- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Collaboration
- Collaboration Knowledge Base
- IPv6 on Cisco Unified Communications Manager
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
05-19-2011 02:28 AM - edited 03-12-2019 09:38 AM
- Introduction
- IPv6 Innovations in CUCM
- IPv6 support in Cisco Unified Communication Devices
- IPv6 Support in Cisco Unified Communications Devices
- IPv6 – CUCM Configuration
Introduction
This document is intended to guide users to learn more about IPv6 deployment in Voice Over IP Network. Also it focuses on IPv6 functionality on Cisco UC Networks. The deployment of IPv6 only devices is discussed, but emphasis is given to the deployment of dual stacked (IPv4 and IPv6 capable) devices which offer a greater degree of functionality and interoperability with existing IPv4 only devices.
IPv6 Innovations in CUCM
With the system release of CUCM 7.1 Cisco systems has introduced IPv6 functionality to a range of UC products. Today Cisco Introduces, Voice Over IPv6 ( VoIPv6) feature includes IPv4 and IPv6 dual stack support on voice gateways and MTP, IPv6 support for SIP trunks, and Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP)-controlled analog gateways.The primary focus of this document is on new IPv6 functionality for Cisco UC networks.
Cisco Recommendations
- Cisco recommend that IPv6 UC deployments be configured with a dual stack mode.
- To maximize IPv6 traffic in the UC network, capable Phones, SIP Gateways and SIP should be configured to support IPv6 signaling and IPv6 media
Why IPv6 ?
IPv6 deployment is primarily driven by IPv4 address space exhaustion. As the world becomes more and more IP centric, the number of applications, devices and services requiring IP addresses is rapidly increasing. Current estimates by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and Regional Internet Registries (e.g. ARIN, LACNIC & APNIC),report that their pools of unallocated IPv4 addresses will be exhausted between Q4 2011 and Q1 2012.
IPv6 has lot of key benefits in comparision with IPv4.
- Larger address space
- Multicasting
- Stateless address auto-configuration (SLAAC)
- Streamlined header format and flow identification
- Network-layer security
- Mobility
- Options extensibility
Are you Ready for IPv6 ?
Lot of IPv6 forum and discussions are happening across the world to Promote and help each other for IPv6 deployments and smooth transition.
Preparing your Network for the future
The first step in IPv6 deployment is to assess which existing entities on your network can support IPv6. In most cases, the network topology-wires, routers, and hosts-can remain unchanged as you implement IPv6. However, you might have to prepare existing hardware and applications for IPv6 before actually configuring IPv6 addresses on network interfaces.
Verify which hardware on your network can be upgraded to IPv6. For example, check the manufacturers' documentation for IPv6 readiness regarding the following classes of hardware:
- Routers
- Firewalls
- Application Servers
- Switches
Here is the IPv6 Address format who are unfamiliar with IPv6.
IPv6 Address Format
IPv6 addresses have two logical parts: a 64-bit network prefix, and a 64-bit host address part. (The host address is often automatically generated from the interface MAC address.[32]) An IPv6 address is represented by 8 groups of 16-bit hexadecimal values separated by colons (:) shown as follows:
A typical example of an IPv6 address is
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
The hexadecimal digits are case-insensitive.
The 128-bit IPv6 address can be abbreviated with the following rules:
- Rule one: Leading zeroes within a 16-bit value may be omitted. For example, the address fe80:0000:0000:0000:0202:b3ff:fe1e:8329 may be written as fe80:0:0:0:202:b3ff:fe1e:8329
- Rule two: A single occurrence of consecutive groups of zeroes within an address may be replaced by a double colon. For example, fe80:0:0:0:202:b3ff:fe1e:8329 becomes fe80::202:b3ff:fe1e:8329
IPv6 support in Cisco Unified Communication Devices
IPv4 and IPv6 – Terminology, Icons
The development of IPv6 introduces new concepts for Unified Communications networks, in particular the concept of a device's IP addressing mode. Devices may now support IPv4 only, IPv6 only, or IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. This document uses the symbols (or icons) shown in Figure 3-1 to represent the IP addressing mode capabilities of devices.

IPv6 Support in Cisco Unified Communications Devices
IPv6 Support in Cisco Unified Communications Devices
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager 7.1 and later Releases
All Cisco Media Convergence Servers (MCS server) platforms
- Cisco IP Phones
3rd Generation Cisco IP Phones running SCCP only :
Cisco 7906G, Cisco 7911G, Cisco 7931G, Cisco 7941G, Cisco 7941GE7971G-GE, Cisco 7975G
Cisco 7942G, Cisco 7945G, Cisco 7961G, Cisco 7961GE, Cisco 7962G,
Cisco 7965G, Cisco 7970G, Cisco 7971G-GE, Cisco 7975G
- Gateways
SIP Gateways ( ISR 28XX & 38XX, AS5400 )
VG224 SCCP Analogue Gateway,
SCCP FXS Ports on Cisco ISR2800 and 3800 Series Routers
IOS MTPs for IPv4 - IPv6 RTP Media conversion
- Cisco Unified CM SIP Trunks
- Applications
CUCM CTI - IPv6 Aware
CUCM AXL/SOAP interface - IPv6 aware
CUCM Unified CM SNMP (IPv6 aware)
Addressing Modes supported for Cisco Unified Communications Devices
IPv4 SupportIPv4 & IPv6 Support
| IPV4 Supported devices - Unified CME - MGCP Gateways - H.323 Gatewys - Unified CM H.323 and Intercluster trunks - video Conferecing Endpoints - Cisco Unified Video Advantage - Soft Phones - WIFI IP Phones - All SIP Phones - Older SCCP Phones | IPV4 & IPV6 Supported devices - CUCM 7.1 and later - SCCP ISR Analogue Ports - SIP ISR Gateways - VG224 Analogue Gateways - Newer SCCP Phones - Unified CM SIP Trunks |
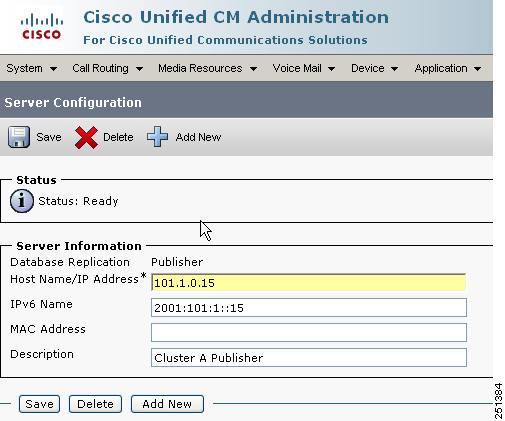
IPv6 – CUCM Configuration
IPv6 - CUCM Addressing
CUCM can support :
• One Link Local Address
• One Unique Local Address or
• One Global Address
• ( and an IPv4 address )
IPv6 – IP Phone Addressing
- IP Phones can support :
- One Link Local Address
- Multiple Unique Local Addresses
- Multiple Global Addresses
- ( and an IPv4 address )
- Almost all IPv6 deployments will run a combination of IPv4 and IPv6
- IP Phone - IPv6 allocation options:
- IPv4 Address Configuration Options
Manual Configuration via Phone User Interface
DHCPv4
- IPv6 Address Configuration Options
Manual Configuration via Phone User Interface
DHCPv6
Auto Configuration
- Phones require a minimum of an IP address and TFTP server address
IPv6 - CUCM System Configuration
- Phone - Enterprise Paramater configuration
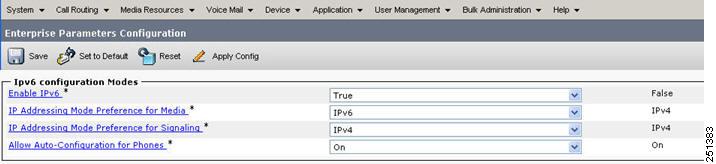
- CUCM - Phone Addressing Mode Configuration
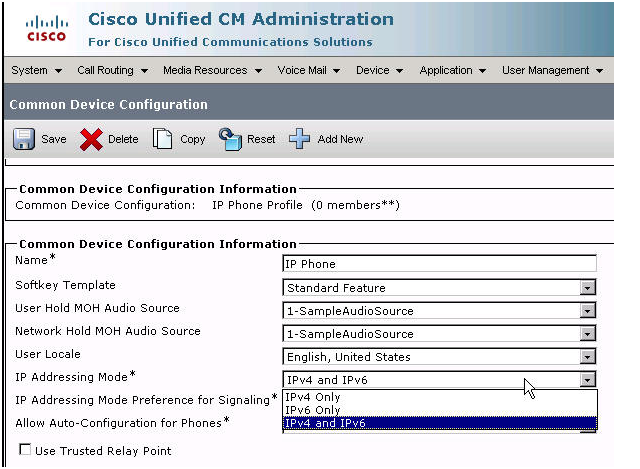
IPv6 - CUCM SIP Trunk Configuration
- CUCM - SIP Addressing Mode Configuration
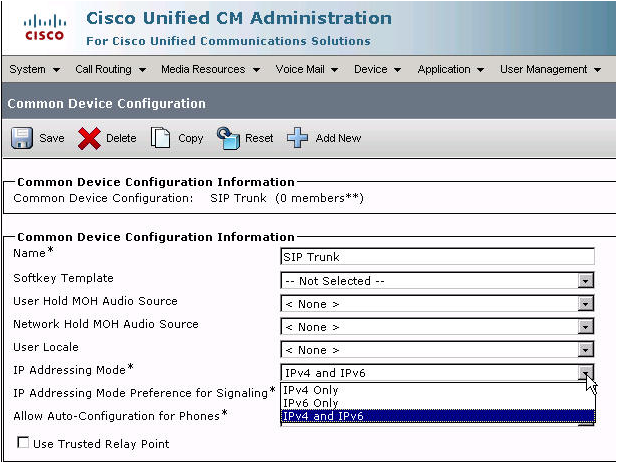
- SIP Profile Configuration
- CUCM - SIP Trunk Configuration
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: