- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Networking Knowledge Base
- EIGRP IPv6 Configuration In Name Mode
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
09-20-2013 03:28 AM - edited 03-01-2019 04:57 PM
- Introduction:
- Components Used:
- Background:
- Configuration Example:
- Configuration Comparision for classic router configuration and eigrp named mode configuration:
- Related Information:
Introduction:
This document describes how to configure Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) for IPv6 using EIGRP name configuration The EIGRP name configuration also support IPv6 VRF-Lite feature provides EIGRP IPv6 support for multiple VRFs and simplifies the management and troubleshooting of traffic belonging to a specific VRF.
Components Used:
The configurations in this document are based on the Cisco 7200 series router running (C7200-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.2(4)S4 IOS.
R1#sh version | in IOS
Cisco IOS Software, 7200 Software (C7200-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.2(4)S4, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc2)
Background:
This document will explain you two things:
1) Simple EIGRP IPv6 configuration
2) EIGRP IPv6 VRF-aware configuration using "EIGRP name" mode.
When you configure the router EIGRP command with the virtual-instance-name argument creates an EIGRP configuration referred to as the EIGRP named configuration or EIGRP named mode. An EIGRP named configuration does not create an EIGRP routing instance by itself; it is a base configuration that is required to define address-family configurations that are used for routing.
Things to be remember:
A) In IPv6, Link-local address is used by EIGRP to source Hello packets and establish adjacency.IPv6 Link-local address is never routed and they are auto assigned when users enable the interface as shown below:
ipv6 unicast routing
!
interface Ethernet1/0
!
ipv6 enable
You can configure this manually on an interface. An IPv6 link-local is prefixed by FE80 and has a prefix length of /10.
interface fa1/0
!
ipv6 address ?
!
X:X:X:X::X IPv6 link-local address
!
X:X:X:X::X/<0-128> IPv6 prefix
B) Router-ID is required and selected :
1) From highest loopback IPv4 address
2) From first IPv4 address found on any physical interface.
If no IPv4 address is available on router, a 32-bit router-id need to be configure manually using the “eigrp router-id x.x.x.x” command under address-family.
Configuration Example:
In this example R1, R2 and R3 are connected and assigned with IPv6 loopback address as show in below figure. We will be configuring EIGRP between R1 and R2 in global routing table and between R1 and R3 under VRF.
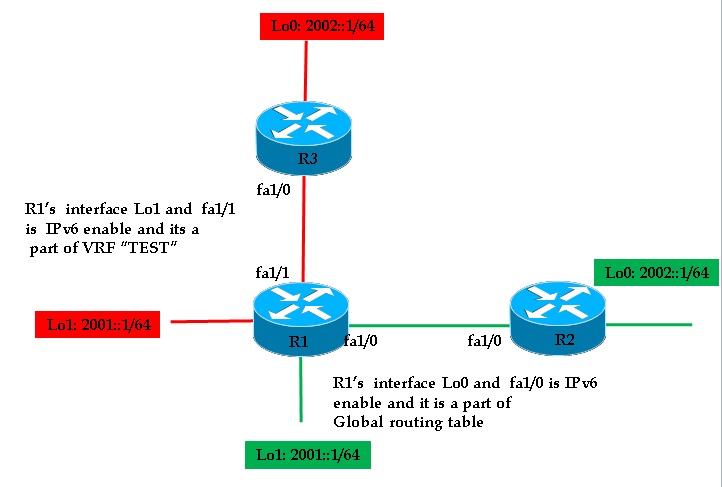
A) Simple EIGRP IPv6 configuration between R1 and R2:
Basic Configuration of R1 and R2:
R1 R2
R1#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R1(config)#int fa1/0 R1(config-if)#ipv6 enable R1(config-if)#no sh R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int lo 0 R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001::1/64 R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)# | R2#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R2(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R2(config)#int fa1/0 R2(config-if)#ipv6 enable R2(config-if)#no sh R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int lo 0 R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2002::1/64 R2(config-if)#exit R2(config)# |
Now we will configure EIGRP on R1 and R2 in Name Mode:
IPv6 EIGRP name mode configuration for R1:
R1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#router eigrp CISCO
R1(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 1
R1(config-router-af)#eigrp router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router-af)#af-interface FastEthernet1/0
R1(config-router-af-interface)# authentication mode hmac-sha-256 cisco
R1(config-router-af-interface)#exit-af-interface
R1(config-router-af)#af-interface Loopback0
R1(config-router-af-interface)#passive-interface
R1(config-router-af-interface)#exit-af-interface
R1(config-router-af)#exit-address-family
R1(config-router)#end
R1#
IPv6 EIGRP name mode configuration for R2:
R2(config)#router eigrp CISCO
R2(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 1
R2(config-router-af)#eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-router-af)#af-interface FastEthernet1/0
R2(config-router-af-interface)#authentication mode hmac-sha-256 cisco
R2(config-router-af-interface)#exit-af-interface
R2(config-router-af)#af-interface Loopback0
R2(config-router-af-interface)#passive-interface
R2(config-router-af-interface)#exit-af-interface
R2(config-router-af)#exit-address-family
R2(config-router)#end
R2#
Verification:
1) The “show ipv6 eigrp neighbors” command displays the neighbors discovered by the EIGRPv6.
R1#
*Sep 20 12:20:52.959: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv6 1: Neighbor FE80::C801:14FF:FE18:1C (FastEthernet1/0) is up: new adjacency
R1#sh ipv6 eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv6 VR(CISCO) Address-Family Neighbors for AS(1)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 Link-local address: Fa1/0 12 00:01:13 1556 5000 0 3
FE80::C801:14FF:FE18:1C
R1#
2) The “show ipv6 route eigrp” command shows R1 has learned R2’s loopback address in its routing table via EIGRP.
R1#sh ipv6 route eigrp
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 4 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, H - NHRP, I1 - ISIS L1
I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP
EX - EIGRP external, ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination
NDr - Redirect, O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1
OE2 - OSPF ext 2, ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2, l - LISP
D 2002::/64 [90/103040]
via FE80::C801:14FF:FE18:1C, FastEthernet1/0
R1#
B) EIGRP IPv6 VRF-aware configuration using "EIGRP name" mode:
In classic way you cannot configure EIGRP for VRF (Virtual routing ta ble), you have to use "EIGRP name" mode for it. A VRF instance and a route distinguisher must be defined before the address family session can be created.
A single EIGRP routing process can support multiple VRFs. The number of VRFs that can be configured is limited only by the available system resources on the device, which is determined by the number running processes and available memory. However, only a single VRF can be supported by each VPN, and redistribution between different VRFs is not supported.
As discussed above we are configuring EIGRP for VRF between R1 and R3.We will configure VRF only on R1 and R3 will be having simple global configuration:
R3 Configuration:
R3#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R3(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R3(config)#int fa1/0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#int lo 0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 address 2002::1/64
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router eigrp CISCO
R3(config-router)#address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 1
R3(config-router-af)#eigrp router-id 3.3.3.3
R3(config-router-af)#af-interface fa1/0
R3(config-router-af-interface)#authentication mode hmac-sha-256 cisco
R3(config-router-af-interface)#exit
R3(config-router-af)#af-interface lo 0
R3(config-router-af-interface)#passive-interface
R3(config-router-af-interface)#exit
R3(config-router-af)#exit
R3(config-router)#end
R3#
R1 configuration:
R1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#vrf definition TEST
R1(config-vrf)#address-family ipv6
R1(config-vrf-af)#exit
R1(config-vrf)#rd 100:100
R1(config-vrf)#exit
R1(config)#int fa1/1
R1(config-if)#vrf forwarding TEST
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int lo 1
R1(config-if)#vrf forwarding TEST
R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001::1/64
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router eigrp CISCO
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv6 unicast vrf TEST autonomous-system 1
R1(config-router-af)#eigrp router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router-af)#af-interface fa1/1
R1(config-router-af-interface)#authentication mode hmac-sha-256 cisco
R1(config-router-af-interface)#exit
R1(config-router-af)#af-interface lo0
%EIGRP: Interface Loopback0 not a member of this routing table
R1(config-router-af)#af-interface lo1
R1(config-router-af-interface)#passive-interface
R1(config-router-af-interface)#exit-af-interface
R1(config-router-af)#exit-address-family
R1(config-router)#end
R1#
Verification:
1) “show eigrp address-family ipv6 vrf TEST neighbors” command used to verify neighborship between R1 and R3.
R1#show eigrp address-family ipv6 vrf TEST neighbors
EIGRP-IPv6 VR(CISCO) Address-Family Neighbors for AS(1)
VRF()
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 Link-local address: Fa1/1 10 00:24:49 1577 5000 0 3
FE80::C802:16FF:FEE4:1C
R1#
2) From the below output you can see R1 learned R3’s loopback in VRF “TEST” routing table and R2’s loopback in “Global routing table”
R1#sh ipv6 route vrf TEST eigrp
IPv6 Routing Table - TEST - 4 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, H - NHRP, I1 - ISIS L1
I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP
EX - EIGRP external, ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination
NDr - Redirect, O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1
OE2 - OSPF ext 2, ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2, l - LISP
D 2002::/64 [90/103040]
via FE80::C802:16FF:FEE4:1C, FastEthernet1/1
R1#
R1#sh ipv6 route eigrp
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 4 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, H - NHRP, I1 - ISIS L1
I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP
EX - EIGRP external, ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination
NDr - Redirect, O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1
OE2 - OSPF ext 2, ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2, l - LISP
D 2002::/64 [90/103040]
via FE80::C801:14FF:FE18:1C, FastEthernet1/0
R1#
C) End to End reachability between R1 and R3 using Ping:
R1#ping vrf TEST 2002::1 source loopback 1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2002::1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 2001::1%TEST
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 28/137/232 ms
R1#
Configuration Comparision for classic router configuration and eigrp named mode configuration:
Classic router configuration:
EIGRP named
mode configuration:
ipv6 unicast-routing ! interface fa1/1 ipv6 enable ! int fa1/1 ipv6 eigrp 1 ! router eigrp 1 no shutdown | ipv6 unicast-routing ! interface Loopback0 ipv6 enable ! interface Ethernet0/0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8::1/64 ! router eigrp CSCO address-family ipv6 autonomous-system 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 af-interface default no shutdown |
Related Information:
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: