Introduction
OSPF External Routes (E2) are advertised into OSPF Autonomous System with a particular cost and the cost is not changed throughout the AS. The routes are learned via redistribution of other routing protocol or static route or a connected subnet. The router performing redistribution is the Autonomous System Border Router (ASBR). By default, all OSPF routes learned via redistribution are of E2 type.
Redisribution of OSPF Routes (E1 or E2) into BGP can be performed via two ways, this document focus on E2 routes.
a) Command " redistribute ospf 1 match external 2"
b) Using Route-Map Match Statement "match route-type external type-2"
Using Route Maps gives more felxibility to the user, as one can match the routes based on different criteria (access-list, tag).
Prerequisite
- Understanding of OSPF Routing Protocol
- Understanding of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Background Summary
In this document the focus is on route-map to match the E2 types routes and then redistributing them into other routing system. Three Routers, R1, R2 and R3 are connected via Serial Interface. Router R1 and R2 are participating in OSPF Area 0 while Router R2 and R3 are forming IBGP peering under AS 100.
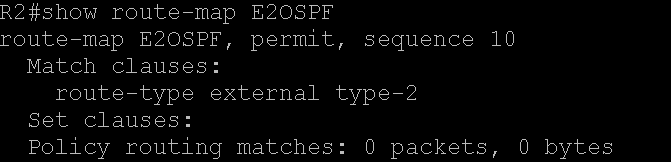
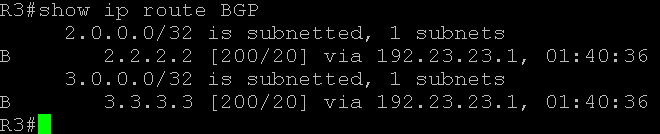
On R1, Loopback Interfaces (Lo 2 and Lo 3), are redsitributed in OSPF. A route-map "connected is configured" to match the specified interfaces and then redistributed via command "redictribute connected route-map connected". On router R2 these loopback prefixes are learned of type E2. On R2, a route-map (route-map E2OSPF in this document, see configuration on Router R2) is configured to match only the E2 type prefixes and redistribiuted into BGP system.
Note: All configurations are tested on C3745 router operating on IOS verison 12.4(15)T14.
Topology Diagram
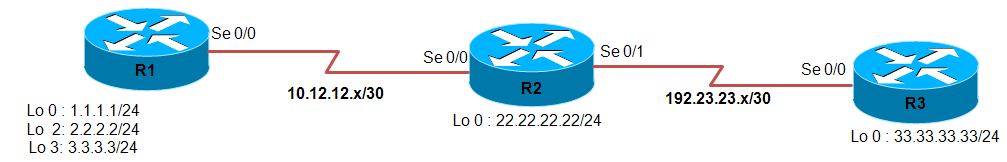
Configuration
R1R2R3
hostname R1 ! ip cef ! no ip domain lookup ! interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback2 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback3 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0/0 ip address 10.12.12.1 255.255.255.252 clock rate 2000000 ! router ospf 10 router-id 1.1.1.1 log-adjacency-changes redistribute connected subnets route-map CONNECTED network 10.12.12.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! route-map CONNECTED permit 10 match interface Loopback2 Loopback3 ! end | hostname R2 ! ip cef ! no ip domain lookup ! interface Loopback0 ip address 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0/0 ip address 10.12.12.2 255.255.255.252 clock rate 2000000 ! interface Serial0/1 ip address 192.23.23.1 255.255.255.252 clock rate 2000000 ! router ospf 10 router-id 22.22.22.22 log-adjacency-changes network 10.12.12.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 ! router bgp 100 no synchronization bgp router-id 22.22.22.22 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.23.23.1 mask 255.255.255.255 redistribute ospf 10 route-map E2OSPF neighbor 192.23.23.2 remote-as 100 neighbor 192.23.23.2 next-hop-self no auto-summary ! route-map E2OSPF permit 10 match route-type external type-2 ! end | hostname R3 ! ip cef ! no ip domain lookup ! interface Loopback0 ip address 33.33.33.33 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0/0 ip address 192.23.23.2 255.255.255.252 clock rate 2000000 ! router bgp 100 no synchronization bgp router-id 33.33.33.33 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.23.23.2 mask 255.255.255.255 neighbor 192.23.23.1 remote-as 100 no auto-summary ! end |
Verification
Command show ip route ospf

Command show route-map {route-map name}
Command show ip route BGP
References
Understanding Redistribution of OSPF Routes into BGP
IP Routing: OSPF Configuration Guide 12.4
IP Routing: BGP Configuration Guide 12.4