- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Collaboration
- Collaboration Knowledge Base
- CUCM Digit Manipulation & Call flow
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-16-2012 05:32 AM - edited 03-12-2019 09:42 AM
Introduction
This document describes the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) Digit Manipulation methods and the Call flow to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). This document intends to help the beginners to understand the basics of Call flow between the CUCM and PSTN service provider network and the process of digit manipulation happening over the call.
CUCM Digit Manipulation
Digit Manipulation is often used to change calling party numbers for caller ID purposes on outgoing PSTN calls. It is also used to strip PSTN access codes before CUCM routes calls to the gateway (PSTN). Digit Manipulation is required for abbreviated dialing and to properly route inbound calls from the PSTN where an abbreviated internal dial plans exists. Inbound calls from the PSTN can be received with a ten digit called party length, but the internal dial plan might use only a subset of those numbers four or five digits.
Mechanics of CUCM Digit Manipulation
An IP Phone with extension 1005 in the below diagram, calls a phone on the PSTN with a Called party number of 1 303555-6007. The user at extension 1005 must first dial a PSTN access code of 9 to route a call to the PSTN. The PSTN Class 5 switch will not be able to route the call unless the access code is dialed before the PSTN Number. The calling party number is transformed in to a ten-digit pattern so that the PSTN is presented with a routable
Caller ID of 1 408 555-3005, not the extenstion 1005. Four digit dialing is not possible in many countries.
Outgoing Call to the PSTN
This diagram illustrates an internal caller at extension 1005 dialing a PSTN Number using a PSTN access code of 9 followed by the 11-digit PSTN Number. The process of digit manipulation occurs as follows,
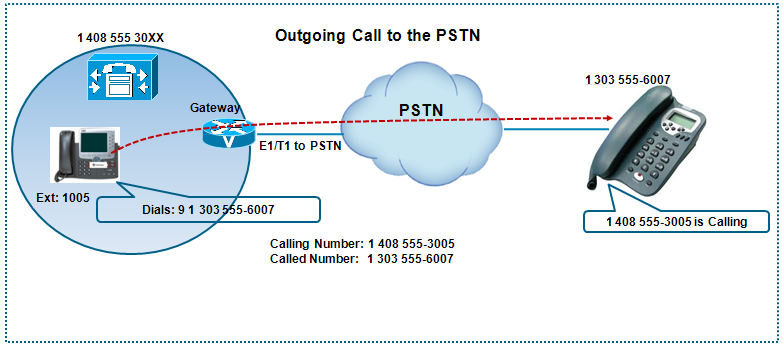
1. Extension 1005 dials 9 1 303 555 6007
2. The dialed number (called party) matches the 9! route pattern, where digit manipulation is taking place. For the sake of simplicity, let's imagine that there is only one gateway with this simple dial plan. The route pattern is pointed directly to the gateway where the following is configured:
- Called party transformations > Discard digits: PreDot
- Calling party transformations: 40855530XX
- Route the call to the gateway
3. CUCM provides digit stripping of the access code from the called party and sends 11 digits (1-303-555-6007) to the PSTN though the gateway. The calling party number is modified from 1005 to 408 555-3005
4. The PSTN phone at (303)555-6007 rings and sees 4085553005 as the calling number.
Incoming Call from the PSTN
This diagram illustrates a call coming from the PSTN network 1 303 555-6008 to an Internal phone extension 1010. 
1. The PSTN phone calls the full E.164 number of the destination. The call is received at the PSTN gateway with a called party number ten digits in length. Digit manipulation is performed to convert the inbound ten-digit called number to a four-digit number matching the internal dial plan. Digit manipulation might occur in the translation configuration of the gateway if the gateway is an H.323 or SIP gateway. MGCP gateways can perform digit manipulation on an individual end point basis using called party transformation patterns. Digit manipulation can be configured in CUCM if the gateway are H.323 or SIP using the same called party transformation patterns beginning with CUCM version 7.0.
2. The called party number received from the PSTN can also be manipulated to align to the internal dial plan using a translation pattern that matches the called party number digits received from the provider. The translation pattern then applies any calling and called party digit manipulations in a manner very similar to the digit manipulation performed at the route list detail level of the route list. Translation patterns are unique in the respect that they do not forward calls to a trunk or gateway device. Translations are leveraged only to perform digit manipulation.
3. Calling party digit manipulation can be more granular if the call is coming in over ISDN Q.931 signaling or H.323 Q.931 signaling. Q.931 signaling used in ISDN and H.323 supports the passing of “Numbering plan type”, allowing the Calling party number to be transformed as follows:
- Calling number (prefix 9) for ten digit dialing indicated by the “subscriber” numbering plan type.
- Calling number (prefix 91) for 11 digit dialing indicated by the “national” numbering plan type.
- Calling number (prefix 9011) for international dialing indicated by the “international” numbering plan type.
4. If the calls are received with the number type as “unknown” then the gateway converts the the call with prefix 91 to the “national” numbering plan type and similarly for the other numbering plan types. All the numbering plan type change is done at the Gateway level.
5. The gateway then forwards the call with the called number 1 408 555 3010 to the CUCM and then the call landed on the desired IP Phone extension 1010.
Digit Manipulation Methods
This table displays some frequently used digit manipulation requirements and the methods in which they are handled in CUCM.
Requirement | Call Type |
Expand calling party directory number to full E.164 PSTN Number | Internal to PSTN |
Strip PSTN access code | Internal to PSTN |
Expand abbreviated number | Internal to Internal |
Convert E.164 PSTN Called party directory number to internal number | PSTN to Internal |
Expand endpoint directory numbers to accommodate overlapping dial plan | Internal to Internal PSTN to Internal |
Digit Discard Instructions 9.5@
Instructions | Discarded Digits | Used for |
PreDot | 95 1 214 555 1212 | Removes access code |
PreAt | 95 1 214 555 1212 | Removes all digits that are in front of a valid numbering plan pattern |
95 1 214 555 1212 | Removes PreDot/PreAt digits and local or long-distance area code | |
95 1 214 555 1212 | Removes long-distance identifier | |
IntlTollBypass | 95 011 33 1234 # | Removes international access (011) and country code |
10-10-Dialing | 95 1010321 1 214 555 1212 | Removes carrier access (1010) and following carrier ID code |
Trailing # | 95 1010321 011 33 1234 # | Removes the # sign for PSTN compatibility |
External Phone Number Mask
The external phone number mask is a directory number (DN) configuration attribute. The external phone number mask is leveraged in call routing to manipulate the internal directory number to digits that can be routed over the PSTN. The external phone number mask is configured on the Directory Number configuration page in CUCM Administration. The use of the external phone number mask is enabled in the route list detail calling party number digit manipulations. The external phone number mask can also be leveraged at the route pattern, translation pattern, calling party transformation pattern, and hunt pilot configurations. Automated alternate routing (AAR) uses the external phone number mask to change the internal dial plan into a PSTN-routable dial plan when rerouting intersite calls from the WAN to the PSTN. The external phone number mask of the first DN of the phone is also used for the following functions:
- To change the display of the main phone number at the top of the LCD screen. A DN of 15223 with an external phone number mask of 21255XXXXX would result in a displayed phone number of 2125515223. Any user on the phone can instantly identify his PSTN direct inward dialing (DID) number by viewing the LCD of the phone.
- AAR technology uses the external phone number mask to manipulate digits for PSTN outbound dialing when bandwidth is not available for a guaranteed-quality call over the WAN (CAC). The AAR call will be rerouted out the PSTN using the full PSTN phone number of the destination as determined by the application of the external phone number mask.
- To change the display of the caller ID for all calls in which the call classification is Off-Net. The calling party number (caller ID) is changed to the full ten-digit DID phone number of the calling party.
Go to CUCM Administration and then Directory Number Configuration page.
Step 1. Choose Device > Phone.
Step 2. Insert the search criteria and click the Find button.
Step 3. Click the phone that has the required directory number (DN).
Step 4. Click the directory number.
The Calling Party Transformations section includes a check box to use the calling party's external phone number mask for the calling party presentation on the PSTN. This same option can be seen in various call-routing configuration elements.
Related Information
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
is there a way to view all calls and their call path taken?
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: