- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Networking Knowledge Base
- QoS troubleshooting and how to collect useful logs
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-25-2014 01:39 AM - edited 03-01-2019 05:04 PM
This document explains about how to collect useful logs for QoS troubleshooting.
Please be careful because this document has been written based on test environment. So, it might not be applicable for production network.
1. Topology on the document
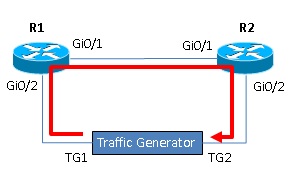
The traffic generator keep sending frames with frame size L2 125bytes@10000pps as above directing arrow.
10000pps * (125*8) = 10000000bps(=10Mbps)
Based on above calculation, the R1 receives 10Mbps traffic on Gi0/2 and then it will be shaped as 5Mbps traffic by QoS and transferred via Gi0/1
2. Useful logs for QoS troubleshooting
Here are minimum sets of useful show commands for QoS troubleshooting.
If you are using specific platform which doing QoS by hardware, you need to collect more platform-dependent show commands.
show policy-map interface # show hqf interface # show interface # show tech show logging # : Please collect 3-5 times during passing traffic
3. Relevant information
In this section, here are some important points when collecting logs which are described on above Chapter 2. If you don't collect these information, the QoS intvestigation will be difficult by TAC engineer.
1) Detail of traffic Information by QoS
You need to understand what kind of traffic is passing on the router and is treated by QoS.
In case of CBWFQ, I would like to recommend to collect the traffic information on each flow like following.。
Traffic#1 for Class#1 : IP L2 100bytes frame (10Mbps/10000pps) Traffic#2 for Class#2 : TCP L2 50bytes frame (5Mbps/10000pps) Traffic#3 for Class#3 : UDP L2 100bytes frame (5Mbps/50000pps)
Type of protocol (IP/TCP/UDP), Packet Size(L2 or L3), Bit per seconds(bps), Packets per seconds(pps). These kind of information are needed when TAC engineer start to investigate the issue of QoS. If there is no information like above, TAC engineer does not understand whether the traffic on a network leads the QoS problem.
2) Additional Information for narrowing issue
Following information would be helpful to move forward.
- certain version has the problem, but some other versions have no problem.
- the problem disappears by changing some parameter of QoS configuration
ex.) changing queue-limit from 64 packets to 256 packets
- the problem disappears by changing characteristic of traffic.
ex.) Frame size from 64 bytes to 1500bytes
3) Configure load-interval 30
Please configure "load-interval 30" on the interface which has the QoS configuration because it accelerates to compute the throughput on that interface.
Router#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#int <interface> Router(config-if)#load-interval 30
4) Should collect the logs during passing traffic
This is most important thing. Almost customer already understood the "show policy-map interface" is commonly needed for QoS troubleshooting. However, sometimes the logs are collected when there is no passing traffic on the router. Please make sure if there is passing traffic before collecting logs.
5) Packet Capture
Packet capture file which causes the QoS problem. I would like to recommend to collect 2 packet captures as below.
1) capture the traffic before doing QoS (=incoming traffic)
2) capture the traffic after doing QoS (=outgoing traffic)
Sometimes, TAC engineer need to check how the traffic are treated by QoS, that's why both captures are desired.
4. Often-opened cases
1) drops due to bursty traffic
Our IOS implemented HQF framework since 12.4(20)T. After that, Tc on Shaping has been changed from 25msec to 4msec.
Therefore, the HQF improves the accuracy of QoS, but on the other hand, it drops more than before against bursty traffic pattern. So, we receives some cases which relates to those issues by bursty traffic from the customer who upgraded from pre-HQF version to HQF version.
If you encounter this issue after upgrading from old version to HQF version, please make sure if the issue is resolved by adjusting Tc as 25msec by changing Bc/Be values.
2) due to overflowing queue-limit
In case of Shaping, some packets are placed in queue-limit to wait for given token when receiving burst traffc.
On this situation, we can assume the default queue-limit (64 packets) will not be enough.
And the drops happens by overflowing queue-limit. If you face this situation, you can see the drop by overflowing queue-limit from following "total drops" which is bold highlighted.
And the output indicates that queue-depth is 64, it means the queue-limit is full and tail drops are happening.
Router#show policy-map int
GigabitEthernet0
Service-policy output: Shape
Class-map: class-default (match-any)
84880256 packets, 127320118758 bytes
30 second offered rate 83539000 bps, drop rate 13087000 bps
Match: any
Queueing
queue limit 64 packets
(queue depth/total drops/no-buffer drops) 64/32749/0
(pkts output/bytes output) 84847504/127270998258
shape (average) cir 10000000, bc 40000, be 40000
target shape rate 10000000
To avoid this drops by overflowing queue-limit, please consider to increase the value of queue-limit like below.
Router#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#policy-map Shape Router(config-pmap)#class class-default Router(config-pmap-c)#queue-limit 128
3) About Delay
We sometimes receive a query where the customer is facing the delay on certain class which "bandwidth" configured. I would like to say, the bandwidth does not guarantee the delay of the traffic. Its function is to reserve the configured bandwidth when happening congestion. If the delay is happening on PQ class, it should be opened to TAC as service request.
Please understand the meaning/function of the commands when you face the issue.
5. In conclusion
I mentioned above, Chapter3 1) adjusting Tc by changing Bc/Be and 2) changing queue-limit against burst traffic. Both are not QoS problem. Those are tuning technique when using QoS. Before opening the service request to TAC, please tune the parameters of QoS by yourself if your problem could be tuning issue.
Even after trying to tune, please contact TAC if you need to address the issue.
Related Information
Original Document:https://supportforums.cisco.com/ja/document/12021346
Author: Takashi Higashimura
Posted on June 1, 2014
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: