- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Switching
- Re: network questions
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-01-2013 04:54 PM - edited 03-07-2019 02:43 PM
Hi guys, I have gone through my exam script that I have just completed and there is one question that I am sure I am getting incorrect. If someone can please answer these few short questions I would be very grateful
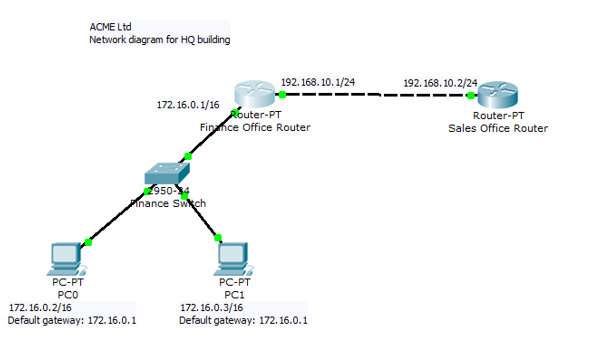
- •a) How many IP networks are in the diagram and what are they?
- •b) If PC0 wishes to ping PC1, how can it determine that PC1 is on the same network?
- •c) If PC0 wishes to ping PC1, and PC0 doesn’t know PC1’s MAC address what will it do?
- •d) Does any problem occur in the network if PC0 and PC1 send frames simultaneously? Explain your answer.
- •e) What information will the Finance Switch have about PC0 and PC1 after they have sent frames?
- •f) What information will the Finance Office router contain to allow it to make routing decisions?
thanks in advance
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
Other Switching
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-01-2013 05:33 PM
How many IP networks are in the diagram and what are they?
Your LAN and your WAN network.
If PC0 wishes to ping PC1, how can it determine that PC1 is on the same network?
PC0 sends out an ICMP packet, goes up to the switch, switch forwards to router. Router looks to the dinning table to determine who owns the IP address and converts to MAC address, sends the ICMP down to switch. Switch looks at the destination MAC address and goes "A HA! You're down this port", forwards the ICMP packet down the port where PC1 is. And they live happily ever after.
If PC0 wishes to ping PC1, and PC0 doesn’t know PC1’s MAC address what will it do?
Same as above.
Does any problem occur in the network if PC0 and PC1 send frames simultaneously? Explain your answer.
No, Full Duplex. I am network engineer. I don't answer silly questions.
What information will the Finance Switch have about PC0 and PC1 after they have sent frames?
MAC Address of both PC0 & PC1.
What information will the Finance Office router contain to allow it to make routing decisions?
The ARP of the MAC address and IP address of PC0 and PC1.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-01-2013 06:54 PM
Disclaimer
The Author of this posting offers the information contained within this posting without consideration and with the reader's understanding that there's no implied or expressed suitability or fitness for any purpose. Information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as rendering professional advice of any kind. Usage of this posting's information is solely at reader's own risk.
Liability Disclaimer
In no event shall Author be liable for any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of use, data or profit) arising out of the use or inability to use the posting's information even if Author has been advised of the possibility of such damage.
Posting
Additional answers to your questions.
a) How many IP networks are in the diagram and what are they?
Two, 192.160.10.0/24 and 172.16.0.0/16.
b) If PC0 wishes to ping PC1, how can it determine that PC1 is on the same network?
PC0 can compare PC1's IP address against its IP address and network mask. This will tell it if the destination IP is in the same subnet.
c) If PC0 wishes to ping PC1, and PC0 doesn't know PC1’s MAC address what will it do?
PC0 will ARP for PC1's MAC.
d) Does any problem occur in the network if PC0 and PC1 send frames simultaneously? Explain your answer.
Mostly depends on whether the two hosts support full duplex and/or whether they have the same bandwidth. If not full duplex, transmitting frames can collide with received frames. If different bandwidths, the faster might congest on the switch port to the slower.
Even if full duplex and same speed, not all host NICs (or even some switches) can handle full capacity. I.e. it's possible a host or the switch might not be able to support full duplex at full wire-speed/line-rate. If both hosts send frames simultaneously, there may be more "work" for host and/or switch interfaces.
e) What information will the Finance Switch have about PC0 and PC1 after they have sent frames?
PC0's and PC1's MAC associated with the port they are connected to.
f) What information will the Finance Office router contain to allow it to make routing decisions?
A routing table contain network destination. The router will implicitly know of directly connected networks. For non-directly connected networks, like what's on the far side of Sales Office Router, it will need to have such routes defined to its routing table.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-01-2013 05:33 PM
How many IP networks are in the diagram and what are they?
Your LAN and your WAN network.
If PC0 wishes to ping PC1, how can it determine that PC1 is on the same network?
PC0 sends out an ICMP packet, goes up to the switch, switch forwards to router. Router looks to the dinning table to determine who owns the IP address and converts to MAC address, sends the ICMP down to switch. Switch looks at the destination MAC address and goes "A HA! You're down this port", forwards the ICMP packet down the port where PC1 is. And they live happily ever after.
If PC0 wishes to ping PC1, and PC0 doesn’t know PC1’s MAC address what will it do?
Same as above.
Does any problem occur in the network if PC0 and PC1 send frames simultaneously? Explain your answer.
No, Full Duplex. I am network engineer. I don't answer silly questions.
What information will the Finance Switch have about PC0 and PC1 after they have sent frames?
MAC Address of both PC0 & PC1.
What information will the Finance Office router contain to allow it to make routing decisions?
The ARP of the MAC address and IP address of PC0 and PC1.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-01-2013 06:54 PM
Disclaimer
The Author of this posting offers the information contained within this posting without consideration and with the reader's understanding that there's no implied or expressed suitability or fitness for any purpose. Information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as rendering professional advice of any kind. Usage of this posting's information is solely at reader's own risk.
Liability Disclaimer
In no event shall Author be liable for any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of use, data or profit) arising out of the use or inability to use the posting's information even if Author has been advised of the possibility of such damage.
Posting
Additional answers to your questions.
a) How many IP networks are in the diagram and what are they?
Two, 192.160.10.0/24 and 172.16.0.0/16.
b) If PC0 wishes to ping PC1, how can it determine that PC1 is on the same network?
PC0 can compare PC1's IP address against its IP address and network mask. This will tell it if the destination IP is in the same subnet.
c) If PC0 wishes to ping PC1, and PC0 doesn't know PC1’s MAC address what will it do?
PC0 will ARP for PC1's MAC.
d) Does any problem occur in the network if PC0 and PC1 send frames simultaneously? Explain your answer.
Mostly depends on whether the two hosts support full duplex and/or whether they have the same bandwidth. If not full duplex, transmitting frames can collide with received frames. If different bandwidths, the faster might congest on the switch port to the slower.
Even if full duplex and same speed, not all host NICs (or even some switches) can handle full capacity. I.e. it's possible a host or the switch might not be able to support full duplex at full wire-speed/line-rate. If both hosts send frames simultaneously, there may be more "work" for host and/or switch interfaces.
e) What information will the Finance Switch have about PC0 and PC1 after they have sent frames?
PC0's and PC1's MAC associated with the port they are connected to.
f) What information will the Finance Office router contain to allow it to make routing decisions?
A routing table contain network destination. The router will implicitly know of directly connected networks. For non-directly connected networks, like what's on the far side of Sales Office Router, it will need to have such routes defined to its routing table.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-02-2013 08:23 AM
great answers, thanks a lot. one last question if you wouldn't mind
c) How does a host know what IP network it is on? How does such a host
know whether another host to which it wishes to send a packet is on
the same or a different IP network?
(8 marks)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-02-2013 10:31 AM
Disclaimer
The Author of this posting offers the information contained within this posting without consideration and with the reader's understanding that there's no implied or expressed suitability or fitness for any purpose. Information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as rendering professional advice of any kind. Usage of this posting's information is solely at reader's own risk.
Liability Disclaimer
In no event shall Author be liable for any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of use, data or profit) arising out of the use or inability to use the posting's information even if Author has been advised of the possibility of such damage.
Posting
c) How does a host know what IP network it is on? How does such a hostknow whether another host to which it wishes to send a packet is on
the same or a different IP network?
(8 marks)
Thought I answered that, but maybe an example to clarify. . .
PC0 IP info is 172.16.0.2/16. To find the network you logically and the IP and network mask.
172.16.0.2 and 255.255.0.0 means the network is 172.16.0.0/16. (If you're unfamiliar with logical and, the mask's zero bits will zero out the IP address bits.)
If we do likewise for PC1's IP info, we'll get the same network value, but if PC1's IP info was 172.15.0.3/16 its network would be 172.15.0.0/16 which is different from 172.16.0.0/16.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-02-2013 10:32 AM
thank you very much
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide