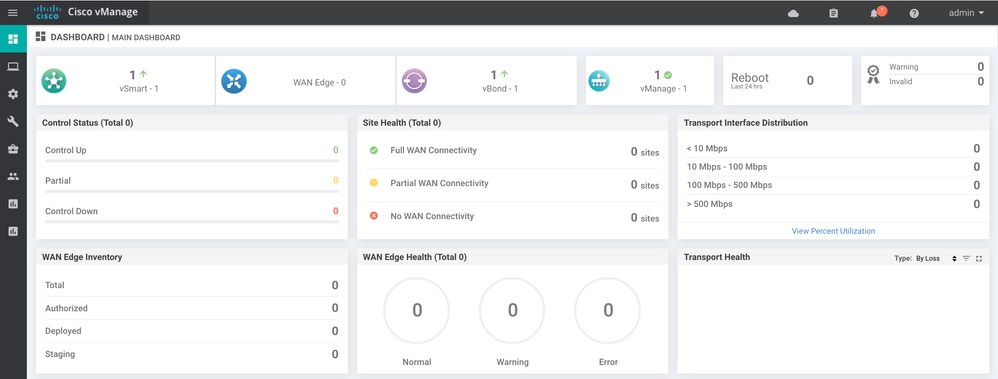
Additionally, information about overall fabric health and connectivity, as well as individual device connectivity can be found on the vManage web console:
In order to view the onboarded devices in vManage, either a Cisco Smart Account must be synced with the vManage instance, or a list of corresponding, authorized WAN edge serial numbers in .csv format must be uploaded to vManage. These options can both be accessed by going to the Configuration tab on the left, then selecting "Devices"
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: