- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Security
- Security Knowledge Base
- How To: Cisco ISE Captive Portals with Aruba Wireless
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-22-2022 06:23 PM - edited 05-21-2024 07:33 AM
How To: Cisco ISE Captive Portals with Aruba Wireless
Authors: Adam Hollifield, Brad Johnson
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Minimum Requirements
- Components Used
- Configuration
- Aruba Wireless Controller
- WLAN Creation
- Authentication Configuration
- Role & Policy Configuration
- Cisco ISE
- Aruba RADIUS Dictionary Addition
- Aruba Network Device Profile
- Aruba Authorization Profiles
- Authentication Allowed Protocols Configuration
- Policy Set Configuration
- Verification
- ISE RADIUS Live Logs
- Aruba Mobility Controller
Introduction
Previous configurations for integrating Cisco ISE portals and Aruba Wireless used a static external captive portal URL to redirect clients to an ISE portal. This required the use of multiple authorization profiles and authorization rules per PSN. Aruba AOS 8.4 added support for the Aruba-Captive-Portal-URL Vendor Specific Attribute (VSA) which allows for dynamic URL redirection similar to what we see when configuring portal rules with Cisco network access devices (NADs). This will enable additional scale, posture flows, and ease of configuration when integrating Aruba wireless with Cisco Identity Services Engine.
Prerequisites
Minimum Requirements
The minimum software requirements for this configuration:
- Aruba AOS 8.4 or later (NOTE: based on various community feedback this configuration does not work with Aruba Instant Mode APs. Aruba Instant Mode does not have support for the Aruba-Captive-Portal-URL VSA)
- Cisco ISE 2.4 or later
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software versions:
- Aruba Wireless Controller with AOS 8.10.0.1
- Cisco ISE 3.1 with Patch 3
Configuration
Aruba Wireless Controller
WLAN Creation
- Navigate to Configuration > Tasks > Create a new WLAN.
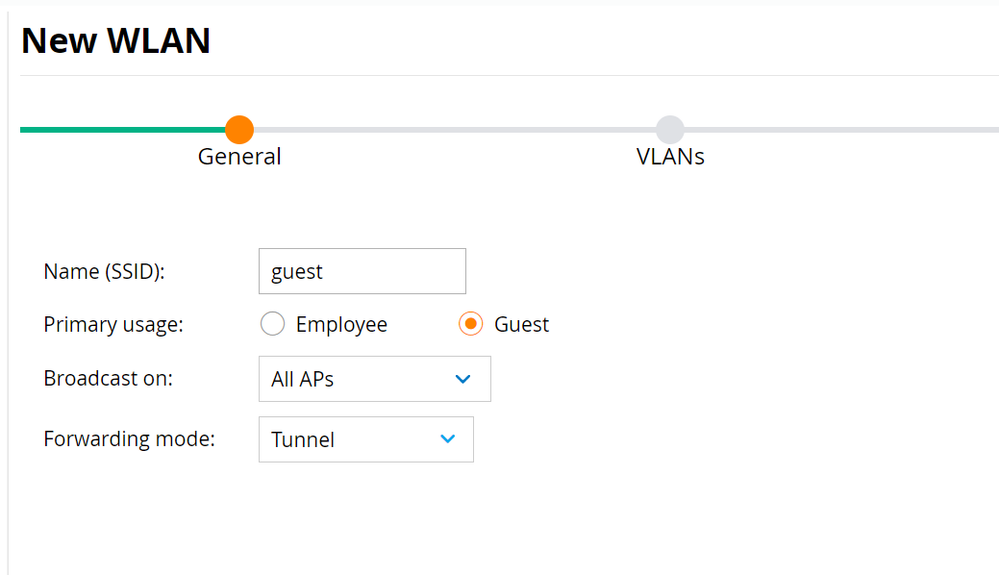
- Fill in the SSID and select Guest as Primary usage. Select AP groups and Forwarding mode as required by the wireless deployment. Click Next.
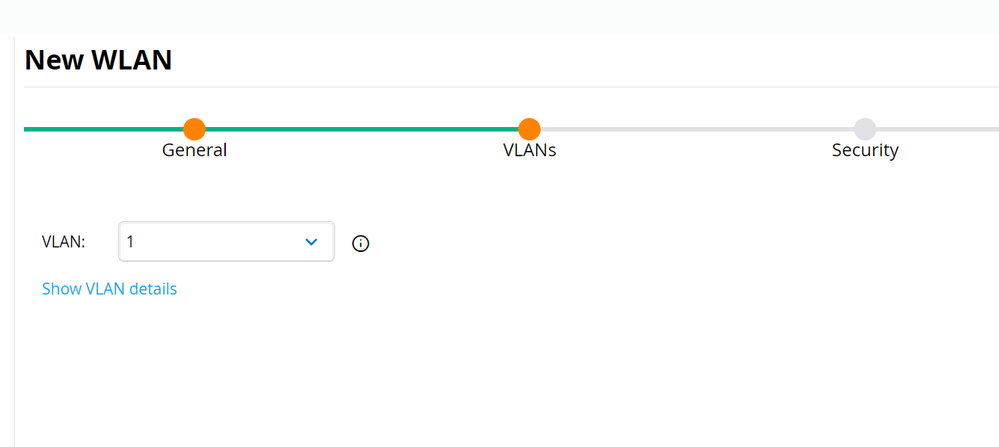
NOTE: it is best practice to broadcast WLANs only on specified AP groups and not use the default group. - Select the VLAN and click Next.
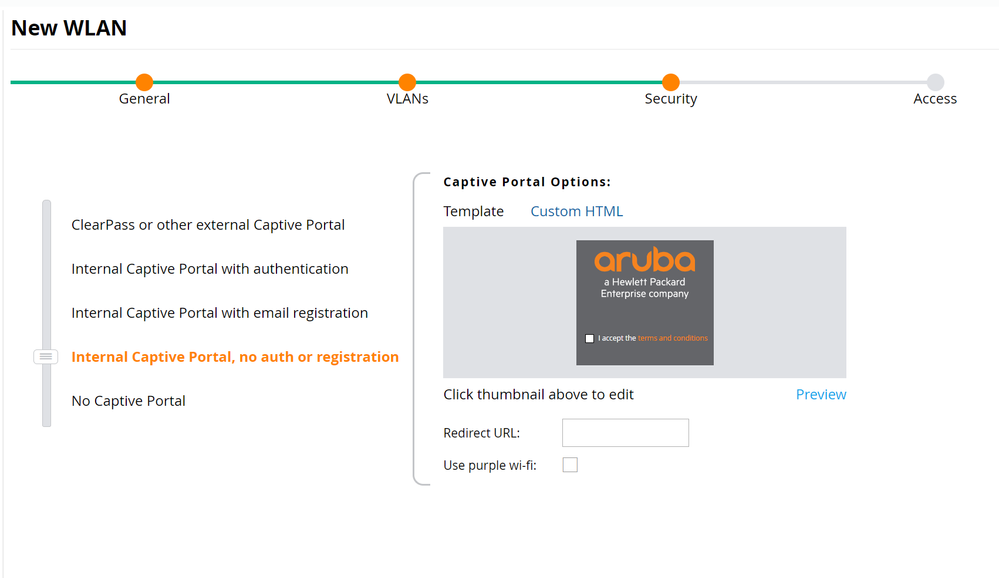
- Set Security to Internal Captive Portal, no auth or registration and click Next.
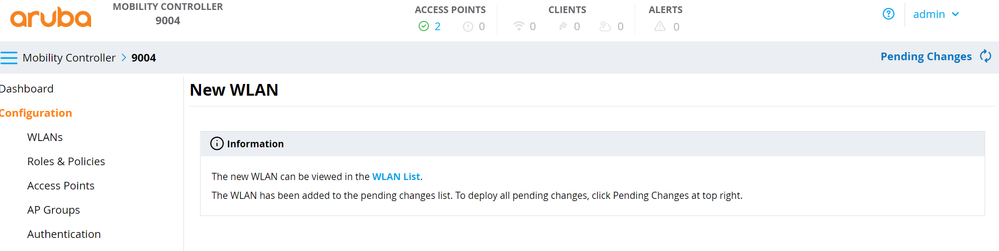
The Internal Captive Portal will not be used here and will be overridden by the captive portal URL supplied by ISE through the Aruba-Captive-Portal-URL VSA. However, the Aruba Mobility Controller requires some form of Captive Portal to be enabled on the WLAN to successfully redirect clients. - Click Next and Finish.
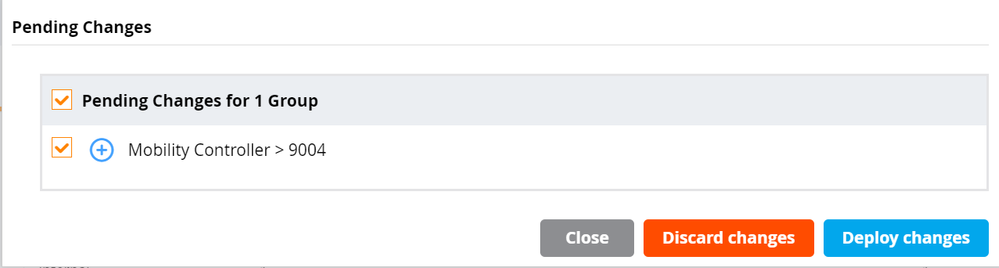
- Click Pending Changes in the top right and click Deploy changes to deploy the configuration to the Mobility Controller.
Authentication Configuration
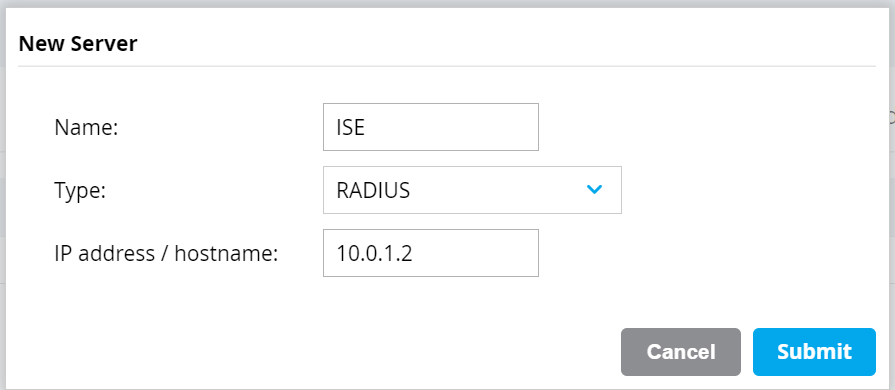
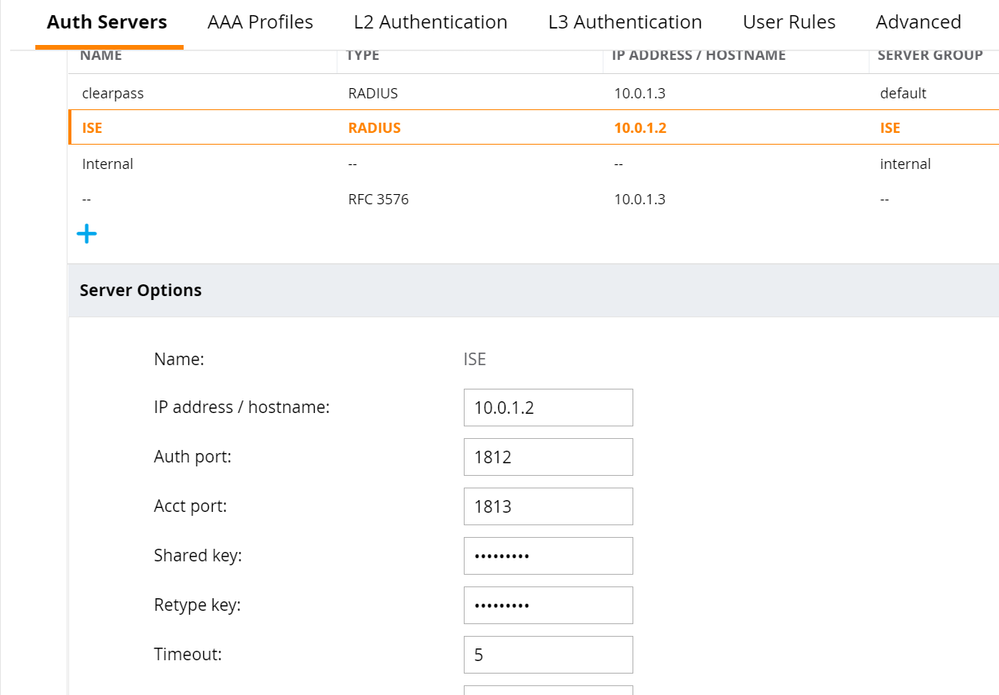
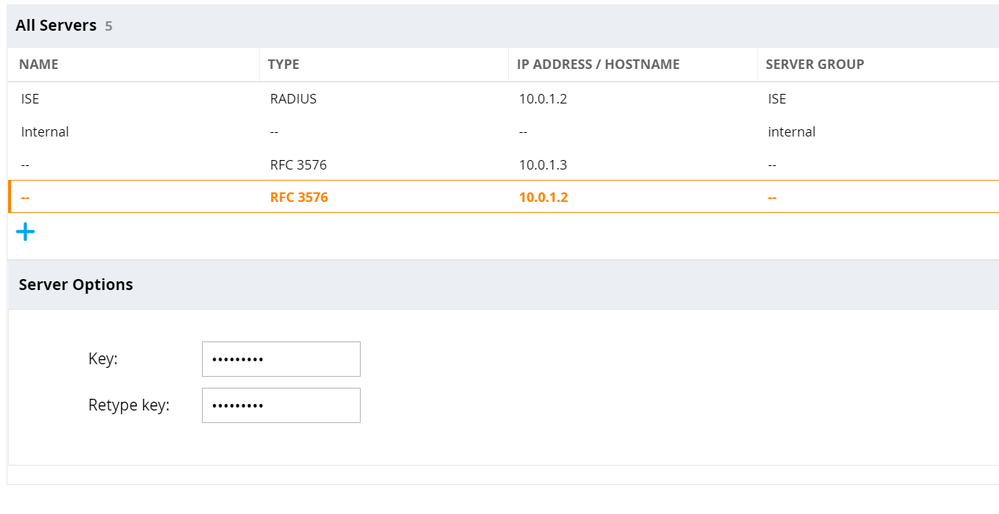
- Navigate to Configuration > Authentication > Auth Servers. Click the + button under All Servers. Fill in name, select type as RADIUS, and fill in the IP address/hostname of the ISE PSN. Click Submit. Repeat for each of the ISE PSNs.
- Select the newly created RADIUS Server definition. Enter the Shared Key and click Submit. Repeat for each of the ISE PSN RADIUS Server definitions.
- Click the + button under All Servers. Change type to Dynamic Authorization and enter the IP address of the ISE PSN. Click Submit. Repeat for each of the ISE PSNs.
- Select the newly created RFC 3576 definition and enter the Key. Click Submit. Repeat for each of the ISE PSN RFC 3576 definitions.
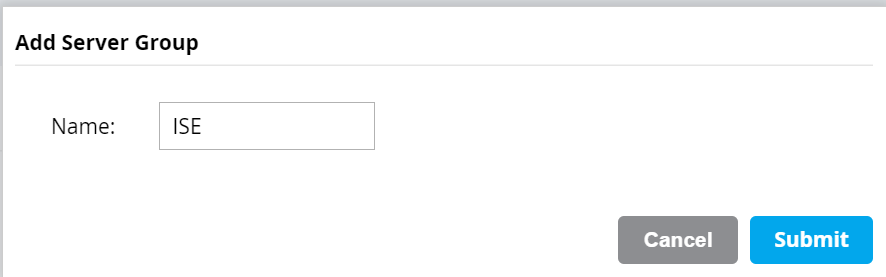
- Click the + button under Server Groups. Enter a name. Click Submit.
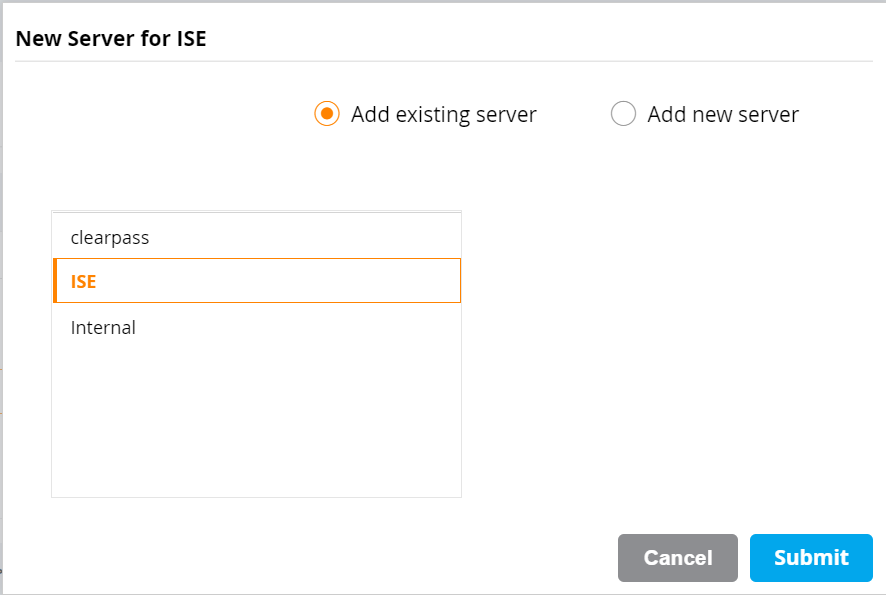
- Select the newly created Server Group and click the + button. Choose Add existing server and select the ISE PSN RADIUS Server definition. Click Submit. Repeat for the rest of the ISE PSN RADIUS Server definitions.
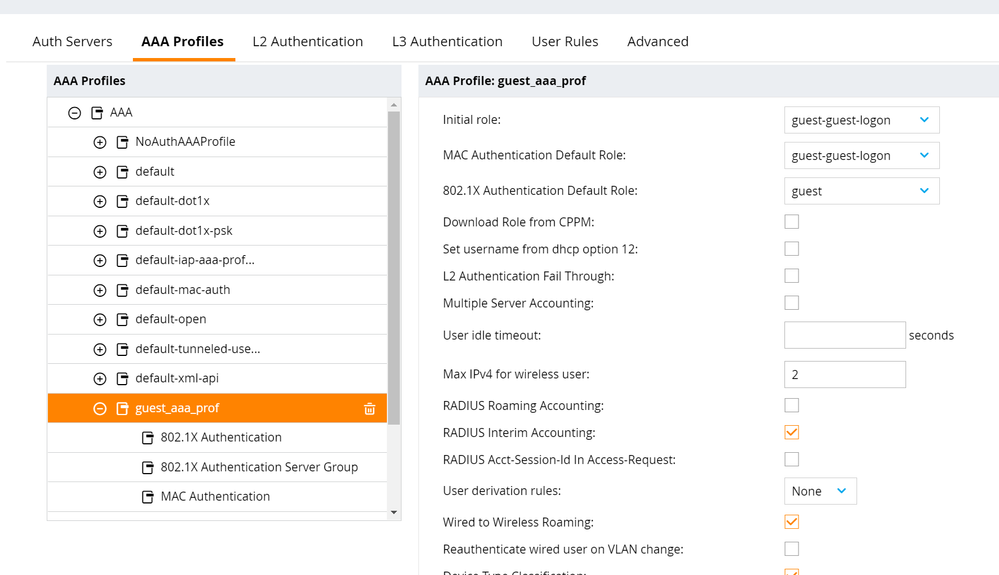
- Navigate to Configuration > Authentication > AAA Profiles. Select the AAA profile for the newly created WLAN, [SSID]_aaa_prof. Enable RADIUS Interim Accounting. Click Submit.
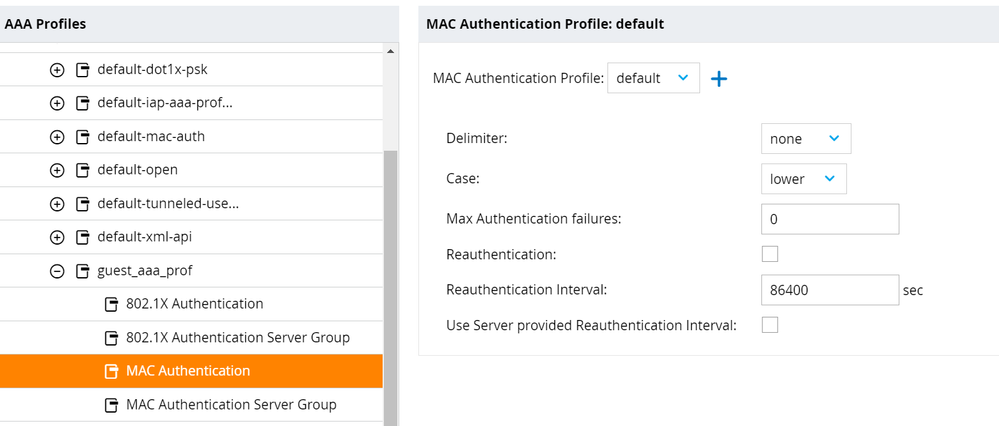
- Select MAC Authentication. Change MAC Authentication Profile to Default. Click Submit.
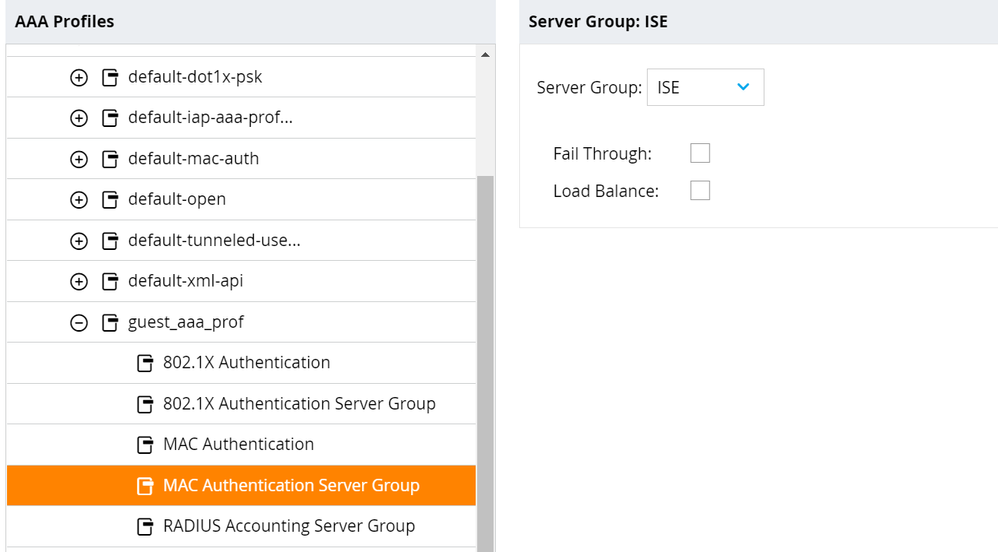
- Select MAC Authentication Server Group. Change Server Group to the ISE Server Group created previously. Click Submit.
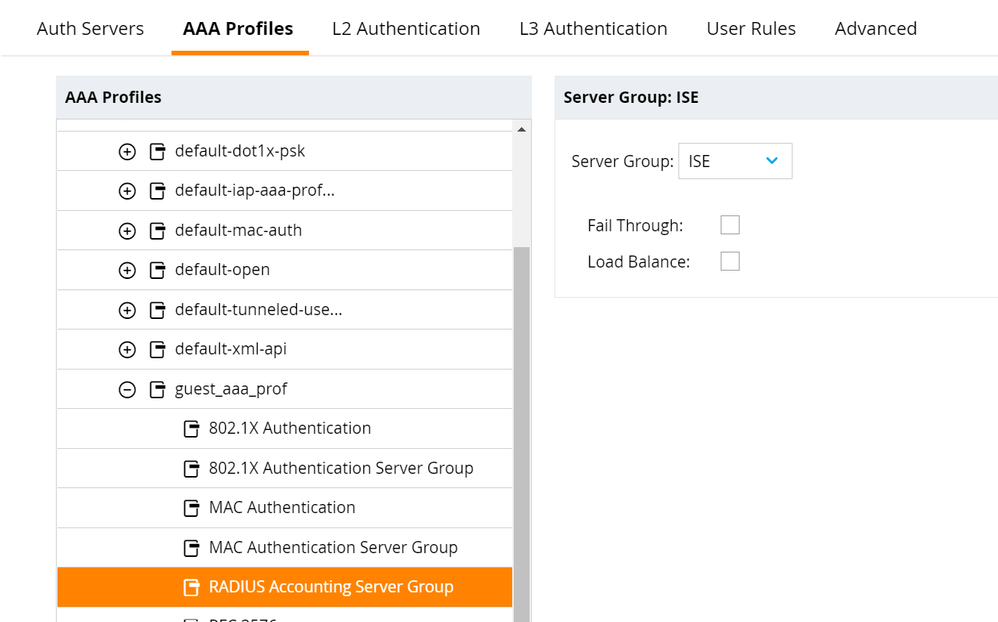
- Select RADIUS Accounting Server Group. Change Server Group to the ISE Server Group created previously. Click Submit.
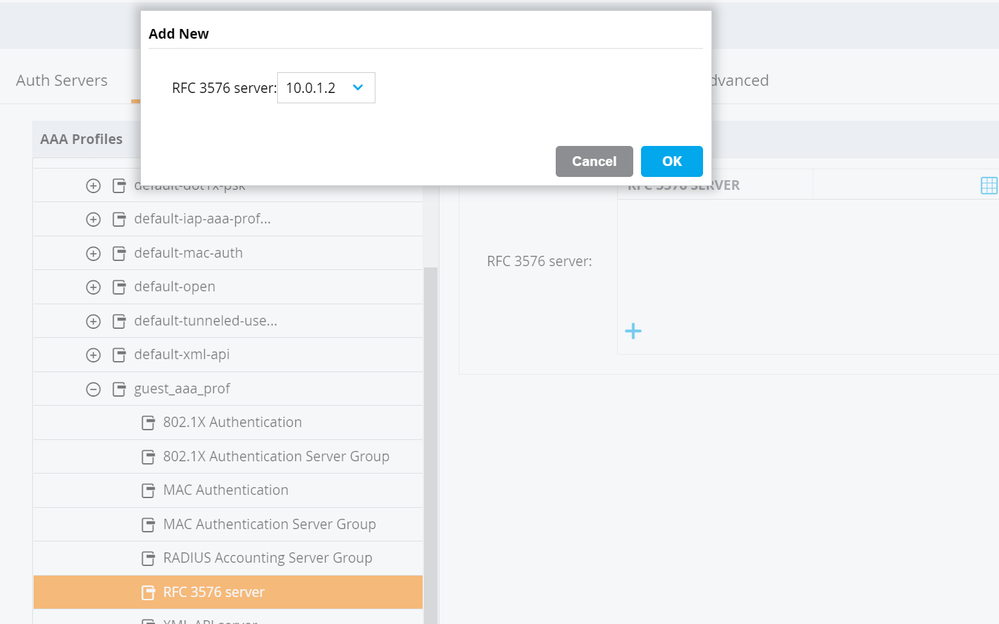
- Select RFC 3576 Server. Click the + button and select the ISE PSN from the drop down. Click Submit. Repeat for each of the ISE PSN RFC 3576 server definitions.
- Click Pending Changes in the top right and click Deploy changes to deploy the configuration to the Mobility Controller.
Role & Policy Configuration
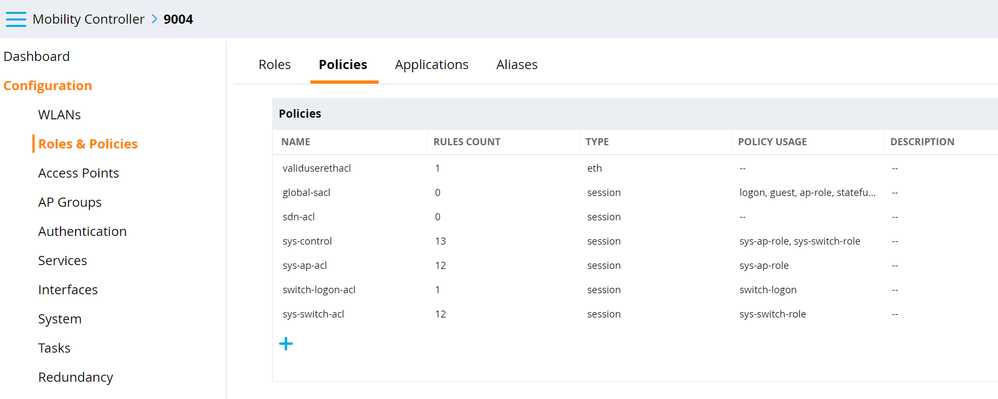
- Navigate to Configuration > Roles & Policies > Policies and click the + button.
- Set Policy Type to Session, enter a Policy Name, and an optional description. Click Submit.
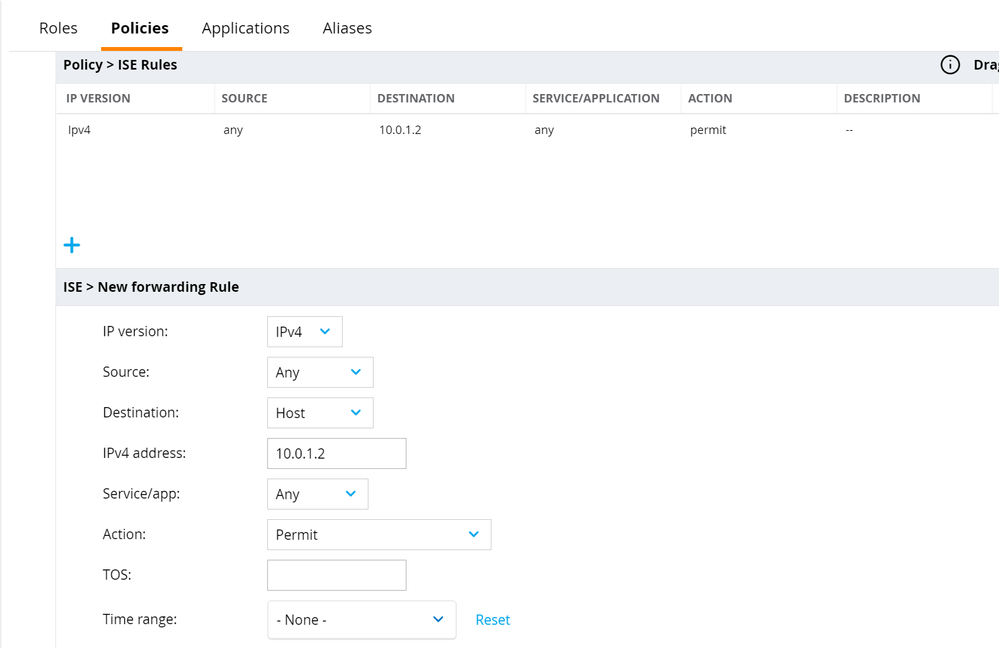
- Select the newly created policy and click the + button. Select Access Control and click OK. Create a new forwarding rule allowing captive portal traffic to the ISE PSNs. Click Submit.
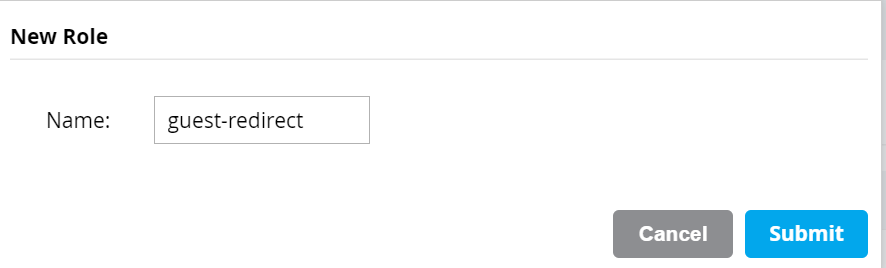
NOTE: This Policy enforces what traffic from the guest WLAN will be allowed BEFORE the guest authenticates to the portal. This Policy can and should be customized for the individual network environment and security requirements. At a minimum, the captive portal ports (typically 8443) must be allowed from the guest users to the ISE PSNs during the redirect phase. - Navigate to Configuration > Roles & Policies > Roles and click the + button to create a new role. Give the Role a Name and click Submit.
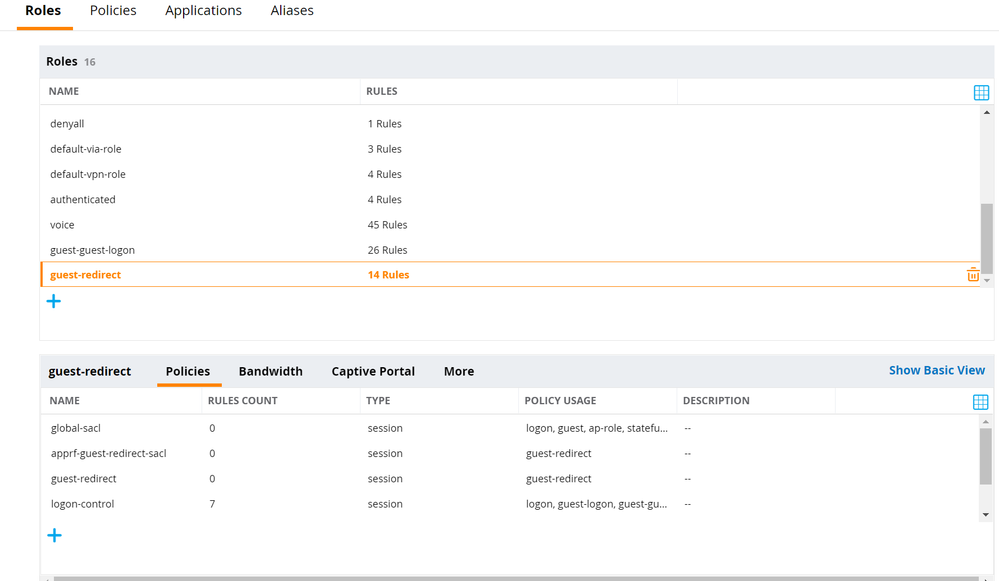
- Select the newly created Role from the list. Click Show Advanced View.
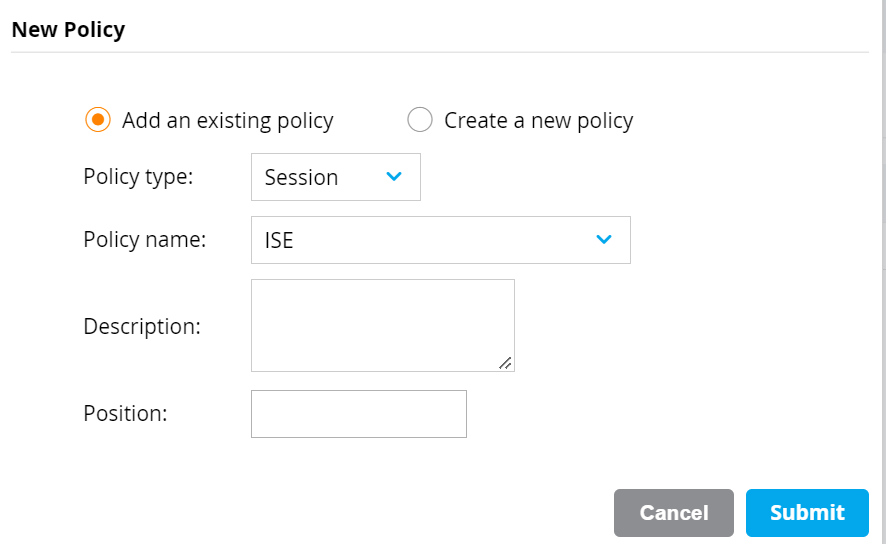
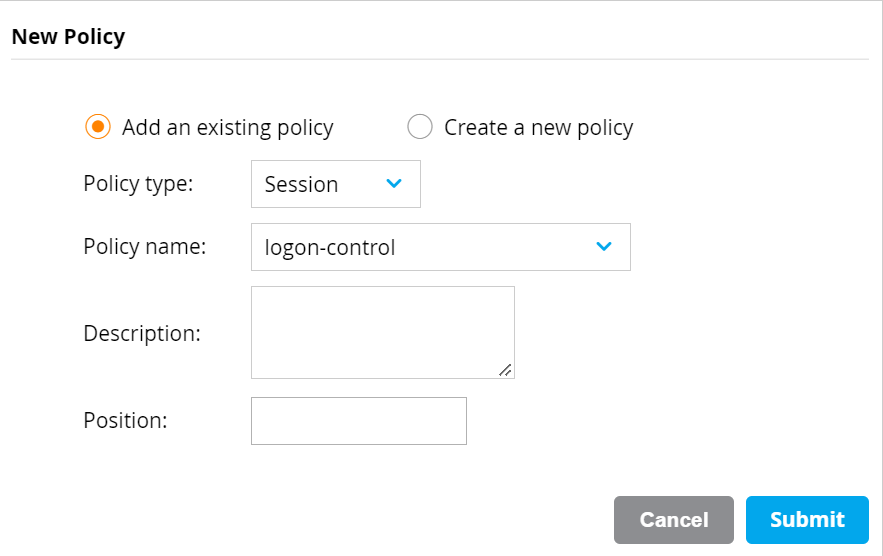
- Click the + button within Policies. Select Add an existing policy. Select type Session and select the policy created in the previous step. Click Submit.
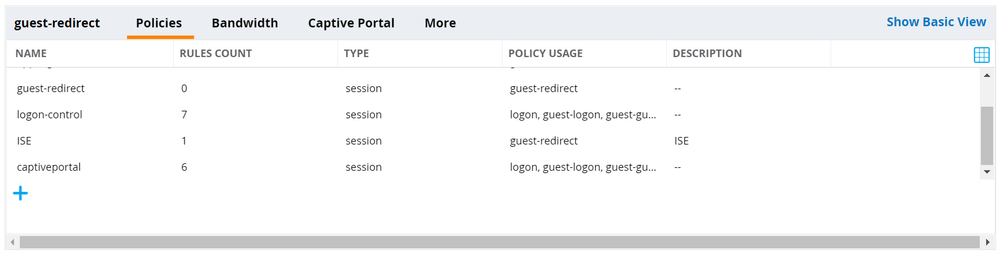
- Repeat this procedure again adding the logon-control and captiveportal Policies to this Role.
- Re-order the policies so that the Policy created previously is listed between logon-control and captiveportal.
- Select the Captive Portal tab. Move slider to Internal Captive Portal, no auth or registration.
The Internal Captive Portal will not be used here and will be overridden by the captive portal URL supplied by ISE through the Aruba-Captive-Portal-URL VSA. However, the Aruba Mobility Controller requires some form of Captive Portal to be enabled on the Role to successfully redirect clients.
- Click Submit.
- Click Pending Changes in the top right and click Deploy changes to deploy the configuration to the Mobility Controller.
You may also wish to create a custom role for the guest users once the user successfully authenticates to the Captive Portal. In this example, the Aruba default guest Role is used for this purpose.
Cisco ISE
Aruba RADIUS Dictionary Addition
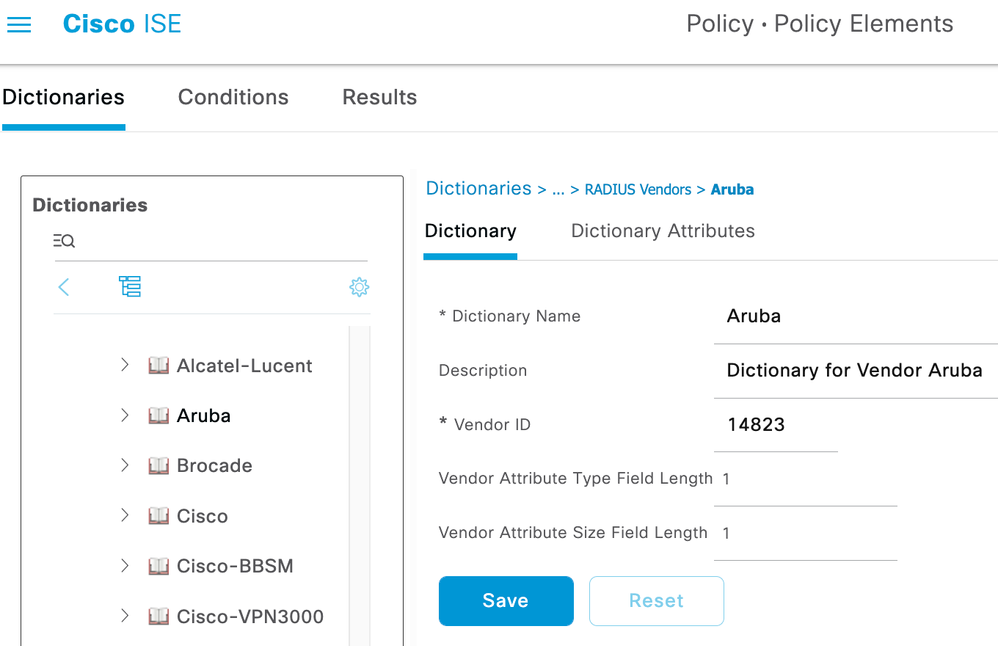
The default Aruba RADIUS dictionary in Cisco ISE does not contain the RADIUS VSA Aruba-Captive-Portal-URL. This must be manually created before configuring the network device profile.
- Navigate to Policy > Policy Elements > Dictionaries.
- Expand System > RADIUS > RADIUS Vendors and click on the Aruba entry.
- Click Dictionary Attributes and then Add.
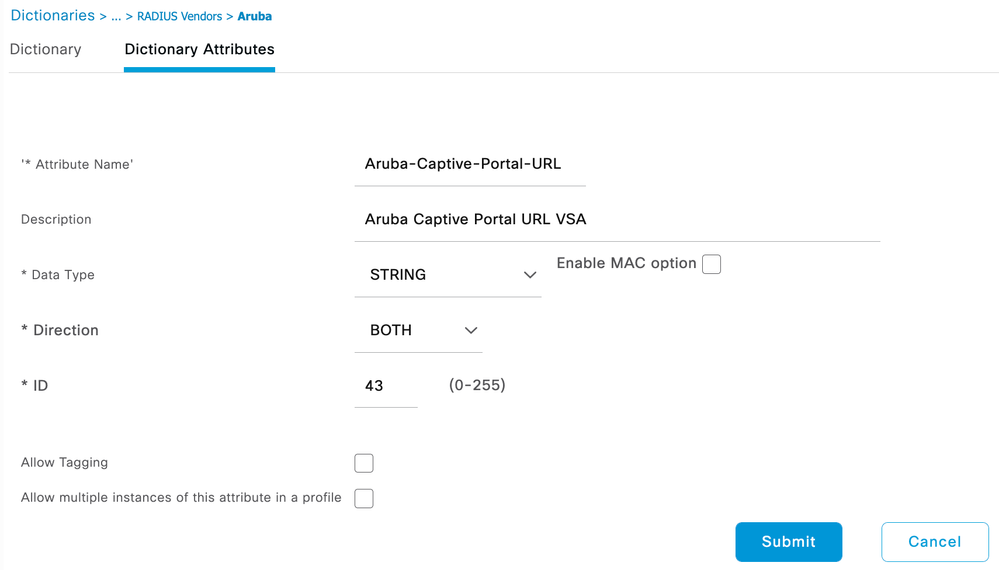
- Fill in the information as follows:
Attribute Name: Aruba-Captive-Portal-URL
Description: [optional]
Data Type: STRING
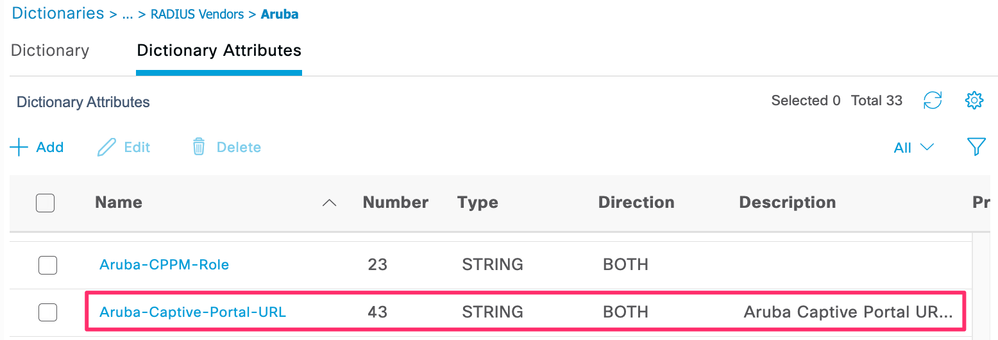
ID: 43 - Click Submit and verify the new attribute shows up under the Dictionary Attributes menu.
Aruba Network Device Profile
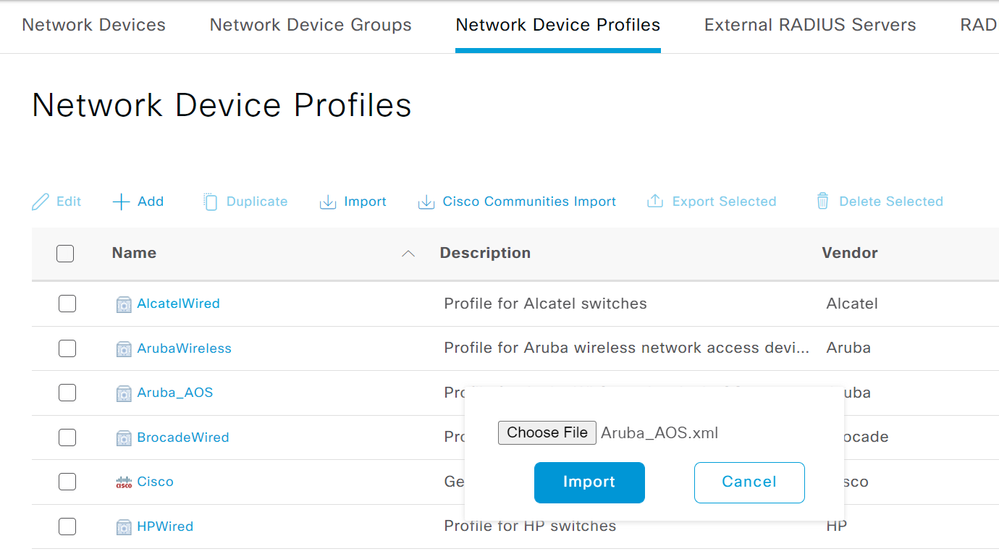
The default Aruba Network Device Profile in Cisco ISE does not support URL redirection via RADIUS VSA. A custom Network Device Profile for Aruba AOS controllers has been created and is attached to this article.
- Navigate to Administration > Network Resources > Network Device Profiles. Click the Import button. Browse the Aruba_AOS.xml file and click Import.
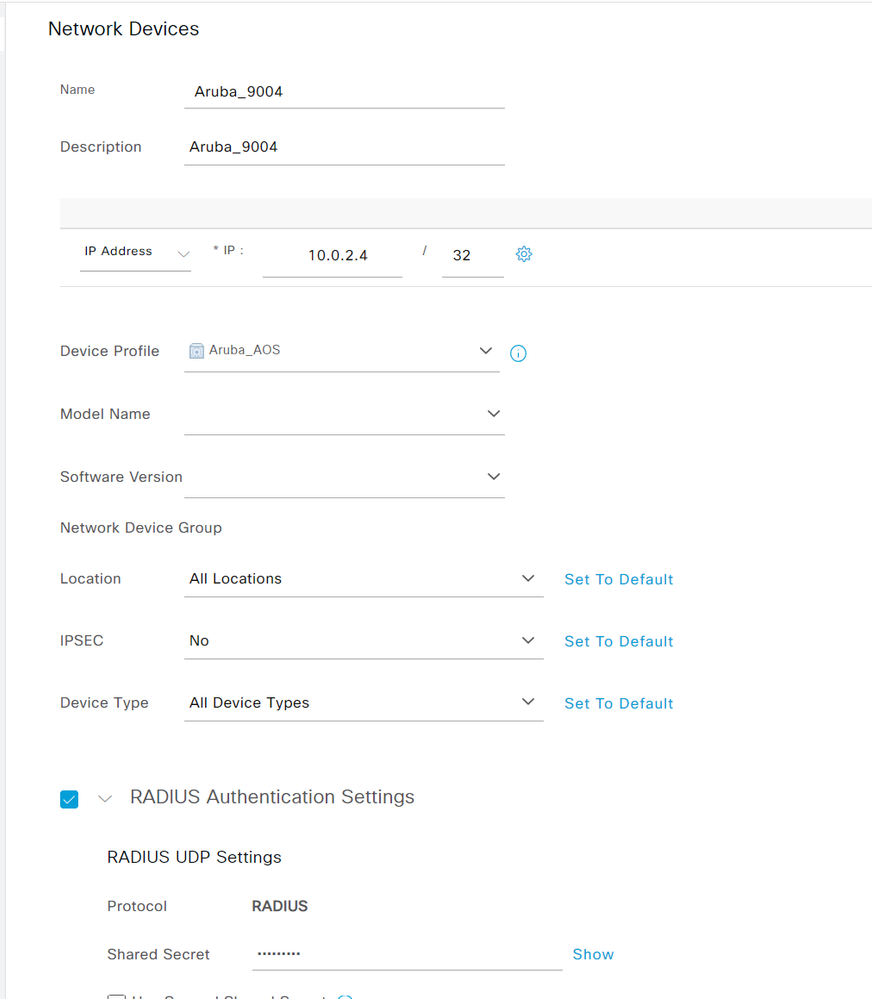
- Navigate to Administration > Network Resources > Network Devices and click the +Add button.
- Add an entry for the Aruba Mobility Controller ensuring to select the custom Aruba_AOS Network Device Profile imported in the previous step. Specify the IP Address of the Mobility Controller and the RADIUS Shared Secret.
- Click Save.
Aruba Authorization Profiles
- Navigate to Policy > Policy Elements > Results > Authorization > Authorization Profiles.
- Click the +Add button.
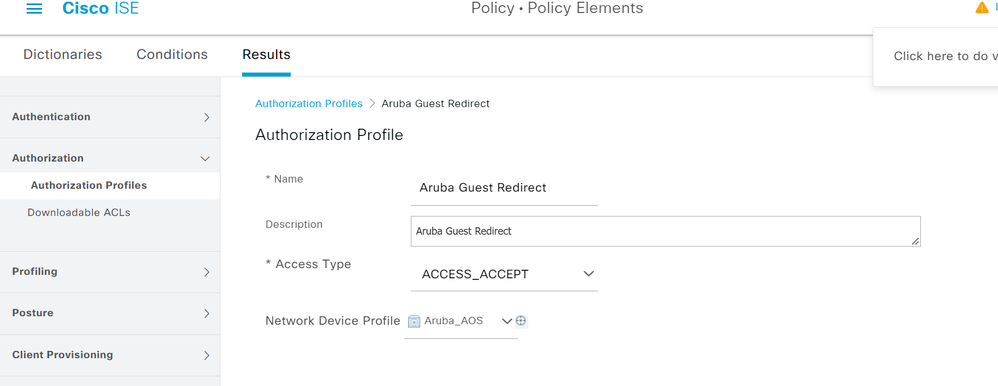
- This authorization (authz) profile will be for redirecting the unknown guest user.
- Give the authz profile a name, select Aruba_AOS as the Network Device Profile.
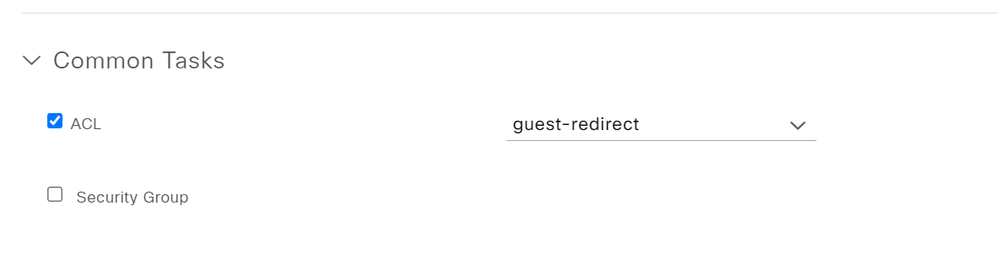
- Within Common Tasks click the checkbox for ACL and specify the name of the Role created for the redirect on the Aruba Mobility Controller. NOTE: these names much match exactly.
- Check the box for Web Redirection and specify the corresponding portal type and portal. Click Save.
This guide does not cover the creation of a portal on ISE. For this example, the Default Hostspot Guest Portal is used.
- Click the +Add button again.
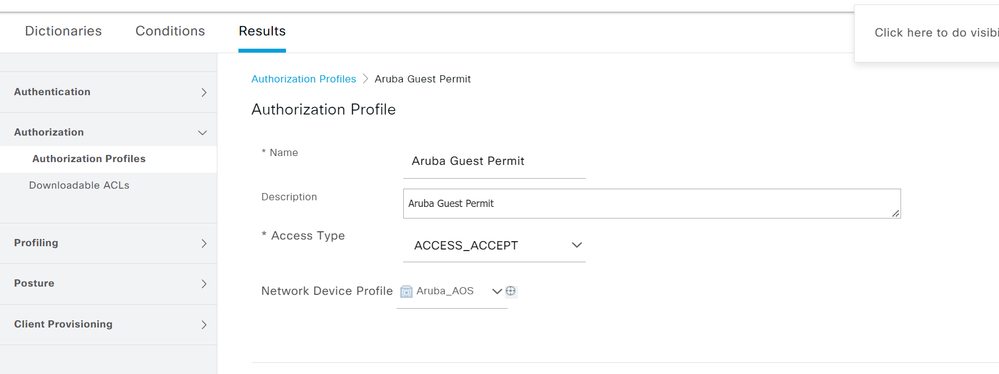
- This authorization profile is for the authenticated guest.
- Give the authz profile a name, select Aruba_AOS as the Network Device Profile.
- Within Common Tasks click the checkbox for ACL and specify the name of the Role for the guest users on the Aruba Mobility Controller.
NOTE: these names much match exactly. You may also wish to create a custom role for the guest users once the user successfully authenticates to the Captive Portal. In this example, the Aruba default guest role is used for this purpose.
Authentication Allowed Protocols Configuration
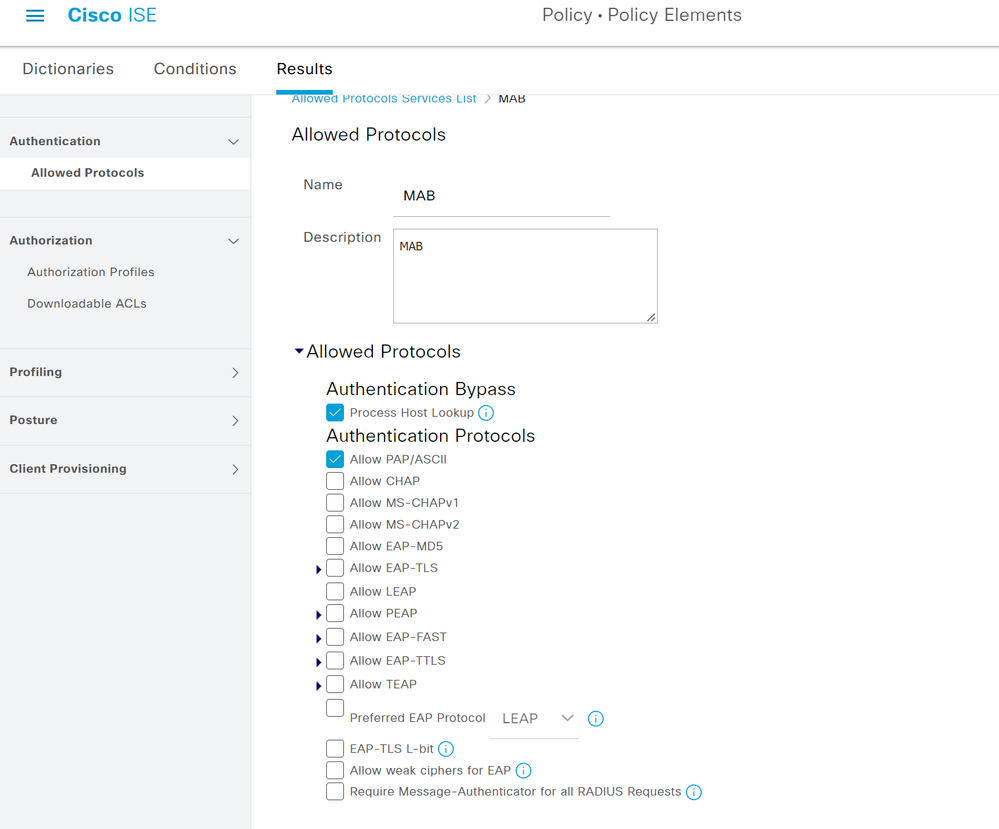
- Navigate to Policy > Policy Elements > Results > Authentication > Allowed Protocols. Click the +Add button to create a new Allowed Protocols Service.
- Give the Allowed Protocols Service a name and optional description. Disable all other protocols except for Process Host Lookup and PAP/ASCII. Click Save.
Policy Set Configuration
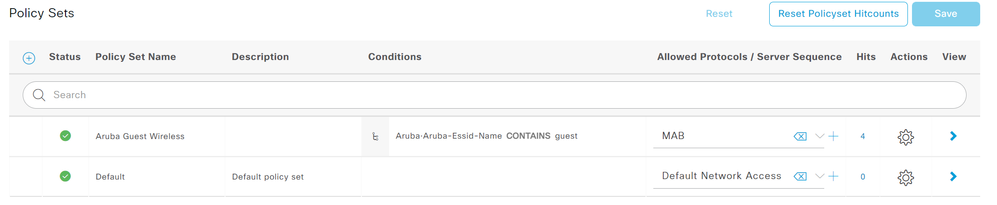
- Navigate to Policy > Policy Sets and click the + button to create a new policy set.
- Give the policy set a name and within conditions, specify Aruba-Aruba-Essid-Name CONTAINS [SSID].
- Replace [SSID] with the name of the SSID configured on the Mobility Controller.
- Replace [SSID] with the name of the SSID configured on the Mobility Controller.
- For Allowed Protocols/Server Sequence, select the MAB allowed protocols created in the previous section.
- Click Save and then click the greater than sign (>) on the far right of the policy set to open the new Policy Set.
- Expand Authentication Policy and specify Internal Endpoints in the Use column of the Default authc policy.
- Change If User not found within Options to Continue.
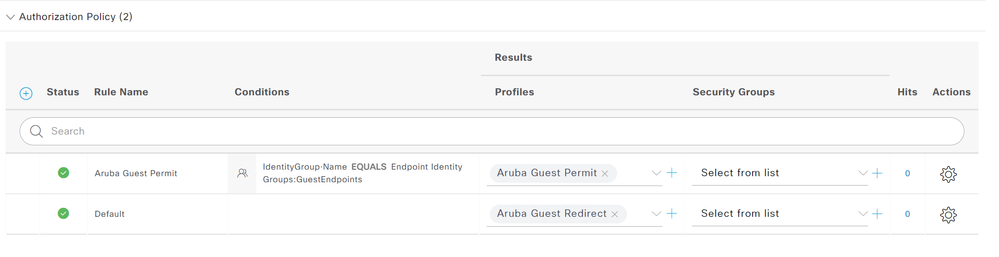
- Expand Authorization Policy and click the plus (+) button to create a new authz policy.
- Specify a name for the policy and for Conditions specify IdentityGroup-Name EQUALS Endpoint Identity Groups:GuestEndpoints.
- This guide is using the Remember Me guest flow so if the endpoint MAC address exists in the specified endpoint group they will automatically be granted guest access.
- Specify the Aruba Guest Permit authorization profile in the Results column.
- Specify the Aruba Guest Redirect authorization profile in the Results column for the Default authz policy.
- Click Save.
Verification
ISE RADIUS Live Logs
Navigate to Operations > RADIUS > Live Logs. From bottom to top in the screenshot below, the Live Logs should first show the Aruba Guest Redirect authz profile. Followed by the Change of Authorization (CoA) once the user logs into the captive portal. Finally, the endpoint re-authenticating to the wireless network and receiving the Aruba Guest Permit authz profile.
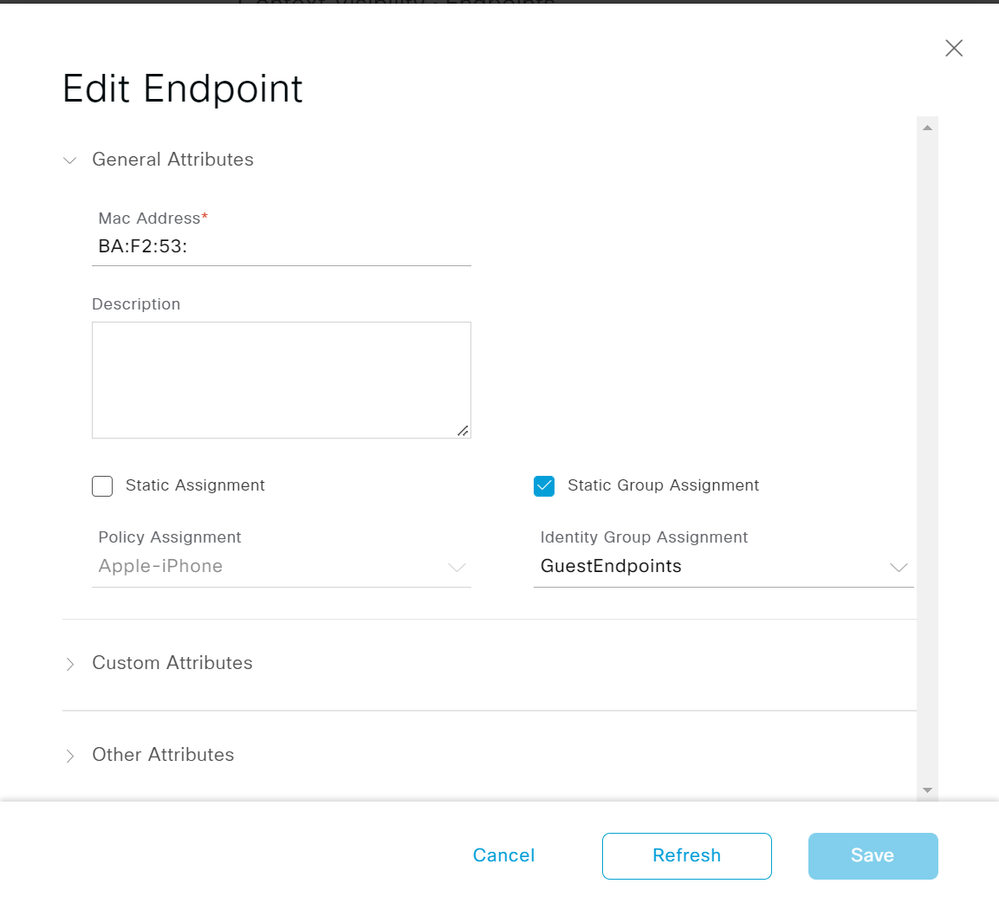
The endpoint should also be a member of the GuestEndpoints Group within Context Visibility > Endpoints after logging into the captive portal.
Aruba Mobility Controller
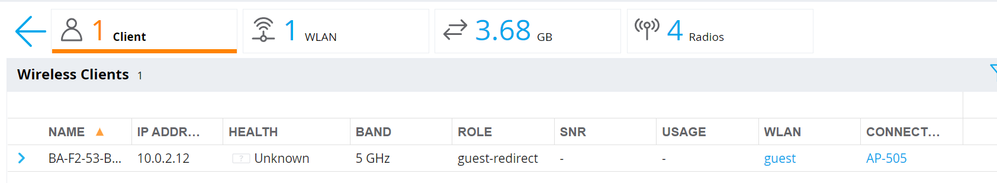
Navigate to Dashboard > Overview and click on the clients view. Before authentication to the captive portal, the client should be assigned the guest-redirect role.
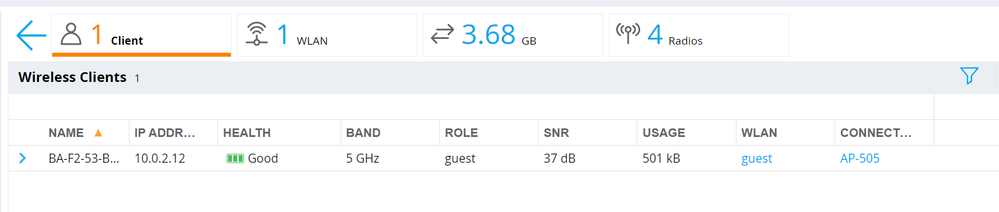
After authentication to the captive portal, the client should be assigned the guest role.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Bradjohnson,
Thanks for your reply on this. Actually, I haven't collected packet capture on this. But I've collected the tcpdump on ISE side. The attribute "Aruba-Captive-Portal-URL" was shown unknown attribute in the packet which it was sent from ISE to controller.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Did you create the Aruba-Captive-Portal-URL dictionary entry in the Aruba RADIUS attributes within ISE?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Yes, it's done.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
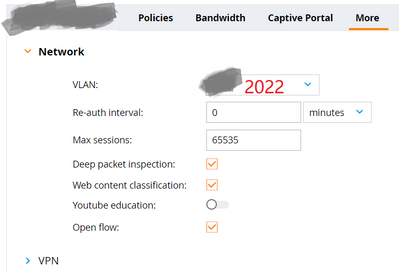
Is it possible to add another attribute to authorization profile to change VLAN assignment of guest after completing self registeration ? If yes, any additional change in Aruba WLC ? Thank you.
Aruba Attribute: Aruba-User-Vlan
Authorization Profile:
Access Type = ACCESS_ACCEPT
Aruba-User-Role = XXX
Aruba-User-Vlan = XXX
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
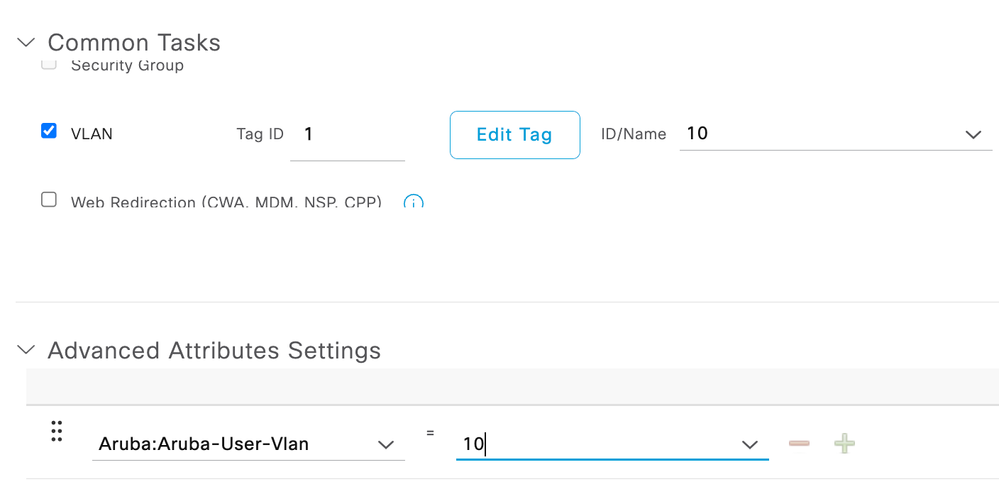
You should be able to utilize VLAN under Common Tasks. If not, simply create a custom attribute under Advanced Attribute Settings. Nothing needs to change on the network device profile since the profile also uses the Aruba dictionary.
Here's the problem, though. How will the endpoint know the VLAN changed, therefore pulling a new IP, after they authenticate? Endpoints don't see a VLAN change on the backend without a connection bounce (disconnect and reconnect). It would be better to change the VLAN on the initial connection and keep them there through the process and post authentication.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks for your reply, bradjohnson
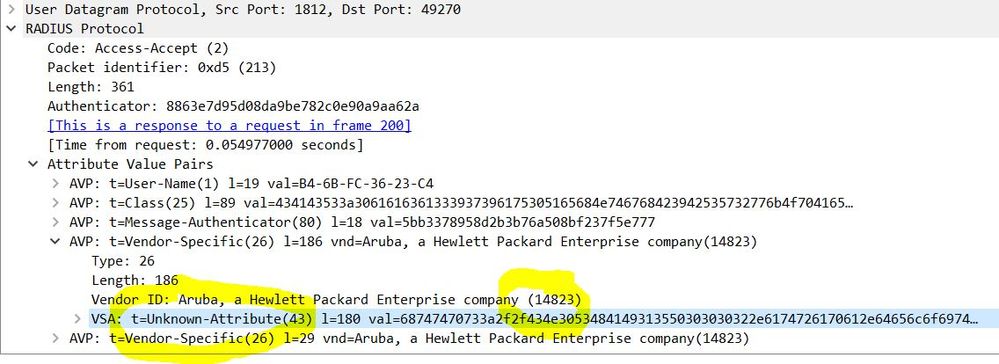
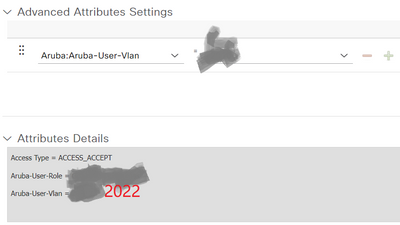
After configuring the VLAN under common task and advanced attributes settings, some unknown attributes was added as well.
May I know what's these unknon attributes ? Additionally, that's my question of how the endpoints know the VLAN changed after completing COA. I will validate and post the result in next week.
Access Type = ACCESS_ACCEPT
Tunnel-Private-Group-ID = 1:2022 (Unknow attribute)
Tunnel-Type = 1:13 (Unknow attribute)
Tunnel-Medium-Type = 1:6 (Unknow attribute)
Aruba-User-Role = XXX
Aruba-User-Vlan = 2022
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thank you, ahollifield.
After many attempts, it takes long time to change the VLAN information of endpoints (suppose COA has completed, I can see the result in Radius Livelog) after inputting the configuraiton in the "Authorization Profile". Do you have any idea of how to address this issue ?
Access Type = ACCESS_ACCEPT
Tunnel-Private-Group-ID = 1:2022 (Unknow attribute)
Tunnel-Type = 1:13 (Unknow attribute)
Tunnel-Medium-Type = 1:6 (Unknow attribute)
Aruba-User-Role = XXX
Aruba-User-Vlan = 2022
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
That is precisely why you should put the VLAN within the Aruba User Role on the controller rather than relying on CoA and additional RADIUS attributes. Any reason why you are not putting VLAN 2022 as an attribute within the XXX role itself on the Mobility Controller configuration?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Both "Authorization Profile" and "User Role" are set to VLAN 2022. But it's randomly failed to change the attribute of VLAN.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thank you, ahollifield.
But it's failed to change the attribute of VLAN for the endpoint if I only leave the VLAN tag within the user role. The endpoint just got the invalid IP "169.254.x.x".
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Yes, the VLAN is trunked to the controllers. The SSID is running in "Tunnel" node. The same VLAN on a different SSID with PSK is working fine without captive portal. Possibly, I fogot to assign the DHCP policy to the user role. Let me modify the user role and test again.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi, I have the same problem with the attribute Aruba-Captive-Portal-URL, ISE sent to the AP the attribute like unknown
did you solve this?
I have a ISE 2.X no 3.1 like the guide, can this be the source of the issue?
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: