- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Networking Blogs
- What’s New? IOS XE 17.7 Routing Release Update
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Cisco's latest release of the IOS-XE train – IOS-XE Cupertino 17.7 on December 15, 2021, brings an expansive list of robust features and enhancements to current networking technologies. Along with the addition of new hardware to the EN Routing portfolio.
New Platform Introduction
Let's start by introducing the newest platform in the EN Routing portfolio…
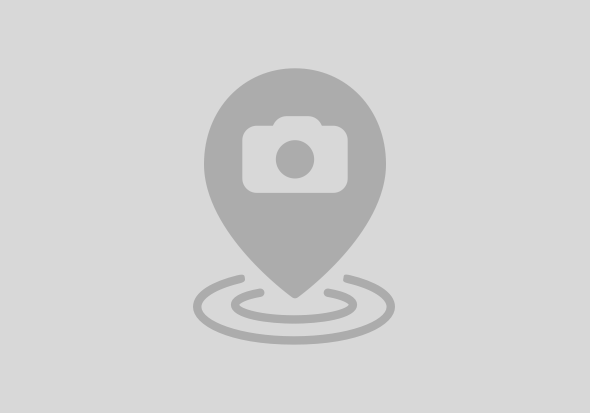
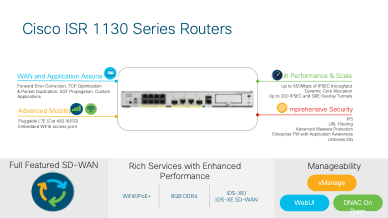
The ISR 1130 Series. The 1130s have full feature parity with the rest of the ISR1K platforms; they come with eight built-in switch ports, optional pluggable LTE modules that can support the speeds of CAT 4, CAT 6, and CAT 18, with 5G on the roadmap, slated for mid-2022 compatibility.
While specifications seem in line with predecessors, a key differentiator for the 1130 series is it is the first router in the EN portfolio to support Wi-Fi6. The unit has an embedded access point with a built-in wireless controller to manage the AP; alternatively, the AP can be configured to reach out to a centralized wireless controller. Finally, the ISR 1130 supports vManage, DNAC on-prem, and a local WebUI for network management.
WiFi6 has helped make our smart devices even more intelligent. We are seeing more IoT devices being deployed today than ever before. From factories, hospitals, enterprise buildings, there are many small IoT sensors counters that show a significant improvement when operating over WiFi6 compared to WiFi5. These advantages can be implemented over to any type of deployment running on Wi-Fi 5 today. The ISR 1130s will help drive this adoption of Wi-Fi 6 across enterprise networks.
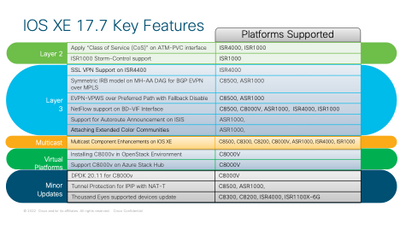
IOS XE 17.7 Key features
In the following sections, we will discuss new software features that this release brings to ISR1000/4000, ASR1000, and Catalyst 8000 routing platforms. Below is a high-level list of features/ enhancements that span Layer 2, Layer3, Multicast, and Virtual Platforms.
 "CoS" or Class of Service
"CoS" or Class of Service
As many are aware, "QoS (Quality of Service)" is used to allocate bandwidth to several types of traffic across the network. It helps reduce packet loss, latency, and jitter. It is implemented with the Class of Service information from Layer 2 – which marks each packet with a priority level and at Layer 3 via the DSCP values.
Why is it implemented?
The command that is used to apply Class of Service is "set cos-inner," followed by a number from 0 to 7 based on the priority. However, the set cos-inner command applies to a QinQ VLAN – which means the packet should have 2 VLAN tags which were acceptable for an ethernet interface, but the packet sent over the ATM interface is a dot1Q packet that has only one VLAN tag.
Enhancements Starting with 17.7
So, a new command has been introduced in 17.7. The "set cos" command is followed by the priority value to overcome this issue.
ISR1000 Strom-Control support
A storm occurs on the LAN when we have an overflow of packets that cannot be processed fast enough. This storm causes some packets to drop, resulting in network performance degradation.
Why does it matter?
Using storm control, we can prevent useful traffic from being disrupted, by configuring a threshold level for each traffic type – that is a separate threshold for broadcast, one for multicast, and one for unicast traffic; so that if a broadcast storm occurs, only broadcast traffic is discarded but any unicast or multicast traffic is passed through the LAN network.
SSL VPN allows remote users to access enterprise network resources over the internet through a secure VPN tunnel, commonly using a software client like AnyConnect. However, SSL VPN was only supported on CSR1K and Catalyst 8KV.
Enhancements Starting with 17.7
From 17.7, we have extended SSL VPN support to the ISR4K series, on the 4431, 4451, and 4461 platforms. This is implemented by creating one virtual access interface per SSL VPN session.
Currently, the restriction is that this feature is not supported for IPv6 or SD-WAN.
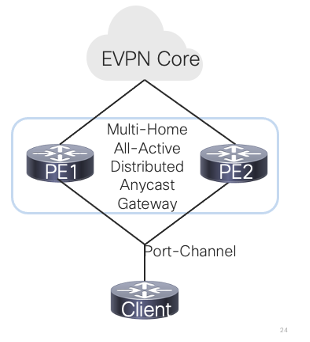
Symmetric IRB model on MH-AA DAG for BGP EVPN over MPLS
The next feature on the list is the Symmetric IRB model of MH-AA DAG for BGP EVPN over MPLS. What a mouthful! Let's break it down!
Symmetric: Both the Provider Edges will equally share packet processing associated with the client.
IRB: Allows the Provider Edge to forward both Layer 2 bridging and Layer 3 routing information.
DAG: Distributed Anycast Gateway. It is an addressing mechanism that allows the client to connect to both PEs as its default gateway.
Symmetric routing and bridging over distributed gateways are already supported for SINGLE HOMING. But in a multihoming setup, traffic from the host may go through either PE
Today's Challenge Complexity is around probing the clients to see if they are alive. When one PE sends a probe to the client, the reply may go to the other. The 2 PE routers must be able to update one another regarding the client's activities.
Enhancements Starting with 17.7 With the release of 17.7, the Multihoming all active feature is supported by implementing the following enhancements.
- Symmetric IRB for IP-VRF to IP-VRF inter-subnet traffic over MPLS Transport
- Distributed Anycast Gateway with Bridge-Domain
- Host MAC-IP Learning on MH-AA DAGs
- ARP/ND (Neighbor Discovery) Synchronization for MH-AA IRB
- MAC-IP Proxy Route for MH-AA IRB
EVPN-VPWS over Preferred Path with Fallback Disable
EVPN-VPWS (Virtual Private Wire Service) utilizes the control plane to distribute Layer 2 MAC and Layer 3 IP information. Using the control plane enables load balancing and improves convergence times in case of network failure. Segment Routing for Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) uses policies to steer traffic through the network.
Enhancements Starting with 17.7 From 17.7, EVPN-VPWS supports Segment Routing policies using the preferred path feature, with a new command that disables the fallback to an alternate path.
The restrictions for this feature are that Segment Routing on Demand Next Hop policy is not supported, we only support static policies in this release; Per Flow Policies are also not supported; only per destination policy support is available.
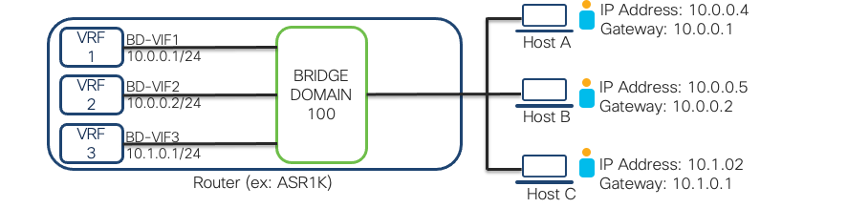
NetFlow support on BD-VIF Interface
17.7 brings the feature of NetFlow on the Bridge Domain Virtual IP interface. Traditionally, one Bridge Domain Interface (or BDI) is associated with a single VRF. Cisco introduced a new logical interface in previous IOS XE releases, called the Bridge Domain Virtual IP Interface (BD-VIF) which allowed you to connect a single Bridge Domain to multiple VRFs.
Today's Challenge Customers want to perform traffic analysis, security monitoring, and network planning features on the BD-VIF interface using NetFlow.
Enhancements Starting with 17.7
In 17.7, we can use the IP flow monitor command to configure FNF (Flexible Netflow) on this interface. In terms of performance and scale, we support 100 BD-VIFs per Bridge Domain on the ASR 1000 and 16 BD-VIFs on the ISR4000 per bridge domain
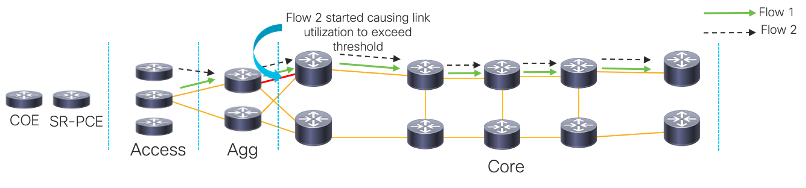
Support for Autoroute Announcement on ISIS
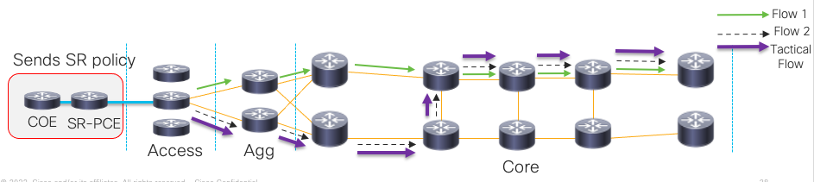
AA is a steering mechanism that can direct some traffic away from congested links and better utilize the network. AA is performed by using CrossWorks Optimization Engine (or COE). COE provides real-time network optimization, which we can use to send Segment Routing Traffic Engineering policies. The Path Computational Element (PCE) and COE compute a suitable path to divert flows and alleviate congestion.
Enhancements Starting with 17.7 Starting from 17.7, When COE detects that the link utilization of any of the links crosses a user-specified threshold, it provisions a tactical SR (Segment Routing) policy in the access router. ISIS running in the access router will receive the SR policy through Autoroute Announcement. And as you can see from this topology, the congestion is alleviated with the tactical flow being implemented.
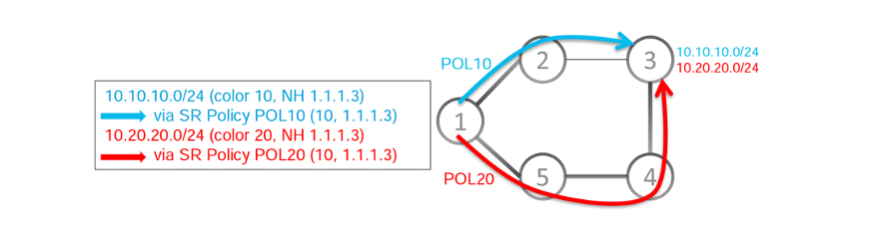
Attaching Extended Color Communities
BGP uses color and next-hop prefix information to create an SR Policy and automatically steer traffic to the destination. The color of a route is specified by its color extended community attribute, and it can be used to indicate specific treatment.
Today's Challenge
Currently, color extended community assignment to a prefix was only possible via neighbor prefix advertisements (identify the neighbor and assign a color for each path). That is assigning a color to the neighbor prefix command.
Enhancements Starting with 17.7
From 17.7, 4 new techniques to assign color have been introduced, allowing greater control, and providing flexibility to the SR-TE policies. This is done using Export VRF, Import VRF, Neighbor inbound, and source-protocol prefixes.
Multicast Enhancements
To improve product usability and manageability, various enhancements have been made to Multicast components on IOS XE. The release of 17.7 includes support for retrieving control plane information for a multicast route; YANG model enhancements for 583 CLIs for IPv4; and supports debugging up to 8 VRFS at the same time.
Installing C8000V in OpenStack.
OpenStack is an open-source cloud infrastructure software that is used by many customers as a hypervisor manager to host virtual machines, including the C8000V.
Today's Challenge
Traditionally, customers used a file injection method to onboard a device to vManage. With the newest version of OpenStack – the TRAIN release – file injection method is not supported since it was considered insecure and not very user-friendly.
Enhancements Starting with 17.7
From 17.7, C8000V VMs (Virtual Machine) can be installed by using a simplified workflow called a "Heat" template. This allows for Day-0 configurations to be added to the router to boot in Controller mode or Autonomous mode as needed. The supported Formats for Day-0 configuration are: iosxe_config.txt, ovf-env.xml, ciscosdwan_cloud_init.cfg.
Support for the Catalyst 8000v on Azure Stack Hub
Using the Azure Public Cloud instance, there is a well-established process to bootstrap Catalyst 8000v devices, using the Azure Meta-Data Service (AMDS), which is a cloud-only feature, that provides the Day-0 configuration files to C8Kv.
Today's Challenge The challenge that we face with the on-prem Azure instance is that AMDS is not supported on it. So, we need to support a different way for Day-0 configuration. One method would be consoling into the router, but we do not have console access for VMs on Azure Stack Hub today. Microsoft plans to support console access in the future, which makes bootstrapping a file onto the C8Kv the only viable solution.
Enhancements Starting with 17.7
Starting from the 17.7 release, the Day-0 configuration will be supported by attaching an OVF file to the C8kv on Azure Stack Hub. And it will be supported only in autonomous mode for this release.
Ship in "install mode" instead of "bundle mode"
In previous releases, images were installed using a .bin file. The router would go through various images before locating the correct one for that device and then boot up. Also, when inserting a new module or chassis, manual intervention was required to get the new switch running on the same version as active switches or modules.
Enhancements Starting with 17.7
With the 17.7 release, Catalyst 8200, 8300, 8500, and 8500L will ship in 'install mode,' which enables a faster boot time, image auto-upgrade, increased flexibility, and improved performance.
Minor Updates
Additional updates that come with the release of 17.7 will bring the C8000V platform up to date with DPDK 20.11, which will address defects, performance, and potential new driver support. The software also includes a Bug fix to Tunnel Protection for IPIP with NAT-T to support features on IOS XE routing platforms. Finally, Thousand Eyes support is brought to the ISR1100X-6G.
Conclusion
A unified software release for Enterprise Networking, 17.7 brings support for new software features and enhancements to numerous routing technologies. Further, 17.7 brings the introduction of the ISR11030 series to the EN routing portfolio aimed to empower the increasing demand for Wi-Fi 6 network deployments. This software enhancement will ensure Cisco's EN technology and platforms can meet the evolving demands of customer networks across various industries.
Please check below for a complete list of features, Release notes, and Configuration guide related to the 17.7 release.
**Author and owner of 17.7 release deck**
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: