- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Security
- VPN
- AnyConnect-Parent Encryption NONE
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-30-2013 11:52 AM - edited 02-21-2020 06:59 PM
Hi Support Community,
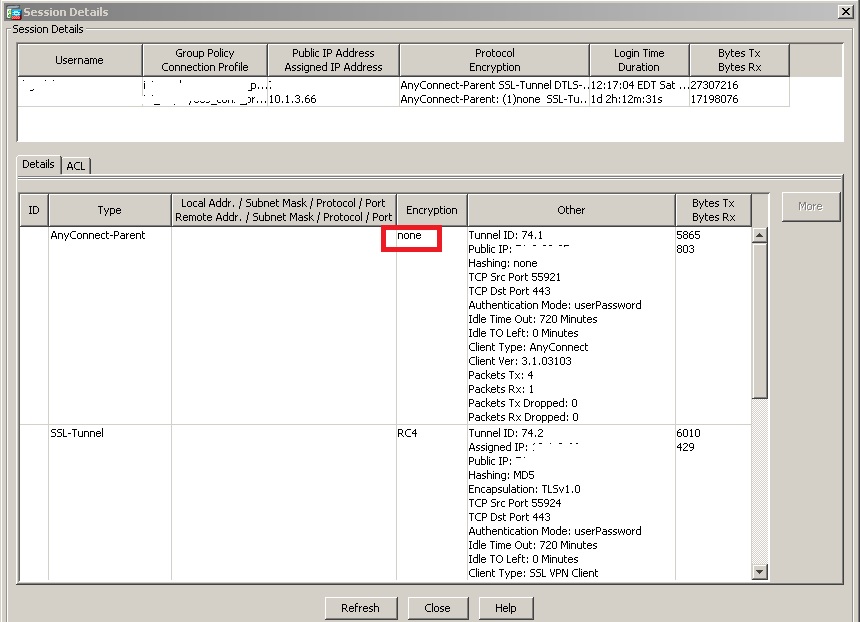
When viewing the VPN sessions in ASDM, AnyConnect-Parent encrytion shows as "none",shouldn't it say RC4 or AES, something like that? is some of the traffic not encrypted ? It's conforting to see the SSL-Tunnel shows as RC4 I'm just trying to have a better understanding of this, if you guys could point me to some articles explaining these behaviors that would be great. thank you for your input.
Delmiro
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
AnyConnect
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-30-2013 11:47 PM
Hi Delmiro,
Here is the basic understanding of the tunnels that are created when we connect to the ssl.
It depends on the mecahnism that is used either you can use the weblaunch or the standalone client
Depending on the connection you will create three different tunnels(sessions) on the ASA, each one with a specific purpose:
Clientless or Parent Tunnel: This is the main session that is created during the negotiation to setup the session cookie that is necessary in case a reconnect is needed due to network connectivity issues or hibernation, etc. Depending of the connection mechanism, the ASA will list the session as Clientless (Weblaunch via the Portal) or Parent (Standalone AnyConnect).
Note: The AnyConnect-Parent represents the session when the client is not actively connected. It does not represent an encrypted tunnel. It's actually a database entry on the ASA.So, if the client shuts down/sleeps, the tunnels (IPsec/IKE/TLS/DTLS) are torn down, but the Parent remains until the idle timer or max connect time kicks in. It allows the user to reconnect without re-authenticating.
SSL-Tunnel: The SSL connection is established first and data is passed over this connection while attempting to establish a DTLS connection. Once the DTLS connection has been established, the client start sending the packets via the DTLS connection instead of the SSL connection. Control packets, on the other hand, always go over the SSL connection.
DTLS-Tunnel: When the DTLS-Tunnel is fully established, all data now moves to the DTLS-tunnel and the SSL-tunnel is only used for occasional control channel traffic. If something should happen to UDP, the DTLS-Tunnel will be torn down and all data will pass through the SSL-Tunnel again.
Hope this helps.
Regards
Raj Kumar
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-30-2013 11:47 PM
Hi Delmiro,
Here is the basic understanding of the tunnels that are created when we connect to the ssl.
It depends on the mecahnism that is used either you can use the weblaunch or the standalone client
Depending on the connection you will create three different tunnels(sessions) on the ASA, each one with a specific purpose:
Clientless or Parent Tunnel: This is the main session that is created during the negotiation to setup the session cookie that is necessary in case a reconnect is needed due to network connectivity issues or hibernation, etc. Depending of the connection mechanism, the ASA will list the session as Clientless (Weblaunch via the Portal) or Parent (Standalone AnyConnect).
Note: The AnyConnect-Parent represents the session when the client is not actively connected. It does not represent an encrypted tunnel. It's actually a database entry on the ASA.So, if the client shuts down/sleeps, the tunnels (IPsec/IKE/TLS/DTLS) are torn down, but the Parent remains until the idle timer or max connect time kicks in. It allows the user to reconnect without re-authenticating.
SSL-Tunnel: The SSL connection is established first and data is passed over this connection while attempting to establish a DTLS connection. Once the DTLS connection has been established, the client start sending the packets via the DTLS connection instead of the SSL connection. Control packets, on the other hand, always go over the SSL connection.
DTLS-Tunnel: When the DTLS-Tunnel is fully established, all data now moves to the DTLS-tunnel and the SSL-tunnel is only used for occasional control channel traffic. If something should happen to UDP, the DTLS-Tunnel will be torn down and all data will pass through the SSL-Tunnel again.
Hope this helps.
Regards
Raj Kumar
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-01-2013 12:48 PM
thank you for the explanation! I appreciate it! by the way, is this explanation on a book? i would want to buy it if it is.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-01-2021 07:33 AM
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide