已接受的解答
This understanding is no problem, Client trusts the root certificate, then it can verify the intermediate certificate and trust the intermediate certificate, but it does not mean that the root certificate can directly verify the server certificate issued by the intermediate certificate.
According to the information on the picture you gave, the server certificate is issued by an intermediate CA, encrypted with the private key of the intermediate CA, and can only be decrypted and verified by the public key of the intermediate CA.
If the certificate chain is incomplete, it is impossible to verify whether the server certificate is trusted. Based on the situation of the enterprise self-built CA, the intermediate certificate needs to be installed in the client's local certificate store, or the server certificate contains the intermediate certificate.
In the scenario of wsa, it is more appropriate to let the client install the intermediate certificate
if you have installed Local Cert, then you need to install cert to end device also to trust that cert
mostly people do centrally push using SCCM.
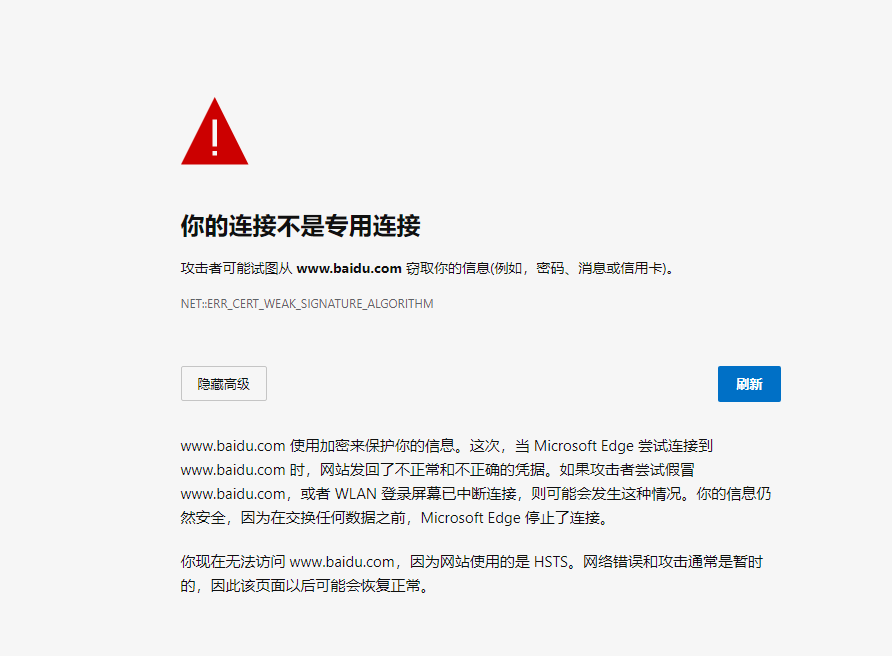
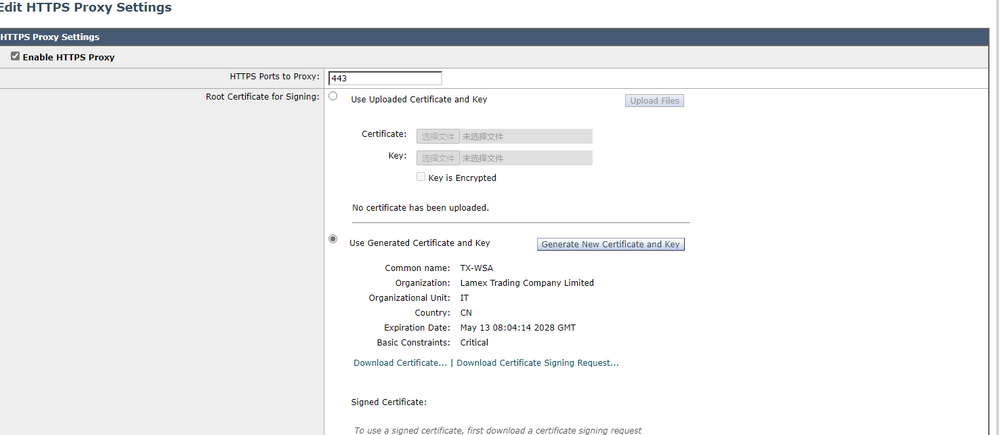
The warning message is "ERR_CERT_WEAK_SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM", which means that the signature algorithm is too weak. It is recommended to adjust the signature algorithm of the generated certificate to SHA256 and change the key length to 2048 or higher.
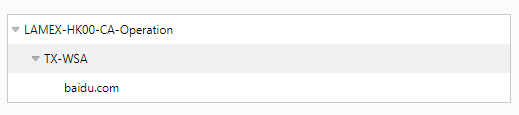
In addition, you need to ensure that the root certificate (LAMEX-HK00-CA-Operation) and the intermediate certificate (TX-WSA) are trusted by the client
The client (trusted root Certification Authority) already has the root certificate, I tried to import TX-WSA into (trusted root Certification Authority) as well, the problem seems to be resolved.
According to my previous understanding, the client (trusted root certificate authority) already has the root certificate, TX-WSA belongs to the root certificate LAMEX-HK00-CA-Operation, the client will trust the TX-WSA certificate, so my previous understanding is wrong?
This understanding is no problem, Client trusts the root certificate, then it can verify the intermediate certificate and trust the intermediate certificate, but it does not mean that the root certificate can directly verify the server certificate issued by the intermediate certificate.
According to the information on the picture you gave, the server certificate is issued by an intermediate CA, encrypted with the private key of the intermediate CA, and can only be decrypted and verified by the public key of the intermediate CA.
If the certificate chain is incomplete, it is impossible to verify whether the server certificate is trusted. Based on the situation of the enterprise self-built CA, the intermediate certificate needs to be installed in the client's local certificate store, or the server certificate contains the intermediate certificate.
In the scenario of wsa, it is more appropriate to let the client install the intermediate certificate