- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Data Center and Cloud
- Data Center and Cloud Knowledge Base
- What is a Service profile in UCS and what are its types
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-25-2009 02:16 AM - edited 03-01-2019 05:50 AM
Introduction
Every server that is provisioned in the Cisco Unified Computing System is specified by a service profile. A service profile is a software definition of a server and its LAN and SAN network connectivity, in other words, a service profile defines a single server and its storage and networking characteristics. Service profiles are stored in the Cisco UCS 6100 Series Fabric Interconnects. When a service profile is deployed to a server, UCS Manager automatically configures the server, adapters, fabric extenders, and fabric interconnects to match the configuration specified in the service profile. This automation of device configuration reduces the number of manual steps required to configure servers, network interface cards (NICs), host bus adapters (HBAs), and LAN and SAN switches.
Service profile Overview
A service profile typically includes four types of information:
a) Server definition: It defines the resources (e.g. a specific server or a blade inserted to a specific chassis) that are required to apply to the profile.
b) Identity information: Identity information includes the UUID, MAC address for each virtual NIC (vNIC), and WWN specifications for each HBA.
c) Firmware revision specifications: These are used when a certain tested firmware revision is required to be installed or for some other reason a specific firmware is used.
d) Connectivity definition: It is used to configure network adapters, fabric extenders, and parent interconnects, however this information is abstract as it does not include the details of how each network component is configured.
A service profile is created by the UCS server administrator. This service profile leverages configuration policies that were created by the server, network, and storage administrators. Server administrators can also create a Service profile template which can be later used to create Service profiles in an easier way. A service template can be derived from a service profile, with server and I/O interface identity information abstracted. Instead of specifying exact UUID, MAC address, and WWN values, a service template specifies where to get these values. For example, a service profile template might specify the standard network connectivity for a web server and the pool from which its interface's MAC addresses can be obtained. Service profile templates can be used to provision many servers with the same simplicity as creating a single one.
Service profile types
There are two types of service profiles in a UCS system:
a) Service profiles that inherit server identity: These service profiles are similar in concept to a rack mounted server. These service profiles use the burned-in values (like MAC addresses, WWN addresses, BIOS version and settings, etc.) of the hardware. Due to the nature of using these burned-in values these profiles are not easily portable and can’t be used from moving one server to the other. In other words these profiles exhibit the nature of 1:1 mapping and thus require changes to be made to them when moving from one server to another.
b) Service profiles that override server identity: These service policies exhibit the nature of stateless computing in UCS system. These service profiles take the resources (like MAC addresses, WWN addresses, BIOS version, etc.) from a resource pool already created in the UCS manager. The settings or values from these resource pools override the burned-in values of the hardware. Hence these profiles are very flexible and can be moved from one server to the other easily and this movement is transparent to the network. In other words these profiles provide a 1: many mapping and require no change to be made to them when moving from one server to another.
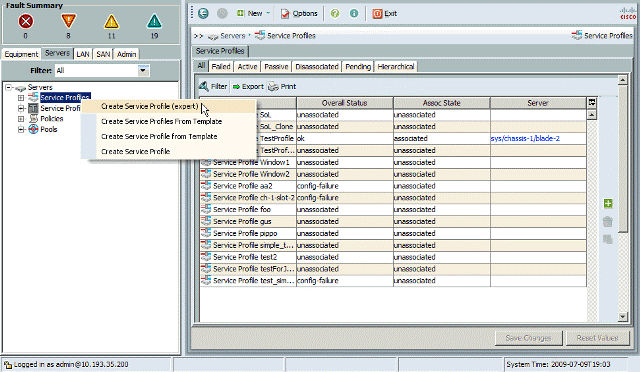
To create a Service profile navigate to the Servers tab, right click on Service Profiles and choose Create Service Profile.
Video
Watch this video to learn more about Service Profiles on UCS.
Related Information
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Short but to the point, nice document Sandeep!
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The video link and the FAQ links are broken. Is it possible to get access to the correct links?
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: