- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Internet of Things Knowledge Base
- Quick Reference: Cisco IE5000 IRIG-B Support
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on 04-08-2021 12:01 PM
Quick Reference: Cisco IE5000 IRIG-B Support
Cisco Industrial Ethernet 5000 series switches (IE 5000) have integrated hardware support for external time sources: GPS antenna and IRIG-B (analog and digital timing I/O) interfaces. These interfaces are complemented with network time distribution protocols like Precision Time Protocol (PTP) and Network Time Protocol (NTP) making the IE 5000 a robust hardened industrial platform with strong precision timing capabilities.
This quick reference document focuses on the IE 5000’s IRIG-B capabilities: support, configuration, and verification.
IRIG-B: Background information
The Inter-Range Instrumentation Group (IRIG) time codes are the result of the US military’s need to standardize test ranges’ timing codes towards the end of the 1950s. This standardization resulted in a common set of time codes that eliminated incompatibility challenges and allowed for the exchange of synchronized test data across ranges. Six IRIG codes variations were developed (A, B, D, E, G, H) of which IRIG time code B (IRIG-B) became widely accepted for time distribution with power, industrial automation, and control industries.
|
Quick Note on IRIG-B |
|
Today, it is believed that ~90% of substations have IRIG-B installations. Modern substation automation networking devices, especially those providing timing / synchronization, should include support IRIG-B. This support in combination with newer, more precise, cost effective, and reliable timing technologies, should safely accelerate substation automation modernization efforts.
IRIG-B: IE 5000 Support Overview
The IRIG protocol in the IE 5000 has been implemented for format-B (IRIG-B) per IRIG standard 200-04 with capabilities to receive (INPUT) or transmit (OUTPUT) 4x Analog (AM) and 4x Digital (TTL) time code formats, see table below.
|
IE5000 IRIG-B Modes |
Format ID |
IRIG Signal |
|
|
Analog (AM) |
AM02 |
AM-B122 |
Amplitude Modulated, 1kHz / 1ms resolution, BCDTOY |
|
AM03 |
AM-B123 |
Amplitude Modulated, 1kHz / 1ms resolution, BCDTOY, SBS |
|
|
AM06 |
AM-B126 |
Amplitude Modulated, 1kHz / 1ms resolution, BCDTOY, BCDYEAR |
|
|
AM07 |
AM-B127 |
Amplitude Modulated, 1kHz / 1ms resolution, BCDTOY, BCDYEAR, SBS |
|
|
Digital (TTL) |
TTL02 |
TTL-B002 |
Unmodulated, DCLS, pulse-width-coded, BCDTOY |
|
TTL03 |
TTL-B003 |
Unmodulated, DCLS, pulse-width-coded, BCDTOY, SBS |
|
|
TTL06 |
TTL-B006 |
Unmodulated, DCLS, pulse-width-coded, BCDTOY, BCDYEAR |
|
|
TTL07 |
TTL-B007 |
Unmodulated, DCLS, pulse-width-code, BCDTOY, BCDYEAR, SBS |
|
IRIG-B INPUT and OUTPUT vs. Time Sources
The IE 5000 hardware has 2 physical interfaces (details in a following section), one for analog (AM) and one for digital (TTL), with INPUT or OUTPUT signal capabilities per interface.
This IRIG-B INPUT / OUTPUT signaling support allows the IE 5000 to be a central timing device in multiple use-cases:
-
INPUT: The IE 5000 receives IRIG-B timing signaling (AM or TTL) from an IRIG-B time source if only available or so required. In this case IRIG-B can be used as the IE 5000’s clock source for PTP (only) - IE 5000 configured as Grand Master Clock (GMC) for time distribution.
-
OUTPUT: The IE 5000 utilizes other precise timing sources, e.g., GNSS/GPS, PTP, NTP, as a clock source. The IRIG-B interface(s) can be used to transmit timing signal to IRIG-B dependent devices in location.
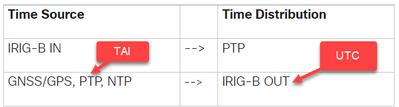
Basically, the IE 5000 supports IRIG-B IN and IRIG-B OUT in addition to the GNSS/GPS interface. The following table shows the mapping of Time Source to time distribution protocol alignment (i.e. one will serve as time source to the other).
|
Time Source |
Time Distribution |
|
|
IRIG-B IN |
--> |
PTP |
|
GNSS/GPS, PTP, NTP |
--> |
IRIG-B OUT |
IRIG-B: IE 5000 Software and Hardware
IOS Software Requirements
As of this publication the latest IE 5000 IOS software supports IRIG-B INPUT and OUTPUT capabilities. However, the following table shows the minimum IOS versions required to support either IRIG-B signaling direction. As always, please review version release notes and follow Cisco’s recommendations before upgrading IOS versions in your IE 5000.
|
IRIG-B Direction |
Minimum IOS support |
|
OUTPUT |
15.2(5)E |
|
INPUT |
15.2(5)E2c |
IRIG-B Physical Interface Characteristics
As mentioned earlier, the IE 5000 has two IRIG-B physical interfaces. The following image and table describe the physical characteristics. Customers will need to purchase or build cables for their IRIG-B connectivity following the IRIG-B standard and IE 5000’s specifics. These cables are NOT provided with the platform.
|
IRIG-B Interface |
Type |
Input High Impedance |
|
Digital Timing I/O |
mini-BNC (female) |
~1 mega-Ohm |
|
Analog Timing I/O |
mini-BNC (female) |
~8 kilo-Ohm |
Note: IRIG Impedance and mini-BNC connectors
- IRIG typically uses 50 Ohm lines vs. IE 5000’s mini-BNC connector being 75 Ohm.
- Given IRIG-B’s 1KHZ frequency (300km wavelength) and the slow signal edges, an unreasonably long cable would be needed before transmission-line impedance mismatches start to matter.
- mini-BNC connector can be found at: https://belfuse.com/product-detail/trompeter-coax-solutions-coax-connectors-mini-bnc-coax-connectors
Configuration Scenario: IRIG-B OUT and IRIG-B IN
This configuration scenario shows two IE 5000 platforms configured to use IRIG-B signaling in different ways. Scenario context:
- Time source GNSS/GPS, IRIG-B TTL07 OUT for time distribution - IE 5000 (v23-ie5000-2)
- Time source IRIG-B TTL07 IN, PTP for time distribution - IE 5000 (v23-ie5000-4)
NOTE: Please check the reference section for links to the IE 5000's GNSS/GPS and PTP configuration guides.
IRIG-B Configuration Statement
A single IRIG-B configuration command statement is used for IRIG-B mode and signal direction (IN and OUT) per interface - a total of two possible IRIG-B configuration statements.
Configuration Command >> irig mode <mode> dir <in/out>
CLI view of configuration options:
v23-ie5000-4(config)#irig mode ?
AM02 AM-B122 format
AM03 AM-B123 format
AM06 AM-B126 format
AM07 AM-B127 format
TTL02 TTL-B002 format
TTL03 TTL-B003 format
TTL06 TTL-B006 format
TTL07 TTL-B007 format
v23-ie5000-4(config)#irig mode TTL07 dir ?
in input direction
out output direction
A. Time Source GNSS/GPS, IRIG-B OUT for Time Distribution
This IE 5000 (v23-ie5000-2) is configured to use its GNSS/GPS interface and consequently GPS as its time source - IRIG-B will source its time from GPS. The IRIG-B digital interface is configured to provide timing signal (OUT) to the other IE 5000 (v23-ie5000-4).
v23-ie5000-2(config)#gnss <<<--- Enabling GNSS
v23-ie5000-2(config)#irig mode TTL07 dir out <<<--- IRIG-B mode TTL07 signal, OUTPUT direction
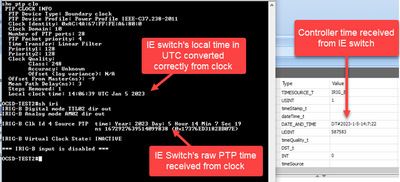
Verifying IRIG-B OUTPUT and GNSS being used as IRIG-B's time source:
v23-ie5000-2#show irig
IRIG-B Digital mode TTL07 dir out <<<--- Confirms IRIG-B mode and direction as configured (OUT)
IRIG-B Analog mode disabled
IRIG-B Clk Id 3 Source GNSS time: Year: 2021 Day: 98 Hour 15 Min 7 Sec 20 <<-- GNSS Clock source
ns 1617894440419015968 (0x1673EA6BED413D20)
IRIG-B Virtual Clock State: INACTIVE <<<--- IRIG-B clock inactive, not an internal time source
*** IRIG-B input is disabled ***
B. Time Source IRIG-B IN, PTP for Time Distribution
This IE 5000 (v23-ie5000-4) is configured to receive IRIG-B TTL07 (IN) timing signal from the other IE 5000 (v23-ie5000-2) and use it as its time source. This in turn will be used as the timing source for PTP for time network distribution. No other timing sources or protocols are configured.
v23-ie5000-4(config)#ptp mode gmc-bc delay-req <<<--- IE5000 configured for PTP as GMC-BC
v23-ie5000-4(config)#irig mode TTL07 dir in <<<--- IRIG-B mode TTL07 signal, INPUT direction
Verifying IRIG-B INPUT as time source and PTP sourcing time from IRIG-B:
v23-ie5000-4#show irig
IRIG-B Digital mode TTL07 dir in <<<--- Confirms IRIG-B mode and direction as configured (IN)
IRIG-B Analog mode disabled
IRIG-B Clk Id 2 Source IRIG-B time: Year: 2021 Day: 98 Hour 15 Min 7 Sec 20 <<-- IRIG-B source
ns 1617894440918157031 (0x1673EA6C0B0186E7)
IRIG-B Virtual Clock State: ACTIVE <<<--- IRIG-B clock active, time source possible for PTP
*** IRIG-B TTL input mode ***
B007 : Year 21 Day 98 Hour 15 Min 7 Sec 19 SBS 0xD4A7(54439) <<-- TTL-B007 signal received
NOTE: Input time shown is the last received frame time
Verifying PTP protocol recognizing IRIG-B as its clock source:
v23-ie5000-4#sh ptp time-property PTP CLOCK TIME PROPERTY Current UTC offset valid: FALSE Current UTC offset: 0 Leap 59: FALSE Leap 61: FALSE Time Traceable: FALSE Frequency Traceable: FALSE PTP Timescale: FALSE Time Source: Other <<--- This denotes IRIG-B (see NOTE below)
NOTE: Time source "Other" is used to identify IRIG-B as there is no IRIG classification in PTP messaging. If NTP was configured as as the source then it would show "Time Source: NTP".
Additional Resources
- Cisco Industrial Ethernet 5000 Series Switches Data Sheet, https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/industrial-ethernet-5000-series-switches/datasheet-c78-734967.html
- Global Navigation Satellite System for IE 5000, https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/connectedgrid/cg-switch-sw-master/software/configuration/guide/gnss/b_gnss.html
- Precision Time Protocol Software Configuration Guide for IE 4000, IE 4010, and IE 5000 Switches, https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/cisco_ie4000/software/release/15-2_4_e/b_ptp_ie4k.html
- Engage Cisco's IOT community for questions:
- IRIG-B Standard, http://www.irigb.com/IRIGB_standard.html
- Overview of IRIG-B Time code standard, https://www.itsamerica.com/assets/publications/TN-102_IRIG-B.pdf
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Ok, thanks.
just to get re-asurance: the IE5000 when sync'd with IRIG-B can not be configured to distribute the time as NTP clock source to attached computers, only PTP is supported.
Is that correct? That is what I understand from the description. It would be ok, just has influence on the time system design.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Great content! Related question: The IRIG connectors visually do look like BNC (Mini-BNC?); but what about the GNSS port? Are they mini BNC? Normal BNC? Micro BNC? I checked the normally extremely detailed Cisco hardware installation guide for the IE-5000 and to my surprise no mention
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
> but what about the GNSS port?
They are SMA connectors (female).
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks for this article. Related question: We are trying to distribute IRIG-B with PTP from a satellite clock as the time source. However, we noticed that the IE5000 does not apply the TAI to UTC offset (37 seconds as of today) to the IRIG-B time out. Since IRIG-B is always UTC, all end devices are receiving a time different than UTC causing problems in the system. Is there something that we are missing to fix this?
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: