- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Wireless - Mobility
- Wireless - Mobility Knowledge Base
- 802.11 Sniffer Capture Analysis - Management Frames and Open Auth
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
05-25-2012 06:03 AM - edited 11-18-2020 02:58 AM
Introduction
802.11 Sniffer Capture Analysis - Management Frames and Open Auth
802.11 – Frames and open authentication
Trying to analyze or troubleshoot a wireless LAN, network using 802.11 packet analyzer will require us to have a thorough understanding of different 802.11 frame types as a basis for finding pointers to localize the causes of the problem area in a wlan network . Taking wlan sniffer traces using tools like omnipeek and or wireshark one can monitor the communications between radio network interface cards (NICs) and access points. We will need to comprehend each frame type occurring in the operation of a wireless LAN and solving network problems. In a wlan RF environment the radio transmission conditions can change so dynamically, coordination becomes a large issue in WLANs. Management and control packets are dedicated to these coordination functions.
To find cause of the wlan problems occurring in the wlan network relating to RF environment it would be best to test the wlan network using open authentication without any security. By taking this approach the RF connectivity issues surface and can be corrected before we can move to stronger encryption and higher layers of the OSI layer.
Authentication in the 802.11 specification is based on authenticating a wireless station or device instead of authenticating a user.
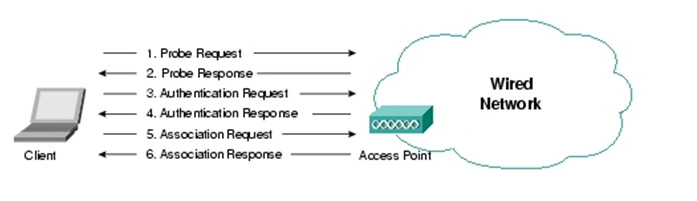
As per the 802.11 specification client authentication process consists of the following transactions as mentioned below
- The Access points continuously sends out Beacon Frames which are picked up by the nearby wlan clients.
- The client can also broadcast on its own probe request frame on every channel
- Access points within range respond with a probe response frame
- The client decides which access point (AP) is the best for access and sends an authentication request
- The access point will send an authentication reply
- Upon successful authentication, the client will send an association request frame to the access point
- The access point will reply with an association response
- The client is now able to pass traffic to the access point
802.11 Client Authentication Process
There are 3 types of frames used in the 802.11 MAC layer 2 communications happening over the air which manages and controls the wireless link.
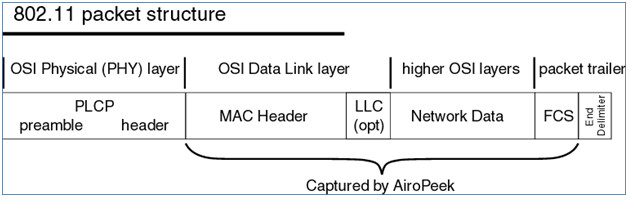
They are Management Frames, Control Frames and Data frames. Let’s take a peek at what those frames consist of in little details to help us in analyze the wlan problems better while working with wlan sniffer traces.
Management Frames
802.11 management frames enable stations to establish and maintain communications. Management packets are used to support authentication, association, and synchronization.
The following are common 802.11 management frame subtypes:
- Authentication frame: This is a frame signifying to the network membership within the wlan topology. 802.11 authentications is a process whereby the access point either accepts or rejects the identity of a radio NIC to create resources. Authentication restricts the ability to send and receive on the network. It is the first step for a device attempting to connect to an 802.11 WLAN. The function is handled by an exchange of management packets .Authentication is handled by a request/response exchange of management packets. The number of packets exchanged depends on the authentication method employed. In this document we are focusssing on the simplest open authentication method to simplify our troubleshooting of RF issues.
wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x0b

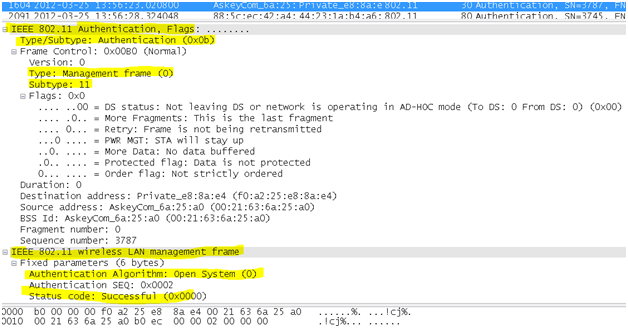
The NIC begins the process by sending an authentication frame containing its identity to the access point. With open system authentication (the default), the radio NIC sends only one authentication frame, and the access point responds with an authentication frame as a response indicating acceptance (or rejection). There is an associated authentication ID associated which is the name under which the current station is authenticated itself on joining the network.
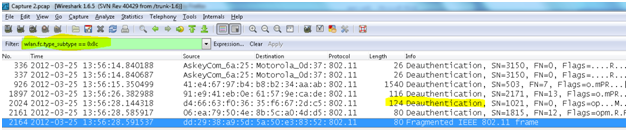
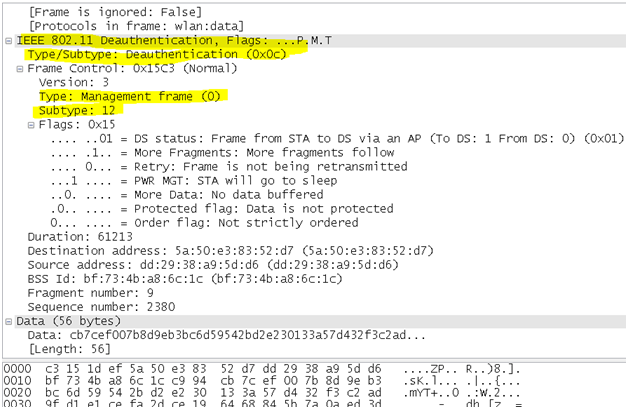
- Deauthentication frame: This is an announcement packet by a station which sends a deauthentication frame to another station if it wishes to terminate secure communications. It is a one-way communication from the authenticating station (a BSS or functional equivalent), and must be accepted. It takes effect immediately.
wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x0c

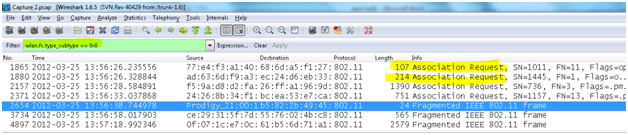
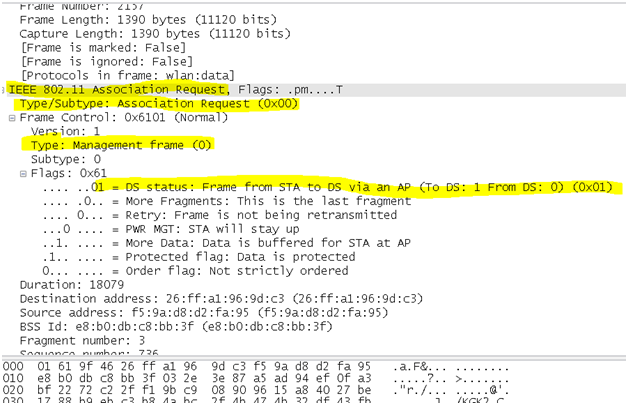
- Association request frame: 802.11 associations enable the access point to allocate resources for and synchronize with a radio NIC. A NIC begins the association process by sending an association request to an access point. This frame carries information about the NIC (e.g., supported data rates) and the SSID of the network it wishes to associate with. After receiving the association request, the access point considers associating with the NIC, and (if accepted) reserves memory space and establishes an association ID for the NIC. Packets can show the current association of the sender. Association and Reassociation are handled by request/response management packets.
wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x0

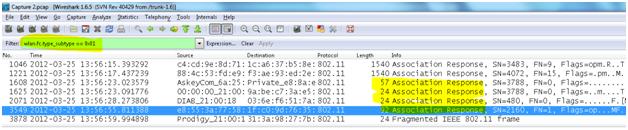
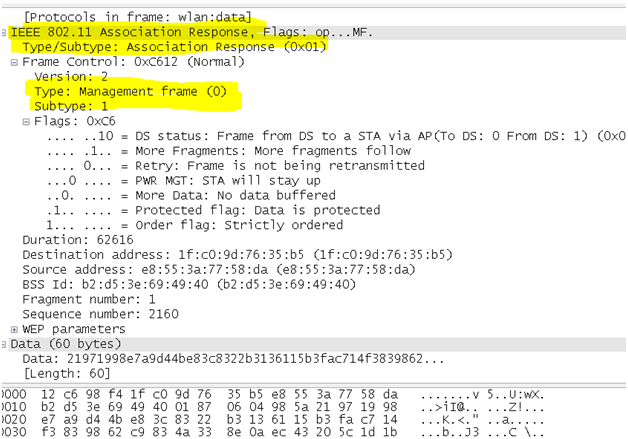
- Association response frame: An access point sends an association response frame containing an acceptance or rejection notice to the radio NIC requesting association and will include the Association ID of the requester. If the access point accepts the radio NIC, the frame includes information regarding the association, such as association ID and supported data rates. If the outcome of the association is positive, the radio NIC can utilize the access point to communicate with other NICs on the network and systems on the distribution (i.e., Ethernet) side of the access point.
wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x01

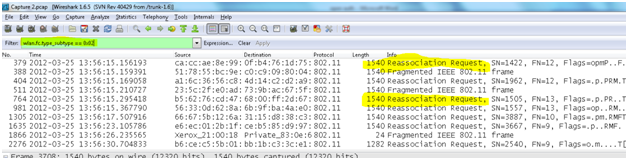
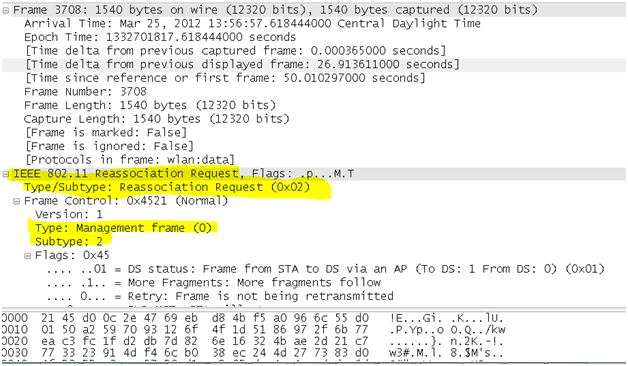
- Reassociation request frame: This frame is similar to a association request but has a different purpose and is mainly useful in client roaming where in If a radio NIC roams away from the currently associated access point and finds another access point having a stronger beacon signal, the radio NIC will send a reassociation frame to the new access point. The new access point then coordinates the forwarding of data frames that may still be in the buffer of the previous access point waiting for transmission to the radio NIC. The sender must already be authenticated in order to gain a successful association.
wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x02

- Reassociation response frame: An access point sends a reassociation response frame containing an acceptance or rejection notice to the radio NIC requesting reassociation. Similar to the association process, the frame includes information regarding the association, such as association ID and supported data rates.
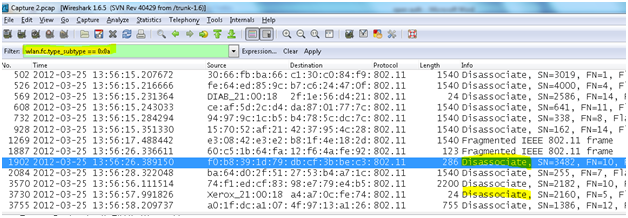
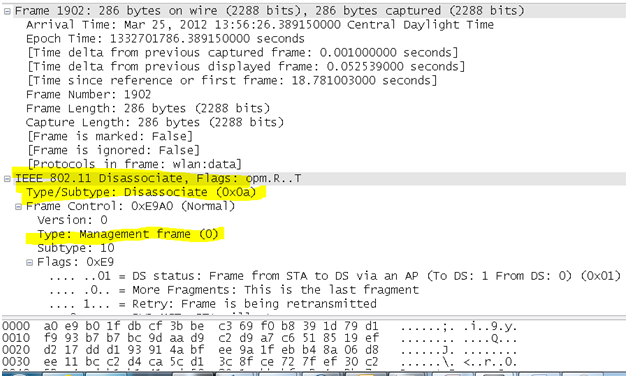
- Disassociation frame: A station sends a disassociation frame to another station if it wishes to terminate the association. For example, a radio NIC that is shut down gracefully can send a disassociation frame to alert the access point that the NIC is powering off. The access point can then relinquish memory allocations and remove the radio NIC from the association table. Disassociation is a simple declaration from either an access point or a device.
The filter used to apply and find only the Disassociation packets is “wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x0a”

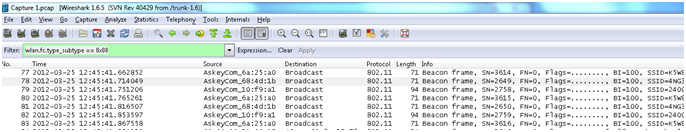
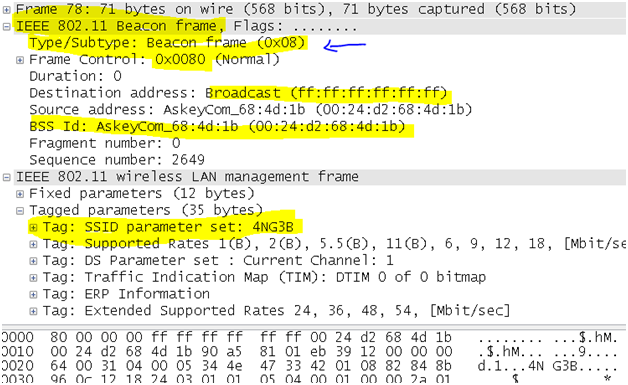
- Beacon frame: The access point periodically sends a beacon frame to announce its presence and relay information, such as timestamp to help synchronize member stations with the BSS, , SSID, and other parameters regarding the access point to radio NICs that are within range. This purpose of this frame is to announce the beginning of a Contention Free period (CF), during which the right to transmit is conferred by the access point by polling. Radio NICs continually scan all 802.11 radio channels and listen to beacons as the basis for choosing which access point is having the best signal and availability to get associate with.
The filter used to apply and find only the Beacon packets is
“wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x08”

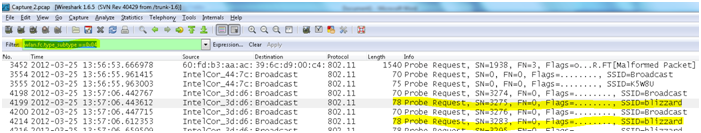
- Probe request frame: A station or client becomes active or on a PC when the wlan card it enabled it becomes active sends a probe request frame when it needs to obtain information from another station or access point. For After a radio NIC sends out a probe request to determine which access points are within range. The probe request frame is sent on every channel the client supports in an attempt to find all access points in range that match the SSID and client-requested data rates .Its upto the client to determine which access point to associate to by weighing various factors like supported data rates and access point load to select optimal access point thus moves to the authentication phase of 802.11 network after getting responses from Aps as probe response. This mechanism support also helps in roaming station the ability to move between cells while remaining connected in the search for new access point.
The filter used to apply and find only the Probe request packets is
“wlan.fc.type_subtype ==0x04”

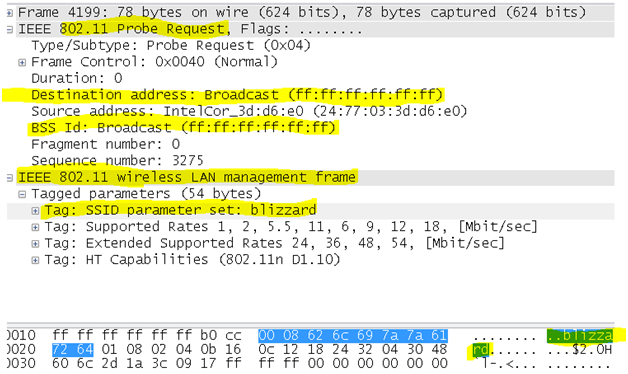
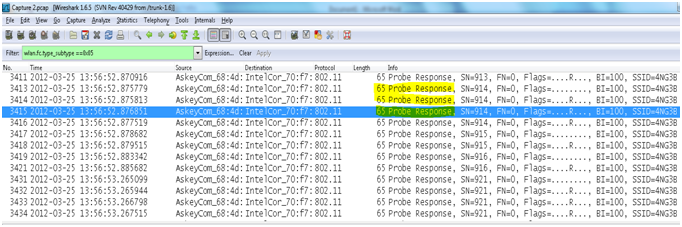
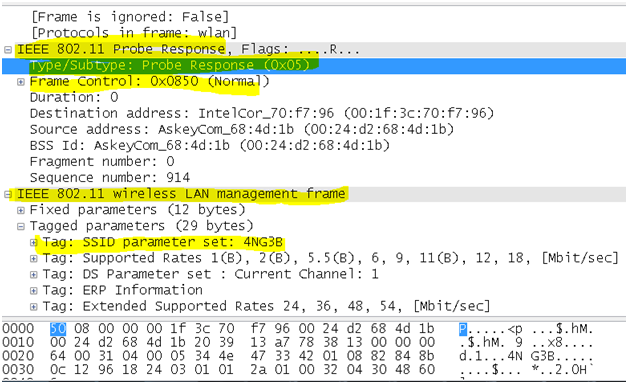
- Probe response frame: In response to the probe request, APS with matching criteria will respond with a probe response frame containing synchronization information and access point load and would contain capability information, supported data rates, etc.
The filter used to apply and find only the Probe request packets is “wlan.fc.type_subtype ==0x05”

Control Frames
802.11 control frames assist in the delivery of data frames between stations. The following are common 802.11 control frame subtypes:
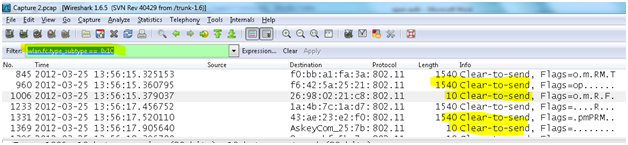
- Request to Send (RTS) frame: The RTS/CTS function is optional and reduces frame collisions present when hidden stations have associations with the same access point. A station sends a RTS frame to another station as the first phase of a two-way handshake necessary before sending a data frame.
wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x1B

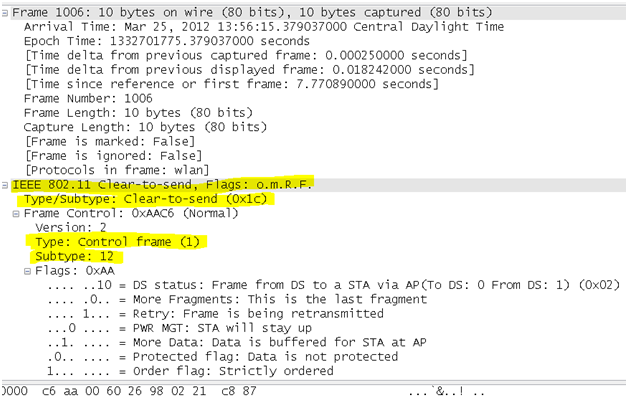
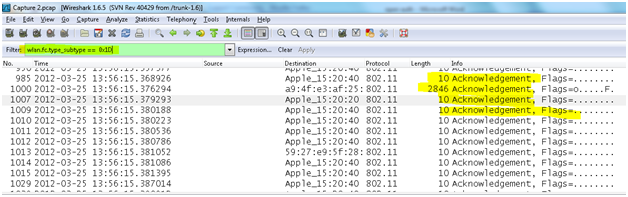
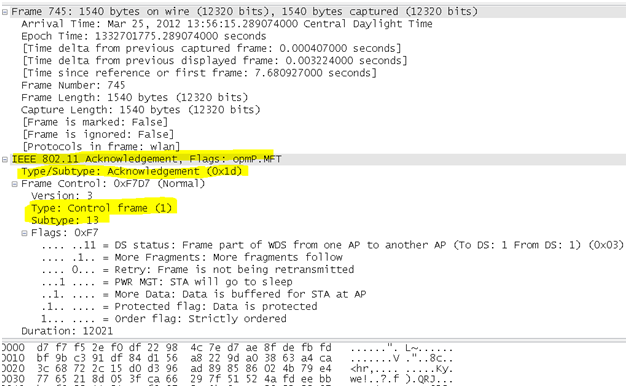
- Acknowledgement (ACK) frame: After receiving a data frame, the receiving station will utilize an error checking processes to detect the presence of errors. The receiving station will send an ACK frame to the sending station if no errors are found. If the sending station doesn't receive an ACK after a period of time, the sending station will retransmit the frame.
wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x1D

Data Frames
These at the frames which come later in the game after the basic wlan communication is already established between the Mobile station and the Access point. We will always reach to this 802.11 data frame for analysis typically to verify and analyze over the air if the protocols and data from higher layers within the frame body is getting through to the wire. These frames transport data packets from higher layers, such as web pages, printer control data, etc., within the body of the frame.
wlan.fc.type_subtype == 0x20

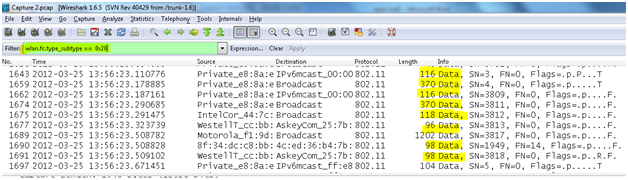
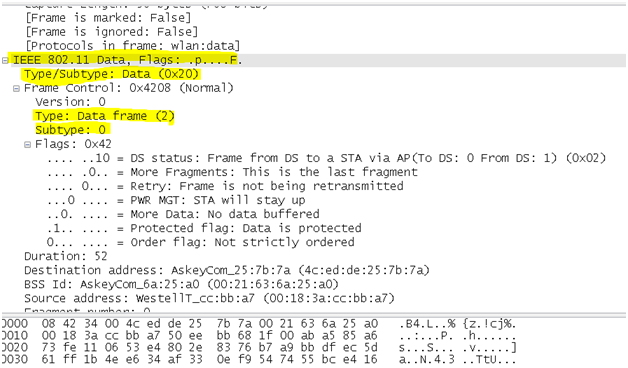
On a packet analyzer we observe the contents of the frame body within 802.11 data frames for interesting traffic in question.
References
- www.wildpackets.com/resources/compendium/wireless_lan/wlan_packets
- http://www.willhackforsushi.com/papers/80211_Pocket_Reference_Guide.pdf
- https://supportforums.cisco.com/docs/DOC-13664
- http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/cc/pd/witc/ao1200ap/prodlit/wswpf_wp.htm#wp39317
- http://www.wildpackets.com/resources/compendium/wireless_lan/wlan_packet_types
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks for sharing, it is a great document. One question...
Right now I'm trying to get some captures but for some reason, the first packet that I see from my client is an Authentication request. I'm not sure why it comes first. I believed the first packet must be a probe request.
I'm using PSK security and then I try with local EAP configuration. I'm using airtool to capture packet and I checked first the transmitting channel like it is my home lab just one client was on the network. Do you have any advice? I'm using a Macbook Pro. I friend told me that I need to try with other channel.
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community:

