
- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Service Providers
- Service Providers Blogs
- General DBDS Information
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- •1. What is DBDS?
Ans. The entire network architecture of the Scientific-Atlanta’s(CISCO’s) digital system that ultimately provides signal to and from a subscriber’s DHCT(set-top box). It consists of five areas:
- •a. Headend: It is the location of the network elements that processes the signal be receiving and preparing source signals and making them ready for transport network.
- •b. Transport Network: Provides the communication link enabling audio, video, and data to be transported from the headend to the hub. It involves a network of switching and transmission equipment and may include AM1 Fiber and SONET2 Technologies.
- •c. Hub: Physical location designed to serve a specific number of subscribers. May be collocated with the headend. Hubs receive, modulate, and boost the signal prior to sending it on the network of HFC3 nodes for distribution to the subscriber. Hubs usually maintain two-way communications with DHCT(set-top box) using QPSK mod/demods.
- •d. Access Network: A HFC network extending from a hub to the HFC nodes(Fiber Optic), and a network extending from the HFC nodes to the set-tops within the subscriber’s home.
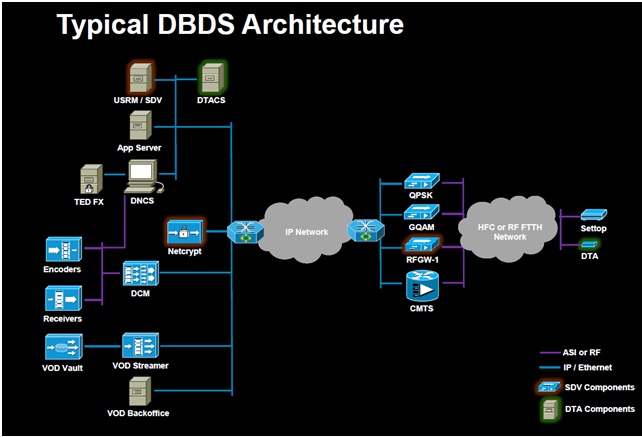
Main components of a DBDS Architecture:
Headend Units
- •2. DNCS(Digital Network Control System)?
Ans. It is considered to be the brain the DBDS. It is a computer server that is used to monitor and control the DBDS network elements. It is generally located at the headend.
- •3. TED(Transaction Encryption Device)?
Ans. It is an integral part of the communication System. ADD MORE
- •4. APP Server(Application Server)?
Ans. A workstation dedicated to applications that are made available to the DHCT’s. Interactive Program Guide is an example of an application residing on the application server. LIST ALL APPLICATIONS
- •5. Encoders?
Ans. The piece of equipment that compresses video and audio data and outputs a multiplexed MPEG Transport Stream. Explain more
- •6. DCM(Digital Content Manager)?
Ans. It is the transmission product that provides MPEG processing including statistical multiplexing,, transrating, interface conversion, digital program insertion and more. Explain it in an easier way.
- •7. Netcrypt?
Ans.
Hub Units
- •8. QAM Modulator?
Ans. A device that uses QAM techniques to modulate a digital signal onto an HFC network.
CQAM, GQAM, RFGW are just different versions of QAM Modulators. CQAM being the oldest, and RFGW being the newest.
- •9. CMTS(Cable Model Termination System)?
Ans. It is a piece of equipment that allows the cable television operators to offer high-speed Internet access to home computers. It sends and receives digital cable model signals on a cable network. It receives upstream signals from a user’s cable modem, converts them into IP packets, and routes them to the Internet Service Provider for internet connection. It can also send signals to the modem, known as downstream signals.
- •10. Demodulator: Receives information such as billing and performance monitoring data in a reverse path from the DHCT and returns it to the DNCS for processing. QPSK DEMOD
- •11. Modulator: Sends control and authorization information from the DNCS to the DHCT. QPSK MOD
IS QPSK A DEMOD????
User End
- •12. DHCT(Digital Home Communication Terminal?
Ans. Another name for a Set-top box.
Other Useful terms to know:
- •1. ASI(Asynchronous Serial Interface): self-clocking serial transmission method interface.
- •2. Broadcast: One-to-All.
- •3. Multicast: Point-to-Many.
- •4. DOCSIS: Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specification. It defines interface standards from cable modems and supporting equipments.
- •5. In-band: Data from DNCS to DHCT.
- •6. Out-band: Date from DHCT to DNCS.
- •7. Vod: Video on Demand.
- •8. SDV: Switch Digital Video. Add more explanation.
- •9. DTA:
- •1. AM: Amplitude Modulation. Modulation by varying the amplitude of a light wave, common in analog/RF applications.
- •2. SONET(Synchronous Optical Network): A standard for optical fiber transmission on telecommunication networks.
- •3. HFC(Hybrid Fiber Coax): A network that uses a combination of fiber optics and coaxical cable to transport signal from one place to another.
DNCS Glossary
alarmCollector
- Retrieves alarms from any network elements. The alarms are sent to Spectrum.
Arris
bfsRemote
- Broadcast File System (BFS) Remote - Manages the processes (dataPump Processes) that continuously transmit BFS data. Note: The BFS facilitates delivery of information to set tops.
bfsServer (Broadcast File System Server)
- Delivers files to servers on or connected to the DNCS. The BFS facilitates delivery of information to the DHCTs. Manages the addition and removal of files from the BFS.
bossServer (Business Operations Support System Server)
- Accepts information to and from billing system, DHCT Manager, PPV, and Admin Console. BOSS manages secure PPV transactions.
bossDiagnosticServer (Business Operations Support System (BOSS) Diagnostics Server)
- Acts as an SNMP proxy agent between the billing system and set-tops by going through the DNCS to retrieve information from set tops for the billing system.
bsm (Broadcast Segment Manager)
- Responsible for fielding broadcast segment definitions.
- Receives notification from the SI Manager when broadcast sources start, and forwards the notifications to the Conditional Access System.
caaServer (Conditional Access Authority (CAA) Server)
- Creates and sends the CAA and entitlement authorization (EA) entitlement management messages (EMMs) required for stagins set tops.
camAm (Conditional Access Manager Authenticated Messaging)
- Creates EMMs for Security Elements, in order to authorize DHCTs for secure events.
camAuditor (Conditional Access Manager Auditor)
- Background process that continually looks for boxes whose EMMs will expire within 20 days and regenerates them making them valid for 30 days.
- Refreshes or creates EMMs on DHCTs, which allow the subscriber to select secure events.
- This process does not transmit EMMs!
camEx (cam Exclusive Sessions)
- Provides conditional access for VOD sessions; generates interactive session keys (ISKs) for each session and ISK EMMs for delivery to the set tops.
- Generates entitlement control messages (ECMs).
- camEx services exclusive sessions, encrypting MSKs and ECMs for the QAMs. (It does for the QAMs what camPsm does for PPV in the DHCTs.)
camFastRefresh
- Queries the database for EMMs, puts the EMMs in files, and puts the files on the BFS (files are refreshed periodically when EMMs are changed in the system); sends staging EMMs over inband
BFS to set tops that are candidates for the Fast Refresh List.
camPsm (cam Program Segment Manager)
- Sends PPV and CA Time-of-Day global broadcast authenticated messages (GBAMs); inserts CA information, including ECMs into the program segment.
camTedChecker (cam Transaction Encryption Device (TED) Checker)
- Indicates whether or not the TED is running as follows:
Green - The TED is in services and the keys have been initialized
Yellow - The TED software is running, but the keys have not been initialized
Red - The TED software is not running.
dncs-snmpd (Simple Network Management Protocol for the DNCS)
- Ensures that network elements that are not SNMP-compliant, can communicate with Spectrum via SNMP protocol. In other words, dncs_snmp acts as a proxy agent.
drm (Digital Resource Manager)
- Manages the allocation of network resources for setting up sessions.
dsm (Digital Session Manager)
- Manages Digital Video Sessions (broadcast and exclusive) on the DNCS.
EARS (Emergency Alert Receiver Server)
- Monitors a designated port on the DNCS to receive Emergency Alert Messages (EAMs).
emmDistributor (Entitlement Management Messenger)
- Distributes entitlement messages to DHCTs out-of-band. emmDistributor is a background process that spins through the database and sends out operational EMMs for each box.
- In the DNCS environment, a parameter named 'EMM_DIST_CYCLE_DAYS' specifies how many days (from 2-10) should be used for a complete EMM distribution cycle. The default for this parameter is 7 days.
eventManager
- Ensures that events critical to RCS processes are routed to appropriate processes.
- For example, when an RNCS/LIONN receives an Emergency Alert Message (EAM), Event Manager is notified of the EAM and passes an "EAM event" on to the MMMserver process on the DNCS.
- By notifying Event Manager, all appropriate set tops - those deployed in the central site as well as those deployed in remote sites - receive the EAM, if the EAS feature is used.
gemServer (The VQE Manager application)
hctmCache (Home Communications Terminal Manager Cache)
- Provides database access for all hctm processes.
hctmConfig (Home Communications Terminal Manager Configuration)
- Exchanges and periodically broadcasts UNconfig information to the DHCTs.
hctmMac (Home Communications Terminal Manager Mac Addressing)
- Responsible for verifying connections and disconnections of DHCTs and modulators. Associates an IP address with the DHCT.
hctmProvision (Home Communications Terminal Manager Provisioning)
- Ensures that setup information is in the database and available for the DHCTs.
idm (Inventory and Directory Manager)
- Serves as an address resolution directory. Provides a repository for public key certificates. Maintains information about network elements and other network entities.
ippvManager (Impulse Pay-Per-View Manager)
- Polls DHCTs for Pay-Per-View order information.
ippvReceiver (Impulse Pay-Per-View Receiver)
- Receives purchased event information from the DHCT. Then, ippvReceiver forwards or returns this information to the Billing System (upon request).
logManager (Logging Manager)
- Enables the configuration of logging levels on a DNCS and RNCS/LIONN through the logging Summary windows on the DNCS.
MMMServer (Multi-Media Message Server)
- Processes Emergency Alert Messages (EAMs) and dispatches them to the targeted geographic area, based on the Federal Information Processing System (FIPS) code information contained in the message.
- EAMs may contain text, audio and force tune information, if the EAS feature is used.
mgrUIServer (GUI Server Manager)
- Facilitates the management of all GUI servers (dbUIServer, logUIServer, rpcUIServer, perfUIServer). GUI servers can be accessed from the GUI Server button under the utilities tab.
- SOAPServers and mgrUIServer services and access to dncsdb through Java/Tomcat processes (CATALINA).
- If problems are encountered with WEB GUIs then you have to restart tomcat-httpd-SOAPServer/mgrUIServer components.
- As dncs stop SOAPServers either through :
- dncsControl (SR 4.3 & later) - 23 SOAPServers change from run to stop, or
- /dvs/dncs/bin > ./stopSOAPServers
- As root stop tomcat with # /etc/rc2.d/S98tomcat stop
- As root stop http service with # svcadm disable svc:/network/http:apache2. To check processes with # svcs -a |grep -i http
- As dncs stop SOAPServers either through :
- Then Start 3 components:
- /etc/rc2.d/S98tomcat start #java type connections using CATALINA
- svcadm enable svc:/network/http:apache2
- As dncs either use dncsControl - 23 SOAPServers to change state from stop to run, or /dvs/dncs/bin > ./startSOAPSServers
- If restart of 3 components does not corrert WEB GUIs then:
lsof java
/usr/ucb/ps -auxww | grep java
- Kill processes still showing java running to finish all tomcat connections still running.
- Then restart 3 components as before
Apache-http logs are found in /var/apache2/logs
tomcat process logs are found in /usr/local/tomcat/logs
osm (Operation System Manager)
- Allows the loading of files into the Broadcast File System (BFS) that can then be distributed to the DHCTs.
- The types of data that can be distributed are ROM, resident applications, software tables.
PassThru
- Sends Digital Storage Media Command and Control (DSMCC) messages directly to DHCTs.
pkeManager (PowerKEY Element Manager)
- Facilitates the management of [Netcrypt] Bulk Encryptors, if used.
qamManager
- Provisions QAMs ([QAM], [MQAM], [GQAM]) to set up sessions, assign frequencies, use ECMs,
and so on.
qpskManager
- Provisions [QPSKs] to set assign frequencies.
ResAppServer (Resident Application Server)
- Provides miscellaneous services for the SARA Servers, including access to data in the DNCS [Informix] database.
saManager (Service Application Manager)
- Ensures that eachservice correlates to the appropriate program. Used to define application parameters for a program service, such as an RPPV channel.
siManager (System Information Manager)
- Facilitates the distribution of SI tuning table information to the QAMs (along with the QAM Manager).
smMix (System Information Manager)
- smMix is a utility that tests if camAuditor is properly doing its job. This utility prints a histogram of EMM expiration times.
- If all EMMs in a DNCS are valid for 20 to 30 days, then camAuditor is functioning properly. If boxes are timing out, but smMix shows no problems, then emmDistributor may be at fault.
SseManager (Server-Side Entitlement Manager)
- Retrieves entitlement information and provides it to a third-party application (Client-Side Entitlement Manager) in the format that application requires.
- The application then matches the information to its entitlement information so authorized customers can view the services the application provides.
- Typically, this service is video-on-demand (VOD). The sseManager is not used for all VOD.
stun Server
- STUN servers make it possible to contact set top boxes through the Residential Gateway, which would otherwise not allow un-solicited incoming traffic.
- (thus the Residential Gateways used must allow STUN servers).
Tandberg
- TANDBERG Television’s OpenStream® Business Manager is a complete
Business Management System (BMS) that provides the core functionality necessary
for cable operators to manage the logistics of offering on-demand services to
their respective customer bases. As a network-based solution, the Business
Manager enables TANDBERG Television customers to monitor and manage
business functions associated with the rollout of On-Demand product
offerings.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: