- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Routing
- Re: EIGRP load balancing with two ISP's
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
EIGRP load balancing with two ISP's
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-08-2013 12:23 AM - edited 03-04-2019 08:08 PM
Dear Expert,
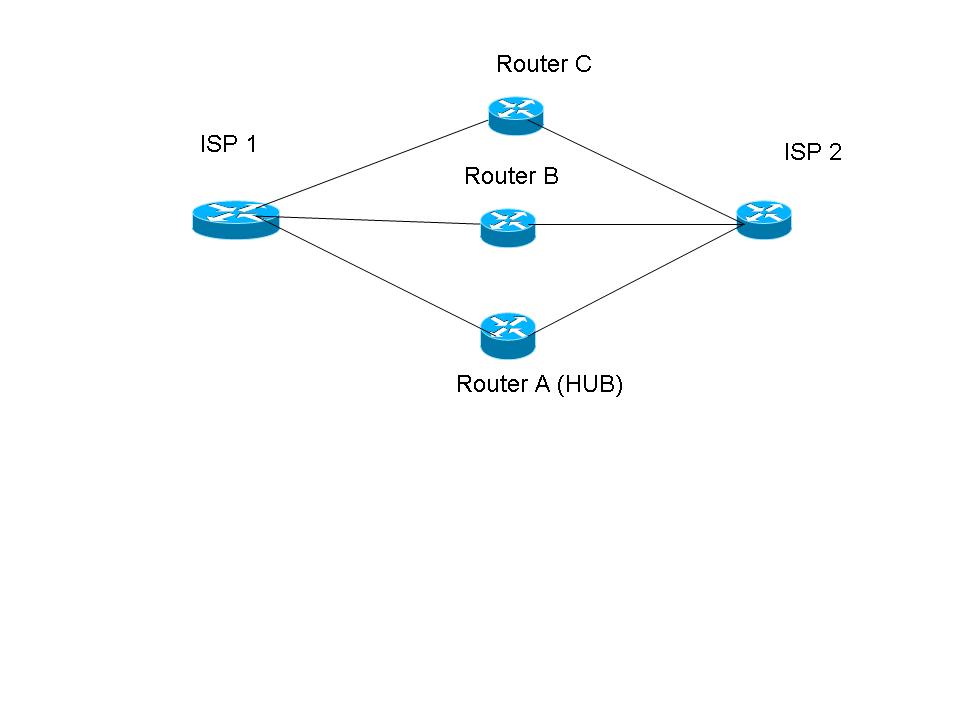
I have two ISP with few MPLS connectivies. i am planning to establish EIGRP with loadbalancing.
any configuration sample..?
attached diagram for ref.
And, what is route-map..? is it possible to apply over EIGRP interfacess...?
Reg.
Frank
- Labels:
-
Routing Protocols
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-08-2013 01:13 AM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-09-2013 03:51 AM
Hello, by default EIGRP puts up to 4 equal cost paths in the routing table, which then the router(s) load balances on those routes. You have three paths here of equal routes if they are the same B/W.
EIGRP LoadBalancing
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cb7.shtml#loadbalancing
Unequal cost LoadBalancing
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a008009437d.shtml
Route Maps
Route maps are used when redistributing routes into an OSPF, RIP, or EIGRP routing process. They are also used when generating a default route into an OSPF routing process. A route map defines which of the routes from the specified routing protocol are allowed to be redistributed into the target routing process.
Route maps have many features in common with widely known ACLs. These are some of the traits common to both:
•![]() They are an ordered sequence of individual statements, each has a permit or deny result. Evaluation of ACL or route maps consists of a list scan, in a predetermined order, and an evaluation of the criteria of each statement that matches. A list scan is aborted once the first statement match is found and an action associated with the statement match is performed.
They are an ordered sequence of individual statements, each has a permit or deny result. Evaluation of ACL or route maps consists of a list scan, in a predetermined order, and an evaluation of the criteria of each statement that matches. A list scan is aborted once the first statement match is found and an action associated with the statement match is performed.
•![]() They are generic mechanisms—Criteria matches and match interpretation are dictated by the way that they are applied. The same route map applied to different tasks might be interpreted differently.
They are generic mechanisms—Criteria matches and match interpretation are dictated by the way that they are applied. The same route map applied to different tasks might be interpreted differently.
These are some of the differences between route maps and ACLs:
•![]() Route maps frequently use ACLs as matching criteria.
Route maps frequently use ACLs as matching criteria.
•![]() The main result from the evaluation of an access list is a yes or no answer—An ACL either permits or denies input data. Applied to redistribution, an ACL determines if a particular route can (route matches ACLs permit statement) or can not (matches deny statement) be redistributed. Typical route maps not only permit (some) redistributed routes but also modify information associated with the route, when it is redistributed into another protocol.
The main result from the evaluation of an access list is a yes or no answer—An ACL either permits or denies input data. Applied to redistribution, an ACL determines if a particular route can (route matches ACLs permit statement) or can not (matches deny statement) be redistributed. Typical route maps not only permit (some) redistributed routes but also modify information associated with the route, when it is redistributed into another protocol.
•![]() Route maps are more flexible than ACLs and can verify routes based on criteria which ACLs can not verify. For example, a route map can verify if the type of route is internal.
Route maps are more flexible than ACLs and can verify routes based on criteria which ACLs can not verify. For example, a route map can verify if the type of route is internal.
•![]() Each ACL ends with an implicit deny statement, by design convention; there is no similar convention for route maps. If the end of a route map is reached during matching attempts, the result depends on the specific application of the route map. Fortunately, route maps that are applied to redistribution behave the same way as ACLs: if the route does not match any clause in a route map then the route redistribution is denied, as if the route map contained deny statement at the end.
Each ACL ends with an implicit deny statement, by design convention; there is no similar convention for route maps. If the end of a route map is reached during matching attempts, the result depends on the specific application of the route map. Fortunately, route maps that are applied to redistribution behave the same way as ACLs: if the route does not match any clause in a route map then the route redistribution is denied, as if the route map contained deny statement at the end.
Route-Maps
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a008047915d.shtml#what
Hope this helps
Please rate useful posts & remember to mark any solved questions as answered. Thank you.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-10-2013 11:00 PM
Hi,
I've established this into my lap tool. i am planing to go for live.
I assumed router A as Hub and Router B&C is spoke locations. A should communicate with B&C, B&C should not communicate each other.
ISP1 has 2 MB line and ISP 2 has 10MB line.
i configured EIGRP 100 for isp 1 and EIGRP 50 for iso 2 also configured EIGRP 100 and 50 for router A(hub)
so, would you advice. am i right or how best can configure to load balancing.
ple verify below config.
ISP2:
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.10.5 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
bandwidth 10240
ip address 10.10.10.9 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Ethernet0/0/0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
router eigrp 50
redistribute static
network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255
network 100.100.0.0 0.0.255.255
auto-summary
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Ethernet0/0/0
bandwidth 2048
ip address 192.168.1.9 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Ethernet0/1/0
no ip address
duplex auto
speed auto
shutdown
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
shutdown
!
router eigrp 100
variance 3
redistribute static
network 192.168.1.0
network 100.100.0.0 0.0.255.255
auto-summary
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Ethernet0/0/0
ip address 100.100.100.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
!
router eigrp 100
variance 2
network 100.100.100.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.1.8 0.0.0.3
auto-summary
!
router eigrp 50
variance 2
network 100.100.100.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.10.10.8 0.0.0.3
auto-summary
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.10.5 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
bandwidth 10240
ip address 10.10.10.9 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Ethernet0/0/0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
ISP2:
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Ethernet0/0/0
bandwidth 2048
ip address 192.168.1.9 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
router eigrp 100
variance 3
redistribute static
network 192.168.1.0
network 100.100.0.0 0.0.255.255
auto-summary
!
Router A:
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Ethernet0/0/0
ip address 100.100.100.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
!
router eigrp 100
variance 2
network 100.100.100.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.1.8 0.0.0.3
auto-summary
!
router eigrp 50
variance 2
network 100.100.100.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.10.10.8 0.0.0.3
auto-summary
Router B:
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.6 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 10.10.10.6 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Ethernet0/0/0
ip address 100.100.150.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
!
ip classless
ip route 100.100.100.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.5
ip route 100.100.100.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.5
Router C:
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Ethernet0/0/0
ip address 100.100.200.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
!
ip classless
ip route 100.100.100.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.1
ip route 100.100.100.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
thx.
Frank
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide