- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Security
- Web Security
- Do I have to deploy the WSA's
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Cisco Anyconnect, WSA, WCCP
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-22-2014 10:07 AM
It is no surprise that filtering your Anyconnect clients with the WSA when the WCCP router is the ASA is not doable. I am trying to figure out what people are doing to filter their remote clients? Does WSA have a remote client that can be installed on remote laptops and some kind of a vm appliance to stick in the DMZ for remote clients to proxy before hitting the internet?
- Labels:
-
Web Security
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-22-2014 10:23 AM
You have a few options:
If you want to force their web connection through the WSA when Anyconnect is connected, you can depoly an Anyconnect config file to the ASA and in that file, set them to explicitly hit the WSA (eg ASA will set the Proxy options in IE/Tools/Internet Options/Connections.) You DON"T have to use a seperate VM/box (you can do it either way). If you upload the PKG file for the Anyconnect client to the ASA, you should be able to modify the profile there. There's also a standalone profile editor available that you can use to create the XML and then upload that to the ASA. On connection the Anyconnect client downloads it and gets configured.
If you want them filtered when NOT connected, you can get the Cisco Web Security service and deploy the AnyConnect Web Security msi (also doable from the ASA), and the laptop is covered. Regrettably you can't point this at a VM or box in your own DMZ...
Ken
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-22-2014 10:39 AM
Do I have to deploy the WSA's as a proxy then? I want to essentially eliminate the proxy functionality in my network.
I am not familiar with deploying config files with anyconnect, can you direct me to some cisco documentation?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-22-2014 10:53 AM
The explicit functionality is always there, even if you're using transparent... so internally you can just use WCCP and be done with it, and only use the explicit proxy for the AnyConnect users.
Configing Anyconnect (as well as depolying the config file) is covered here:
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-22-2014 10:36 PM
Hi Steven,
You could try the Cloud based Web Security solution for remote users as well :
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/CVD/Dec2013/CVD-CloudWebSecurityUsingCiscoAnyConnectDesignGuide-DEC13.pdf
Regards,
Sagar Kadambi.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-08-2020 12:03 PM
Hello All,
Let me break this down into pieces:
@Steven Williams, the limitation you refer to is documented here but there is a workaround.
In this document you can see the different architectures supported when it comes to Anyconnect users and it depends on your needs:
For the limitation you mentioned, focus on scenario 1. This is how it works:
The Anyconnect client connects to the ASA on the outside, we force that packet to be sent out of the inside interface (this is due to the 'tunneled' keyword we use on the default route. Please note that only VPN traffic will be forced to use this as the default route). When the inside router (doing WSA redirection) sees this packet, if it is non port 80/443 traffic its sends the packet back to the ASA. If it is web traffic, it is redirected to the WSA for policy enforcement.
Test 1: Anyconnect client (10.1.1.1) connecting to Google:
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Inbound packet flow: 10.1.1.1 ---------> outside (ASA) inside ----------->InsideRTR (this will happen because you have route inside 0 0 tunneled)
The inside router will check the L4 information in the packet and redirect it to the WSA device.
WSA device will rewrite the packet with its own IP address, let's assume that it is 192.168.1.3.
Outbound packet flow:
WSA (192.168.1.3)-------------->inside(ASA)outside----------------->Google
Google responds,
Google --------------->outside(ASA)inside------------->192.168.1.3
WSA forwards the packet to the AC client (ASA will use the /32 route created for the AC client to route this packet out)
192.168.1.3 ------------>inside(ASA)outside------------->10.1.1.1
Test 2: AC client connecting to a telnet server (non-web traffic)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Inbound packet flow: 10.1.1.1 ---------> outside (ASA) inside ----------->InsideRTR
Inside router will send this packet back to the ASA based on its default route.
InsideRTR ----------->inside(ASA)outside----------->Telnet server
Please note that this is the same packet, it was simply u-turned by the inside router, but the ASA will create a 'new' flow for this packet due to the syn flag.
Telnet server responds,
TS -------------->outside (ASA) inside--------->Router
Please note that the ASA must have a route to the AC pool (10.1.1.0) pointing to the inside router for this to work. The ASA will not use the /32 route that it originally installed pointing to the outside interface since the SYN-ACK is part of a flow that was initiated from the inside (from the ASA's perspective). So you need a route which looks like this: route inside 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 <Inside router>
The inside router will u-turn this packet back to the ASA as expected,
Inside RTR :------->inside(ASA)outside--------->10.1.1.1
In the above packet flow the ASA will use the original /32 route to route it to the AC client.
So, in the end we STILL have a symmetric packet flow through the ASA.
Outside ASA Inside
SYN 1 --------------> SYN 1
SYN 2 <--------------- SYN 2
SYN-ACK 1 --------------> SYN-ACK 1
SYN-ACK 2 <-------------- SYN-ACK 2
SYN1 and SYN-ACK 2 create a symmetric flow and SYN 2 and SYN-ACK1 create a symmetric flow.
@SriSagar Kadambi , SWG was announced EOL since 2018
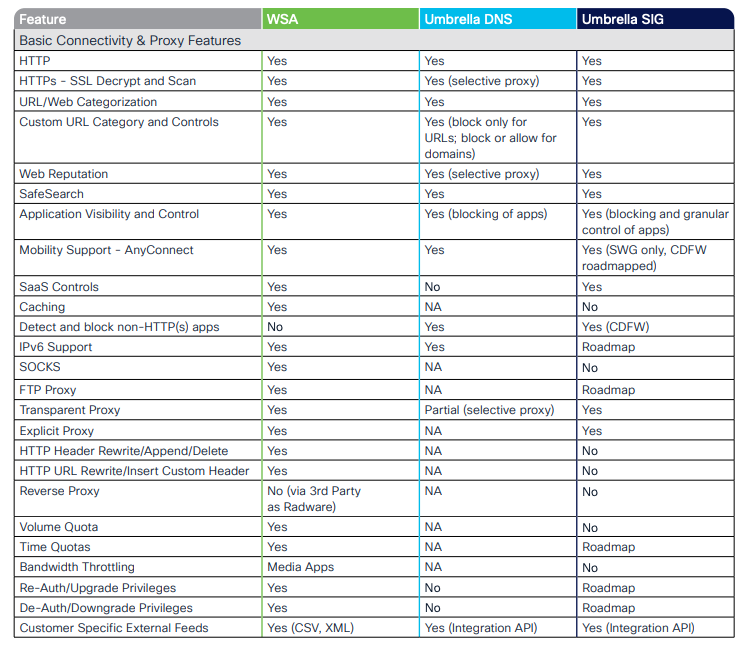
Also, notice you can use Cisco Umbrella to protect those Anyconnect users. Umbrella has 2 flavors: DNS Protection and Secure Internet Gateway (SIG/SASE solution). Depending on your needs you can choose the right solution to protect your users but it should be a consulting discussion based on on your use-cases, what you are looking for, management requirements, devices, growth plan, etc. Here is feature comparison between the solutions:
Full document is here:
https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/products/collateral/security/fb-wsa-umb-fc.pdf
Hope this helps.
-Gustavo
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide