- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Security
- Security Knowledge Base
- ISE Authentication and Authorization Policy Reference
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
05-06-2019 12:07 PM - edited 07-09-2025 04:56 PM
Contents
- ISE Default Policy Set
- Policy Sets ➡ Default
- Authentication Policy
- Authorization Policy - Local Exceptions
- Authorization Policy - Global Exceptions
- Authorization Policy
- Secure Default Authorization Policy
- Default Authorization Policy for Monitor Mode
- Default Conditions
- Policy Sets
- Policy Set Conditions
- Authentications
- Virtual Private Network (VPN)
- Exceptions
- Blocklists
- Quarantine
- Certificate Renewal
- Authorizations
- Internal User Authorization
- RADIUS Probes
- Microsoft Active Directory Groups Authorizations
- User Authentication with Microsoft Active Directory
- Machine Authentication with Active Directory (802.1X with EAP-TLS to AD)
- Machine Authentication with Duo 2FA/MFA (802.1X with Web Authentication)
- EAP-Chaining: User and Machine Authentication using EAP-FAST)
- TEAP-Chaining with Tunneled EAP (TEAP)
- Wireless Authorization Matching a Specific SSID
- MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) Authorizations
- Single MAC Address
- Multiple MAC Addresses
- MAC OUI Wildcard
- Random MAC Addresses
- Static Endpoint Group(s)
- Profiling Authorizations
| ? | Have a comment or question about this document? Please start a new discussion in the ISE Community and link to this document or specific section where you have a comment or question! |
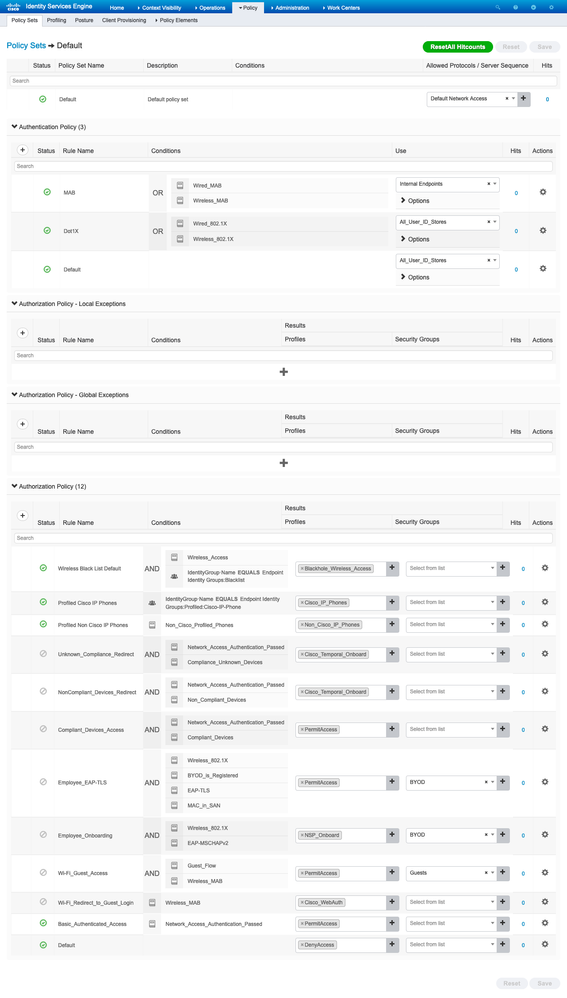
ISE Default Policy Set
Navigate to Policy > Policy Sets in ISE 2.4 and later to see the default Policy Set :
| ISE 2.x | ISE 3.x |
|
|
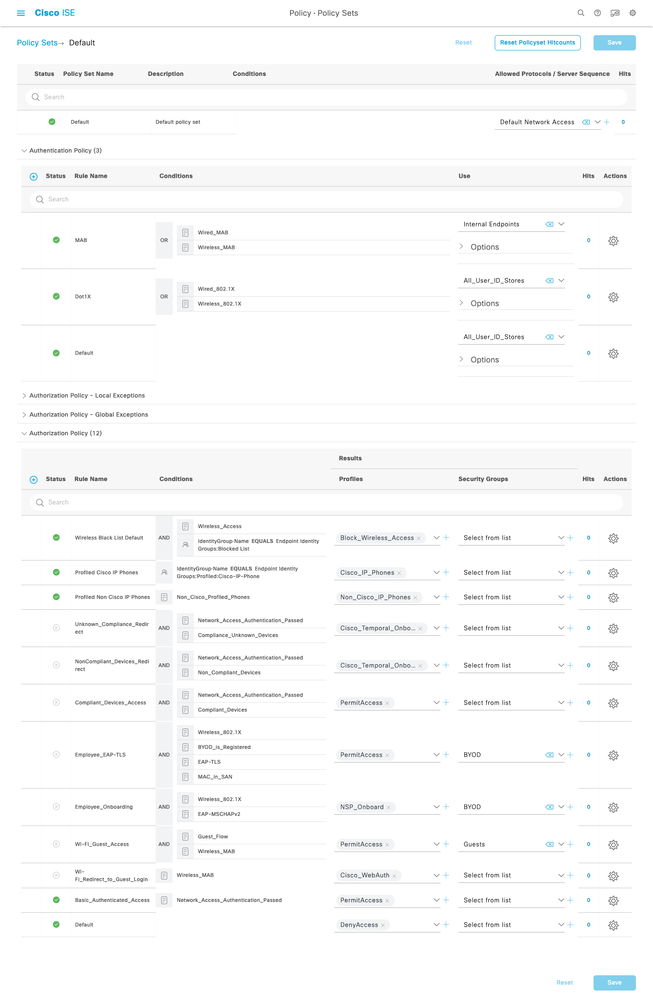 |
Policy Sets ➡ Default
Click on ⊕ or + to create a new policy set.
| ⊕ | Status | Policy Set Name | Description | Conditions | Allowed Protocols / Server Sequence | Hits | Action | View |
| + | ||||||||
| ✔ | Default | Default Policy Set | Default Network Access | 0 | ⚙ | ❯ | ||
Click on ❯ to View the details of a policy set:
| ❯ Authentication Policy |
| ❯ Authorization Policy - Local Exceptions |
| ❯ Authorization Policy - Global Exceptions |
| ❯ Authorization Policy |
Authentication Policy
In ISE, there are 3 default authentication policies:
- MAB
- Dot1X
- Default
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Use | Hits | Actions | ||
| ✔ | MAB |
|
Internal Endpoint ∨ Options If Auth fail: REJECT If User not found: CONTINUE If Process fail: DROP |
0 | ⚙ | ||
| ✔ | Dot1X |
|
All_User_ID_Stores ∨ Options If Auth fail: REJECT If User not found: REJECT If Process fail: DROP |
0 | ⚙ | ||
| ✔ | Default | All_User_ID_Stores ∨ Options If Auth fail: REJECT If User not found: REJECT If Process fail: DROP |
0 | ⚙ |
Each authentication policy has Options for what to do inerroneous conditions
- Reject: Send ‘Access-Reject’ back to the NAD
- Continue: Continue to authorization regardless of authentication outcome
- Drop: Drop the request and do not respond to the NAD – NAD will treat as if RADIUS server is dead
Authorization Policy - Local Exceptions
There are no Local Exceptions by default. Click on ⊕ or ➕ to create a new exception.
| ⊕ | Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | Hits | Actions |
| ➕ |
Authorization Policy - Global Exceptions
There are no Local Exceptions by default. Click on ⊕ or ➕ to create a new exception.
| ⊕ | Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | Hits | Actions |
| ➕ |
Authorization Policy
There are 12 authorization policies provided by default:
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | Hits | Actions | ||
| ✔ | Wireless Block List Default |
|
Block_Wireless_Access | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ✔ | Profiled Cisco IP Phones | IdentityGroup-Name EQUALS Endpoint Identity Groups:Profiled:Cisco-IP-Phone | Cisco_IP_Phones | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ✔ | Profiled Non Cisco IP Phones | Non_Cisco_Profiled_Phones | Non_Cisco_IP_Phones | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ⃠ | Unknown_Compliance_Redirect |
|
Cisco_Temporal_Onboard | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ⃠ | NonCompliant_Devices_Redirect |
|
Cisco_Temporal_Onboard | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ⃠ | Compliant_Devices_Access |
|
PermitAccess | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ⃠ | Employee_EAP-TLS |
|
PermitAccess | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ⃠ | Employee_Onboarding |
|
NSP_Onboard | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ⃠ | Wi-Fi_Guest_Access |
|
PermitAccess | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ⃠ | Wi-Fi_Redirect_to_Guest_Login | Wireless_MAB | Cisco_WebAuth | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ✔ | Basic_Authenticated_Access | Network_Access_Authentication_Passed | PermitAccess | Select from list | 0 | ⚙ | ||
| ✔ | Default | DenyAccess | Select from list | 0 |
Secure Default Authorization Policy
In order to provide a secure default for wireless endpoints and closed-mode deployments, the default ISE Policy Set's Default authorization policy is configured to deny access with the DenyAccess authorization profile.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | Hits | Actions |
| ✔ | Default | DenyAccess | Select from list | 0 |
If instead your goal is to get Visibility on your wired network, you will want to change the Default to PermitAccess so all endpoints will continue to get open access and you may collect profiling information until you are ready to begin enforcement.
Default Authorization Policy for Monitor Mode
If you first deploy ISE to get visibility on your wired network with a "monitor mode" switchport configuration, you should change the default Authorization Profile to be PermitAccess . This will ensure that every user and device gets full network access until you are ready to start doing enforcement.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | Hits | Actions |
| ✔ | Default | PermitAccess | Select from list | 0 |
Default Conditions
| Named Condition | Conditions | Description |
| BYOD_is_Registered | Endpoints:BYODRegistration EQUALS Yes | Default condition for BYOD flow for any device that has passed the network supplicant provisioning (NSP) process |
| Catalyst_Switch_Local_Web_Authentication | Radius:Service-Type EQUALS Outbound Radius:NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Ethernet |
Default condition used to match authentication requests for Local Web Authentication from Cisco Catalyst switches |
| Compliance_Unknown_Devices | Session:PostureStatus EQUALS Unknown | Default condition for unknown posture compliance devices |
| Compliant_Devices | Session:PostureStatus EQUALS Compliant | Default condition for posture compliant devices |
| EAP-MSCHAPv2 | Network Access·EapAuthentication EQUALS EAP-MSCHAPv2 | Default condition for BYOD onboarding flow |
| EAP-TLS | Network Access·EapAuthentication EQUALS EAP-TLS | Default condition for BYOD flow for any device that has passed the network supplicant provisioning (NSP) process |
| Guest_Flow | Network Access:Use Case EQUALS Guest Flow | Default condition for guest flow |
| MAC_in_SAN | Certificate:Subject Alternative Name EQUALS Radius:Calling-Station-ID | Default condition for BYOD flow for any device that has passed the network supplicant provisioning (NSP) process |
| Network_Access_Authentication_Passed | Network Access:AuthenticationStatus EQUALS AuthenticationPassed | Default condition used for basic network access requiring that the authentication was successful |
| Non_Cisco_Profiled_Phones | Endpoints:LogicalProfile EQUALS IP-Phones | Default condition used to match IP Phones |
| Non_Compliant_Devices | Session:PostureStatus EQUALS Non-Compliant | |
| Switch_Local_Web_Authentication | Radius:Service-Type EQUALS Outbound Radius:NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Ethernet |
Default condition used to match authentication requests for Local Web Authentication from Cisco Catalyst switches |
| Switch_Web_Authentication | Normalized Radius:RadiusFlowType EQUALS WiredWebAuth | A condition to match requests for web authentication from switches according to the corresponding Web Authentication attributes defined in the network device profile |
| Wired_802.1X | Normalized Radius:RadiusFlowType EQUALS Wired8021_X | A condition to match requests for 802.1X authentication from switches according to the corresponding 802.1X attributes defined in the network device profile |
| Wired_MAB | Normalized Radius:RadiusFlowType EQUALS WiredMAB | A condition to match the MAC Authentication Bypass request from switches according to the corresponding MAB attributes defined in the network device profile |
| Wireless_802.1X | Normalized Radius:RadiusFlowType EQUALS Wireless8021_X | A condition to match requests for 802.1X authentication from wireless LAN controllers according to the corresponding 802.1X attributes defined in the network device profile |
| Wireless_Access | Radius:NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Wireless - IEEE 802.11 | Default condition used to match any authentication request from a Cisco Wireless LAN Controller |
| Wireless_MAB | Normalized Radius:RadiusFlowType EQUALS WirelessMAB | A condition to match the MAC Authentication Bypass request from wireless LAN controllers according to the corresponding MAB attributes defined in the network device profile |
| WLC_Web_Authentication | Normalized Radius:RadiusFlowType EQUALS WirelessWebAuth | A condition to match requests for web authentication from wireless LAN controllers according to the corresponding Web Authentication attributes defined in the network device profile |
Policy Sets
You may create additional policy sets to handle requests using conditions from attributes sent in the initial RADIUS request. You typically want to create different policy sets for different access methods (wired, wireless, VPN) or authentication types (MAB, 802.1X) or scenarios (Corporate, IOT, Guest) or locations (country, region, zone, department) or any combinations of these. Remember that not all attributes are known from the initial RADIUS request (EAP protocols are negotiated!) so some things will not be available to you when choosing a Policy Set.
Below are some of the most commonly used RADIUS attributes for Policy Set conditions:
| RFC | RADIUS Attribute | # | Type | Example |
| RFC-2865 | User-Name | 1 | string | thomas |
| RFC-2865 | User-Password | 2 | string | C1sco12345 |
| RFC-2865 | NAS-IP-Address | 4 | 4 x octets | 1.2.3.4 |
| RFC-2865 | NAS-Port | 5 | integer | 1 |
| RFC-2865 | Service-Type | 6 | integer | Login (1) | Framed (2) | Call-Check (10) |
| RFC-2865 | Vendor-Specific | 26 | string | vendor type / vendor length / value fields |
| RFC-2865 | Called-Station-Id | 30 | string | 555-867-5309 | 12:34:56:78:90:AB | 2C-3F-0B-56-E3-6C:.corp |
| RFC-2865 | Calling-Station-Id | 31 | string | 555-867-5309 | 12:34:56:78:90:AB | 8E-69-06-36-6F-6B |
| RFC-2865 | NAS-Identifier | 32 | string | sjc-9300-1 |
| RFC-2865 | NAS-Port-Type | 61 | integer | Virtual (5) | Ethernet (15) | Wireless - IEEE 802.11 (19) |
| RFC-2869 | Connect-Info | 77 | string | CONNECT 54.00 Mbps / 802.11ac / RSSI: 68 / Channel: 60 CONNECT 11Mbps 802.11b |
| RFC-2869 | NAS-Port-ID | 87 | string | GigabitEthernet0/1 |
| RFC-2869 | Framed-Pool | 88 | string | the name of an assigned address pool on the NAS |
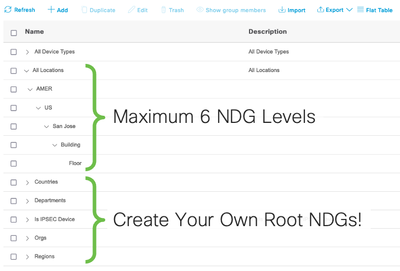
In addition to the attributes above, you may also use Network Device Groups (NDGs) in ISE which are labels that you create and assign to your network devices. ISE has the default NDGs All Device Types, All Locations, and Is IPSEC Device by default, but you may create your own with a maximum of 6 NDG levels!
Policy Set Conditions
Below are some example policy set conditions that you may find useful. To create a new policy set, click on ⊕ or + :
| ⊕ | Status | Policy Set Name | Description | Conditions | Allowed Protocols / Server Sequence |
| + | |||||
| ✔ | Manufacturing | NDG | DEVICE•Department EQUALS Department:Department:Manufacturing | MAB_Only | |
| ✔ | 802.1X_Corp_Wireless | Radius•NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Wireless - IEEE 802.11 Radius Service-Type EQUALS Framed Radius Called-Station-ID ENDS_WITH :.corp |
EAP | ||
| ✔ | 802.1X_Corp_Wired | Radius•NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Ethernet Radius•Service-Type EQUALS Framed |
EAP | ||
| ✔ | MAB_IOT_Wireless | Radius•NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Wireless - IEEE 802.11 Radius Service-Type EQUALS Call Check Radius Called-Station-ID ENDS_WITH iot |
MAB_Only | ||
| ✔ | MAB_IOT_Wired | Radius•NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Ethernet Radius Service-Type EQUALS Call Check |
MAB_Only | ||
| ✔ | Guest_Web_Auth | Radius•NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Wireless - IEEE 802.11 Radius Service-Type EQUALS Login Radius Called-Station-ID ENDS_WITH guest |
Default Network Access | ||
| ✔ | Wired_Web_Auth | Radius•NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Ethernet Radius•Service-Type EQUALS Login |
Default Network Access | ||
| ✔ | VPN | Radius•NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Virtual | |||
| ✔ | Default | Default Policy Set | Default Network Access | ||
Authentications
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
You may use Radius:NAS-Port-Type = Virtual to filter on all VPN policies.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Use |
| ✔ | VPN | Radius:NAS-Port-Type EQUALS Virtual | All_User_ID_Stores > Options |
Exceptions
Any of the following exceptions may be applied to Global Exceptions for all policy sets or to Local Exceptions for individual policy sets.
| ⚠ | Remember that any and all Exceptions will be processed before any policy set authorization rules! The processing order for every request is: Global Exceptions ❯ Policy Set Local Exceptions ❯ Policy Set Authorizations The creation of Global Exceptions and the attributes you use in their conditions should be evaluated carefully to prevent a degradation of your authorization speed and the general performance of ISE! |
Blocklists
Users or devices may be moved into the Blocklist Endpoint Identity Group in order to temporarily prevent access. This is typically done for :
- lost BYOD devices
- any user or device that you want to block for any reason
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups |
| ✔ | BlockList | IdentityGroup:Name STARTS_WITH Endpoint Identity Groups:Blocklist | DenyAccess | Quarantine |
Quarantine
Similar to using a blocklist, you may want to Quarantine a user or device based on a security integration that uses the ISE EPS or ANC APIs to temporarily limit their access until a security patch is made that brings the device into compliance.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups |
| ✔ | Quarantine | Session:EPSStatus EQUALS Quarantine | DenyAccess | Quarantine |
Certificate Renewal
If ISE detects that a certificate has expired or will expire soon, it's a good to be proactive and redirect them to get a new certificate.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | ||
| ✔ | Certificate_Renewal |
|
Certificate_Expiry_Redirect | Select from list |
If you're interested in what the Certificate_Expiry_Redirect looks like, here it is:
Authorizations
Internal User Authorization
Sometimes you may want to test RADIUS access with an internal test user account.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups |
| ✔ | Test_User | Network Access:Username EQUALS test_user | PermitAccess | Employees |
RADIUS Probes
You may configure network devices or load balancers to send synthetic RADIUS queries to test availability. It's OK to send a RADIUS Access-Reject (DenyAccess) because the load balancers just need to get a response to know the server is OK.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups |
| ✔ | RADIUS_Probe | Radius:User-Name STARTS_WITH radtest | DenyAccess | - |
Microsoft Active Directory Groups Authorizations
User Authentication with Microsoft Active Directory
You can do it by requiring the EAP-MSCHAPv2 protocol
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | ||
| ✔ | Employee |
|
PermitAccess | Employees |
ⓘ We recommend using the Employees security/scalable group tag (SGT) to classify your users or devices by role. You may do this even if you are not doing software-defined access or group-based policy enforcement. If your network device does not support SGTs, it will simply ignore the RADIUS vendor-specific attribute (VSA) for the SGT.
Or by explicitly requiring a wired or wireless 802.1X authentication:
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | ||||
| ✔ | Employee |
|
PermitAccess | Employees |
Machine Authentication with Active Directory (802.1X with EAP-TLS to AD)
Machine authentication using EAP-TLS for domain-joined computers with a certificate.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | ||
| ✔ | Domain Computer |
|
PermitAccess | Domain_Computers |
ⓘ There is no Domain_Computers security/scalable group in ISE by default so you would need to create it.
Machine Authentication with Duo 2FA/MFA (802.1X with Web Authentication)
Machine authentication using EAP-TLS for domain-joined computers with a certificate followed by web authentication of a user against Duo Security with 2FA/MFA.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | ||
| ✔ | Employee |
|
PermitAccess | Employee | ||
| ✔ | Domain Computer |
|
MachineAuth | Domain_Computers |
ⓘ There is no Domain_Computers security/scalable group in ISE by default so you would need to create it.
EAP-Chaining: User and Machine Authentication using EAP-FAST)
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | ||
| ✔ | EAP-Chaining |
|
PermitAccess | Employees |
TEAP-Chaining with Tunneled EAP (TEAP)
TEAP is a new EAP protocol supported in ISE 2.7 and later. See TEAP for Windows 10 using Group Policy and ISE TEAP Configuration for details.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | ||
| ✔ | TEAP-Chaining |
|
PermitAccess | Employees | ||
| ✔ | TEAP-Machine |
|
MachineAuth | Machine | ||
| ✔ | TEAP-User |
|
EmployeeOnly | Employees |
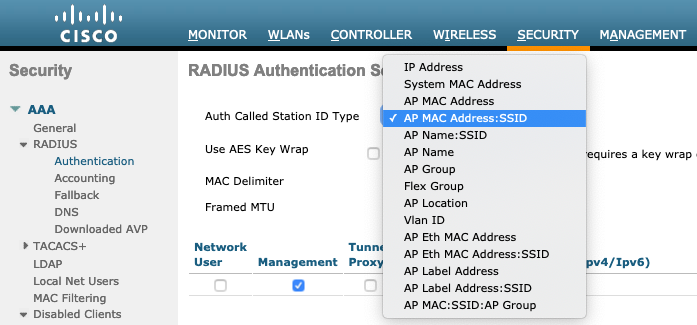
Wireless Authorization Matching a Specific SSID
Wireless controllers offer many options for the RADIUS Called-Station-ID. If you want to match on a specific SSID, you will need to ensure that your Wireless controller sends the SSID in the RADIUS Called-Station-ID :
This allows you to match the SSID in your ISE authorization policy to provide the appropriate level of access for your wireless services (Guest vs Corporate vs BYOD, etc.) with a rule like:
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | ||
| ✔ | Guest_Wireless |
|
Internet_Only | Guest |
Remember that if you change your WLC's RADIUS:Called-Station-ID to something that does not end with :SSID then you affect your existing authorization policy rules with potentially bad affects!
MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) Authorizations
Single MAC Address
When testing your policies, you may want to filter on one or more specific MAC addresses for your test device. For this you would use the Radius:Calling-Station-ID attribute:
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups |
| ✔ | Test_Printer | ⌸ Radius:Calling-Station-ID EQUALS 11-22-33-44-55-66 | PermitAccess | Printers |
Multiple MAC Addresses
When testing your policies, you may want to filter on one or more specific MAC addresses for your test device. For this you would use the Radius:Calling-Station-ID attribute:
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | ||
| ✔ | Test_Printers |
|
PermitAccess | Printers |
MAC OUI Wildcard
Similar to filtering on a single or multiple MAC, you may simply filter on the first 6 digits of the MAC address known as the IEEE Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) :
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups |
| ✔ | Test_Printers | ⌸ Radius:Calling-Station-ID STARTS_WITH 11-22-33 | PermitAccess | Printers |
Random MAC Addresses
"Random" or "locally administered" MAC addresses are in use or detected when the 2nd hexadecimal digit of the MAC address is a 2,6,A, or E. While random MAC addresses are fine for a Guest network for privacy, you probably do not want to allow them on your wired or wireless networks because your managed endpoints shouldn't be randomizing their MACs unless have certificates. Wireless IOT endpoints that rely on iPSK should not be changing their MAC addresses, either.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups |
| ✔ | Random_MAC | ⌸ Radius:Calling-Station-ID MATCHES ^.[26AEae].* | DenyAccess | - |
Static Endpoint Group(s)
This is the fastest way to authorize groups of devices using MAC addresses using Endpoint Identity Groups. There is an example of this in the default ISE Authorization Policy for blocking wireless endpoints.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups | ||
| ✔ | Wireless Block List Default |
|
Block_Wireless_Access | Select from list |
You can use the same
IdentityGroup-Name EQUALS Endpoint Identity Groups:group_name
condition to authorize endpoints with any authorization profile you want!
Use this for IP phones and IOT devices that cannot or will not be configured for 802.1X authentication and you do not want to use profiling.
- Create an endpoint identity group for your devices under Administration > Identity Management > Groups > Endpoint Identity Groups
- Go to Context Visibility > Endpoints and download the CSV template from the Import option or Export your existing devices as a CSV for reference if you don't already have a complete list of your endpoint MAC addresses.
- Update the template - or filter your export of existing devices for the desired endpoints - then set the IdentityGroup field to the endpoint identity group you created and change the StaticGroupAssignment field to TRUE.
- Import the CSV of your devices.
- Create an Authorization policy to allow endpoints using this group:
Status Rule Name Conditions Profiles Security Groups ✔ MyPhones IdentityGroup-Name EQUALS Endpoint Identity Groups:MyIPPhones Cisco_IP_Phones Select from list
Profiling Authorizations
The default ISE Authorization Policy has examples of how to do this for IP phones. You may duplicate these authorization rules and change them to match your other profiled endpoints and authorization profiles.
| Status | Rule Name | Conditions | Profiles | Security Groups |
| ✔ | Profiled Cisco IP Phones | IdentityGroup-Name EQUALS Endpoint Identity Groups:Profiled:Cisco-IP-Phone | Cisco_IP_Phones | Select from list |
| ✔ | Profiled Non Cisco IP Phones | Non_Cisco_Profiled_Phones | Non_Cisco_IP_Phones | Select from list |
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: