- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Security
- Security Knowledge Base
- ASA: Best practices for remote access VPN performance optimization (AnyConnect)
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on
04-21-2020
06:43 AM
- edited on
11-28-2023
06:15 PM
by
Taisuke Nakamura
![]()
- Introduction
- ASA data sheet
- Main bottleneck locations and examples of countermeasures
- Best practices for performance optimization
- Use of split tunnel
- Only internal communication is split tunneling
- Exclude tunneling only for communication to specific domain (Dynamic Split Tunneling)
- Terminal security measures
- Use of DTLS
- Use the right MTU
- Reduction of unnecessary functions and settings
- Speed and quality of lines and routes
- Check and disconnect users with high traffic
- Check for AnyConnect sessions with heavy traffic
- Check connections and users with high communication volume
- Change the maximum number of connectable AnyConnect
- ASAv performance optimization
- High-end model performance optimization
- Upgrade or Configuration Change
- Upgrade to higher model
- Operation of multiple ASAs and use of server list function
- Operation of multiple ASAs and use of VPN load balancing function
- Comparison of configuration changes
- Troubleshooting
- Check CPU usage
- Case Study 1: Overload due to heavy communication or connection
- Case Study 2: Overload due to overuse of CP function
- Check the number of VPN sessions
- Check traffic volume and average packet size
- Cryptographic processing engine load check (only for high-end models)
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How do I download AnyConnect software?
- I want to use AnyConnect, but my ASA can only terminate two VPNs
- Will I be disconnected when connecting more than the number of AnyConnect licensed users I have purchased?
- Is it possible to connect more than the maximum number of connections for each model?
- What happens when a large number of simultaneous connections occur and the allocated IP of the address pool is insufficient?
- What is the Parent-Tunnel that can be confirmed with the show vpn-sessiondb detail command?
- Is FTD available for AnyConnect termination?
- How to increase VPN speed on AnyConnect device
- The throughput of AnyConnect terminal is up to about 100Mbps
- Will AnyConnect's Compression feature improve performance?
- Does using DTLSv1.2 improve performance other than ASAv?
- Please tell me how to check the automatically adjusted MTU of AnyConnect
- VPN throughput of ASA does not follow the datasheet
- Is QoS for each AnyConnect session possible?
- Reference information
Note:
This document is translation from Taisuke Nakamura Japanese document https://community.cisco.com/t5/-/-/ta-p/4061565 and some best practices and tips are added/modified by Firas and Taisuke.
Introduction
With the promotion of telework, the demand for remote access VPN (RA VPN) is ever increased. However, as the number of remote access VPN users has rapidly increased, access is concentrated on the remote access VPN servers, Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) and Firepower Threat Defense (FTD), which terminate the access, and the performance of ASA and FTD is reduced. There are quite a few cases that suffer from deterioration.
This document introduces best practices for improving / optimizing the performance of ASA remote access VPNs, configuration changes, and logs that should be checked in the event of performance degradation.
The information in this document is created for those who have a certain level of experience in handling networks and products. Please use the information in this document at your own discretion and responsibility. We recommend that you verify settings and configuration changes in advance and perform them during maintenance hours and during times when communication is less affected.
If you need specific design and setting / installation support for performance optimization, please consider using our optimization service or the optimization support service of a Cisco product distributor.
ASA data sheet
The VPN throughput and maximum number of AnyConnect VPN user sessions can be found in the datasheet. The throughput of DTLS at the time of AnyConnect connection can be expected to have processing performance close to VPN throughput. Please note that the data sheet values are based on the test data with the minimum settings in the test environment. The final performance will vary depending on the functions used, settings, number of processes, communication content, etc.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Data Sheet
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/asa-firepower-services/datasheet-c78-742475.html
Cisco ASA 5585-X Stateful Firewall Data Sheet
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/asa-5500-series-next-generation-firewalls/datasheet-c78-730903.html
Cisco ASA with FirePOWER Services Data Sheet
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/asa-5500-series-next-generation-firewalls/datasheet-c78-733916.html
Cisco Adaptive Security Virtual Appliance (ASAv) Data Sheet
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/adaptive-security-virtual-appliance-asav/datasheet-c78-733399.html
Cisco Firepower 1000 Series Data Sheet
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/firepower-1000-series/datasheet-c78-742469.html
Cisco Firepower 2100 Series Data Sheet
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/firepower-2100-series/datasheet-c78-742473.html
Cisco Firepower 4100 Series Data Sheet
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/firepower-4100-series/datas
Cisco Firepower 9300 Series Data Sheet
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/security/firepower-9000-series/datasheet-c78-742471.html
Main bottleneck locations and examples of countermeasures
The performance of a remote access VPN on the ASA is affected by many factors. Below are the major bottleneck locations and examples of countermeasures.
|
Bottleneck location |
Explanation |
Countermeasure example |
|
throughput |
The higher the communication volume, the heavier the load on the ASA for processing that communication. Therefore, how to reduce the traffic is important for maintaining performance. Throughput can be expected to improve by using DTLS with good communication efficiency |
|
|
Number of sessions |
Each model has a maximum number of hard-coded connections and cannot exceed AnyConnect connections. Also, if the rate of new AnyConnect connection is high, the load of session establishment processing will also increase. |
|
|
Functions and settings |
In general, the more you use features and settings, the less performance you experience. The best way to maximize the performance of a remote access VPN termination is to make the ASA a dedicated remote access VPN termination. |
|
|
Optimization by model |
The performance of the ASAv virtual firewall changes depending on the performance of the installed server. For high-end models such as ASA5585 and FPR4100, SSL processing of the engine can be optimized. |
|
Best practices for performance optimization
Use of split tunnel
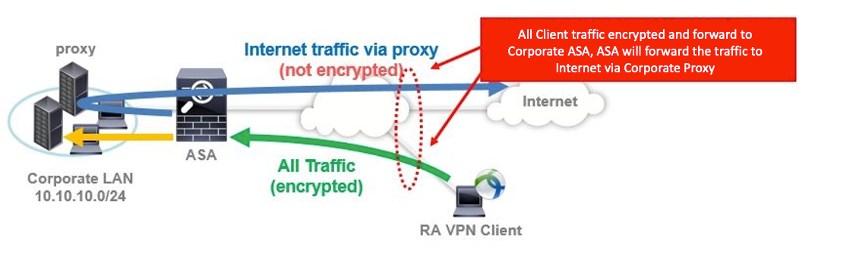
AnyConnect tunnels all traffic by default. Communication to the Internet is also tunneled, so when accessing a website via an internal proxy, performance of both remote access VPN and website access speed will be degraded.
One of the simplest and most effective ways to maximize the performance of your device and ASA is to "tunnel only the traffic you really need". This support can be expected to reduce traffic between the AnyConnect terminal and ASA, and can be expected to improve the performance of both the terminal and ASA.
This section introduces an example of using a split tunnel, which is a technology that splits communication for specific destinations, and terminal security measures when using this function.
-
Only internal communication is split tunneling
You can expect the performance improvement of both client and ASA by letting the client directly access the communication to the Internet and tunneling only the communication to the company. Please see the below link about configuration.
-
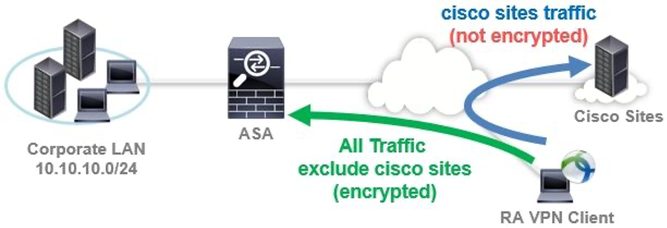
Exclude tunneling only for communication to specific domain (Dynamic Split Tunneling)
While tunneling all communications, there may be cases where you want to directly access the Internet only for cloud applications such as Office 365 and Webex, or for communications to designated domains or FQDNs. In this case, and when using AnyConnect 4.5 or later, it is possible to exclude only the specified domain from the tunneling target by using the Dynamic Split Tunneling function. Please see the below link about configuration. Please note that maximum configurable character of Dynamic Split Tunneling (DST) up to 5,000 characters, excluding separator characters (roughly 300 typically-sized domain names). If you wants to configure many domains/FQDNSs more than 5,000 characters, please use "Static split tunneling for not tunneling all internet traffic" and "Umbrella" instead of DST.
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/security/anyconnect-secure-mobility-client/215383-asa-anyconnect-dynamic-split-tunneling.html
- https://community.cisco.com/t5/-/-/ta-p/4050866
-
Terminal security measures
For businesses that frequently access the Internet, such as in the cloud, by effectively using split tunnels, you can tunnel only the necessary traffic and greatly improve the performance of the terminal and ASA. However, direct Internet access from the device directly exposes the device to threats.
The following additional modules are available for AnyConnect to secure your device.
-
Cisco Umbrella- DNS Web security. Malicious URL, arbitrary URL, application filtering, etc.
-
Cisco AMP ... Advanced malware protection. Supports machine learning, integrated management, and infection route visualization
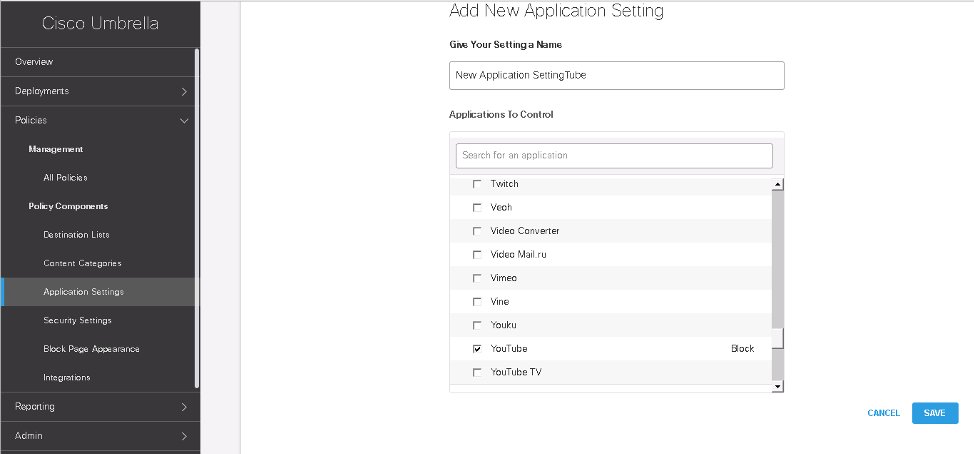
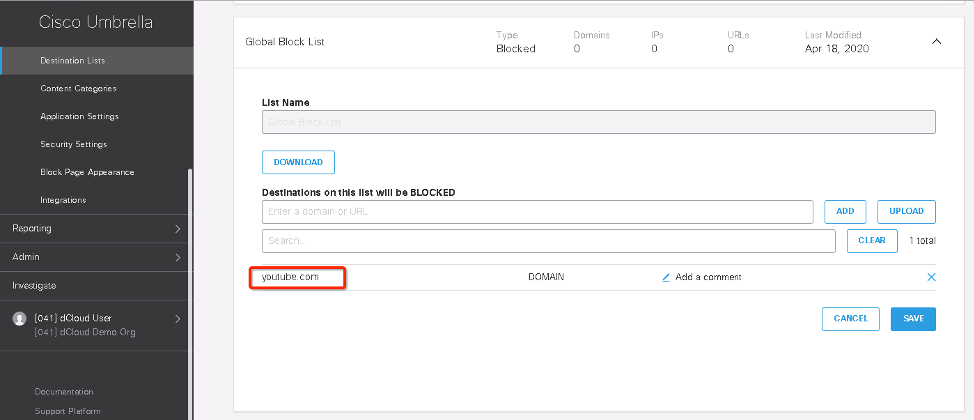
The following is an example of access control of YouTube application from Umbrella Dashboard.
The following is an example of YouTube domain access control from Umbrella Dashboard.
For details on each module and how to install it, please contact your Cisco sales representative or Cisco account team.
For more information about Cisco's teleworking solutions and features, please refer to the guides below.
Use of DTLS
AnyConnect client ASA connection proceeds in the following steps.
-
Establish a session by connecting to ASA using SSL (TCP443) ( * ) and exchanging certificates, authentication, profile information, etc.
-
While transferring data with SSL ( * ), if UDP443 is available, it automatically switches to data transfer with DTLS tunnel using UDP443.
-
If UDP443 cannot be used, continue data transfer using SSL Tunnel (TLS) that uses TCP443
* In reality, more secure TLS is used instead of SSL, but on the CLI display, SSL is used.
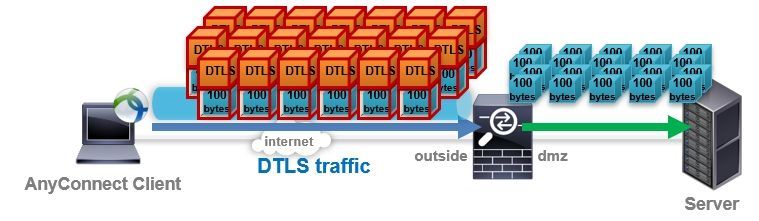
The reason for switching to using DTLS when UDP443 is available is that because UDP is a high-speed protocol with little overhead, data transfer efficiency can be expected. The AnyConnect client will actively attempt to transfer data over the DTLS Tunnel if UDP443 is available.
In the case of data transfer by TCP-based TLS, processing peculiar to TCP such as sequence and order control occurs, and especially in the case of low quality or congested network, re-transmission and delay due to packet drop or order change etc. also occur, and these will improve performance. It becomes a factor to lower. Depending on the communication environment, the performance of TLS may be less than half that of DTLS.
If you want to make an AnyConnect connection using DTLS, the route must allow both SSL (TCP 443) and DTLS (UDP 443). For example, if a teleworker connects remotely, make sure that the router in the home's home allows UDP443 as well as TCP443.
You can check the connection method and data exchange status with DTLS with the show vpn-sessiondb detail anyconnect command. In the example below, you can see that AnyConnect client 1.176.100.101 is connected with DTLSv1.2, encryption is done with AES-GCM-256, and there is about 400Mbytes send (Tx) and about 6Mbytes receive (Rx).
ciscoasa(config)# show vpn-sessiondb detail anyconnect
--- snip ---
DTLS-Tunnel:
Tunnel ID : 10.3
Assigned IP : 1.176.100.101 Public IP : 100.0.0.1
Encryption : AES-GCM-256 Hashing : SHA384
Ciphersuite : ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
Encapsulation: DTLSv1.2 UDP Src Port : 62389
UDP Dst Port : 443 Auth Mode : userPassword
Idle Time Out: 30 Minutes Idle TO Left : 30 Minutes
Client OS : Windows
Client Type : DTLS VPN Client
Client Ver : Cisco AnyConnect VPN Agent for Windows 4.7.04056
Bytes Tx : 392005089 Bytes Rx : 5888313
Pkts Tx : 283106 Pkts Rx : 142874
Pkts Tx Drop : 0 Pkts Rx Drop : 0
You can check the usage status of DTLS and TLS with the show vpn-sessiondb detail command. In the case of the following example, you can see that one client that uses DTLS (= DTLS-Tunnel) and one client that uses TLS (= SSL-Tunnel), that is, two AnyConnect clients are connected. . Note that the SSL-Tunnel also includes the number of clients using DTLS, as clients using DTLS also maintain an SSL tunnel for backups. AnyConnect-Parent is a special tunnel used for management and backup.
ASA5555# show vpn-session detail
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
VPN Session Summary
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Active : Cumulative : Peak Concur : Inactive
----------------------------------------------
AnyConnect Client : 2 : 8 : 2 : 0
SSL/TLS/DTLS : 2 : 8 : 2 : 0
Clientless VPN : 0 : 3 : 2
Browser : 0 : 3 : 2
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Active and Inactive : 2 Total Cumulative : 11
Device Total VPN Capacity : 5000
Device Load : 0%
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tunnels Summary
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Active : Cumulative : Peak Concurrent
----------------------------------------------
Clientless : 0 : 3 : 2
AnyConnect-Parent : 2 : 8 : 2
SSL-Tunnel : 2 : 8 : 2
DTLS-Tunnel : 1 : 7 : 1
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Totals : 5 : 26
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
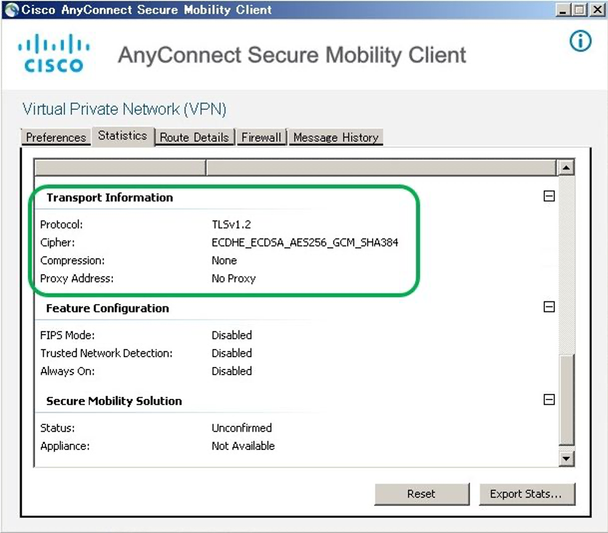
On the AnyConnect terminal side, you can check whether DTLS or TLS is used for the connection from the Statistics tab of the Advanced Window. If the device is connecting with TLS, it is possible that UDP 443 is blocked somewhere along the route between the device and the ASA.
[When using DTLS (UDP443) for data transfer]
[When using TLS (TCP443) for data transfer]
In addition, especially in the environment where many users such as large companies and ISPs remotely access, UDP443 is not allowed in some end user communication environments (or UDP is forgotten), and DTLS and It's not uncommon to have mixed TLS connections. It is difficult to make all connections only DTLS connections, but you can expect performance improvement by increasing the connection ratio of DTLS.
Use the right MTU
Basically, the larger the packet size, the more data that can be sent at one time, and the easier it is to get good performance. In addition, the larger the amount of data that can be sent at one time, the smaller the number of packets that need to be exchanged, which reduces the number of times each packet is encrypted and decrypted, and improves ASA performance. However, if the packet size exceeds the MTU of the route, fragmentation (packet division) and reassembly (packet reassembly) are required, and performance is likely to deteriorate. Therefore, it is easier to get high performance using packet sizes that are not fragmented.
When using DTLS, the MTU between AnyConnect terminals is automatically tuned, so individual customization is usually not required. Since the maximum DTLS encapsulation and encryption overhead is 94 bytes, the AnyConnect terminal uses the value obtained by subtracting 94 bytes from the MTU of the NIC to be used, and also automatically checks whether there is a problem with the MTU of the route. For example, if the terminal's physical adapter has an MTU of 1300, AnyConnect will first try to use the (1300-94) MTU 1206. If MTU1206 detects fragments in the route, it will automatically adjust to use a lower MTU.
Even when using TLS, MTU automatic tuning is supported, but if customer environment is not allowed DTLS(UDP443), for avoiding reconnect issue after 1 minute, configure static anyconnect MTU is available. Please see https://community.cisco.com/t5/-/-/td-p/2217458 in detail about TLS reconnect issue due to MTU.
Please note that the AnyConnect connection also supports IKEv2, but when using IKEv2, it is not compatible with automatic tuning of MTU, so please note that manual setting is required.
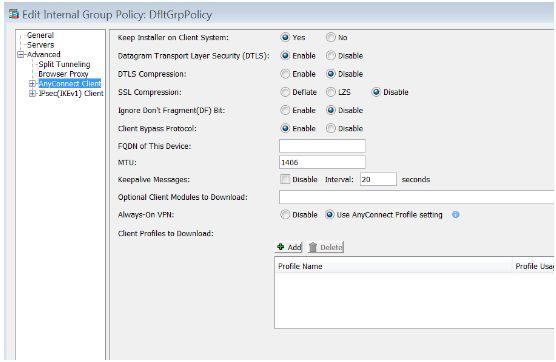
You can check default MTU from Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Group Policies. MTU default is 1406.
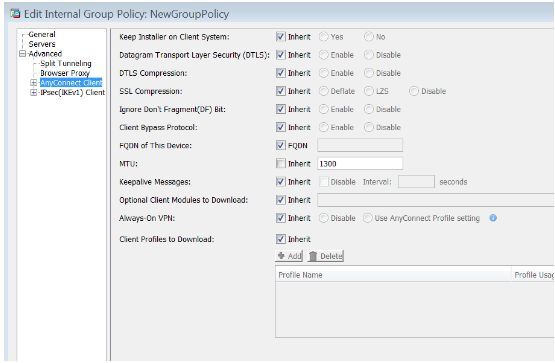
You can configure MTU on each group policy from Advanced > AnyConnect Client.
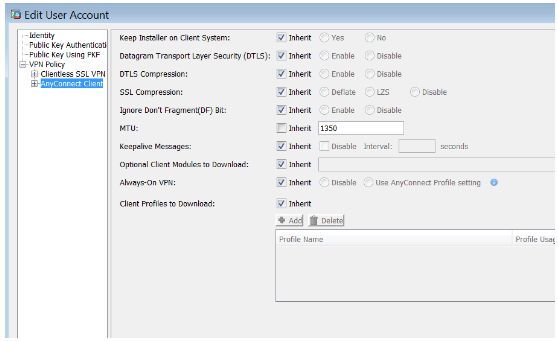
You can configure MTU on each local user from Configuration > Remote Access VPN > AAA/Local Users > Local Users and VPN Policy > AnyConnect Client.
Reduction of unnecessary functions and settings
Since many ASA functions are processed by software, the performance decreases little by little as the number of functions used, the set amount, and the frequency of use (= AnyConnect sessions and the number of connections) increases.
For example, if the ASA is used not only as a remote access VPN termination but also as a PAT / Firewall device for Internet access for in-house communication, the ASA performance is also used for NAT and Firewall processing. This reduces the performance reserve for. Conversely, if you use the ASA as a remote access VPN termination-only machine, you can maximize the performance of the remote access VPN processing of the ASA.
For example, when using VPN filter for access control of AnyConnect, the ACL inspection load for each connection increases as the number of ACL setting lines increases. For example, the ACL inspection load can be reduced by reducing the ACL setting amount by implementing "Control on a segment-by-segment basis rather than IP-based as much as possible" and "Control destination ports as little as possible". Alternatively, the access load on the ASA is reduced or minimized, and ACL access control is performed on the assigned IP address by another device on the route (such as a switch or router), which reduces the processing load on the ASA. Is possible.
For example, if you are using Dynamic Access Policy (DAP), reduce the number of records to 20-30 at the maximum (do not make it too complicated) to improve Control Point (CP) performance and prevent problems by setting DAP.
For example, in an environment where the Syslog function is heavily used, Syslog settings that output a huge amount of logs may lead to performance degradation due to Syslog generation processing and bandwidth pressure due to Syslog messages. You can reduce the logging load by setting logging to an appropriate level. For example, do not enable logging on console/monitor, debug logging should be avoided in normal operation, and reduce multiple syslog servers if configured like the below.
The processing load of communication control functions such as ACL and DAP and management functions such as Syslog is small. However, if the number of connections increases sharply due to the rapid increase in the number of users due to telework, and if a large amount of control such as ACL and DAP is performed for each connection or a huge amount of communication logging occurs, the load may increase in a multiplicative manner, resulting in a non-negligible amount of load. Keeping the configuration simple and optimizing the ASA to concentrate on handling remote access VPN connections can improve ASA performance.
Speed and quality of lines and routes
The reason why VPN performance does not appear is that the maximum speed and quality of the devices and lines on the communication path between the AnyConect terminal and the ASA termination device are bottlenecks. For example, even if you use an ASA with a VPN processing performance of 1 Gbps, if the maximum speed of the communication path line is about 500 Mbps, the ASA can also process only up to about 500 Mbps. In addition, delays and drops due to processing congestion on lines and routing devices can also cause packet retransmissions and communication failures, which can also cause major performance degradation.
Depending on the network operator (ISP) and housing complex equipment, there are cases in which the passage of UDP443 (= DTLS) is refused, or the speed limit of TCP or UDP is applied. As a result, DTLS with good performance cannot be used. , It may lead to the result that the expected speed is not obtained.
If the line or route equipment is the bottleneck, it is necessary to switch to a line or equipment with excellent speed and quality to improve it.
The simple way to identify whether the home line or communication path of a teleworker is a bottleneck is to switch the AnyConnect connection from the home line to another line / equipment such as tethering on a smartphone or a public WLAN. And to see if the quality improves.
Check and disconnect users with high traffic
If you're looking for high-traffic sessions, and you're seeing over-utilization that can hurt overall performance, you can encourage high-traffic users to refrain from using them, or force them to disconnect.
-
Check for AnyConnect sessions with heavy traffic
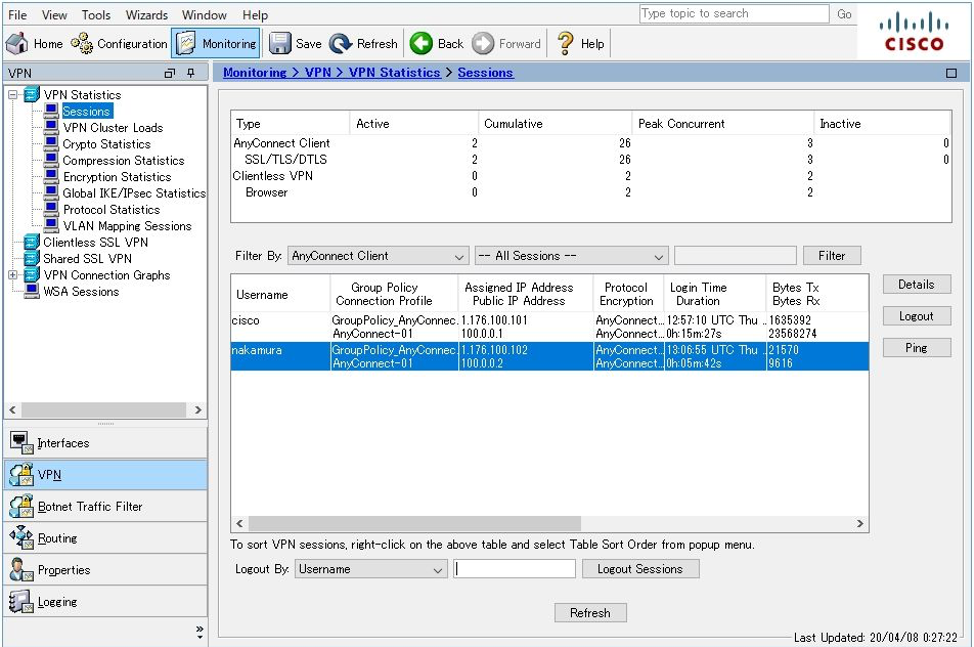
It is convenient to execute the " show vpn-sessiondb anyconnect | in Username | Bytes | Duration " command to check the traffic volume and connection time for each user name . In the output example below, Mr. Nakamura (nakamura) has a connection time of about 10 minutes and about 5 GB (≈ 5,156,556,220) of data is sent (Tx) from the ASA, and cisco has a connection time of about 1 minute. You can confirm that the ASA is receiving (Rx) data of 23MB (≈23,545,802).
ASAv10(config)# show vpn-sessiondb anyconnect | in Username|Bytes|Duration Username : nakamura Index : 35 Bytes Tx : 5156556220 Bytes Rx : 75519009 Duration : 0h:10m:31s Username : cisco Index : 36 Bytes Tx : 661625 Bytes Rx : 23545802 Duration : 0h:01m:08s ASAv10(config)#
You can disconnect the AnyConnect session of the specified user name with the "vpn-session logoff name <Username>" command. In the output example below, Mr. Nakamura, who has a particularly large amount of communication, is disconnected.
ASAv10 (config) # vpn-session logoff name nakamura
Do you want to logoff the VPN session (s)? [Confirm]
INFO: Number of sessions with name "nakamura" logged off: 1
The following is an excerpt of the log when manually disconnecting. You can also check the number of bytes sent (xmt) and received (rcv) from the disconnection log.
Apr 02 2020 13:00:57:% ASA-4-722037: Group <GroupPolicy_AnyConnect-01> User <nakamura> IP <100.0.0.2> SVC closing connection: Administrator Reset.
Apr 02 2020 13:00:57:% ASA-6-716002: Group <GroupPolicy_AnyConnect-01> User <nakamura> IP <100.0.0.2> WebVPN session terminated: Administrator Reset.
Apr 02 2020 13:00:57:% ASA-4-113019: Group = AnyConnect-01, Username = nakamura, IP = 100.0.0.2, Session disconnected. Session Type: AnyConnect-Parent, Duration: 0h: 13m: 10s, Bytes xmt: 5306488447, Bytes rcv: 77713985 , Reason: Administrator Reset
When disconnected, the AnyConnect terminal will pop up the reason for disconnecting "The secure gateway has terminated the VPN connection. The following message was received from the secure gateway: Administrator Reset".
Even if you disconnect, the AnyConnect client can reconnect to the ASA. If you want to always reject the connection from that user, you need to take additional measures such as deleting or suspending the user account.
When using ASDM, you can perform communication status with the user and disconnect (Logout) the specified user from Monitoring> VPN> VPN Statistics> Sessions .
-
Check connections and users with high communication volume
For example, the following is a confirmation example of a connection with a traffic volume of 100 Mbytes or more and less than 1 Tbyte. From 1.176.100.101 to 1.0.0.1, you can confirm that about 500MB (≈532,227,750bytes) of communication is occurring.
ASAv10 (config) # show conn long | in (bytes .........,) | (bytes ..........,) | (bytes ........ ...,) | (bytes ............,)
TCP outside: 1.176.100.101/12056 (1.176.100.101/12056) dmz: 1.0.0.1/10355 (1.0.0.1/10355) ), flags UxOB, idle 0s, uptime 1m1s, timeout 1h0m, bytes 532227750 , xlate id 0x7f12b410c980
It is possible to find the user name from the assigned IP address with the " show vpn-sessiondb anyconnect filter a-ipaddress <IP Address> " command. In the example below, the source of communication is Mr. Nakamura, and it can be confirmed from the ASA that the total number of transmitted bytes (Tx) is about 2.1 GB.
ASAv10(config)# show vpn-sessiondb anyconnect filter a-ipaddress 1.176.100.101 Session Type: AnyConnect Username : nakamura Index : 38 Assigned IP : 1.176.100.101 Public IP : 100.0.0.1 Protocol : AnyConnect-Parent SSL-Tunnel DTLS-Tunnel License : AnyConnect Premium Encryption : AnyConnect-Parent: (1)none SSL-Tunnel: (1)AES-GCM-256 DTLS-Tunnel: (1)AES256 Hashing : AnyConnect-Parent: (1)none SSL-Tunnel: (1)SHA384 DTLS-Tunnel: (1)SHA1 Bytes Tx : 2159997739 Bytes Rx : 31630830 Group Policy : GroupPolicy_AnyConnect-01 Tunnel Group : AnyConnect-01 Login Time : 13:22:29 UTC Thu Apr 2 2020 Duration : 0h:06m:15s Inactivity : 0h:00m:00s VLAN Mapping : N/A VLAN : none Audt Sess ID : 019600a9000260005e85e715 Security Grp : none
Change the maximum number of connectable AnyConnect
The ASA accepts RA VPN connections by default up to the maximum number of connections allowed. However, if the number of accesses is concentrated and all units communicate at the same time, or if bursty traffic occurs on some terminals, the throughput that can be used per unit will decrease, and depending on the application you are using, business The throughput may not be practical enough. In addition, the higher the number of simultaneous connections and the rate of new connections, the greater the load on the ASA in managing and processing them.
By lowering the maximum number of connections with the following command, you can reduce the risk of overall performance degradation due to connection and communication congestion.
vpn-sessiondb max-anyconnect-premium-or-essentials-limit [number]
For ASDM, the maximum number of AnyConnect sessions can be set from the menu below.
Configuration> Remote Access VPN> Advanced> Maximum VPN Sessions
For example, if you want to secure a communication speed of about 10 Mbps per desk on a product with a VPN throughput of 1 Gbps, you can secure the throughput per unit by setting the maximum number of connections to 100. (However, in reality, not all of the terminals communicate at the same time, so the maximum number of connections may be increased.)
In addition, the connection exceeding the maximum connectable number will be rejected with the following syslog output. Disconnected AnyConnect users need to manually switch to another remote access VPN server.
Mar 31 2020 13:31:38:% ASA-6-113012: AAA user authentication Successful: local database: user = cisco
Mar 31 2020 13:31:38:% ASA-6-113009: AAA retrieved default group policy (GroupPolicy_AnyConnect-01) for user = cisco
Mar 31 2020 13:31:38:% ASA-6-113008: AAA transaction status ACCEPT: user = cisco
Mar 31 2020 13:31:38:% ASA-4-113029: Group <GroupPolicy_AnyConnect-01> User <cisco> IP <100.0.0.1> Session could not be established: session limit of 1 reached.
Mar 31 2020 13:31 : 38:% ASA-4-113038: Group <GroupPolicy_AnyConnect-01> User <cisco> IP <100.0.0.1> Unable to create AnyConnect parent session.
In addition, the above-mentioned specific number of connections is not limited. First, the number of VPN connections is monitored by SNMP polling, and if any threshold is exceeded, check the user connection status, appropriately tune, and consider measures such as expansion decisions. Is also one of the effective operations.
ASAv performance optimization
ASAv is a virtual appliance and can be installed and used on a virtual infrastructure such as ESXi, KVM, AWS, and Hyper-v. Below are some best practices and verification examples for ASAv performance optimization.
-
Deploy ASAv on new high-performance server
The ASAv VPN performance is affected by the CPU core clock and DRAM processing speed used. Therefore, by deploying ASAv on a high-performance and / or new-generation Intel CPU, or a high-performance server equipped with high-performance memory and NIC, it is possible to improve the VPN performance of the ASAv.
-
With ASA version 9.12 or later and AnyConnect 4.7 or later
DTLSv1.2 is now available on AnyConnect 4.7 and ASA 9.10 and above. Since ASA9.10 has already announced EoL, it is recommended to use the successor stable version 9.12 and even the second-digit even train after that. The latest version of AnyConnect is recommended. DTLSv1.2 uses AES-GCM as the encryption method by default, and supports high-speed processing of AES-GCM depending on the CPU used, so you can expect improved performance.
3. ASAv10 performance comparison example
The following is a performance comparison when using DTLSv1.0 and DTLSv1.2 for each server to which ASAv10 is deployed in the verification environment. The VPN throughput on the ASAv10 data sheet is 150Mbps.
From the following test results, it can be confirmed that high performance is easily obtained when the CPU generation is new (v3 is the 3rd generation) or when the frequency of the CPU core is high. In addition, the following are the test results in a simple environment and settings, and please use the reference level until the throughput varies depending on the settings, functions, environment, etc.
|
Version |
Usage server and |
Tunnel |
Encryption method |
Download speed (measured) |
ASA CPU |
|
AnyConnect 4.7 |
C240-M4 |
DTLSv1.2 |
AES-GCM-256 |
77Mbps |
22 % |
|
AnyConnect 4.6 |
C240-M4 |
DTLSv1.0 |
AES256 |
70Mbpos |
31% |
|
AnyConnect 4.7 |
C240-M3 |
DTLSv1.2 |
AES-GCM-256 |
81Mbps |
30% |
|
AnyConnect 4.6 |
C240-M3 |
DTLSv1.0 |
AES256 |
77Mbps |
32% |
|
AnyConnect 4.7 |
C240-M3 |
DTLSv1.2 |
AES-GCM-256 |
80Mbps |
21 % |
|
AnyConnect 4.6 |
C240-M3 |
DTLSv1.0 |
AES256 |
77Mbps |
27% |
Test method:
-
Paste one DTLS session between AnyConnect terminal and ASAv10 and download large file from FTP server
-
The average packet size is about 1,000 bytes. AnyConnect MTU is 1390 bytes
-
The DTLSv1.2 connection test uses AnyConnect version 4.7 and ASAv 9.12 (3) 9. By default, it automatically connects with DTLSv1.2, and the encryption method is automatically used with AES-GCM-256.
-
The DTLSv1.2 connection test was conducted with the AnyConnect version reduced to 4.6. Since AnyConnect 4.6 does not support DTLSv1.2, the tunnel protocol replaces DTLSv1.0. For DTLSv1.0, AES256 is automatically used as the encryption method.
-
In this test, the settings and configurations of the ASAv and terminals were not changed, except for the AnyConnect version change.
-
AnyConnect connection settings are the simplest remote access VPN connection settings.
5. ASAv throughput limit
Please note that even if you use a high-performance server, ASAv will not outperform the throughput specified in advance. If the throughput limit is exceeded, the rate limit will be applied with some grace.
|
model |
vCPU / RAM |
Maximum throughput |
|
ASAv5 (100 M) |
1 vCPU / 1 GB |
100 Mbps |
|
ASAv10 (1 GB) |
1 vCPU / 2 GB |
1 Gbps |
|
ASAv30 (2 GB) |
4 vCPU / 8 GB |
2 Gbps |
|
ASAv50 (10 GB) |
8 vCPU / 16 GB |
10 Gbps |
6. ASAv Network Adaptor
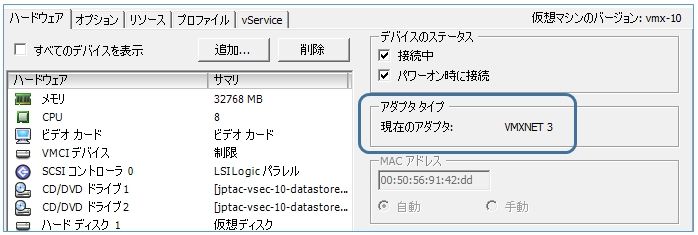
If ASAv is deployed on VMware environment, good performance can be expected when network adapter type is VMXNET3 or IXGBE-VF. You can check the network adapter you are using by editing the virtual machine settings. In the case of the following example, you can see that you are using VMXNET3.
Alternatively, you can check with the show interface command. In the following example, you can see that you are using E1000.
ciscoasa# show interface m0/0 Interface Management0/0 "management", is up, line protocol is up Hardware is net_e1000_em, BW 1000 Mbps, DLY 1000 usec
| Type | Output | Description |
| E1000 | net_e1000_em | Old VMware default (deprecated) Supported in ASAv 9.2(1) and later |
| VMXnet3 | net_vmxnet3 | VMware default Supported on ASAv 9.9(2) and later (*LRO should be disabled) |
| IXGBE-VF | net_ixgbe_vf | AWS default Required for SR-IOV support Supported on ASAv 9.8(1) and later |
| Virtio | net_virtio | KVM default Supported on ASAv 9.3(2.200) and later |
When using VMXnet3, LRO should be disabled to optimize performance. Please refer to the VMware guide or the configuration guide of the version used by ASAv about the method of disabling LRO. For exmaple, the below is quoted from ASAv 9.14 configuration guide.
Disable LRO for VMware and VMXNET3 Large Receive Offload (LRO) is a technique for increasing inbound throughput of high-bandwidth network connections by reducing CPU overhead. It works by aggregating multiple incoming packets from a single stream into a larger buffer before they are passed higher up the networking stack, thus reducing the number of packets that have to be processed. However, LRO can lead to TCP perfomance problems where network packet delivery may not flow consistently and could be "bursty" in congested networks. Important VMware enables LRO by default to increase overall throughput. It is therefore a requirement to disable LRO for ASAv deployments on this platform.
High-end model performance optimization
Note: If you use AnyConnect SSL connection on high-end model, please consider tuning.
High-end models such as the ASA5545 / 5555/5585 and FPR4100 / 9300 series ( * ) are equipped with a dedicated encryption processing engine for high-speed processing, and the processing priority of the encryption processing engine is either IPsec, SSL, or Balanced. You can change the crab. ASA5545 / 5555/5585 has IPsec as the default value, and FPR4100 / 9300 series has Balanced as the default value.
(* As of April 2020, the latest models of the FPR4100 series, FPR4115 / 4125/4145 and FPR9300 module SM-40 / 48/56, do not support this tuning. Expansion request: CSCvt78848)
For example, in most environments where SSL is used , executing the " crypto engine accelerator-bias ssl " command causes the core in the cryptographic processing engine to switch to SSL processing priority assignment, maximizing the performance of AnyConnect during SSL connection. Can be converted.
For example, in an environment where the processing loads of SSL and IPsec are similar, by executing the " crypto engine accelerator-bias balanced " command, the core in the cryptographic processing engine becomes 50% for IPsec processing and 50% for SSL processing. Well both cryptographic operations are possible.
You can use the " show vpn-sessiondb detail" command to check which of SSL and IPsec is used most in your environment . For example, in the output example below, SSL occupies almost 100% of the entire VPN session, and IKEv1 and IPsec are extremely small, so if this usage continues, " crypto engine accelerator-bias ssl " I find it best to prioritize SSL processing in the command.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
VPN Session Summary
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Active : Cumulative : Peak Concur : Inactive
----------------------------------------------
AnyConnect Client : 2121 : 12111 : 3086 : 8
SSL/TLS/DTLS : 2121 : 12111 : 3086 : 8
Load Balancing(Encryption) : 1 : 50 : 2
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Active and Inactive : 2130 Total Cumulative : 12151
Device Total VPN Capacity : 10000
Device Load : 21%
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tunnels Summary
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Active : Cumulative : Peak Concurrent
----------------------------------------------
IKEv1 : 1 : 10 : 2
IPsec : 1 : 3 : 2
AnyConnect-Parent : 2109 : 12111 : 3086
SSL-Tunnel : 2034 : 25859 : 3055
DTLS-Tunnel : 1496 : 13451 : 2279
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Totals : 5651 : 51434
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note that the execution of the " crypto engine accelerator-bias [IPsec | balanced | ssl]" command may be affected by communication, so please execute it during maintenance time or during a time when communication is not significantly affected.
You can check the allocation ratio and processing status of the core with the " show crypto accelerator load-balance " command.
For example, the following is an example of command execution and confirmation on the ASA5555. In the case of default IPsec priority, the core usage ratio is "IPSEC 5, SSL 3", after changing to Balanced it is "IPSEC 4, SSL 4", and after changing to SSL it is "IPSEC 1, SSL 7" You can see that
ASA5555 (config) # show crypto accelerator load-balance ssl
Crypto SSL Load Balancing Stats:
==================================
Engine Crypto Cores SSL Sessions Active Session
Distribution (%)
====== ============== =========================== === =============
0 IPSEC 5, SSL 3 Total: 2422 Active: 3 100.0%
--- abbreviation ---
ASA5555 (config) #
ASA5555 (config) # crypto engine accelerator-bias?
configure mode commands / options:
balanced Equally distribute crypto hardware resources
ipsec Allocate crypto hardware resources to favor IPsec / Encrypted Voice (SRTP)
ssl Allocate crypto hardware resources to favor SSL
ASA5555 (config) #
ASA5555 (config) # crypto engine accelerator-bias ssl
ASA5555 (config) #
ASA5555 (config) # show crypto accelerator load ssl
Crypto SSL Load Balancing Stats:
==================================
Engine Crypto Cores SSL Sessions Active Session
Distribution (%)
====== ============== =========================== === =============
0 IPSEC 4, SSL 4 Total: 2423 Active: 2 100.0%
--- abbreviation ---
ASA5555 (config) #
ASA5555 (config) # crypto engine accelerator-bias ssl
ASA5555 (config) #
ASA5555 (config) # show crypto accelerator load ssl
Crypto SSL Load Balancing Stats:
==================================
Engine Crypto Cores SSL Sessions Active Session
Distribution (%)
====== ============== =========================== === =============
0 IPSEC 1, SSL 7 Total: 2426 Active: 4 100.0%
The following is an example of command execution and confirmation with the FPR4150 of the FPR4100 series. You can see that FPR4150 has two engines for cryptographic processing, IPSEC 28: SSL 28 in the case of default Balanced, and IPSEC 4: SSL 52 when switching to SSL priority processing. The cryptographic engine and number of cores differ depending on the model, and the number of assigned cores also differs.
FPR4150 (config) # show crypto accelerator load
Crypto IPSEC Load Balancing Stats:
==================================
Engine Crypto Cores IPSEC Sessions Active Session
Distribution (%)
====== ============== =========================== === =============
0 IPSEC 28, SSL 28 Total: 0 Active: 0 0.0%
1 IPSEC 28, SSL 28 Total: 0 Active: 0 0.0%
----- abbreviation -----
FPR4150 (config) #
FPR4150 (config) # crypto engine accelerator-bias ssl
FPR4150 (config) #
FPR4150 (config) # show crypto accelerator load
Crypto IPSEC Load Balancing Stats:
==================================
Engine Crypto Cores IPSEC Sessions Active Session
Distribution (%)
====== ============== =========================== === =============
0 IPSEC 4, SSL 52 Total: 0 Active: 0 0.0%
1 IPSEC 4, SSL 52 Total: 0 Active: 0 0.0%
Configuration change
Upgrade or Configuration Change
If the existing ASA does not have sufficient performance or processing capacity due to an increase in throughput or the number of simultaneous connections even if it is optimized, it will be necessary to replace it with a higher-level device or add an ASA. The following is an example of how to respond by changing the configuration.
-
Upgrade to higher model
By replacing the existing device and migrating the settings to a higher model, it is possible to improve the performance and the maximum number of connectable devices without significantly changing the settings and configurations. The simplest and most reliable method.
-
Operation of multiple ASAs and use of server list function
You can operate each ASA as a simple Active / Active configuration by adding more ASAs and dividing the connection destinations by area and number of people.
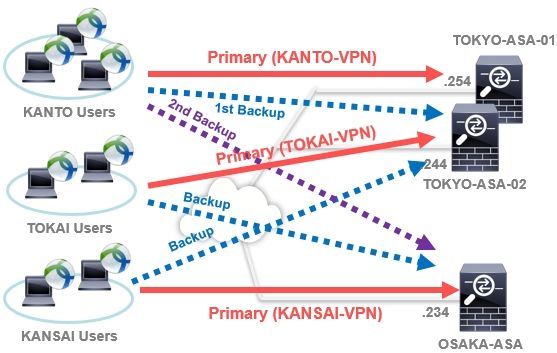
For example, as in the configuration below, users in the Kanto area use TOKYO-ASA-01, users in the Tokai area use TOKYO-ASA-02, and users in the Kansai area use OSAKA-ASA as the primary server and other ASAs. By designating as the backup server, you can ensure load balancing on each ASA and ensure redundancy in case of failure. Each ASA requires a public IP address.
Because each ASA operates independently, there is no configuration or state synchronization between ASAs. Therefore, each ASA needs individual management.
Especially in an environment where multiple ASAs are already used as Internet firewalls, it is an advantage that this configuration can be used relatively easily if remote access VPN server settings are made for each ASA.
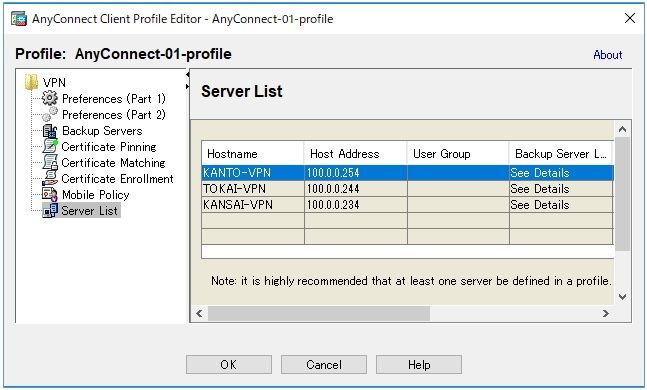
The backup server can be specified using AnyConnect Client Profile. The below is example of configuring client profile in Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > AnyConnect Client Profile.
You can add "Backup Server" from Server List > Add > Backup Servers.
The below is configuration example of xml file when the above scenario.
Created client profile will be automatically distributed to client and used, when the AnyConnect client is connected on the ASA. You can check downloaded client profile in C:\ProgramData\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client\Profile folder if using windows 10/8/7/Vista, or /opt/cisco/vpn(or anyconnect)/profile forlder if using MAC OS X and Linux.
-
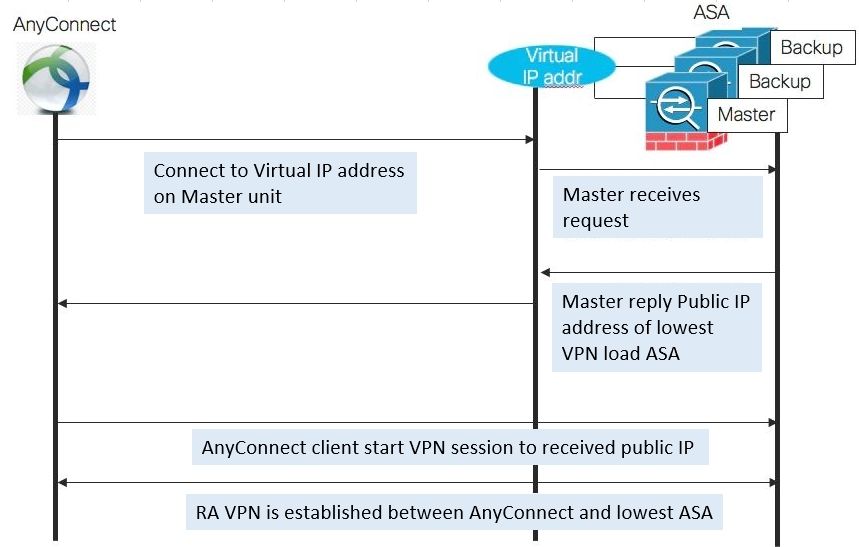
Operation of multiple ASAs and use of VPN load balancing function
By adding an ASA and configuring VPN load balancing on each ASA, the AnyConnect terminal can automatically connect to the ASA with the lightest load.
VPN load balancing has the following features.
-
Load balancing configuration dedicated to VPN access that can be configured with 2 to 10 ASAs
-
Different models are also available. Use of the same version recommended for each device
-
One becomes a Master machine and manages the VPN connection status of other Backup machines
-
AnyConnect first connects to the shared virtual IP address of the Master machine. The master machine responds with the ASA's public IP address, which is less loaded
-
You need +1 public IP address for the number of the shared virtual IP address and the public IP address of each ASA. For example, if you want to use VPN load balancing with 4 ASAs, you need 5 public IP addresses.
-
Settings and states are not synchronized on each device
For example, if you configure VPN Load Balancing with 2 ASAs, each of which can terminate up to 500 VPNs, you can terminate up to 1000s. Since the remote access VPN processing load is distributed to each device, it is possible to avoid bottlenecks caused by concentrated connections on one device.
Note that settings and states are not synchronized on each device, so if one ASA fails, the remote access VPN connection terminated by that ASA must be restarted from the beginning. Therefore, VPN load balancing is suitable for environments where there is a margin in the ASA or public IP address and performance and the number of simultaneous connections are especially important.
For details on VPN load balancing, refer to the configuration guide for your version. For example, the following is an example configuration guide for ASA version 9.12.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/asa/asa912/configuration/vpn/asa-912-vpn-config/vpn-ha.html.
-
Comparison of configuration changes
Advantages and disadvantages differ for each configuration. Below is a comparison table.
|
Configuration change example |
Minimum public IP address |
Maximum number of simultaneous connections |
Switch on failure |
load distribution |
|
In the upper model upgrade |
One |
One car only |
With session protection |
One unit only |
|
With multiple ASAs Server list |
Required for the number of units |
Sum of each unit |
Automatic switching No session protection |
Manual |
|
With multiple ASAs VPN load balancing |
Required for the number of units and +1 for virtual IP |
Sum of each unit |
Automatic switching No session protection |
Automatic |
Troubleshooting
Check CPU usage
CPU usage directly affects VPN performance. The CPU usage rate increases as the number of encryption and decryption processes increases, so when the VPN throughput is close to the limit, you can almost always see a high CPU usage rate. Even if the same VPN throughput is generated, the CPU usage rate will be affected by various factors such as the products and functions used, the setting amount, the number of simultaneous connections, the traffic pattern, the usage version, and the environment.
The following three commands are particularly useful for checking CPU usage and load. The following commands are also included when the show tech command is acquired.
-
show cpu usage
-
show process cpu-usage non
-
show cpu detail
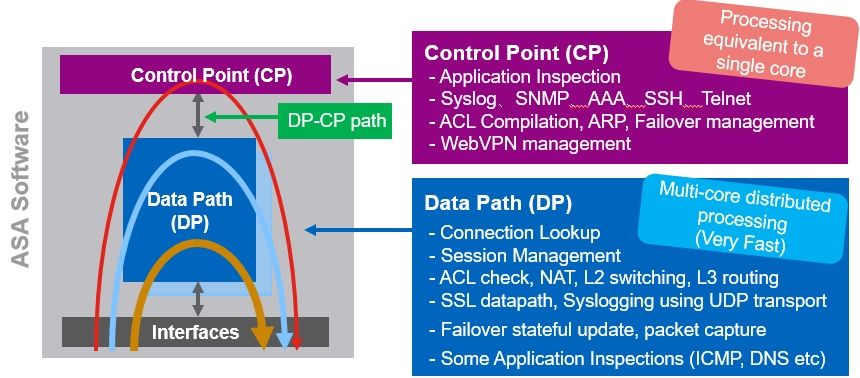
You can check total cpu usage by "show cpu usage" command. You can check processing load by "show process cpu-usage non" command. You can check each load of "data path" and "control point" by "show cpu detail" command. The below is software processing architecture overview of ASA software.
The load status of the entire CPU and each core can also be monitored by SNMP polling. Please refer to the following sample for the monitoring method by SNMP polling. In addition, it is necessary to check from the command line for detailed confirmation of each process load and Control Point (CP) load.
5 seconds CPU usage 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.10. cpmCPUTotalMonIntervalValue 1 minutes CPU usage 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7. cpmCPUTotal1minRev 5 minutes CPU usage 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.8. cpmCPUTotal5minRev
ASA5555(config)# show cpu core Core 5 sec 1 min 5 min Core 0 13.4% 5.1% 2.2% Core 1 13.6% 5.2% 2.3% cisco@ubuntu:~$ snmpwalk -v 2c -c test 1.0.0.100 .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.1 = Gauge32: 5 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.2 = Gauge32: 4 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.3 = Gauge32: 5 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.4 = Gauge32: 5 cisco@ubuntu:~$ snmpwalk -v 2c -c test 1.0.0.100 .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.8 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.8.1 = Gauge32: 2 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.8.2 = Gauge32: 2 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.8.3 = Gauge32: 2 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.8.4 = Gauge32: 2 cisco@ubuntu:~$ snmpwalk -v 2c -c test 1.0.0.100 .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.1 = Gauge32: 5 <--- System CPU load iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.2 = Gauge32: 4 <--- Core 0 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.3 = Gauge32: 5 <--- Core 1 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.109.1.1.1.1.7.4 = Gauge32: 5 <--- Aggregate system load
Case Study 1: Overload due to heavy communication or connection
The most common overload case.
In the example below, the CPU usage is 88%, which is clearly an overload. The breakdown of 88% CPU usage is that DATAPATH is 44%, and it can be confirmed that a small CPU load is generated in other processes such as Logger, ARP, and CP Processing. DATAPATH is a process that distributes relatively simple processing such as VPN (SSL and IPsec) and Firewall (ACL / NAT / Routing / Session management, etc.) with multi-core and at high speed. In other words, in the case of the following example, it can be confirmed that the basic processing of VPN / Firewall uses 88% of CPU and is overloaded.
ASA# show cpu usage CPU utilization for 5 seconds = 88%; 1 minute: 88%; 5 minutes: 82% ASA# show processes cpu-usage non-zero PC Thread 5Sec 1Min 5Min Process 0x00000000019da592 0x00007fffd808b040 0.0% 0.0% 0.5% Logger 0x0000000000844596 0x00007fffd807bd60 0.0% 0.0% 0.1% CP Processing 0x0000000000c0dc8c 0x00007fffd8074960 0.1% 0.1% 0.1% ARP Thread - - 43.8% 43.8% 40.3% DATAPATH-0-2209 - - 43.9% 43.8% 40.3% DATAPATH-1-2210
Generally, if the CPU usage of the ASA is 80% or more, it may cause communication drop or instability, which can be said to be an overload. If it is difficult to improve the CPU high load even after tuning this document, it is necessary to consider configuration changes such as equipment upgrades and expansions. The higher the model, the more cores and CPUs it usually has, and the higher-performance cryptographic processing engine is installed. Therefore, the performance is improved by the distributed processing of the data paths of many cores.
Case Study 2: Overload due to overuse of CP function
The ASA process includes DATAPATH processing optimized for VPN / Firewall processing that supports multi-core distributed processing, and "other processing" (Failover management, logging, SNMP, SSH / Telnet / Console, and fine control of WebVPN. Etc.). "Other processing" is usually processed in the Control Point (CP) area. The Control Point has a maximum processing capacity of 1 core.
In the following example, the CPU usage rate is 9%, but the processing capacity of the CP is almost at its limit, and the CP becomes a bottleneck, causing an overload. The CP load status can be confirmed by adding the right figure in parentheses of the show cpu detail command.In the example below, it is 24.4 + 22.6 + 21.0 + 24.8, and it can be confirmed that the CP load is 92% and overloaded. . Alternatively, it can be calculated by multiplying the total process load other than DATAPATH of the show process cpu-usage command by the number of cores. For example, in the following output example, it can be seen that the CP load is (5.3% + 0.2%) x 16 = approximately 88%.
In the case of the following example, it can be seen that Unicorn Proxy Thread, which performs detailed control of WebVPN, uses about 85% (= 5.3% x 16) of CP processing capacity, which is a bottleneck. When the CP is overloaded, delays, process failures, and instability of a wide range of functions such as connection management of AnyConnect, which is a CP function, Failover, VPN load balancing management, SSH / Telnet / Console operation, logging and SNMP processing, etc. Will lead to serious problems such as.
Since CP processing hits the brain of ASA, it is important to keep the CP load low in order to keep ASA stable. We recommend that the CP processing load be at most 30-40% or less.
ASA# show cpu usage CPU utilization for 5 seconds = 9%; 1 minute: 7%; 5 minutes: 6% ASA# show cpu detail Break down of per-core data path versus control point cpu usage: Core 5 sec 1 min 5 min Core 0 27.1 (2.6 + 24.4) 16.7 (2.6 + 14.1) 14.9 (2.5 + 12.5) Core 1 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) 3.3 (3.3 + 0.0) 3.1 (3.1 + 0.0) Core 2 4.0 (4.0 + 0.0) 3.5 (3.5 + 0.0) 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) Core 3 3.0 (3.0 + 0.0) 3.3 (3.3 + 0.0) 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) Core 4 25.5 (2.8 + 22.6) 16.3 (2.7 + 13.6) 14.5 (2.5 + 12.0) Core 5 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) 3.0 (3.0 + 0.0) Core 6 3.6 (3.6 + 0.0) 3.4 (3.4 + 0.0) 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) Core 7 3.0 (3.0 + 0.0) 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) 3.1 (3.1 + 0.0) Core 8 24.0 (3.0 + 21.0) 16.3 (2.7 + 13.6) 14.7 (2.6 + 12.2) Core 9 3.8 (3.8 + 0.0) 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) 3.1 (3.1 + 0.0) Core 10 3.6 (3.6 + 0.0) 3.3 (3.3 + 0.0) 3.1 (3.1 + 0.0) Core 11 2.8 (2.8 + 0.0) 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) 3.0 (3.0 + 0.0) Core 12 27.3 (2.4 + 24.8) 16.2 (2.5 + 13.7) 14.7 (2.5 + 12.3) Core 13 3.6 (3.6 + 0.0) 3.3 (3.3 + 0.0) 3.1 (3.1 + 0.0) Core 14 4.0 (4.0 + 0.0) 3.3 (3.3 + 0.0) 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) Core 15 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0) 3.4 (3.4 + 0.0) 3.2 (3.2 + 0.0)
ASA# show process cpu-usage sorted non-zero Hardware: ASA5585-SSP-40 Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance Software Version 9.x(x)x ASLR enabled, text region xxxxxxxxx-xxxxxxxxxx PC Thread 5Sec 1Min 5Min Process 0x00007f5a311dfd8c 0x00007f59f813e640 5.3% 3.2% 2.8% Unicorn Proxy Thread <--- - - 0.3% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-2-2622 - - 0.3% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-14-2634 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-9-2629 0x00007f5a30bc780d 0x00007f59f8166440 0.2% 0.0% 0.0% ssh <--- - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-6-2626 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-10-2630 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-13-2633 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-1-2621 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-5-2625 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-15-2635 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-7-2627 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-8-2628 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-3-2623 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-4-2624 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-0-2620 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-11-2631 - - 0.2% 0.2% 0.2% DATAPATH-12-2632
This is due to overloading of CP processing, often due to misconfiguration or excessive use of features or settings with a large number of sessions. In many cases, it can be improved by reviewing the used functions and settings and reducing or disabling the functions and settings as appropriate.
Even if it is reviewed, if the CP load does not decrease and the CP overload causes a problem because it is difficult to reduce it with the necessary functions and settings in the security policy , add a device and perform communication and processing. It is necessary to consider distributing the CP processing load. For example, if one unit has AnyConect termination, it can be distributed with two and have AnyConnect termination, and the actual CP processing capacity will be approximately doubled.
In the case of CP overload scenario, the CP performance improvement effect by upgrading to a higher model is limited. This is because the CP processing capacity of each model is limited to one core.
The below is list of main processes on ASA. Almost processes exclude DATAPATH/Dispatch Unit are processed on CP.
| Process Name | Explanation |
| aaa | process related to AAA feature |
| ARP Thread | process related to ARP processing |
| arp_timer | ARP timer to monitor and clear the ARP cache |
| ci/console | Console session |
| CP Processing |
Main thread for event packet processing from data path to control point |
| DATAPATH-X-YYY | Main thread in data path processing. A different thread operates for each core (X) |
| Dispatch Unit | Main thread in data path processing of single core model |
| emweb/https | HTTPS server thread used for SSL VPN, etc. |
| fover_FSM_thread | Failover monitoring thread |
| IKE Daemon | Main threads in IKE processing |
| Logger | Syslogging thread (e.g. Syslog server logging, console, buffer, monitor) |
| Session Manager | VPN session database timer thread |
| snmp | Thread that receives and processes SNMP polls |
| SNMP Notify Thread | Thread that sends SNMP traps |
| ssh | SSH session thread |
| telnet/ci | Telnet session thread |
| tmatch compile thread | Compile thread for speeding up ACL / NAT processing after changing ACL / NAT If ASA is reloaded, full ACL/NAT compilation will happen |
| Unicorn Admin Handler | ASDM session thread |
| Unicorn Proxy Thread | Threads related to WebVPN processing such as AnyConnect VPN session |
| aaa_shim_thread | Thread used in WebVPN DAP and dACL |
| vpnfol_thread_msg | VPN failover related main thread |
Check the number of VPN sessions
There are several reasons why it is important to check the number of VPN sessions and maintain an appropriate number of sessions, but most importantly, as the number of VPN sessions increases, VPN throughput is shared among connected users. The available throughput per user is reduced. It is desirable to be able to provide business-free throughput, but if VPN access is concentrated and the number of users increases, the available throughput per user will decrease accordingly. However, it is usually necessary to provide each connected user with the minimum required throughput for performing business, even under the condition that access is extremely concentrated, even if there is delay or stress.
For example, when using a product with a VPN throughput of 1 Gbps, "comfortable work throughput is 10 Mbps or more for stress-free work" and "minimum required throughput for work is 1 Mbps or more" Can be considered to be limited to 100 and the latter to 1000. (In fact, accommodating a large number of connections adds additional processing overhead to the ASA, so it's a good idea to leave some performance margin for the ASA.)
Also, as the number of VPN sessions increases, the new VPN session processing load and the management processing of the number of simultaneous VPN sessions become necessary, which increases the CPU load on the ASA.
Also, as the number of simultaneous connections increases, the maximum number of VPN connections for that usage model may be reached. If the maximum number of VPN connections is reached, subsequent new connections will be rejected. If there are more connections than expected, you may need to investigate where the connections are coming from, and disconnect or distribute connections as needed and add ASAs.
You can use the show vpn-sessiondb summary command to check the current number of VPN sessions, the number of peak sessions, the capacity of the device used , and so on. In the following example, the number of VPN sessions (Total Active and Inactive) is 4 and the maximum accessible number of devices (Device Total VPN Capacity) is 250, so the usage rate of the number of VPN sessions (Device Load) is 2%. You can see that
ASAv10(config)# show vpn-sessiondb summary
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
VPN Session Summary
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Active : Cumulative : Peak Concur : Inactive
----------------------------------------------
AnyConnect Client : 3 : 36 : 4 : 1
SSL/TLS/DTLS : 3 : 36 : 4 : 1
Clientless VPN : 0 : 2 : 2
Browser : 0 : 2 : 2
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Active and Inactive : 4 Total Cumulative : 38
Device Total VPN Capacity : 250
Device Load : 2%
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
Active |
Number of active session connections exchanging data |
|
Cumulative |
Total number of active sessions included in the past (including disconnected sessions) |
|
Peak Concur |
Peak number of active sessions |
|
Inactive |
Number of inactive sessions that cannot exchange data |
|
Total Active and Inactive |
Total number of VPN connections |
|
Device Total VPN Capacity |
Maximum number of VPN connections that can be stored on your device |
You can check how many sessions are currently exchanging data by checking the Active number. You can check the peak number of AnyConnect connections by checking Peak Concur.
If you wants to monitor total active and inactive sessions and maximum VPN session, following OID is available. MIB is CISCO-REMOTE-ACCESS-MONITOR-MIB.
| OID | Object Name | Explanation |
| 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.392.1.1.1 | crasMaxSessionsSupportable | Maximum number of sessions that can be supported |
| 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.392.1.3.1 | crasNumSessions | Session number |
ASAv10(config)# show vpn-sessiondb summary --------------------------------------------------------------------------- VPN Session Summary --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Active : Cumulative : Peak Concur : Inactive ---------------------------------------------- AnyConnect Client : 2 : 35 : 4 : 1 SSL/TLS/DTLS : 2 : 35 : 4 : 1 Clientless VPN : 0 : 2 : 2 Browser : 0 : 2 : 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total Active and Inactive : 3 Total Cumulative : 37 Device Total VPN Capacity : 250 Device Load : 1% ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
## SNMP Polling Test ##
cisco@ubuntu:~$ snmpwalk -v 2c -c cisco 1.150.0.169 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.392.1.1.1 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.392.1.1.1.0 = INTEGER: 250 cisco@ubuntu:~$ cisco@ubuntu:~$ snmpwalk -v 2c -c cisco 1.150.0.169 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.392.1.3.1 iso.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.392.1.3.1.0 = Gauge32: 3 cisco@ubuntu:~$
Check traffic volume and average packet size
You can see the throughput and average packet size for each interface on the ASA with the show traffic command.
For example, the following is a sample output of the show traffic command when uploading 100 bytes of UDP data at a speed of about 23 Mbps from the AnyConnect terminal to the file server via the ASA . I am using DTLS (default) for data transfer.
ASAv10 # show traffic
outside:
received (in 764949.640 secs):
58046368 packets 8402724238 bytes
2 pkts / sec 10002 bytes / sec
transmitted (in 764949.640 secs):
37863434 packets 46137328134 bytes
4 pkts / sec 60005 bytes / sec
1 minute input rate 23069 pkts / sec, 5005932 bytes / sec
1 minute output rate 2 pkts / sec, 1349 bytes / sec
1 minute drop rate, 0 pkts / sec
5 minute input rate 100 pkts / sec, 111376 bytes / sec
5 minute output rate 1 pkts / sec, 1307 bytes / sec
5 minute drop rate, 0 pkts / sec
dmz:
received (in 764949.640 secs):
42560852 packets 43254954890 bytes
5 pkts / sec 56001 bytes / sec
transmitted (in 764949.640 secs):
57972736 packets 3845145682 bytes
2 pkts / sec 5004 bytes / sec
1 minute input rate 16 pkts / sec, 2092 bytes / sec
1 minute output rate 23075 pkts / sec, 2953414 bytes / sec
1 minute drop rate, 0 pkts / sec
5 minute input rate 7 pkts / sec, 1545 bytes / sec
5 minute output rate 100 pkts / sec, 102823 bytes / sec
5 minute drop rate, 0 pkts / sec
|
|
Average throughput (bps) |
Average packet size (bytes) |
|
formula |
([input bytes / sec] + [output bytes / sec]) x 8 |
([input bytes / sec] + [output bytes / sec]) |
|
Outside side |
(5005932 + 1349) x 8 = 40,058,248 |
( 5005932 + 1349) ÷ (23069 + 2) |
|
DMZ side |
(2092 + 2953414) x 8 = 23,644,048 |
(2092 + 2953414) ÷ (16 + 23075) |
In the above example, the DMZ side (file server side) has about 23 Mbps of traffic and the average packet size is 127 bytes, which can be seen from the show traffic command. Also, if the average packet size to be exchanged is small, it can be seen that a huge packet exchange of nearly 23,000 packets per second is required to obtain the throughput of 23Mbps. The larger the number of packets processed, the more time it takes for DTLS encryption, decryption, and processing on both the ASA and AnyConnect terminals, resulting in an increase in the CPU load on each device and a decrease in performance.
On the Outside side (Internet side), you can see that the traffic has increased by about 17 Mbps and the average packet size has also increased by 90 bytes due to the overhead of DTLS encryption. In particular, as the number of packets to be exchanged increases and the size of each packet decreases, the DTLS overhead occupying the line band increases, and the line band is squeezed.
The above is the data when using the light "DTLS" for data transfer. If UDP 443 is not allowed on the route and TLS (= TCP443) is used for data transfer, TLS is TCP-based, so processing such as acknowledgment and flow control and additional packets are AnyConnect. It increases between the terminal and ASA. In other words, if "TLS" is used, the line overhead, the number of packets between the AnyConnect terminal and the ASA, and the processing load thereof will increase, and this will cause a decrease in the performance of the line and ASA / AnyConnect terminals. Since "TLS" is slow, it is recommended to use "DTLS" as the main and minimize the number of AnyConnect terminals that use "TLS" to maximize the performance of the remote access VPN.
Cryptographic processing engine load check (only for high-end models)
When using a high-end machine that supports tuning of cryptographic processing engines, you can check the processing load status of each cryptographic processing engine and its core by using the " show crypto accelerator load-balance ssl " command. Cryptographic processing performance is improved by distributing and processing each engine and core. The higher the model, the more engines and cores for cryptographic processing.
For example, the following is a log example when a high load communication occurs when one DTLS session is pasted between the ASA5555 and AnyConnect terminal. The ASA5555 has one cryptographic processing engine, and you can see that the Core 7 allocated for SSL processing the DTLS connection.
ASA5555(config)# show crypto accelerator load-balance ssl
Crypto SSL Load Balancing Stats:
==================================
Engine Crypto Cores SSL Sessions Active Session
Distribution (%)
====== ============== =========================== ================
0 IPSEC 1, SSL 7 Total: 182 Active: 6 100.0%
--- 略 ---
Encrypted Data 1 second 5 second 60 second
================== ======== ======== =========
Core 1 (load) 0.0% 0.0% 0.0%
Core 2 (load) 0.0% 0.0% 0.0%
Core 3 (load) 0.0% 0.0% 0.0%
Core 4 (load) 0.0% 0.0% 0.0%
Core 5 (load) 0.0% 0.0% 0.0%
Core 6 (load) 0.0% 0.0% 0.0%
Core 7 (load) 100.0% 100.0% 99.9% <--- This
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I download AnyConnect software?
You can download it from the URL below.
https://software.cisco.com/download/home/286281283/type/282364313/release/4.8.03036
To download the software, it is necessary that your account is linked to an appropriate contract.
I want to use AnyConnect, but my ASA can only terminate two VPNs
For the ASA5505 and ASA5500-X series, if the Activation key of the AnyConnect license is not enabled in hardware, the maximum number of remote access VPN terminations is 2 in the single configuration and 4 in the redundant configuration. Limited to one.
If you have purchased the AnyConnect license and this limitation exists, issue PAK in Product License Registration (http://www.cisco.com/go/license), then activate the activation key of the target device by the below procedure.
After that, you will receive mail, which has activation-key. You can activate AnyConnect license limitation to full on the ASA5505/ASA5500-X device.
ASA# conf t ASA(config)# ASA(config)# activation-key 6b3bc050 88fd9b64 cd4035dc f900549c c32fc7ae Validating activation key. This may take a few minutes... Both Running and Flash permanent activation key was updated with the requested key. ASA(config)#
If you do not have an AnyConnect license and you need to use AnyConnect in a hurry as part of measures against corona virus (COVID-19), you can remove the default connection limit for up to 13 weeks by referring to the following document. This application is possible until July 1, 2020 (as of April 2020). If you wish to continue using it for more than 13 weeks, you need to purchase and reapply the AnyConnect license.
When the restriction is released, the number of remote access VPNs that can be terminated by show version is released up to the maximum value of the hardware used. The following is an output example after actually applying the AnyConnect Plus / Apex (ASA) Demo License and Emergency COVID-19 License.
ASA5516# show version Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance Software Version 9.12(3)9 SSP Operating System Version 2.6(1.192) --- 略 --- Licensed features for this platform: Maximum Physical Interfaces : Unlimited perpetual Maximum VLANs : 150 perpetual Inside Hosts : Unlimited perpetual Failover : Active/Active perpetual Encryption-DES : Enabled perpetual Encryption-3DES-AES : Disabled perpetual Security Contexts : 2 perpetual Carrier : Disabled perpetual AnyConnect Premium Peers : 300 91 days AnyConnect Essentials : Disabled perpetual Other VPN Peers : 300 perpetual Total VPN Peers : 300 perpetual AnyConnect for Mobile : Enabled 91 days AnyConnect for Cisco VPN Phone : Enabled 91 days Advanced Endpoint Assessment : Enabled 91 days Shared License : Disabled perpetual Total TLS Proxy Sessions : 1000 perpetual Botnet Traffic Filter : Disabled perpetual Cluster : Disabled perpetual VPN Load Balancing : Enabled perpetual
It should be noted, that's the case Encryption-3DES-AES as in the above example is Disable, because it does not use the AES to be used in the AnyConnect, separately Product License Registration , Licenses> Get Licenses> IPS, Crypto, Other .. Cisco ASA from You can unlock Encryption-3DES-AES by searching and selecting 3DES / AES Licenses, issuing an activation key, and applying the key to the device in the same procedure.
The emergency license is a time-based license. The license you purchase and apply for the AnyConnect license is perpetual. If both are applied at the same time, the permanent license will be automatically used after the time-based license expires.
Will I be disconnected when connecting more than the number of AnyConnect licensed users I have purchased?
However, AnyConnect connection is possible up to the maximum number of connections of the terminating ASA. However, use of more than the number of contract users is a license violation, so if you expect to use more than the number of AnyConnect license users you have, please purchase additional licenses.
Is it possible to connect more than the maximum number of connections for each model?
Connections that exceed the limit are rejected. Therefore, it is recommended to select a device with a sufficient number of simultaneous connections. If the number of devices that can be connected simultaneously is less than the number of terminals that use a remote access VPN, consider a configuration change such as upgrading or adding an ASA.
What happens when a large number of simultaneous connections occur and the allocated IP of the address pool is insufficient?
If there are not enough IP addresses in the Address Pool after the AnyConnect connection, the following syslog message will be output on the ASA side and the AnyConnect connection will fail. Please set the address pool with a margin.
% ASA-3-722020: TunnelGroup tunnel_group GroupPolicy group_policy User user-name IP IP_addressNo address available for SVC connection
What is the Parent-Tunnel that can be confirmed with the show vpn-sessiondb detail command?
The Parent-Tunnel is a special tunnel used for exchanging information when connecting for the first time, controlling for Reconnect, and upgrading AnyConnect image.
Is FTD available for AnyConnect termination?
Yes, FTD can also terminate AnyConnect remote access VPNs, and some of the information in this document can be used to optimize performance. However, FTD has limited AnyConnect features available. For example, FTD does not support authentication by the local user database, so an external authentication server is required. In addition, FTD does not support Split Tunnel, Hostscan, DAP, VPN load balancing function. You can check FTD RAVPN limitation from configuration guide like the below in "Unsupported Features of AnyConnect" section. Please note that FTD RA VPN feature may be varied by version.
On the other hand, when using ASA, it supports the full functionality of AnyConncet, and various tunnings and performance optimizations described in this document are possible.
How to increase VPN speed on AnyConnect device
It is easy to obtain good performance when using a terminal with excellent performance such as CPU, memory, NIC I / O, and that the transmission speed and quality of the line and communication path used by that terminal are good, and when using DTLS. .
The throughput of AnyConnect terminal is up to about 100Mbps
The reason why the throughput does not appear on the terminal side even though there is sufficient VPN processing performance on the ASA side is often due to the terminal performance, the speed and quality of the communication route, and the communication method (using TLS, etc.). is. Check if the CPU usage of the terminal core is high.
Note that the lower the maximum speed of each AnyConnect terminal, the lower the total throughput when the AnyConnect terminals connect simultaneously, so the load on the ASA side will be lower.
Also, in the case of teleworking, it is usually more important to "ensure a throughput (that is the minimum required) for each terminal to perform its work" rather than "maximize the speed of each terminal". is.
Will AnyConnect's Compression feature improve performance?
The compression function is a very old function and is a technology that is intended for use on low-speed WAN lines. As of 2020, this function will not be used under the mainstream high-speed internet connection. If you use compression on a high-speed line, compression processing may cause delays or slowdowns. Therefore, do not enable the compression function without the instruction or support of an engineer. Also, this function is disabled by default.
Does using DTLSv1.2 improve performance other than ASAv?
As you can expect, physical appliances typically have their own crypto engine and have a different architecture than the ASAv. Therefore, it may not be possible to expect as much performance improvement as the ASAv. Also, ASA5506 / 5508/5516 does not support DTLSv1.2 due to platform limitation (enhancement request: CSCvn63389). In addition, it may vary depending on the performance, the model of use, usage settings / functions, etc. Therefore, it is recommended to perform a preliminary verification according to the usage environment, if necessary.
Please tell me how to check the automatically adjusted MTU of AnyConnect
It can be confirmed by connecting AnyConnect with debug webvpn anyconnect enabled. The following is an excerpt of an example debug output.
ASA5555 # show run logging
logging enable
logging timestamp
logging buffer-size 100000
logging buffered errors
logging debug-trace
logging message 711001 level alerts
ASA5555 #
ASA5555 # debug webvpn anyconnect
INFO: 'logging debug-trace' is enabled.All debug messages are currently being redirected to syslog: 711001 and will not appear in any monitor session.
INFO: debug webvpn anyconnect enabled at level 1.
ASA5555 #
- - AnyConnect connection start ---
ASA5555 # Show Log
--- abbreviation ---
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: Iphdr = 20 base-mtu = 1500 def-mtu = 1500 conf-mtu = 1406
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: tcp-mss = 1460
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: path-mtu = 1460 (mss)
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: TLS Block size = 16, version = 0x303
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: mtu = 1460 (path-mtu)-0 (opts)-5 (ssl)-16 (iv) = 1439
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: mod-mtu = 1439 (mtu) & 0xfff0 (complement) = 1424
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: tls-mtu = 1424 (mod-mtu)-8 (cstp)-48 (mac)-1 (pad) = 1367
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: DTLS Block size = 16
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: mtu = 1500 (base-mtu)-20 (ip)-8 (udp)-13 (dtlshdr)-16 (dtlsiv) = 1443
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: mod-mtu = 1443 (mtu) & 0xfff0 (complement) = 1440
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: dtls-mtu = 1440 (mod-mtu)-1 (cdtp)-48 (mac)-1 (pad) = 1390
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: computed tls-mtu = 1367 dtls-mtu = 1390 conf-mtu = 1406
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: DTLS enabled for intf = 2 (outside)
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: tls-mtu = 1367 dtls-mtu = 1390
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: SVC: adding to sessmgmt
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: Sending X-CSTP-DNS: xx.xx.xx.xx
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: Sending X-CSTP-DNS: xx.xx.xx.xx
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: Sending X-CSTP-Split-Include msgs: for ACL-TEST-split-tunnel-acl: Start
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: Sending X-CSTP-Split-Include: 1.0.0.0/255.0.0.0
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: Sending X-CSTP-MTU: 1367
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: Sending X-DTLS-MTU: 1390
Apr 05 2020 18:23:17:% ASA-1-711001: Sending X-DTLS12-CipherSuite: ECDHE-ECDSA -AES256-GCM-SHA384
VPN throughput of ASA does not follow the datasheet
Most of the ASAs released in 2020 are multi-core models, and the processing capacity is improved by distributing and processing with multiple cores. When testing in a single flow, processing speed is limited because only some cores are used. Especially in the case of higher models, dozens to hundreds of AnyConnect connections are required to maximize the processing performance of the ASA.
VPN throughput is the sum of transmission (tx) and reception (Rx). For example, in the case of TCP communication, while a terminal is downloading a file via the ASA (= Rx), there is also some communication (= Tx) of a confirmation response (ACK) from the terminal to the ASA. If you want to obtain 100 Mbps performance for both sending and receiving, you need to select a model with VPN throughput of 200 Mbps or more.
If you want to test the performance of AnyConnect on a high-end model, pre-enable the crypto engine accelerator-bias ssl command. If this command is not enabled, the maximum SSL processing performance will not be obtained.
When performing AnyConnect Performance tests on the ASAv, you can expect good results by deploying the ASAv on a new high-performance server or CPU. Good performance can be expected when network adapter type is VMXNET3 or IXGBE-VF.
The data in the data sheet is based on the test results with the minimum simple settings. If there is a difference in Performance after enabling a function or setting compared to when the function or setting of the device is simple (minimum setting in almost default state), the difference affects the usage function, setting, environment, etc. It can be considered that the load caused by is that Performance has decreased.
In most cases, VPN Performance described in data sheets is based on communication when using UDP 450 bytes. If your network has an average packet size smaller than 450 bytes, performance may be lower than the data sheet. You can see the average packet size for each interface with the show traffic command. In the case of networks with many short packets, a common problem is the communication method and behavior of the application being used. As a countermeasure, it is possible to improve VPN performance of both the AnyConnect client and ASA as a result by increasing the amount of data in one packet sent at one time on the application side and reducing the frequency of acknowledgments. However, in general, it is often difficult to immediately modify (or enhancement) the communication method on the application side. For cloud-type applications, it is also effective to let the client directly access the cloud through a split tunnel and not send short packets to the VPN.
Especially in a business-critical environment, when it is expected to use many functions and settings, or in an environment where many applications with many short packets are used, it is recommended to select and introduce a device with sufficient performance capacity. .
Is QoS for each AnyConnect session possible?
Unfortunately it is not supported. If you try to set the tunnel-group QoS, the following error occurs and you cannot set it.
ASAv10 # show ver | in Ver
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance Software Version 9.12(3)9
SSP Operating System Version 2.6(1.192)
Device Manager Version 7.13(1)
ASAv10 (config) #
ASAv10 (config) # tunnel-group a1 type webvpn
ASAv10 (config) # tunnel-group a1 webvpn-attributes
ASAv10 (config-tunnel-webvpn) # class-map c1
ASAv10 (config-cmap) # match tunnel-group a1
ASAv10 ( config-cmap) # match flow ip destination-address
ASAv10 (config-cmap) # policy-map p1
ASAv10 (config-pmap) # class c1
ASAv10 (config-pmap-c) # police output 100000
ERROR: tunnel with WEBVPN attributes doesn't support police!
ASAv10 (config-pmap-c) #
In addition, the use of QoS leads to equipment load. Therefore, if you want to limit the download speed via the tunnel of the AnyConnect terminal for some reason, you can limit the download speed and the number of simultaneous downloads on the connected file server, and set the QoS for the IP address and segment assigned to the AnyConnect terminal. It is effective to maintain the performance of the entire system by distributing the processing load by using the device of the route (for example, L3 switch accommodating ASA or another device of the route).
Reference information
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I have released a video on how to speed up "Cisco AnyConnect" on the terminal side, such as Windows and Mac OS X. Please refer to the video if you wish. English subtitle is available.
AnyConnect Speed Up Methods "TOP 4"
https://youtu.be/RzmucDOzxjA
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks a lot
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: