This is a blog about how to deploy multicast in an OpenStack cloud. Unlike broadcast and unicast, multicast is used for one-to-many communications.
What is multicast?
- One-to-many communication
- Driven by receivers (On the contrary, unicast is driven by senders)
- A multicast “group” is identified by a multicast IP address
- Without multicast, sender must duplicate each packet
- Analogy: TV and radio broadcasting
Components of multicast
- Multicast addressing
- Group addresses range from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 (class D addresses)
- Mac addresses range from 01-00-5E-00-00-00 to 01-00-5E-7F-FF-FF
- Multicast group management (IGMP)
- Multicast routing (Protocol Independent Multicast or PIM) and IGMP querying
- Unicast routing (OSPF, IS-IS, RIP) is needed for PIM
- Multicast clients that receive multicast traffic/streams
Multicast use cases
- One-to-many corporate communications such as
- Employee training videos
- Quarterly company meetings
- Company-wide corporate communications
- Executive announcements
- Music/media streaming
- Video podcasts
- IPTV services
- One-to-many software updates/patches
- Social networking (Facebook, Twitter feeds, Instagram)
- Financial services, banks, stock exchange
- Government/Federal agencies
- RTP (Real Time Protocol) applications
State of Multicast in OpenStack
- No multicast available out-of-the-box
- Open vSwitch 2.5 (virtual L2 switch) supports IGMP snooping (Open vSwitch)
- Linux Bridge 2.4 (virtual L2 switch) supports IGMP snooping (https://wiki.linuxfoundation.org/networking/bridge)
- Neutron virtual router (L3-Agent) does not support multicast routing, PIM and querying
- No CLI or API to configure multicast
- Multicast cannot be configured in the Horizon GUI
- Anti-spoofing rules and security groups drop multicast packets
- No plugin support/architecture for multicast
How to deploy Multicast in OpenStack?
- Enable IGMP snooping in OVS/Linux bridge
- Add rules to allow multicast UDP port in security groups
- Disable neutron port-security for ports in multicast path
- Use neutron’s --allowed-address-pairs attribute and allow multicast group's destination IP address and MAC addresses
- SR-IOV ports may also be used
- Three recommended network architectures to deploy Multicast in OpenStack:
- Use provider networks without neutron router (L3-agent) and do multicast and unicast routing on upstream L3 devices connected to TOR outside OpenStack
- Use Cisco’s ASR1k plugin for neutron instead of L3-agent
- Use Cisco’s ACI and APIC driver for neutron
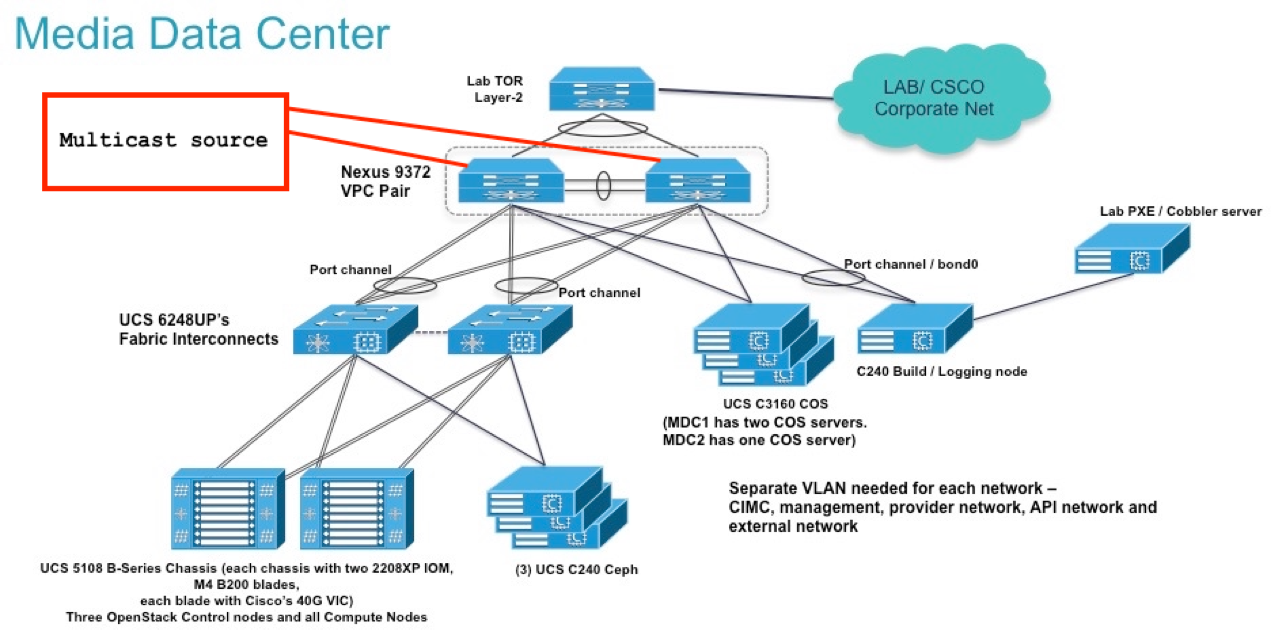
Using provider networks without neutron router (L3-agent)
- Don’t use Neutron-L3-Agent (OpenStack’s virtual router not used)
- Neutron does not route any multicast or unicast traffic
- Use Neutron provider network
- Use lab-routable public VLAN configured on top-of-rack switches
- Use lab's router outside OpenStack
- Use lab's gateway outside OpenStack
- Attach Nova instances directly to provider network with no neutron router
- Configure multicast routing / PIM and unicast routing (OSPF) on the lab upstream router (N9k)
- OVS does IGMP snooping
- Multicast source sends multicast UDP streams
- PIM on lab's upstream router (N9k) forwards multicast packets to OpenStack VMs
- Nova VMs receive/consume multicast streams
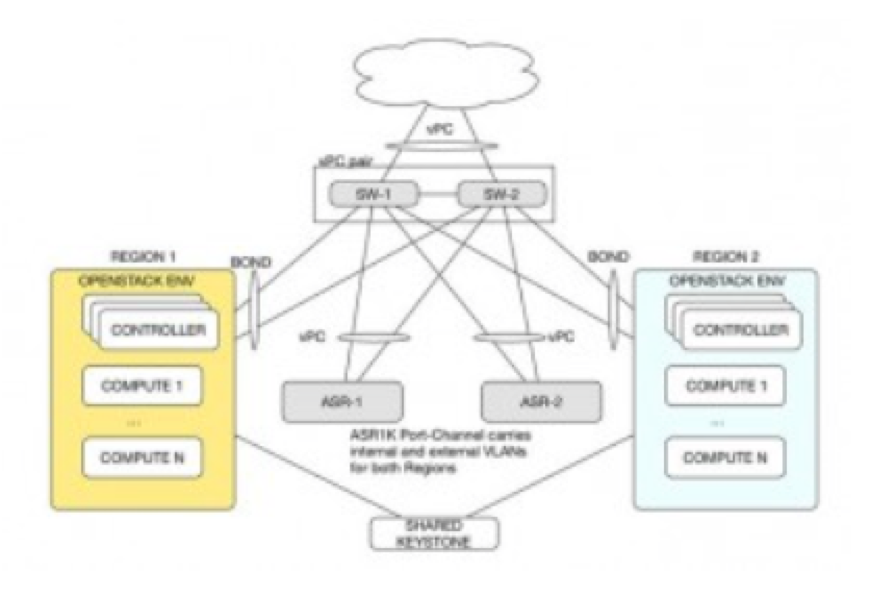
Use Cisco’s ASR1k plugin for neutron instead of L3-agent
- Use Cisco’s ASR1k plugin for OpenStack Neutron instead of neutron-L3-agent
- GitHub - openstack/networking-cisco: Cisco Vendor Code for Neutron
- Neutron-L3-Agent (OpenStack’s virtual router) not used
- ASK1k plugin does both unicast and multicast routing
- Two ASR1000s used in VPC pair
- Neutron talks to ASR1k using Cisco’s config agent (using NETCONF)
- Neutron does not route any multicast or unicast routing traffic
- Configure multicast routing / PIM and unicast routing (OSPF) on the ASRs
- OVS does IGMP snooping
- Multicast source sends multicast UDP streams
- PIM on the ASRs forwards multicast packets to OpenStack VMs
- Nova VMs receive/consume multicast streams
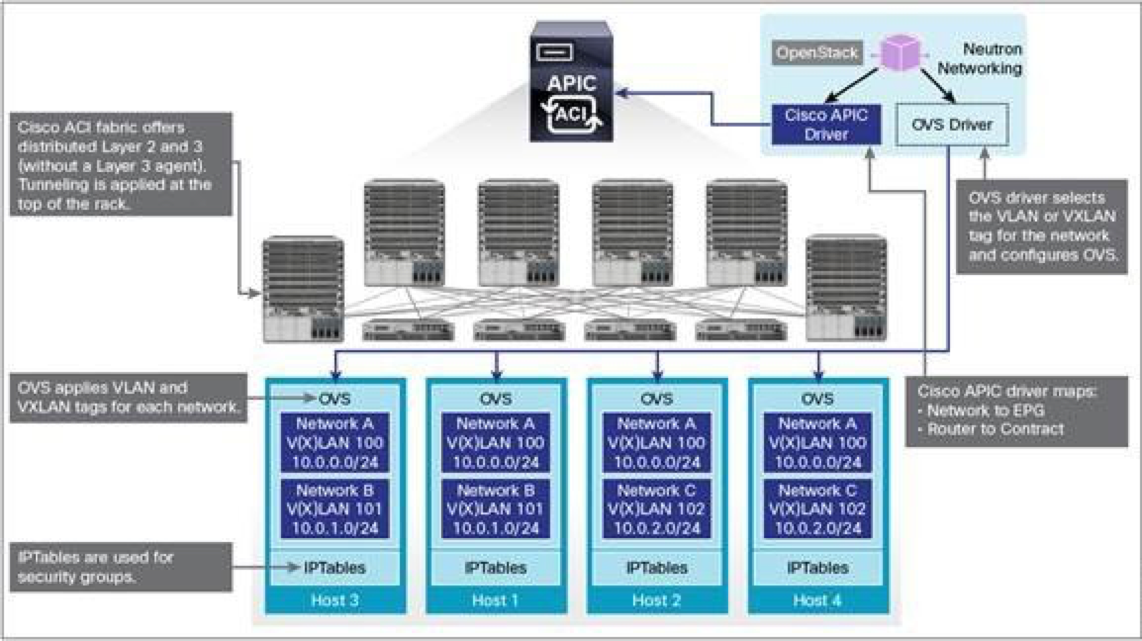
ACI and APIC driver for neutron
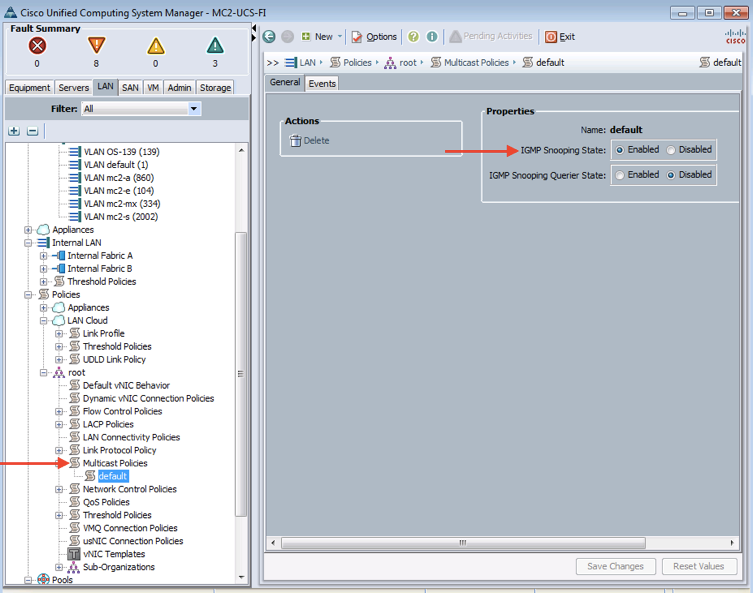
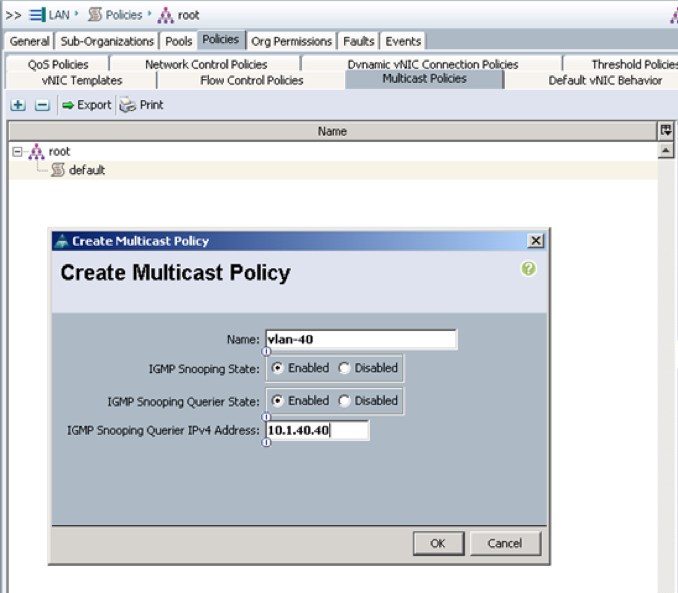
UCSM multicast policy
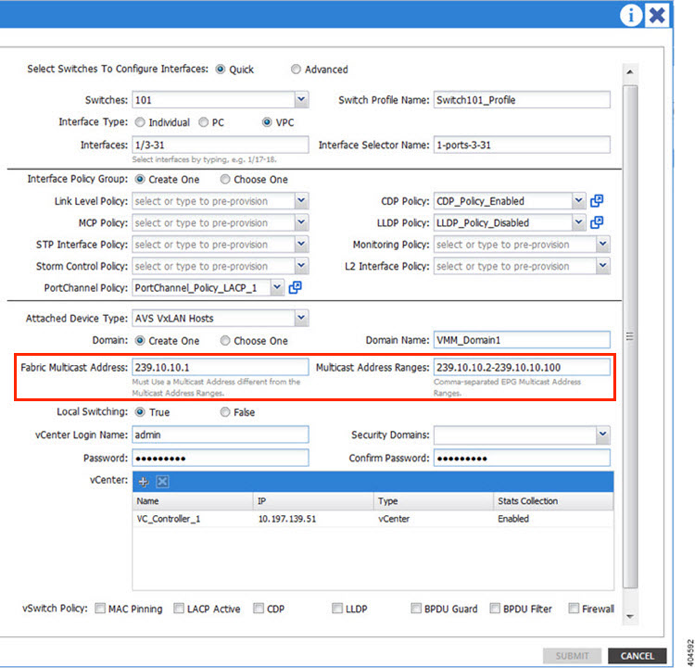
ACI/APIC multicast policy
Multicast for media applications
Multicast limitations
- IGMP snooping degrades performance of layer-2 switch
- High bandwidth multicast traffic degrades unicast routing
- Needs plugin (ASR1k, APIC) integration with neutron
- Best-effort and out-of-sequence delivery (UDP is unreliable)
- Lack of TCP windowing results in network congestion
- Duplicate packets and occasional loops when unicast routing is broken
Multicast testing tools
Multicast talk I gave at Cisco Live in Las Vegas in 2016
Multicast in OpenStack
Hope this blog is helpful to anyone deploying Multicast with OpenStack using Cisco's Nexus9000 and UCS! 
