Description
1. Extended Services Processor (ESP)
2. Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
Complete Definition
1. Extended Services Processor.
Encapsulating Security Payload
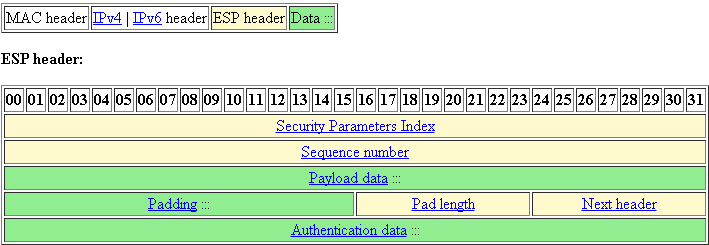
The ESP header is designed to provide a mix of security services in IPv4 and IPv6. ESP may be applied alone, in combination with AH, or in a nested fashion.
Security services can be provided between a pair of communicating hosts, between a pair of communicating security gateways, or between a security gateway and a host. The ESP header is inserted after the IP header and before the next layer protocol header (transport mode) or before an encapsulated IP header (tunnel mode). ESP can be used to provide confidentiality, data origin authentication, connectionless integrity, an anti-replay service (a form of partial sequence integrity), and (limited) traffic flow confidentiality. The set of services provided depends on options selected at the time of Security Association (SA) establishment and on the location of the implementation in a network topology.
RFC:
- IP Authentication Header - RFC 4302
- Cryptographic Algorithm Implementation Requirements for Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH) - RFC 4835
- IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) - RFC 4303
Also See: