- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Wireless - Mobility
- Wireless - Mobility Knowledge Base
- EAP Authentication via Active Directory with ACS 4.0 and Windows 2003
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-26-2012 04:39 AM - edited 11-18-2020 02:59 AM
- Introduction
- Scenario 1
- Scenario 2
- Solution
- Scenario 3
- Solution
- More Information
- PEAP Overview
- PEAP phase one: TLS encrypted channel
- PEAP phase two: EAP-authenticated communication
- Packet flow
- Topology
- Reference
Introduction
In this document, we will see how to perform EAP Authentication via Active Directory with ACS 4.0 and Windows 2003.
Scenario 1
How to authenticate AP via Active Directory instead of WPA2 using Windows 2003 Domain Controller acting as DNS / DHCP?
Solution
If we have a Microsoft IAS or NAP radius server, we can use WPA2/AES PEAP for encryption / authentication method. Refer to the URL below that explains the setup:
PEAP Under Unified Wireless Networks with Microsoft Internet Authentication Service (IAS)
if we have Cisco ACS 4.2 and configured external database for Active Directory, please refer to the documents at the URL below:
EAP Authentication with WLAN Controllers (WLC) Configuration Example
PEAP under Unified Wireless Networks with ACS 4.0 and Windows 2003
Scenario 2
Is Cisco Aironet Desktop Utility (ADU) is required in the above mentioned Scenario 1? Is that free or licensed?
Solution
We don't need ADU specifically because we would need the Cisco wireless card for that, but most of the cards out there support PEAP. Depending on the wireless card, we can configure PEAP. Here is one example for windows.
Ultimate wireless security guide: Manual PEAP deployment for Windows Wireless Client
Protected EAP (PEAP) Application Note
Scenario 3
Cisco aironet 1142n (APs are standalone) access point without ACS / WLC. Is it possible to authenticate end users 802.1x with Active directory 2003/2008 using RADIUS (IAS/NPS)? So "How to authenticate end users with active directory using Cisco 1142n Standalone (Without WLC/ACS)".
Solution
Here it is a configuration example of EAP with wep encryption if you want you can change the encryption and key management to WPA or WPA2 and that will be it...
EAP Authentication with RADIUS Server
Also Use these other documents as reference for setting up the Microsoft side. So whether you use AP as standalone or unified with a WLC this will be helpful.
More Information
PEAP Overview
PEAP uses Transport Level Security (TLS) to create an encrypted channel between an authenticating PEAP client, such as a Wireless laptop, and a PEAP authenticator, such as Microsoft Internet Authentication Service (IAS) or any RADIUS server. PEAP does not specify an authentication method, but provides additional security for other EAP authentication protocols, such as EAP-MSCHAPv2, that can operate through the TLS encrypted channel provided by PEAP. The PEAP authentication process consists of two main phases:
PEAP phase one: TLS encrypted channel
The Wireless client associates with the AP. An IEEE 802.11-based association provides an Open System or Shared Key authentication before a secure association is created between the client and Access Point (LAP). After the IEEE 802.11-based association is successfully established between the client and the Access Point, the TLS session is negotiated with the AP. After authentication is successfully completed between the Wireless client and IAS server, the TLS session is negotiated between them. The key that is derived within this negotiation is used to encrypt all subsequent communication.
PEAP phase two: EAP-authenticated communication
EAP communication, which includes EAP negotiation, occurs inside the TLS channel created by PEAP within the first stage of the PEAP authentication process. The IAS server authenticates the Wireless client with EAP-MS-CHAP v2. The LAP and the Controller only forward messages between the Wireless client and RADIUS server. The WLC and the LAP cannot decrypt these messages because it is not the TLS end point.
After PEAP stage one occurs, and the TLS channel is created between the IAS server and the 802.1X Wireless client, for a successful authentication attempt where the user has supplied valid password-based credentials with PEAP-MS-CHAP v2, the RADIUS message sequence is this:
Packet flow
- The IAS server sends an identity request message to the client: EAP-Request/Identity.
- The client responds with an identity response message: EAP-Response/Identity.
- The IAS server sends an MS-CHAP v2 challenge message: EAP-Request/EAP-Type=EAP MS-CHAP-V2 (Challenge).
- The client responds with an MS-CHAP v2 challenge and response: EAP-Response/EAP-Type=EAP-MS-CHAP-V2 (Response).
- The IAS server sends back an MS-CHAP v2 success packet when the server has successfully authenticated the client: EAP-Request/EAP-Type=EAP-MS-CHAP-V2 (Success).
- The client responds with an MS-CHAP v2 success packet when the client has successfully authenticated the server: EAP-Response/EAP-Type=EAP-MS-CHAP-V2 (Success).
- The IAS server sends an EAP-TLV that indicates successful authentication.
- The client responds with an EAP-TLV status success message.
- The server completes authentication and sends an EAP-Success message using plaintext. If VLANs are deployed for client isolation, the VLAN attributes are included in this message.
Topology
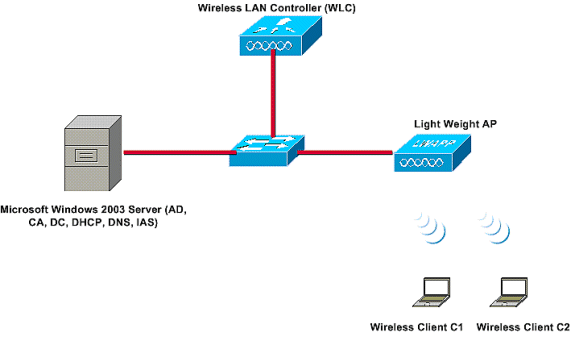
in case of PEAP under Unified Wireless Networks with ACS 4.0 and Windows 2003
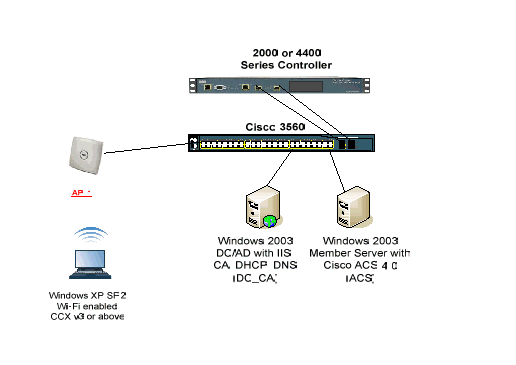
Reference
- PEAP Under Unified Wireless Networks with Microsoft Internet Authentication Service (IAS)
- EAP Authentication with RADIUS Server
- PEAP under Unified Wireless Networks with ACS 4.0 and Windows 2003
- Protected EAP (PEAP) Application Note
This document was generated from the following discussion: Authentication via Active Directory
- 2003
- 4.0
- acs
- active
- active_directory
- and
- application
- authentication
- authentication_windows_2003
- client
- configuration
- configuration_example
- controllers
- deployment
- directory
- eap
- eap_authentication
- example
- for
- ias
- internet
- manual
- microsoft
- networks
- note
- peap
- protected
- radius
- security
- server
- service
- ultimate
- under
- unified
- windows
- wireless
- wlan
- wlc
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: