- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Routing
- Re: OSPF Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
OSPF Options
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-20-2017 09:07 AM - edited 03-12-2019 04:48 PM
Hi,
OSPF options are carried in all types of ospf packets like hello,Database Description and LS-Update. What is the need for carrying this in all the above? Isnt it duplicate?
Thanks
- Labels:
-
Other Routing
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-21-2017 12:08 PM
It is not true.
Each type of packet carry only some informations, necessary to the operation that it belongs.
You can capture a hello and a LSA and see on Wireshark that they are different.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-21-2017 06:13 PM
I captured the packets and options are there in all types of packets.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-22-2017 12:37 AM
Hello,
as far as I recall, only the Hello and Database Descriptor packets contain the 1-byte options field.
Check the link below which gives a pretty good explanation:
OSPF Packet Types
https://sites.google.com/site/amitsciscozone/home/important-tips/ospf/ospf-packet-types
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-22-2017 01:01 AM
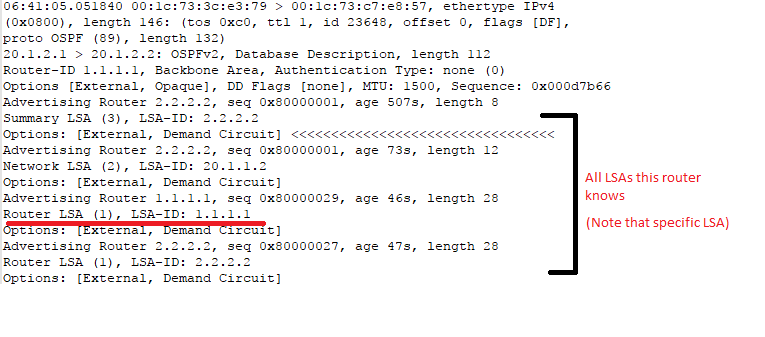
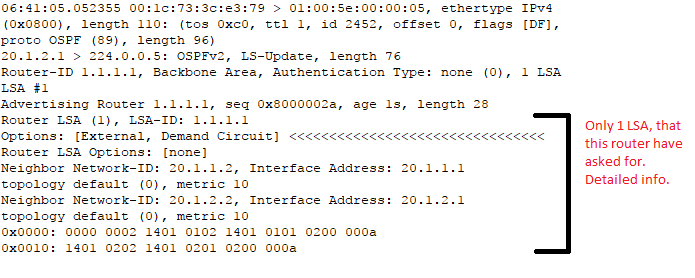
Thanks for your time. I am copying the LS-Update and Database
Description packets I captured from my switch. You can see the options in
the highlighted.
06:41:05.052355 00:1c:73:3c:e3:79 > 01:00:5e:00:00:05, ethertype IPv4
(0x0800), length 110: (tos 0xc0, ttl 1, id 2452, offset 0, flags [DF],
proto OSPF (89), length 96)
20.1.2.1 > 224.0.0.5: OSPFv2, LS-Update, length 76
Router-ID 1.1.1.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0), 1 LSA
LSA #1
Advertising Router 1.1.1.1, seq 0x8000002a, age 1s, length 28
Router LSA (1), LSA-ID: 1.1.1.1
Options: [External, Demand Circuit] <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
Router LSA Options: [none]
Neighbor Network-ID: 20.1.1.2, Interface Address: 20.1.1.1
topology default (0), metric 10
Neighbor Network-ID: 20.1.2.2, Interface Address: 20.1.2.1
topology default (0), metric 10
0x0000: 0000 0002 1401 0102 1401 0101 0200 000a
0x0010: 1401 0202 1401 0201 0200 000a
06:41:05.051840 00:1c:73:3c:e3:79 > 00:1c:73:c7:e8:57, ethertype IPv4
(0x0800), length 146: (tos 0xc0, ttl 1, id 23648, offset 0, flags [DF],
proto OSPF (89), length 132)
20.1.2.1 > 20.1.2.2: OSPFv2, Database Description, length 112
Router-ID 1.1.1.1, Backbone Area, Authentication Type: none (0)
Options [External, Opaque], DD Flags [none], MTU: 1500, Sequence: 0x000d7b66
Advertising Router 2.2.2.2, seq 0x80000001, age 507s, length 8
Summary LSA (3), LSA-ID: 2.2.2.2
Options: [External, Demand Circuit] <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
Advertising Router 2.2.2.2, seq 0x80000001, age 73s, length 12
Network LSA (2), LSA-ID: 20.1.1.2
Options: [External, Demand Circuit]
Advertising Router 1.1.1.1, seq 0x80000029, age 46s, length 28
Router LSA (1), LSA-ID: 1.1.1.1
Options: [External, Demand Circuit]
Advertising Router 2.2.2.2, seq 0x80000027, age 47s, length 28
Router LSA (1), LSA-ID: 2.2.2.2
Options: [External, Demand Circuit]
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-22-2017 04:12 AM
Well, you can see they are different, though in this specific case they may have some similarity.
Link-state routing protocol must have the link-state databases for all routers synchronized and OSPF uses Database Descriptor (DBD) packets for this purpose.
DBD are used to exchange LSA headers during the initial topology exchange, so that a router knows a list of that neighbor’s LSAs including their versions.
It is like a index.
Then the router can ask the complete LSAs it doesn´t have to its neighboor . The router uses Link-State Request (LSR) for that.
The neighboor answer the LSR with a LSU - Link-State Update, A packet that contains fully detailed LSAs.
Here (LSU) are the content, not only the headers.
So again, it is not the same.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-22-2017 04:16 AM
Sorry, only now I saw that you was talking about just about the Options and not about the full content of the packets.
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide