- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Service Providers
- Service Providers Knowledge Base
- Designing Multicast VPN Using MLDP
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
05-03-2013 05:35 AM - edited 03-01-2019 01:52 PM
- Introduction:
- Label Switched Multicast (LSM):
- Why LSM ?
- MPLS vs IP:
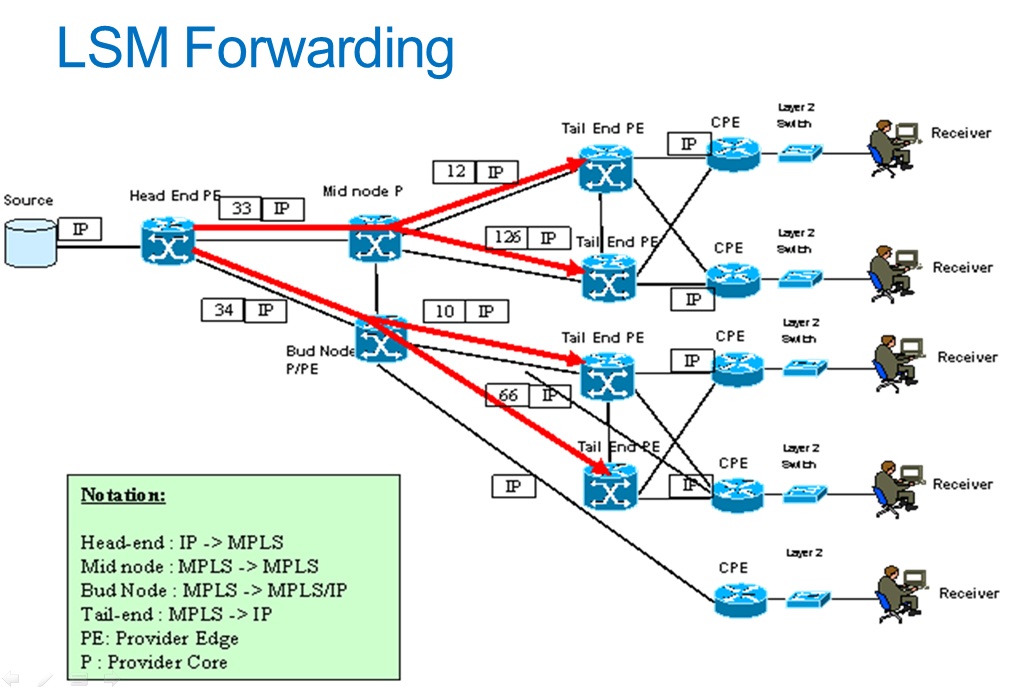
- LSM FORWARDING:
- Advantages of MPLS over IP:
- Multicast LDP:
- MLDP - FEC:
- Multicast LSP Types:
- MP2MP – Basic Operation:
- P2MP – Basic Operation:
- LSP-VIF:
- MVPN:
- Related Information:
Introduction:
In this document, we will discuss how LSM (mLDP) replaces the native multicast solution of providing MVPN in a service provider environment.
The MLDP-based MVPN feature provides extensions to Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) for the setup of point-to-multipoint (P2MP) and multipoint-to-multipoint (MP2MP) label switched paths (LSPs) for transport in the Multicast Virtual Private Network (MVPN) core network.
Label Switched Multicast (LSM):
- Label Switched Multicast
First step of MPLS into MULTICAST Technologies
Multicast traffic is sent over MPLS core
- Control Plane builds
P2MP trees using RSVP TE
MP2MP trees using MLDP
- Data plane does MPLS replications
Why LSM ?
- Simple P2MP and MP2MP LSP in the core
- No PIM sparse-mode operations in the core i.e. no PIM registers, data-driven events and asserts
- No DF election for MP2MP LSPs.
- Reliable signalling
- Support for transit aggregate trees
MPLS vs IP:
MPLS
IP
|
|
LSM FORWARDING:
Advantages of MPLS over IP:
- Due to generalized RPF check based on labels we have the following benefits.
- No asserts (duplicate forwarders on a LAN)
- No DF election for MP2MP. (Designated Forwarder for upstream traffic)
- Build divergent trees based on FEC for the same multicast stream. (life-life scenarios).
Multicast LDP:
- LSPs are build from the receiver to the root, which is a scaling advantage.
- Supports P2MP and MP2MP LSPs.
- No periodic signalling, reliable using TCP.
- Control plane is P2MP or MP2MP.
- Data plane is P2MP.
- No PHP – The top label used to identify tree
- Downstream on demand label allocation.
MLDP - FEC:
- FEC – Forwarding Equivalence Class
- FEC is built using Opaque Values in mLDP.
- EachMP LSP is identified by a unique opaque value
- Is used to uniquely identify the MP LSP
- Combined with root address to build the MP LSP tree
- The opaque contents varies per application
- Opaque Value only has meaning to Ingress & Egress PE, Core router does not need to parse/understand the value
- In case of mLDP based MVPN, the opaque values used are:
Multicast LSP Types:
1:Multi-Point to Multi-point (MP2MP)
- Bidirectional, Many-2-Many (Multi-party audio/video).
- All the leafs of the LSP can inject and receive packets from the LSP
- Comparable to PIM BiDir trees
2:Point to Multi-Point (P2MP)
- Unidirectional, One-2-Many (IPTV)
- Allows only the root of the P2MP LSP to inject packets into the tree
- Comparable to PIM SSM trees
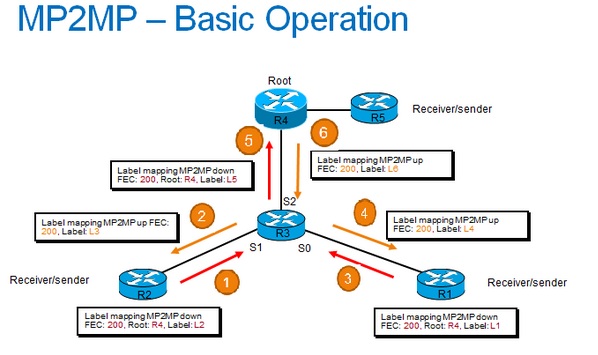
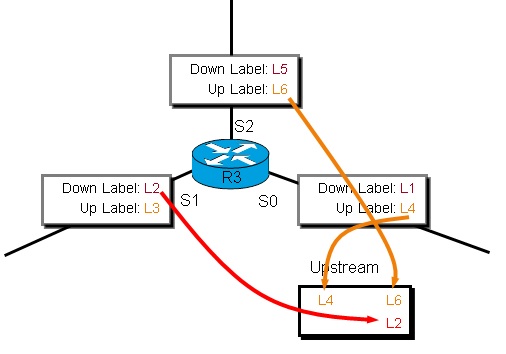
MP2MP – Basic Operation:
- Building a MP2MP LSP we setup a downstream path and an upstream path.
- Downstream path is like a normal P2MP LSP.
- Upstream path is setup like a P2P LSP to the upstream router, but inherits downstream labels from the downstream P2MP LSP.
- Used for Default MDT in MVPN.
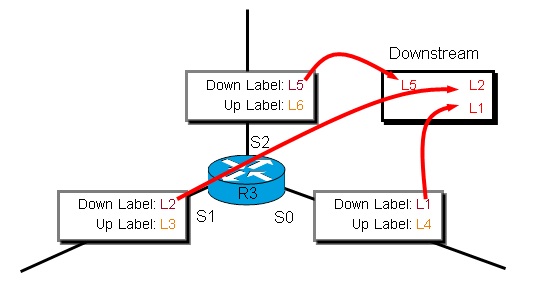
We look at R3 downstream label replication table from S2:
We look at R3 upstream label replication table from S1
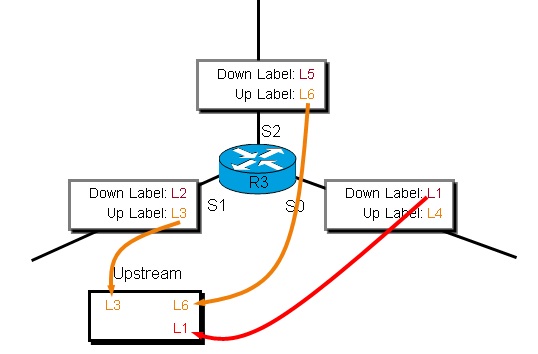
We look at R3 upstream label replication table from S0.
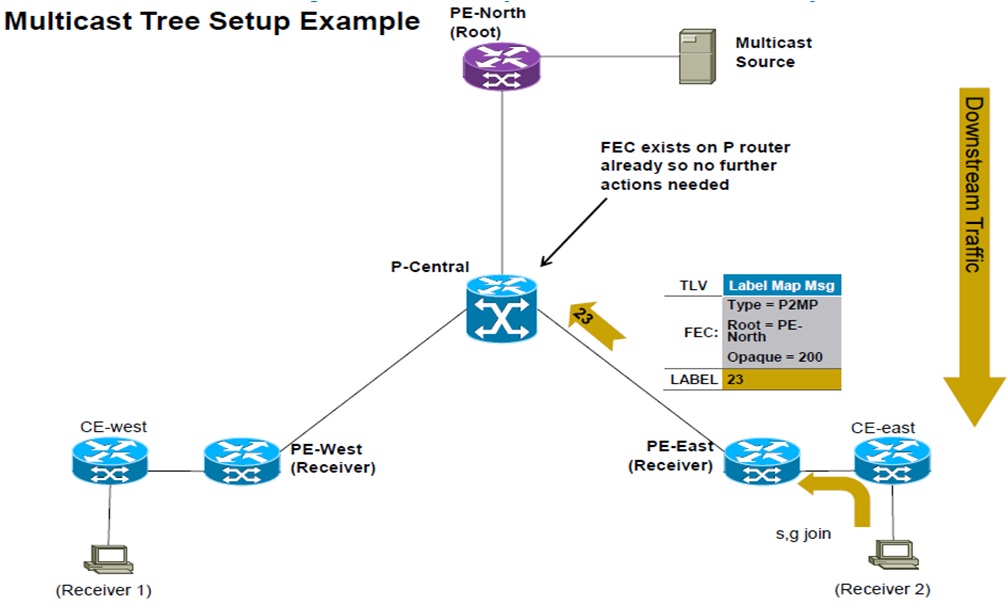
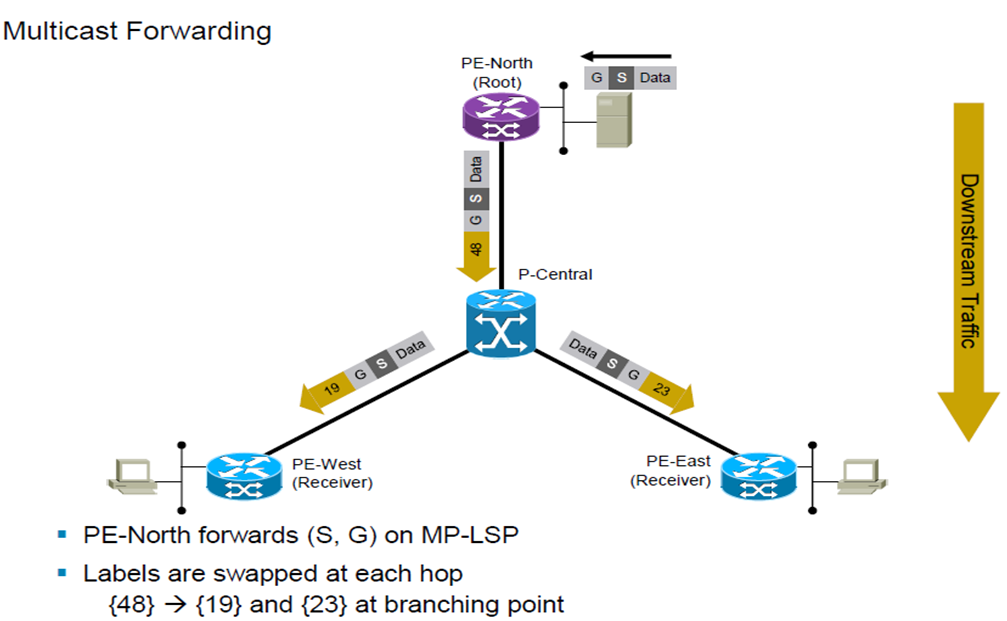
P2MP – Basic Operation:
- P2MP LSP is rooted at Ingress LSR.
- P2MP LSP is unidirectional.
- Egress LSRs initiate the tree creation using the unicast reachability to the root address.
- Receiver driven, hop-by-hop to root.
- When a leaf wants to leave, msg is only sent to the next branch point, not all the way to ingress PE.


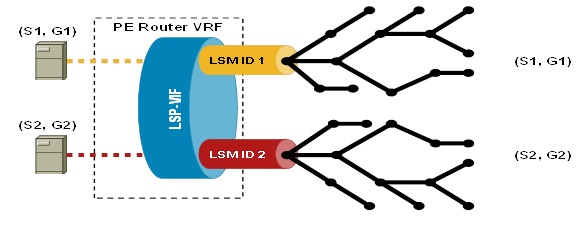
LSP-VIF:
- LSP-VIF is a logical interface dynamically created on Ingress & Egress LERs. It’s like the dynamically created GRE MDT interface in mVPN. It is an unnumbered interface preferably with the loopback ip addresses.
- It represents the head & tail end of the LSP. It appears as incoming or outgoing interface in global or VRF multicast routing table.
MVPN:
MVPN – Terminology:
Multicast VRF (MVRF): A VRF that supports both unicast and multicast forwarding tables
- Per VRF multicast routing and forwarding.
- PIM/IGMP/MSDP and other multicast protocols operate in the context of the VRF.
- RPF check using unicast routing information in the same VRF.
- Special configuration not required to create or enable an MVRF.
Multicast Distribution Tree (MDT): Used to carry multicast C-packets among PE routers in a common Multicast Domain (set of VRFs that can send Multicast packets to each other)
Default MDT Groups:
- Configured for every MVRF if MPLS or IP core network present.
- Used for PIM control traffic, low bandwidth sources, and flooding of dense-mode traffic.
Data MDT Groups:
- Optionally configured.
- Used for high bandwidth sources to reduce replication to uninterested PEs.
PE-CE:
A multicast routing protocol is run on the PE-CE interfaces, such that the PE and CE are multicast routing adjacencies on that interface.
- CEs at different sites do not become multicast routing adjacencies of each other.
Protocols
- PIM Sparse Mode (PIM-SM), supporting the ASM service model.
- PIM Sparse Mode, supporting the SSM service model.
- PIM Bidirectional Mode (BIDIR-PIM), which uses bidirectional C-trees to support the ASM service model.
- MLDP, "Carrier's Carrier" model.
MVPN – Call flow using mLDP:
- In the following section, we will discuss that how a end to end multicast flow through the MPLS backbone.
- In MLDP scenario there won’t be any PIM configured in the core and the multicast packets are MPLS encapsulated.
- The default MDT will be created using MP2MP LSP to support low bandwidth and control traffics between the VRFs.
- The data MDT will be created using P2MP LSP to support high bandwidth traffic from a particular source.
The MDT is signalled as a MP2MP LSP. Each PE router configured with VPN-ID 1:1 creates the same FEC TLV, but with a different downstream label. The FEC Type will be "MP2MP Down" which prompts the receiving LSR to respond with an upstream label mapping message to create the Upstream Path.
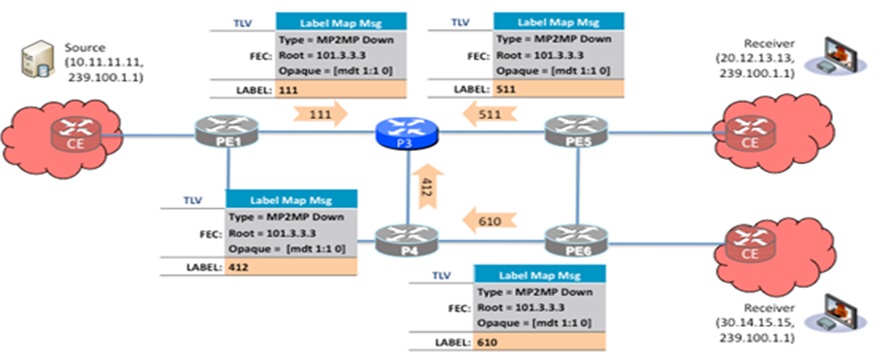
For each downstream label received a corresponding upstream label is sent. Thus P3 sends out 3 upstream labels {309}, {308} and {313} to each downstream directly connected neighbor then these neighbors send out upstream labels as well.

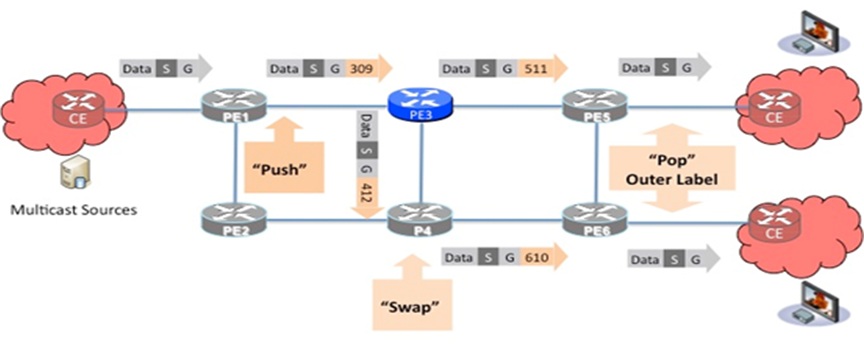
Packets arriving as native multicast packets at a PE / VRF interface are encapsulated using a single label which is the mLDP label. This label relates to forwarding in the backbone, determines packet forwarding over the MDT, and also identifies the VPN. This label is swapped at every hop on the way from the sending PE to the receiving PE.
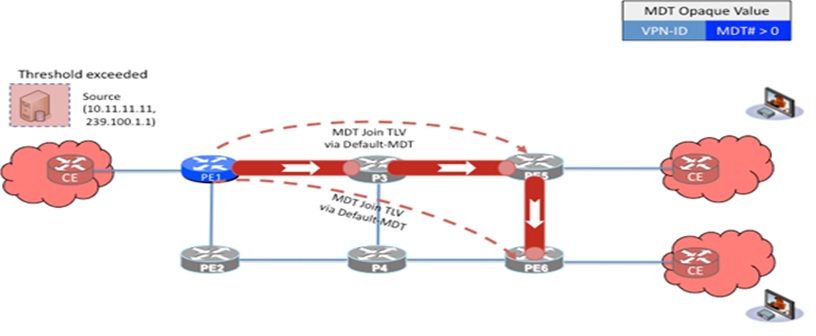
In an MVPN, traffic that exceeds a certain threshold can move off the Default-MDT onto a Data-MDT. If a source on the site connected to PE1 exceeds a configured threshold, PE1 will initiate a MDT Join TLV over the Default-MDT MP2MP LSP advising all PE routers that a new Data-MDT is being created. If PE5 has an interested receiver it will build a MP LSP using a P2MP procedure to PE1 (which will be the root of the P2MP tree). If PE6 does not have a receiver for this source it will simply cache the Join TLV.
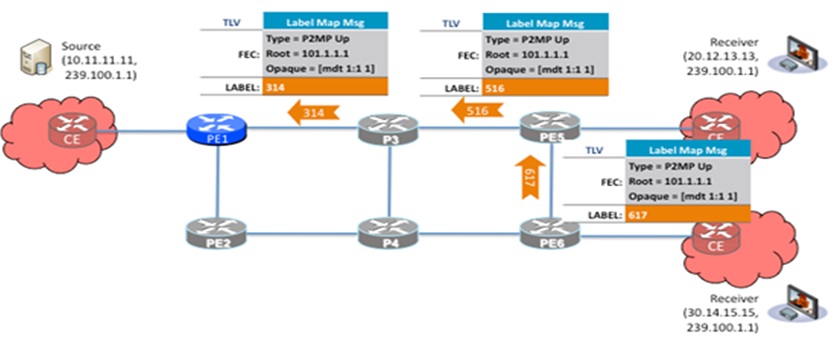
A new P2MP Data-MDT is created for each high-bandwidth multicast source. All labels are allocated from the platform label space (the same pool as is used by unicast MPLS). Downstream on demand label allocation is used.
MVPN – VRF Configuration:
Only the VRF configuration changes and rest configuration remains the same as Native Multicast VPN.
ip vrf test-mvpn
rd 17627:2017627
vpn id 17627:1017627
mdt default mpls mldp 10.25.2.131
mdt data mpls mldp 60
mdt data threshold 10
route-target export 17627:234
route-target import 17627:234
Related Information:
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
All the documentation, examples, whatever are using this old style MDT configuration. Has anyone ever configured Profile-14? That is based on partitioned-MDT. Why do Cisco hide all the details about Profile-14? This should be an interoperable, multivendor solution...
Most of the commands and troubleshooting information needed for proper, high-availibility MVPN are undocumented. Anycast-RP over Profile-14 is not working. Neither the route-policy based configuration. Actually, the example in the config guide with RTs is wrong. It will generate unusable Tzpe-1 advertisements. The Type-5 routes are not advertised as they should according to RFC 6513, RFC 6514. Cisco claims that ASM shall work over Profile-14, but only SSM is operational with IOS XR v6.1.
Does someone have a working configuration for ASM over Profile-14 with Anycast-RP?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
To get more detail on Multicast Profile 14
Refer below
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: