- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Routing
- I appreciate your patience!
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-12-2015 07:15 AM - edited 03-05-2019 01:39 AM
Here I have an excerpt from a Cisco documentation:
The following example shows how to configure two Ethernet interfaces to obtain the next-hop router IP address from the DHCP server:
ip route 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 dhcp 200
ip route 10.10.20.1 255.255.255.255 ethernet 1 dhcp
The first command is quite clear, but the second command is not. I thought host-only networks are only used with loopback interfaces. I do not understand the prefix and prefix mask in the second command. Please, enlighten me.
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
Routing Protocols
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-22-2015 08:52 AM
Nope, it doesnt matter :-) i'd rather call it a prefix rather than ip address. It is a host route, with /32 netmask.
All you are doing is telling the router where the specified "prefix" is. It can be a host route or a network route. It doesn't matter, as long as you set the correct remote subnet and mask.
If I only wanted to get to a particular host for whatever reason, I would put a host route in exactly as you have stated above.
A prefix could be any length.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-12-2015 07:23 AM
This route is also known as a "host route". A single route to a host via the next hop which is set. Please share the documentation, because there may be some context as to what the literature was trying to explain.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-12-2015 08:50 AM
If you look at the complete book, the excerpt above is on page 52.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-14-2015 04:08 PM
R2#conf term
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R2(config)#ip route ?
A.B.C.D Destination prefix
profile Enable IP routing table profile
static Allow static routes
vrf Configure static route for a VPN Routing/Forwarding instance
R2(config)#ip route 10.10.20.1 ?
A.B.C.D Destination prefix mask
R2(config)#ip route 10.10.20.1 255.255.255.255 ?
A.B.C.D Forwarding router's address
Async Async interface
BVI Bridge-Group Virtual Interface
CDMA-Ix CDMA Ix interface
CTunnel CTunnel interface
DHCP Default Gateway obtained from DHCP
Dialer Dialer interface
FastEthernet FastEthernet IEEE 802.3
Lex Lex interface
Loopback Loopback interface
MFR Multilink Frame Relay bundle interface
Multilink Multilink-group interface
Null Null interface
Tunnel Tunnel interface
Vif PGM Multicast Host interface
Virtual-PPP Virtual PPP interface
Virtual-TokenRing Virtual TokenRing
R2(config)#ip route 10.10.20.1 255.255.255.255 fastetehrnet ?
R2(config)#ip route 10.10.20.1 255.255.255.255 fastethernet ?
<0-0> FastEthernet interface number
R2(config)#ip route 10.10.20.1 255.255.255.255 fastethernet 0 ?
<1-255> Distance metric for this route
A.B.C.D Forwarding router's address
DHCP Default Gateway obtained from DHCP
name Specify name of the next hop
permanent permanent route
tag Set tag for this route
track Install route depending on tracked item
<cr>
R2(config)#ip route 10.10.20.1 255.255.255.255 fastethernet 0 dhcp ?
<1-255> Distance metric for this route
<cr>
R2(config)#
Please, I need to be clear about this. Does 10.10.20.1 255.255.255.255 refer to the IP address of the FastEthernet interface of R2 or does it refer to the IP address of some remote host such as that shown in the figure below?
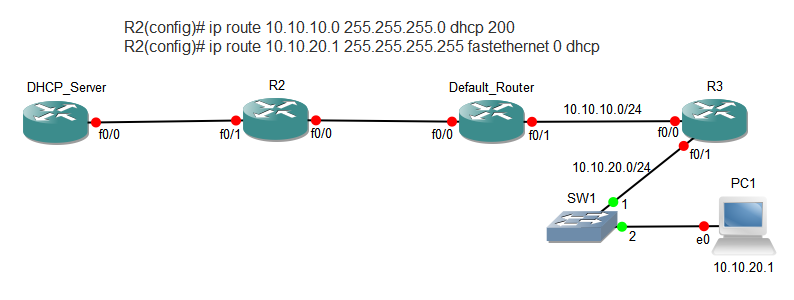
If 10.10.20.1 is not an IP address on R2, and 10.10.20.1 is not a network address then 10.10.20.1 would not be in any of the routing tables. So, how would the Default_Router know to reach host 10.10.20.1?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-22-2015 02:55 AM
Apology for resurrecting this thread. I will very much appreciate it if the command
Router(config)# ip route 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.255 dhcp
can be explained in a way that a newbie can understand. I thought a static route command needs to specify a remote network address and the mask associated with the network address. The command above looks like a host-only network. Does a host-only network have a next hop? Thanks.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-22-2015 05:55 AM
I'll try to explain. A static route to a remote subnet can have any suitable netmask, whether it be a host route or not, the above command, next hop is the DHCP default gateway that the router receives from the dhcp server.
It doesnt have to be host only, all static routes need a next hop or next exit interface, the router needs to know where to forward packets to.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-22-2015 08:13 AM
Thanks a lot Mr. Nawaz. I need one more confirmation. Is the IP address 209.165.200.255 the address of the exit interface or is it the address of an interface on a remote router?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-22-2015 08:17 AM
it is the remote network. I'll break it down for you here
IP ROUTE [remote network address] [remote network subnetmask] [via next hop e.g. interface, x.x.x.x or dhcp]
So we tell the router, the remote network address, followed by the remote network mask, then we tell the router which way to go, or who to go to, to get to this network.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-22-2015 08:48 AM
Thanks once again. My confusion lies in the fact that 209.165.200.255 255.255.255.255 specifies an IP address rather than a network address. Does it not matter?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-22-2015 08:52 AM
Nope, it doesnt matter :-) i'd rather call it a prefix rather than ip address. It is a host route, with /32 netmask.
All you are doing is telling the router where the specified "prefix" is. It can be a host route or a network route. It doesn't matter, as long as you set the correct remote subnet and mask.
If I only wanted to get to a particular host for whatever reason, I would put a host route in exactly as you have stated above.
A prefix could be any length.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-22-2015 09:11 AM
I appreciate your patience!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-13-2015 12:41 AM
Hello
"host-only networks "
As Bilal correctly says that is static pertaining a host iand its just stating how to reach that host... then go via this Ethernet interface.
32 bit as in the second static is specifying a single host and not a network
Alsothe administrative distance has been specifically lowered on these statics to a value of 1 and 200 respectively instead of the default value this router obtains from the dhcp allocation which is 254 so to make it more preferable path..
res
Paul
Please rate and mark as an accepted solution if you have found any of the information provided useful.
This then could assist others on these forums to find a valuable answer and broadens the community’s global network.
Kind Regards
Paul
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide