- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Networking Knowledge Base
- IPv6 - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
05-11-2011 04:51 AM - edited 03-01-2019 04:40 PM
Introduction
This document contains Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ's) about Internet Protocol Version 6(IPv6).
Q. How to limit clients getting an IPv6 address without using a DHCP server ?
A. Use the command"ipv6nd prefix <prefix> no-advertise".This will set a bit in theIPv6 NA packets to tell hosts not to use this prefix for autoconfiguration.
.
Q. When configuring Dual Stack VRF,IPv6 address family is not listed as shown in the example
Ex: Router(Config-vrf)#address-family
ipv4 Address family
Router(config)#interface GigabitEthernet0/0.901
Router(config-subif)#ipv6 en
Router(config-subif)#ipv6 enable
%GigabitEthernet0/0.901 is linked to a VRF. Enable IPv6 on thatVRF first.
A. In ""show version"", check if the Data license is activated.
Router# show version
Technology Package License Information for Module:'c2900'
Technology
Technology-package
Technology-package
Technology-package
| Current | Type | Next reboot | |
| ipbase | ipbasek9 | permanent | ipbasek9 |
| security | None | None | None |
| uc | None | None | None |
| data | None | None | None |
Activate the data license then check, the IPv6 address family will be enabled
Router(config-vrf)#address-family ?
ipv4 Address family
ipv6 Address family
Q. What is the equivalent command in IPv6 to the "ip igmp helper-address"command?
A. The command is "ipv6 mld host-proxy".MLD proxy feature works in 15.1.2T or later IOS release.
Q. Why Windows 2003 machine not getting IPv6 address from a DHCP server configured on Cisco 1800 series router?
A. Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 do not support DHCPv6-based IPv6 address configuration. For further information
refer http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb726956.aspx
Q. In a dual stack network, does the HSRP configuration for an existing interface use the same group ID as the IPv4 group?
A. HSRP for IPv4 and IPv6 do not have the same group number. One can use any valid group number for either protocol
Q. Is MHSRP supported on IPv6?
A. Yes,here is a sample IPv6 MHSRP (Multi HSRP) configuration.
Rtr1 Configuration
------------------
interface Vlan10
ipv6 address 2620:A3::188/64
standby 100 ipv6 FE80:2620:A3::189
standby 100 timers 1 4
standby 100 priority 101
standby 101 ipv6 FE80:2620:A3::190
standby 101 timers 1 4
standby 101 priority 200
standby 101 preempt
!
Rtr2 Configuration
------------------
interface Vlan10
ipv6 address 2620:A3::187/64
standby 100 ipv6 FE80:2620:A3::189
standby 100 timers 1 4
standby 100 priority 200
standby 100 preempt
standby 101 ipv6 FE80:2620:A3::190
standby 101 timers 1 4
standby 101 priority 101
!
On Router 1
Router1#show standby brief
P indicates configured to preempt.
|
Interface Grp Pri P State Active Standby Virtual IP
Vl10 100 101 Standby FE80::5675:D0FF:FE39:F77F
local FE80:2620:A3::189
For IPv6 HSRP Configuration example, refer document "IPv6 HSRP Configuration Example"
Q. What's the recommended method to inform IPv6 clients about a dhcpv6 server?
A. The command that enables IPv6 Relay Agent on an interface:ipv6 dhcp relay destination <IPv6 address>
For more information on this command refer :http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/docs/ios/ipv6/configuration/guide/ip6-dhcp.html#wp1054443
Q. Getting Error Message when creating address-family for IPv6 on the 7600 as shown in the example:
Example : Router(config-vrf)#address-family ipv6
% VRF address family ipv6 is not supported or not enabled
% Can't activate address-family 'ipv6'
A. In order to enable IPv6 in a VRF, enter the ""mls ipv6 vrf"" command in global configuration mode. If this command is not used, a VRF is supported only for the IPv4 address family. Example: Router(config)# mls ipv6 vrf.For further information on this command refer:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/command/reference/ipv6_09.html#wp2335362
Q. Can I use two different BGP public AS's like 13445 and 109, one for IPv4 and one for IPv6.
A. No, for ASes one can only configure one BGP instance(AS) per box. This is a restriction of both IPv4 and IPv6.
Q. What is the different between IPv6 Multicast Address and Anycast Address ?
A. Both Multicast address and Anycast Address identifies a group of nodes or interfaces.Traffic destined for a multicast address is forwarded to
all the nodes in the group where as the traffic destined to an anycast address is forwarded to the nearest node in the group. An anycast address
is essentially a unicast address assigned to more than one interface. For example to identify the set of routers attached to a particular subnet,
Subnet-Router anycast address is used. The Subnet-Router anycast address is represented by which has a host ID of 0 (0000:0000:0000:0000)
and "subnet prefix" in an anycast address is the prefix that identifies a specific link.
Q. Does a 7206VXR router support IPV6 Dual Stack Implementation?
A. Yes. It is supported.
.
Q. On configuring an IPv6 HSRP standby group, run into an error message: "%FHRP group not consistent with already configured groups on the switch stack."
A. Only HSRP version 2 supports both IPv4 and IPv6. So configure "standby version 2" under interface.
Q. Error message: "% BGP context not been initialized properly." when Configuring neighbor under address-family IPv6
A. The issue is with the feature set. If the feature set is SP services, the following services are not supported.
- IPv6 Routing: Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IPv6
- IPv6 Routing: Multiprotocol BGP Link-local Address Peering
To use these features,change the feature set to Advanced Enterprise Services.
.
Q. How to configure IPv6 netflow?
A. Configuring IPv6 netflow means configuring collection of hardware-routed IPv6 flows. IPv6 netflow is independent of IPv4 netflow except for export configuration, which is same for both. For commands and configuration example, check: How to configure Netflow v9 for IPv6
Q. When configuring IPv6 Netflow on Catalyst 6500 at the interface level,there is no ability to specify the direction of flow export !
A. 6500 platform cannot support egress netflow due to platform limitation, only ingress is supported.For more information, check NDE Configuration Guidelines and Restrictions.
Q.How to configure ICMP rate limiting in an IPv6 environment?
A. ICMP rate limiting is enabled by default with a default interval between error messages of 100 milliseconds and a bucket size (maximum number of tokens to be stored in a bucket) of 10. The command is "ipv6 icmp error-interval". This can be checked by giving "show ip interface <Interface Type> and the output is shown as below:
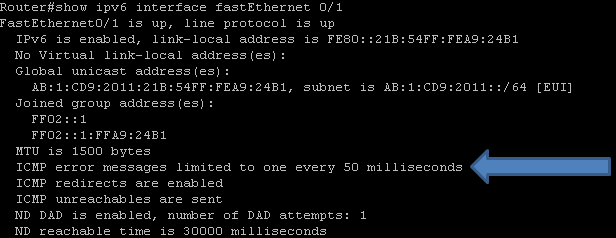
For further information refer http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst2350/software/12.2_46_ey/configuration/guide/swipv6.html#wp1117074
Q. How is summarization done for IPV6 OSPF?
A. The command for IPv6 summarization is summary-prefix.
In the following example, the summary prefix FEC0::/24 includes addresses FEC0::/1 through FEC0::/24. Only the address FEC0::/24 is advertised in an external link-state advertisement.
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 172.16.3.3
summary-prefix FEC0::/24
redistribute static
Native ospf (non-external) routes are summarized using the Area range command. For more information refer to
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipv6/command/reference/ipv6_01.html#wp2113662
The following example specifies one summary route to be advertised by the ABR to other areas for all subnets on network 10.0.0.0 and for all hosts on network 192.168.110.0:
interface Ethernet0/0
no ip address
ipv6 enable
ipv6 ospf 1 area 1
!
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 192.168.255.6
log-adjacency-changes
area 1 range 2001:1DB8:0:1::/64
Q.How to configure IPv6 under vrf as we need to activate bgp?
A. Here is a configuration guide for Multiprotocol VRF Configuration.
Q.On a 3750 Catalyst switch, IPv6 ping doesn't work when "switchport block multicast" is configured.
A. Change the sdm template on switch to "dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 routing". To check the current sdm template, use the command show sdm prefer
To change the sdm template, in the config mode use the command sdm prefer dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 routing.
Note that changing the sdm template requires a reload.
Example:
Switch_3750(Config)# sdm prefer dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 routing
Switch_3750(Config)# exit
Switch_3750# reload
For more information on configuring the sdm templates refer Configuring SDM Templates
Q.Is IPv6 NAT-PT supported by IPv6 cef?
A. NAT-PT is not supported in IPv6 cef path, disable IPv6 cef for NAT-PT. Other option is to go for NAT64, which is available in ASRs currently.
Q.Error message: "% VRF address-family IPv6 is not supported or not enabled" is received when configuring IPv6 address-family within a VRF?
A. Configure the command "mls ipv6 vrf" in the global configuration mode in order to enable IPv6 in VRF.
Q.Can I configure a vlan for IPv6? How do I go about doing this?
A. To configure a vlan for IPv6, you can change your /48 into /64s (per RFC). /64 can be configured on the SVI by doing the following steps:
1.) Enable IPv6 Unicast routing
"ipv6 unicast-routing"
2.) Enable IPv6 CEF
"ipv6 cef"
3.) Configure the IPv6 address
interface vlan 100
ipv6 address 2620:0046::1/64
Q.When peering with eBGP peer using link local IPv6 address an error message is followed:
% BGP(v6): Invalid scope. Unable to configure link-local peer.
Router(config-router)#neighbor FE80::222:83FF:FEDF:5852%te2/2 remote-as 65222
% BGP(v6): Invalid scope. Unable to configure link-local peer.
A. The correct syntax for establishing BGP session with link-local IPv6 address is as follows:
neighbor link-local-address%interface-name remote-as #
Please note that the %interface-name must be the complete interface name:
Router(config-router)#neighbor FE80::A8BB:CCFF:FE00:C800%Ethernet0/0 remote-as 1
Q.Do you have a chart or documentation on the compatibility of routing protocols, including IPv4 and IPv6, running in the same router?
A. IPv6 and IPv4 routing protocols do co-exist on the same device and there is no compatibility issues between two.
Q.Not able to enable IPv6 addressing scheme on a port-channel interface.
Example:
Router(config)#int port-channel 1
Router(config-if)#ipv6 ?
% Unrecognized command
Router(config-if)#ipv6
^
% Invalid input detected at '^' marker.
A. IPv6 Addresses on a port-channel are unsupported at this time.
Q.Does the Catalyst 3560/3750 supports IPv6 policy based routing (PBR)?
A. Catalyst 3560/3750 does not supports IPv6 policy based routing (PBR). For more details please refer to Unsupported IPv6 Unicast Routing Features on Catalyst 3750 guidelines.
Q. What are major differences between IPv4 and IPv6?
A. A detailed journal is available; please read IPv6 Internal.
Q. What is the default route in IPv6.
A. The default route (any) in IPv6 is specified by ::/0. For example, route to any network in IPv6 (static) will be configured as
Router(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 serial 1/0
Q. Does ASR1K supports tunnel mode gre IPv6?
A. As of now the feature is not available on ASR1K platform. For complete configuration refer to Implementing Tunnels.
Q. Is GLBP for IPv6 supported on 3560E?
A. No, please see Configuring IPv6 Unicast Routing section of configuration for 3560E switches.
Q. What is the feature on IPv6 on Catalyst 6500 similar to ip-helper address?
A. A DHCP relay agent, which may reside on the client's link, is used to relay messages between the client and server. DHCP relay agent operation is transparent to the client. A client locates a DHCP server using a reserved, link-scoped multicast address. Therefore, it is a requirement for direct communication between the client and the server that the client and the server be attached to the same link. However, in some situations in which ease of management, economy, or scalability is a concern, it is desirable to allow a DHCP client to send a message to a DHCP server that is not connected to the same link.
Perform this task to enable the DHCPv6 relay agent function and specify relay destination addresses on an interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. interface type number
4. ipv6 dhcp relay destination ipv6-address [interface-type interface-number]
For a detailed information on when and where to configure the above command, please click on the following link: Implementing DHCP For IPv6
Q. How to find the IPv6 address assigned to a host via DHCP over VPDN?
A. Use command "show ipv6 int virtual-access 2.1 prefix".
For example,
Router# show ipv6 int virtual-access 2.1 prefix
IPv6 Prefix Advertisements Virtual-Access2.1
Codes for 1st column:
A - Address, P - Prefix-Advertisement, O - Pool
U - Per-user prefix
Codes for 2nd column and above:
D - Default
N - Not advertised, C - Calendar
PD default [LA] Valid lifetime 2592000, preferred lifetime 604800
OD 2404:B800:AD32::/64 [LA] Valid lifetime 2592000, preferred lifetime
604800
Q. IPv6 VRF support is available from which IOS release?
A. The feature is available on IOS XE 3.1.0S onwards on ASR 1000 platform.
Also, check Cisco Feature Navigator for further validation (Requires user id and password).
Q. What is the command that can be used to re-sequence IPv6 access control list (ACL)?
A. IPv6 acl re-sequence feature is not available in IOS.
Q. What are the ICMPv6 messages used by the neighbor discovery protocol?
A. There are 5 ICMPv6 messages used by the neighbor discovery protocol. They are listed as below:
- Router Solicitation (RS)
- Router Advertisement (RA)
- Neighbor Solicitation (NS)
- Neighbor Advertisement (NA)
- Redirect
Q. IPv4 to IPv6. What happened to IPv5?
A. According to Wikipedia, Internet Protocol Version 5 was used by the Internet Stream Protocol, an experimental streaming protocol. The second version (of Internet Stream Protocol), known variously as ST-II or ST2, distinguishes its own packets with an Internet Protocol version number 5, although it was never known as IPv5. The Internet Stream Protocol family was never introduced for public use, but many of the concepts available in ST are similar to later Asynchronous Transfer Mode protocols and can be found in Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS). They also presaged Voice over IP. Since the number 5 was already allocated, this number was not considered for the successor to IPv4. Several proposals were suggested as the IPv4 successor, and each was assigned a number. In the end, it happened that the one with version number 6 was selected.
Q. Not able to configure IPv6 on a WS-SUP32-GE-3B with IP Services Cisco IOS. Does Sup32 supports IPv6?
Switch(config)#ipv6?
% Unrecognized commandA. Sup32 does support IPv6 but on 12.2(33) SXI or later then you can use IP services.
Q. Does the Cisco IPSec VPN Client support IPv6 ?
A.The IPSEC client can only form tunnels between IPv4 endpoints, and will only transport IPv4 packets inside the tunnel.If you are using something
that will tunnel IPv6 inside IPv4 (ISATAP,6in4),the IPv6 will be transported but only because it looks like an IPv4 packet at the driver layer.
The classic Cisco VPN client only carries IPv6 over IPSEC if the IPv6 is tunneled inside IPv4.For native IPv6 transport, you can use
Cisco AnyConnect VPN client.
Q. What is the reason for a dedicated link local address for each VLAN?
A. One of the advantages of IPv6 is the fact that every link has a link local addresses that are significant only for that link, in addition to having at least one global address. The fact that the same link-local address can appear on multiple different links should be embraced as a benefit.
The ability to have many different addresses on an interface is one of the useful traits of IPv6 that can provide an advantage over IPv4
Related Information
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Another good resource for related information is the IPv6 Knowledge Base Portal.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
"An anycast address is essentially a unicast address assigned to multiple devices with a host ID = 0000:0000:0000:0000."
I believe this should be:
"An anycast address is essentially a unicast address assigned to multiple interfaces and/or devices. One example of an anycast address is the Subnet-Router anycast address which has a host ID of 0 (0000:0000:0000:0000)."
Please reference RFC 4291 written by the legendary Steve Deering of none other than Cisco Systems. :-)
--Jim
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: