- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Collaboration
- Collaboration Knowledge Base
- Unified Communications Call flow in an Enterprise Network
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-28-2013 07:24 PM - edited 03-12-2019 10:00 AM
Introduction
This document explains the various Unified Communications call flow scenario in an Enterprise Network. Idea of creating this document is to help the beginners to understand the various Call flows and protocol messages.
Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge about Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) and the protocols SIP, H.323 and ISDN.
Call Flow Examples
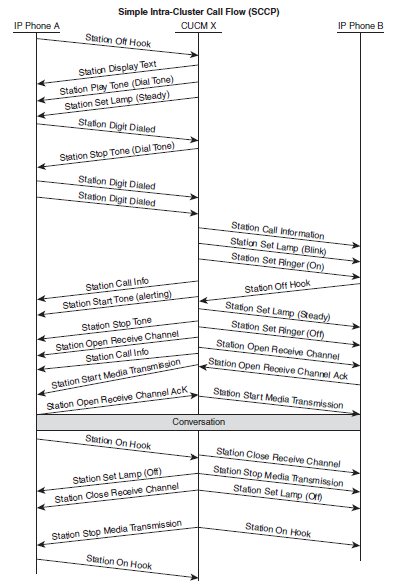
1. IP Phone to IP Phone - Successful Intracluster Call
In this scenario, Phone A is registered to Cisco Unified Communication Manager X denoted by CUCM X. Phone B is registered to the same CUCMX.
A call is placed from Phone A (1000) to Phone B (1006). Basic setup for a call between two IP phones registered to the same CUCM.

Below call flow illustrates the sequence of Skinny Call Control Protocol (SCCP) messages exchanged between the Unified CM (CUCM X) and the two IP phones described in the setup.
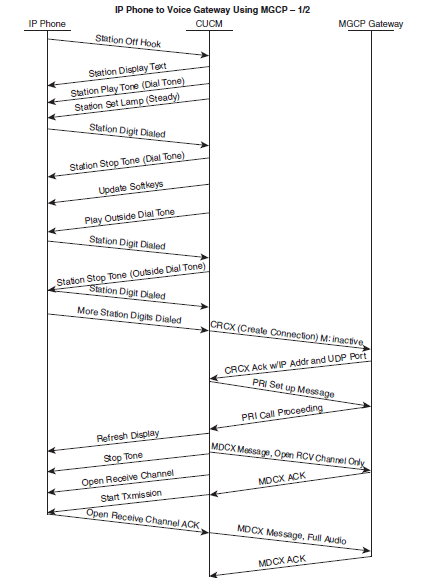
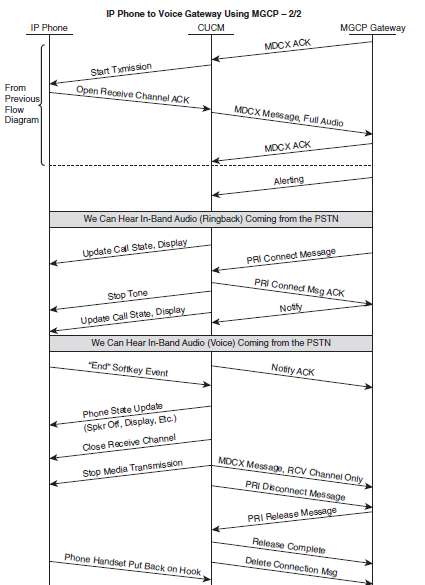
2. Call flow: IP Phone to Voice Gateway using MGCP
In this scenario, Phone A is registered to the Unified CM (CUCM). Phone B is connected to a carrier’s central office (CO) Switch. CUCM will access Phone B through the voice gateway. Below diagram illustrates this basic setup for a call set up between an IP phone registered to the CUCM and another phone connected to a CO switch in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) through a voice gateway. This voice gateway is registered with the CUCM using Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP).
A call is placed from Phone A (1000) to Phone B (555-1212). Phone A will hang up first. MGCP is used to relay ISDN messages that go between the CUCM and the actual CO switch.

Below figure, include call flows that show ISDN messages going to the gateway (GW); they are really being sent to the CO switch through the gateway. Detailed call flow is shown here,
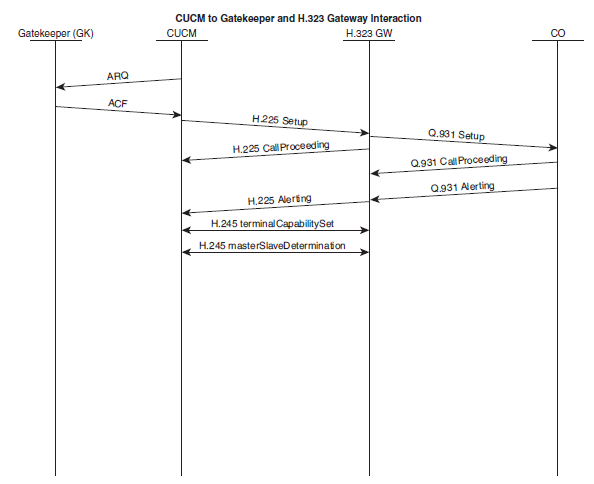
3. Call flow: IP Phone to H.323 Voice Gateway with Gatekeeper
In this scenario, Phone A is registered to the CUCM. Phone B is connected to a carrier’s CO switch. Below diagram illustrates this call setup between two IP phones registered to the same CUCM. A call is placed from Phone A (555-2001) to Phone B (555-2001). Phone B hangs up first. The CUCM must register with the gatekeeper prior to placing any calls, and the gatekeeper will police the bandwidth by implementing Call Admission Control (CAC).
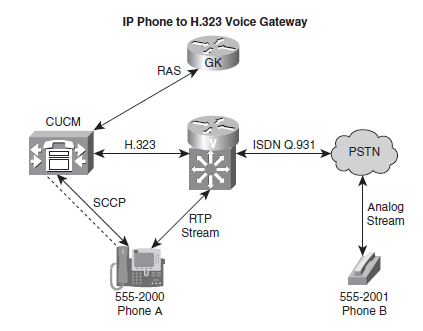
Because the initial call setup phases between the IP phone and the CUCM have been covered earlier, they are not repeated in this call flow. Below figure includes all the steps involving CUCM registration with the gatekeeper, skips the initial IP Phone A interaction with the CUCM when it goes off-hook to call Phone B in the PSTN, and then illustrates the CUCM and H.323 gateway interaction, including the ISDN Q.931 messaging exchange with the CO in the PSTN to set up the call with Phone B. The communication beyond the CO, which would include SS7 messages, with the CO serving Phone B is not part of this overall example.
Related Information
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks for the Explanation with detailed Call flow...
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thank you Saravana.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks for the detailed flow.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
This is awesome. Thank you very much!!
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I could not understand the third call flow.
as you mentioned Phone A and Phone B both are registered on same CUCM then what is the need of Voice Gateway?
It would be appreciated if someone explain me.
Thanks
Parm
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: