- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Other Network Architecture Subjects
- Re: Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)(1024B).What is the meaning of 10
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 09:20 PM
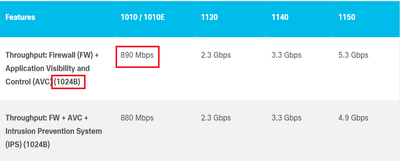
Throughput: FW + AVC + Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) (1024B)
Throughput: Firewall (FW) + Application Visibility and Control (AVC) (1024B)
Throughput: NGIPS (1024B)
IPSec VPN throughput (1024B TCP with Fastpath)
All of those cases. What is the meaning of 1024B? I can't understand this. Please help me.
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
Other Network
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 09:52 PM
Hello @Md. Shahariar Rahaman
In this specific context of network throughput measurements, "1024B" typically refers to the packet size used for testing. It represents a packet size of 1024 Bytes. When evaluating the throughput of various network devices or features like FX, IPS, the chosen packet size can impact the observed throughput.
Measuring throughput with a specific packet size, such as 1024 bytes, allows for standardized testing conditions.
Different devices or features may have varying levels of performance depending on the packet size, as processing overhead and efficiencies can differ.
In the context of IPSec VPN throughput (1024B TCP with Fastpath), it specifies the IPSec VPN throughput for a 1024-byte TCP packet size with the Fastpath technology. This information helps assess the VPN performance under specific conditions.
.ı|ı.ı|ı. If This Helps, Please Rate .ı|ı.ı|ı.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 10:08 PM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 10:18 PM - edited 01-15-2024 10:23 PM
890 Mbps is throughput
there is not we can called relation but when cisco engineer test throughput for these series, they must fix some detail like packet size, l4 protocol use and etc.
then they measure the throughput with add some feature like SI.
MHM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 11:02 PM
The throughput, measured here in Mbps, is the rate at which data can be transmitted through a network. The packet size, on the other hand, represents the amount of data in each individual packet.
Understanding the relationship between throughput and packet size involves considering how many packets can be transmitted per unit of time.
.ı|ı.ı|ı. If This Helps, Please Rate .ı|ı.ı|ı.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-18-2024 04:00 AM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 09:52 PM
Hello @Md. Shahariar Rahaman
In this specific context of network throughput measurements, "1024B" typically refers to the packet size used for testing. It represents a packet size of 1024 Bytes. When evaluating the throughput of various network devices or features like FX, IPS, the chosen packet size can impact the observed throughput.
Measuring throughput with a specific packet size, such as 1024 bytes, allows for standardized testing conditions.
Different devices or features may have varying levels of performance depending on the packet size, as processing overhead and efficiencies can differ.
In the context of IPSec VPN throughput (1024B TCP with Fastpath), it specifies the IPSec VPN throughput for a 1024-byte TCP packet size with the Fastpath technology. This information helps assess the VPN performance under specific conditions.
.ı|ı.ı|ı. If This Helps, Please Rate .ı|ı.ı|ı.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 10:16 PM - edited 01-15-2024 10:16 PM
Here If 1024B is packet size then 890Mbs is what? I can't understand the relation between them. If we can explain this it will be helpful for me.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 10:18 PM - edited 01-15-2024 10:23 PM
890 Mbps is throughput
there is not we can called relation but when cisco engineer test throughput for these series, they must fix some detail like packet size, l4 protocol use and etc.
then they measure the throughput with add some feature like SI.
MHM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 10:25 PM
Thanks for your information. However, I still can't understand the relationship between packet size (1024B) and throughput (890Mbps). If you can explain this to me, it will be helpful for me. I googled it and also used AI, but it was still not clear.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 10:36 PM
if FW need to inspect packets
the packet is 1000
the packet is 1500
which packet is faster inspect ?
MHM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 10:42 PM
1000 packets will be faster to inspect.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 10:55 PM - edited 01-15-2024 10:56 PM
so if I want to compare throughput of two firepower can I make one inspect 1000B packet and other inspect 1500B packet
and then compare?
or I match the packet size and compare ?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-16-2024 12:52 AM - edited 01-16-2024 09:06 PM
My calculation is right or wrong.
That means 111.25MBps/1024B = 111250000 Byte packets per second.
Am I right?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-18-2024 04:00 AM
Yes !
.ı|ı.ı|ı. If This Helps, Please Rate .ı|ı.ı|ı.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 11:02 PM
The throughput, measured here in Mbps, is the rate at which data can be transmitted through a network. The packet size, on the other hand, represents the amount of data in each individual packet.
Understanding the relationship between throughput and packet size involves considering how many packets can be transmitted per unit of time.
.ı|ı.ı|ı. If This Helps, Please Rate .ı|ı.ı|ı.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 11:11 PM - edited 01-16-2024 09:06 PM
The throughput of 890 Mbps in MBps is 890/8 = 111.25 MBps.
That means 111.25MBps/1024B = 111250000 Byte packets per second.
Am I right?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-15-2024 10:08 PM
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide