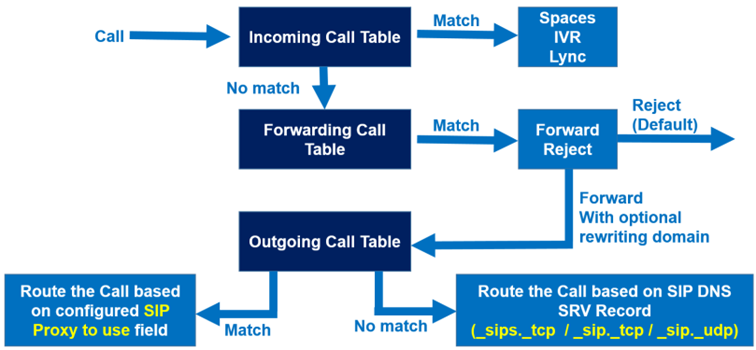
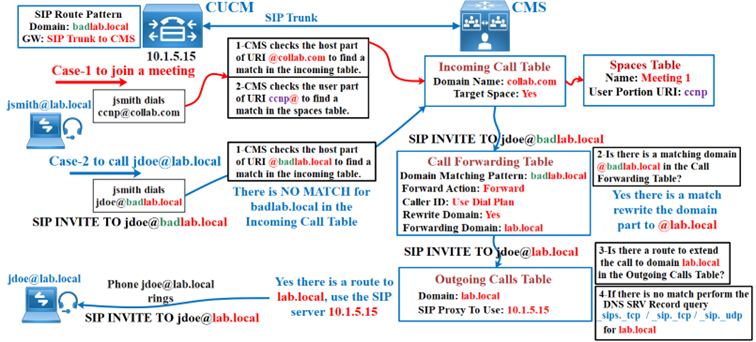
The call routing on CMS involves three call routing tables.
Outbound Dial Plan Rules
It is important to understand how Cisco Meeting Server establishes SIP trunk connections out to other devices and how it manages calls that come from other devices on the network. Cisco Meeting Server uses three dial plan rules to manage all its connections. The first is the Outbound dial plan rule. These rules establish SIP trunks to other devices such as Cisco Unified CM and Cisco Expressways.
Inbound Dial Plan Rules
Inbound rules are the first rules used when a SIP call is received by Cisco Meeting Server. The inbound rules determine what the call is allowed to access if it matches one of the configured domains. For example, the diagram shows that if a call was dialed to the meet.cll-collab.internal domain then they can be connected to any spaces or Interactive Voice Response (IVR) URIs that are configured but they cannot access any Lync conferences.
Call Forwarding Dial Plan Rules
Call forwarding rules are used where a SIP call is received that doesn’t match any of the inbound rules. The assumption is made that the call wants to go out of one of the configured SIP trunks. In the diagram, the Call Forwarding rule shows that if a call is received that has a domain of example.com they are allowed to call this domain and the caller ID will be preserved as the original calling party’s ID (pass through). If you want to transform the dialed domain then by setting the Rewrite domain field to Yes, you can enter the changed domain in the Forwarding domain field. For example, if a call was received to lab.local you could transform the domain to lab.local.ge to potentially affect the calls routing.
Order of call processing:
- Incoming Call Matching Table
- Incoming Call Forwarding Table
- Outbound Call Table
The only exception would be for CMS initiated calls (either CMS directly for TelePresence Management Suite (TMS) scheduled outbound calls or CMA client calls out) in which the call forwarding table is bypassed.
Below the chart flow.