- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Security
- Network Access Control
- Re: EAP-TLS with ISE 3.1 fails
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-15-2023 07:33 AM
We are setting up a wireless network with EAP-TLS. However, when I try to connect a W11 laptop to this network the connection fails. I see this message in ISE:
| Event | 5400 Authentication failed |
| Failure Reason | 12507 EAP-TLS authentication failed |
| Resolution | Check whether the proper server certificate is installed and configured for EAP in the Local Certificates page ( Administration > System > Certificates > Local Certificates ). Also ensure that the certificate authority that signed this server certificate is correctly installed in client's supplicant. Similarly, verify that the certificate authority that signed the client's certificate is correctly installed in the Certificate Authorities page (Administration > System > Certificates > Certificate Authority Certificates). Check the previous steps in the log for this EAP-TLS conversation for a message indicating why the authentication failed. Check the OpenSSLErrorMessage and OpenSSLErrorStack for more information. |
| Root cause |
EAP-TLS authentication failed. |
| AcsSessionID | NLDC0101ISE01/460343116/28104895 |
| OpenSSLErrorMessage | SSL alert: code=0x22E=558 ; source=local ; type=fatal ; message="certificate unknown.ssl/statem/statem_srvr.c:3800 error:1417C086:SSL routines:tls_process_client_certificate:certificate verify failed [error=337100934 lib=20 func=380 reason=134]" |
| OpenSSLErrorStack | 140097471612672:error:1417C086:SSL routines:tls_process_client_certificate:certificate verify failed:ssl/statem/statem_srvr.c:3800: |
We are using our internal PKI infrastructure. However, when I use the Microsoft Intune certificate store, it works fine. So I think there is something wrong with the certicate. But maybe I'm wrong.
In our client certificate we use client authentication in the Enhanced Key usage.
Does anyone has seen this before?
Solved! Go to Solution.
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-30-2023 11:09 PM - edited 04-30-2023 11:10 PM
We did find the issue. The client certificate EKU was set to critical for Client authentication. After we changed it to non-critical it worked.
You can't see if a key is set to critical or non-critical when you open the certificate in Windows. But with open SSL we compared the both certificates and saw the difference:
openssl x509 -in ep.cer -text -noout
X509v3 Extended Key Usage: critical
E-mail Protection, Microsoft Encrypted File System, TLS Web Client Authentication
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-15-2023 10:43 AM
M.
-- Each morning when I wake up and look into the mirror I always say ' Why am I so brilliant ? '
When the mirror will then always repond to me with ' The only thing that exceeds your brilliance is your beauty! '
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-16-2023 01:18 AM
I know, but after deleting the reg keys, it still didn't work. These laptops are configurered via autopilot and Intune. I'm going to give it a try with a W10 build 22H2 devices.
Thanks
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-16-2023 04:53 AM
You need to run these commands as administrator and then restart the machine. After restart manually select the root and intermediate certificates to fix the issue.
Did you restart the machine and then manually select the root and intermediate certificates?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-16-2023 04:53 AM
You need to run these commands as administrator and then restart the machine. After restart manually select the root and intermediate certificates to fix the issue.
Did you restart the machine and then manually select the root and intermediate certificates?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-16-2023 05:30 AM
Yes, I ran these commands as administrator. However, not all keys could be deleted.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-16-2023 10:58 PM - edited 03-16-2023 11:05 PM
Using MMC, check IF in your USER ACCOUNT FOLDER --- > TRUSTED ROOT CA and TRUSTED INTERMEDIATE CA folders you have respectively your internal PKI Trusted CA certs in there. It works for Intune because Microsoft Trusted CA's are installed by default on the USER OR COMPUTER ACCOUNT TRUSTED CA FOLDERS..We have our own PKI but we do not user USER ACCOUNT for EAP-TLS authentication, instead we use COMPUTER ACCOUNT because the PKI signs the cert for the computer using its serial number. (Since that you did not provide more information, I am assuming that you are not doing both machine + user authentication). You also need to check for the WIRELESS SSID profile how did you configure the authentication: "user authentication, computer authentication, user or computer authentication" (those are the 3 options). Depending on that, your computer will select the folder where your computer cert (signed by your own PKI) was installed.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-17-2023 01:22 AM
Hi ajc,
Thanks for helping out. We are using machine authentication. The certificates are in the corresponding folders. the Wireless SSID is also configured for machine authentication.
The main difference between our own CA and intermediate certifcates and those of intune is that we don't explicit allow Client Authentication in Enhanced Key usage. However, that's what I've been told, we allow all enhanced keys in those certificates.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-17-2023 07:23 AM - edited 03-17-2023 07:27 AM
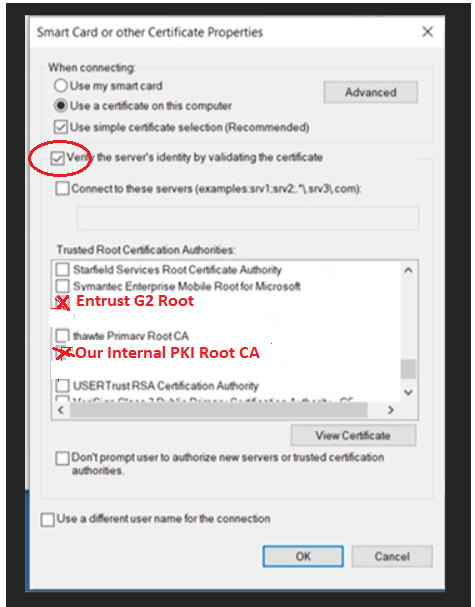
Another detail, Microsoft changed the way EAP-TLS authenticates for Windows 11, before you only needed the certificates in the corresponding TRUSTED CA Folders for machine authentication and that worked fine. In our case, we assigned an entrust signed cert for EAP authentication on ISE and our EAP-TLS was failing with a similar error message as the one you got NO matter we had Entrust Root CA and Entrust L1K CA in the corresponding folders. We talked to Microsoft and they told us that the SSID Profile configured on the computers had to have CHECKED all the TRUSTED CA in the following section (see screenshot). On previous Windows versions you only needed to have those TRUSTED CA listed without checking specifically in the box. We deployed this new profile using GPO and it worked right away.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-30-2023 11:09 PM - edited 04-30-2023 11:10 PM
We did find the issue. The client certificate EKU was set to critical for Client authentication. After we changed it to non-critical it worked.
You can't see if a key is set to critical or non-critical when you open the certificate in Windows. But with open SSL we compared the both certificates and saw the difference:
openssl x509 -in ep.cer -text -noout
X509v3 Extended Key Usage: critical
E-mail Protection, Microsoft Encrypted File System, TLS Web Client Authentication
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide