Introduction
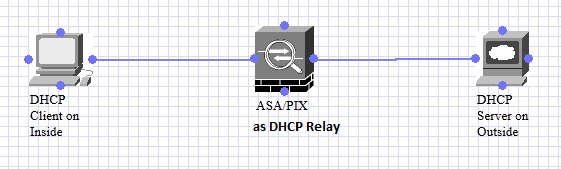
ASA/PIX as DHCP Relay and packet flow
Topology
Configuration
Minimum Configuration needed:
dhcprelay server 192.168.17.49 outside
dhcprelay enable inside
For detailed information on feature and configuration, refer following link:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6120/products_configuration_example09186a008075fcfb.shtml
As per above document:
The DHCP protocol supplies automatic configuration parameters such as an IP address with a subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server address, and WINS address to hosts. Initially, DHCP clients have none of these configuration parameters. They obtain this information by sending a broadcast request for it. When a DHCP server sees this request, the DHCP server supplies the necessary information. Due to the nature of these broadcast requests, the DHCP client and server must be on the same subnet. Layer 3 devices such as routers and firewalls do not typically forward these broadcast requests by default.
An attempt to locate DHCP clients and a DHCP server on the same subnet might not always be convenient. In such a situation, you can use DHCP relay. When the DHCP relay agent on the security appliance receives a DHCP request from a host on an inside interface, it forwards the request to one of the specified DHCP servers on an outside interface. When the DHCP server replies to the client, the security appliance forwards that reply back. Thus, the DHCP relay agent acts as a proxy for the DHCP client in its conversation with the DHCP server.
A DHCP relay agent allows the security appliance to forward DHCP requests from clients to a router or other DHCP server connected to a different interface.
These restrictions apply to the use of the DHCP relay agent
-The relay agent cannot be enabled if the DHCP server feature is also enabled.
- Clients must be directly connected to the security appliance and cannot send requests through another relay agent or a router.
- For multiple context mode, you cannot enable DHCP relay, or configure a DHCP relay server on an interface that is used by more than one context.
Note: DHCP relay services are not available in transparent firewall mode. A security appliance in transparent firewall mode only allows ARP traffic through. All other traffic requires an access control list (ACL). In order to allow DHCP requests and replies through the security appliance in transparent mode, you need to configure two ACLs:
One ACL that allows DHCP requests from the inside interface to the outside and One ACL that allows the replies from the server in the other direction.
Now, let us quickly run through how DHCP relay works with the help of packet captures on ASA's inside and outside interface.
Make a note of content highligted in RED, the way ASA modifies various fields:
1. Client boots up and starts the DHCP process by sending a broadcast DHCPDISCOVER message to destination address 255.255.255.255 - UDP port 67
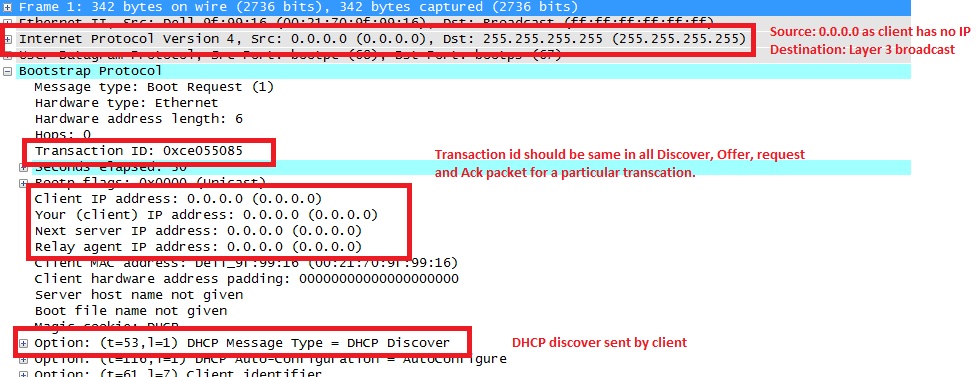
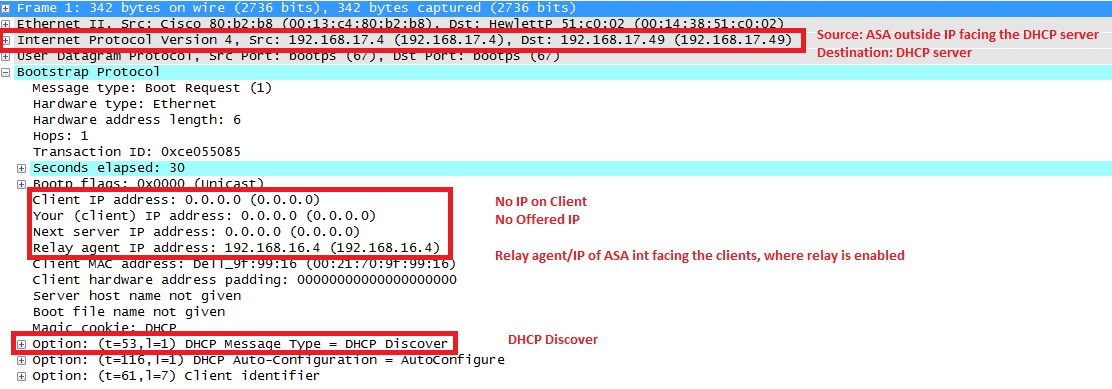
2. Normally, ASA would drop this broadcast but because it is configured to act as DHCP relay, it forwards the DHCPDISCOVER message as a unicast packet to the DHCP server's IP sourcing from the interface IP facing the server. In this case the outside interface IP address. Notice the change in IP header and relay agent field.
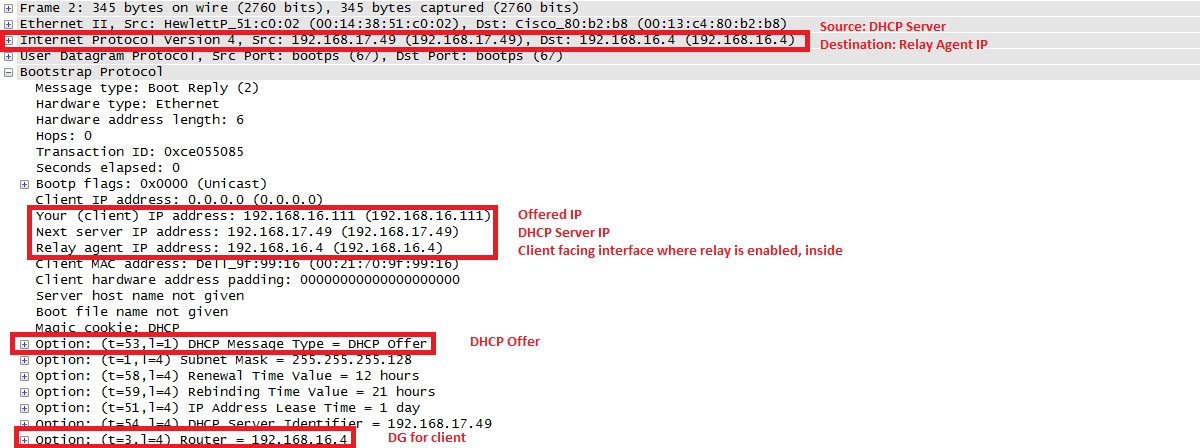
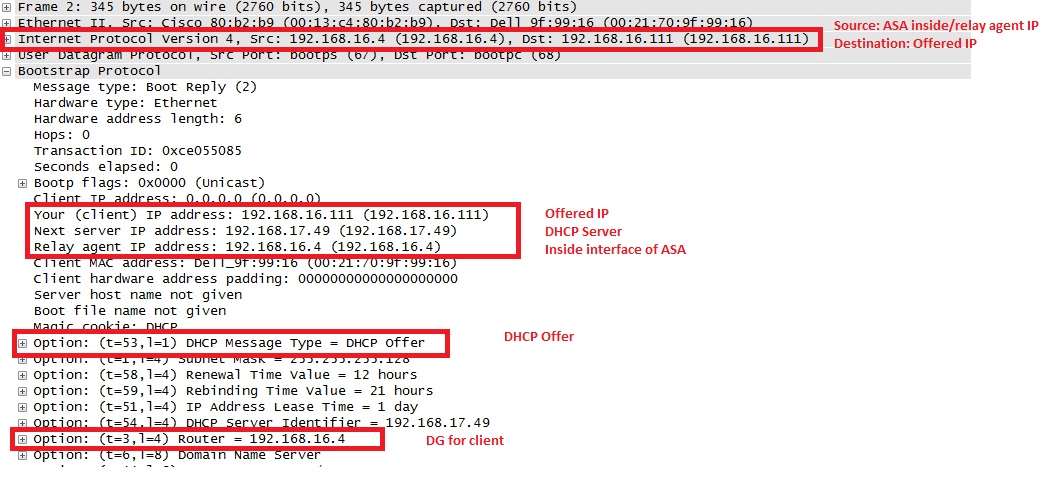
3. Server sends back DHCPOFFER as a unicast packet to the ASA destined to relay agent IP set up ASA in DHCPDISCOVER- UDP port 67. In this case, the IP address of the inside interface (giaddr) where we have dhcprelay enabled. Notice the destination IP in layer 3 header:
4. ASA will send this packet out the inside interface - UDP port 68. Notice the change in IP header while packet leaves inside interface:
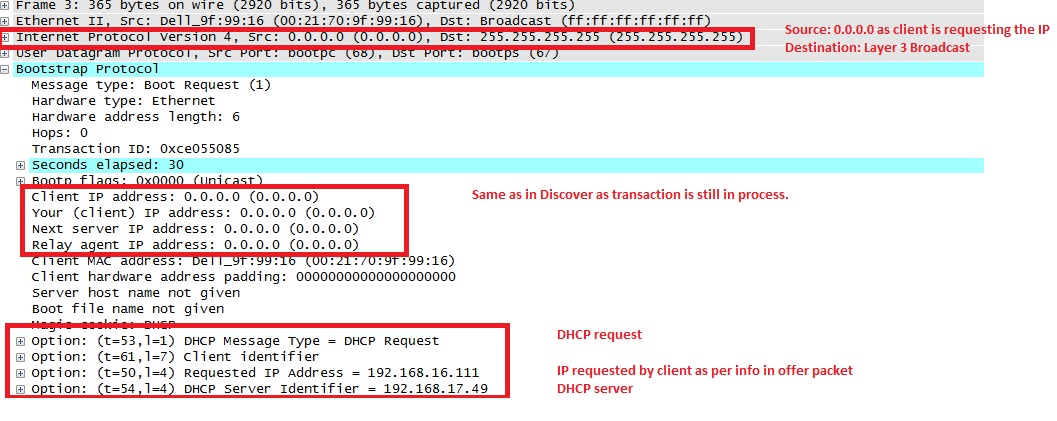
5. Client sends a DHCPREQUEST message to the server once it receives the DHCPOFFER, indicating that it accepts the offer.
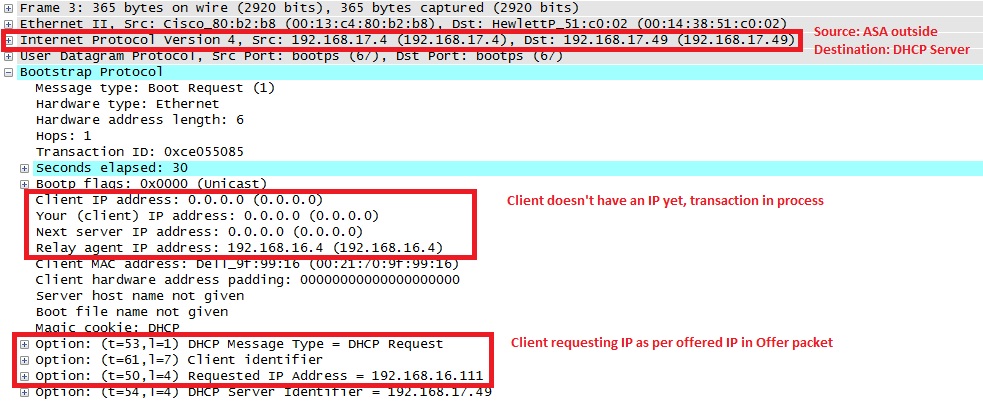
6. ASA passes this DHCPREQUEST to DHCP server:
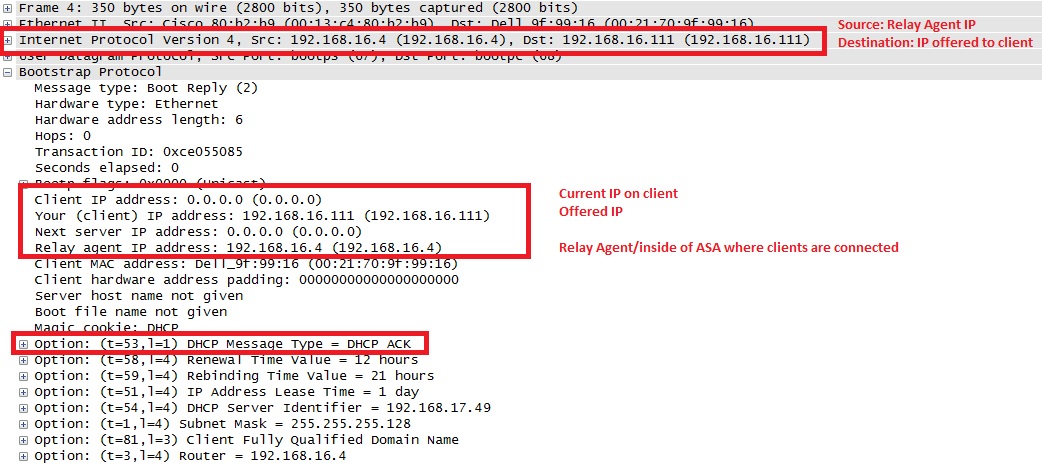
7. Once server gets the DHCPREQUEST, it sends the DHCPACK back to client:
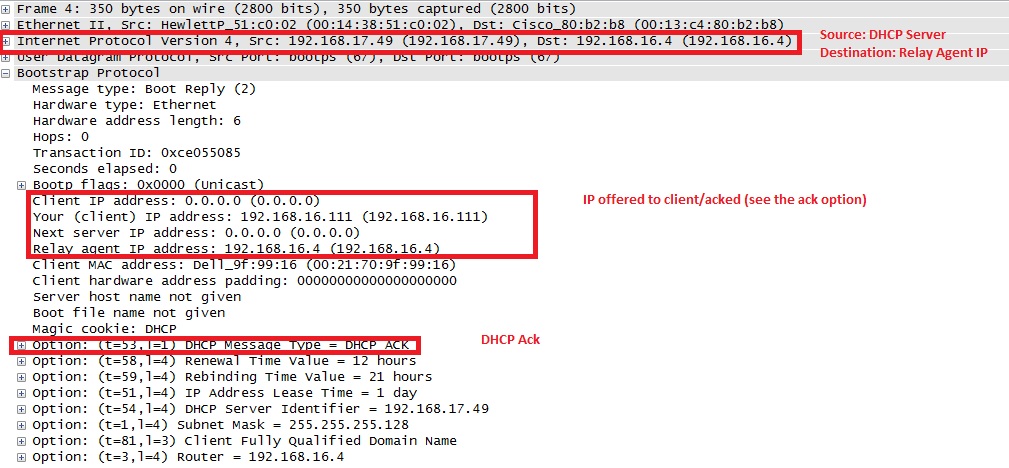
8. ASA passes this DHCPaCK from DHCP server to client:
Once client receives the DHCPACK, it will start communicating on the network.
-
Sourav Kakkar