- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Routing
- BGP attributes in selecting path in two ISPs
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
BGP attributes in selecting path in two ISPs
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-18-2022 09:28 AM
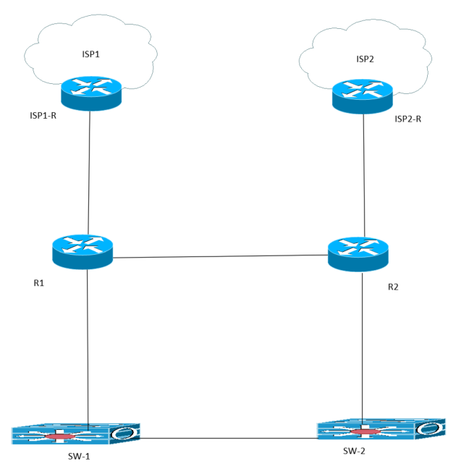
Hello, Please see the below diagram. We want R1 to be primary path in connection to ISP1 bgp. we setup higher local pref for inbound routes at R1. For outbound routes, shorter as-path would be at R1. Do you think if this is good choice? because we are not sure if there is connection between ISP1-R and ISP2-R. If not, the as-path would not work, right?
- Labels:
-
ISR 4000 Series
-
Routing Protocols
-
WAN
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-18-2022 09:35 AM
""because we are not sure if there is connection between ISP1-R and ISP2-R. If not, the as-path would not work, right?""
I dont get this can you more elaborate ??
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-18-2022 09:48 AM
if there is a cable connection between ISP1-R and ISP2-R, ISP1-R can compare as-path value: between route from R1 and route from ISP2-R. if there is not this cable, ISP1-R cannot have route from ISP2-R to compare. Thanks
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-18-2022 09:55 AM - edited 11-18-2022 10:43 AM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-18-2022 10:08 AM - edited 11-18-2022 10:31 AM
thanks
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-18-2022 10:08 AM
Hi @Leftz ,
If this is simulate a real life scenario, you need to bear in mind the way service providers operate.
Most service providers use the local preference to set the following preference for the routes they receive.
Customer routes preferred over Peering routes, Peering routes preferred over Transit routes.
Given that the in BGP best path selection, the evaluation of the local preference takes precedence over the AS path length, ISP2 would prefer the customer routes even if as path prepending has been used.
So in most cases prepending the local ASN is not a predictable way to force inbound traffic one way or the other. If you want to guarantee that inbound traffic will come through ISP1, you could use conditional advertisement, which consists of advertising your local routes to ISP2 only if ISP1 is down.
Regards,
Harold Ritter, CCIE #4168 (EI, SP)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-18-2022 10:26 AM
@Harold Ritter Thanks for your reply.
What's term meaning "Customer routes", "Peering routes" ... ?
"Customer routes preferred over Peering routes, Peering routes preferred over Transit routes. "
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-18-2022 11:37 AM - edited 11-18-2022 11:49 AM
Hi @Leftz ,
From the service provider point of view, there are generally 3 categories of routes.
- The customer routes are the routes received directly from their customers. The traffic received and sent from the customer is paid by the customer.
- The peering routes are generally exchange between two service providers and traffic between them is generally free of charge, but can generate charges if a certain pre-established threshold is crossed by one of the peers.
- The transit routes are received from another service provider (tier 1) and traffic sent to and received from that service provider is paid.
Hopefully you can see why the service provider prefers customer routes (traffic charged to customer) over peering routers (generally free, but can generate charges to the service provider) over transit routes (will generate charges to the service provider).
Regards,
Harold Ritter, CCIE #4168 (EI, SP)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-18-2022 01:59 PM
@Harold Ritter Its good to know. Thanks. Can you provide a link which shows real ISP topology example for bgp path selection? I saw example before, but it was simulated one. Appreciate.
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide