In traditional IPsec, two IKE tunnels are built in order to establish a VPN Site to Site
Phase 1 Isakmp Tunnel: Negociated between peers to protect the Phase 2 IPsec Tunnel negociation. In this step the authentication occurs between peers using either PSK or Certificates, the type of encryption and hashing.
Phase 2 IPsec Tunnel: parameters are negociated securely through the Tunnel of Phase 1 such as Encryption Algorithm and HMAC, AH or ESP protocols. This tunnel is to protect the users’s Data.
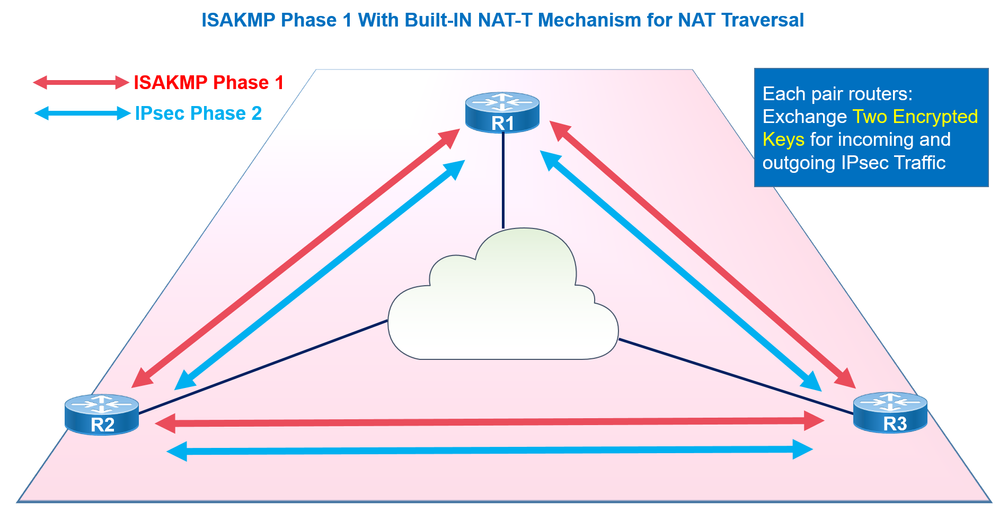
Now the Encrypted Key of the Encryption Algorithm that will be used to protect our Data in the IPsec Tunnel is negociated via Diffie-Hellman in the Phase 1 and protected by the ISAKMP Tunnel.
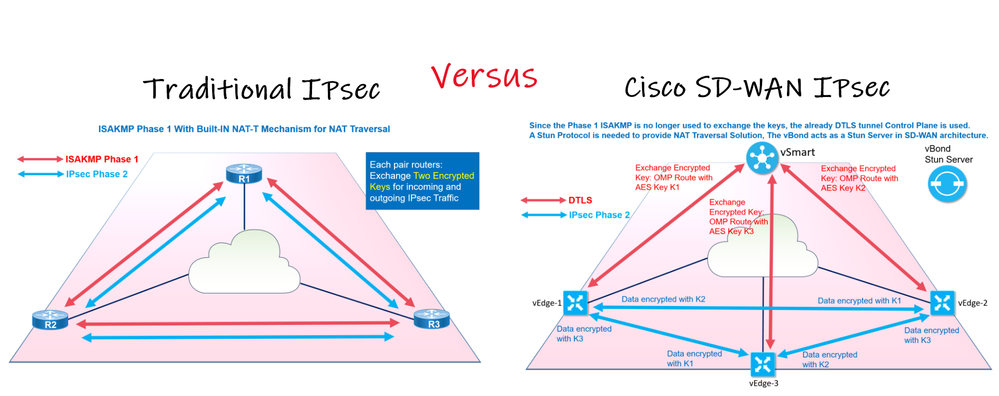
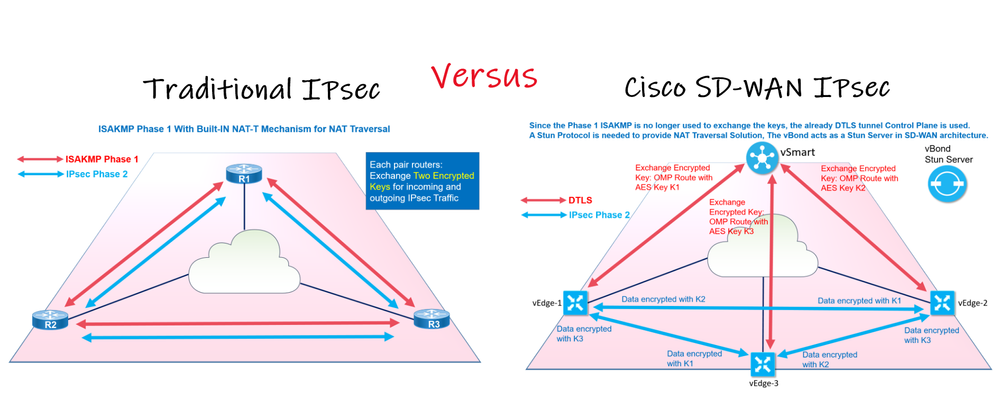
In SD-WAN, the developpers changed and optimized the IPsec Operation by removing the Phase 1 (ISAKAMP Tunnel) which traditionally handles key exchanges because the IKE negociation can become a scalability issue when a network grows larger and larger and impact the CPU.
-First: there is no need for peers to authenticate each other, since the vEdges routers are initially joined the Overlay SD-WAN by authenticatin these devices.
-Second: a secure control plane with DTLS is already built between vEdges and vSmart and we can leverage this for Data Plane negociation (our Phase 2 IPsec Tunnel), so instead of having several IKE negociation and phases 1 between each pair of vEdges, each vEdge will generate its own encrypted key and sent it to vSmart through OMP Route inside the DTLS tunnel, the vSmart replicates these encrypted keys between vEdges using also the same DTLS.
In short the traditional phase 1 negociation is done within the control plane. Since the vEdges has already a Tunnel (DTLS) to the Control Plane vSmart.
Removing the Phase 1 optimizes the IPsec negociation by reducing CPU resources for vEdges by centralizing the KEY exchanges negociation through vSmart.
But we lost the RFC 3947 Negotiation of NAT-Traversal built-in in the Traditional IPsec in order to solve the NAT issue when a peer is behing a NAT device.
To overcome this problem, a Stun Protocol is introduced to replace the traditional NAT-T mechanism. Like in Collaboration either in MRA deployment or WebRTC with Cisco CMS where Cisco Expressway-E plays a role of the Stun/Turn Server. The vBond is the Expressway in the SD-WAN architecture, it is the Stun server that the vEdge behind the NAT will solicit in order to discover its own Public IP.
