- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Routing
- Re: Load Balancing and Failover for ISP links
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-28-2020 02:52 AM
Dear All,
Please find my requirement in the two figures below
Brief Synopsis
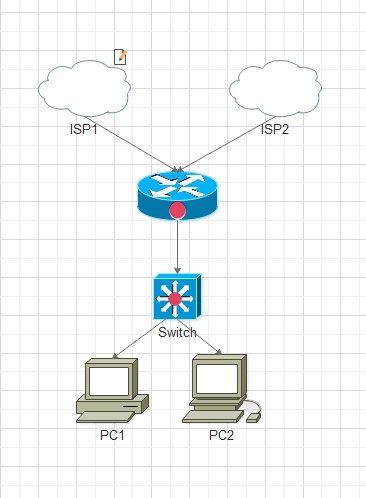
In Figure A
I have a Router and two ISP links connected to it. The other end of the Router is connected to the LAN via the Switch
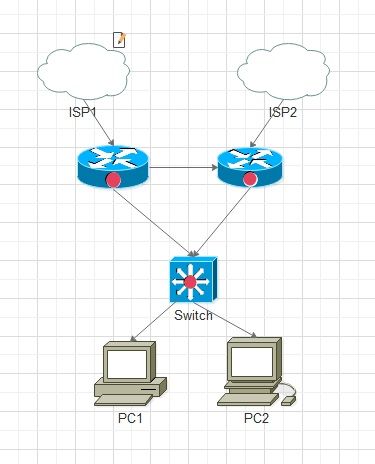
In Figure B
I have two Routers with two different ISP links connected to each of the Routers respectively, for the purpose of maximum uptime. The other end of the Router is connected to the LAN via the Switch.
My Requirement
1. I want to configure Load Balancing and Fail over for the two ISP links. As it is apparent from my requirement, when one ISP link goes down users should be able to access the Internet via the other ISP link.
2. I need the solution in both the cases, with a single Router and two Routers connecting to the ISP links
What would be the most ideal and optimal solution, used as per the Industry standards, to achieve this requirement?
Kindly help me with your suggestions
Cheers!
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
WAN
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-28-2020
04:33 AM
- last edited on
07-27-2023
10:53 PM
by
Translator
![]()
Hello,
in both scenarios, since you have (and pay for) two links, you might as well use them both.
In the first scenario, you would have two static default routes which automatically load balance all traffic. The IP SLAs track the Internet connections and remove the static routes when the respective link is down; it also clears the NAT translations.
The configuration would look like this (IP addresses are arbitrary, obviously):
R1
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description Link to ISP1
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
description Link to ISP2
ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
description LAN
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
!
track 1 ip sla 1 reachability
track 2 ip sla 2 reachability
!
ip sla 1
icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/0
timeout 500
threshold 500
frequency 2
!
ip sla 2
icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
timeout 500
threshold 500
frequency 2
!
ip sla schedule 1 start-time now life forever
ip sla schedule 2 start-time now life forever
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.2
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2.2.2.2
!
ip nat inside source list 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/0 overload
ip nat inside source list 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 overload
!
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
!
event manager applet ISP_1_DOWN
event track 1 state down
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.2
action 4.0 cli command "exit"
action 5.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 6.0 cli command "end"
!
event manager applet ISP_1_UP
event track 1 state up
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.2
action 4.0 cli command "exit"
action 5.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 6.0 cli command "end"
!
event manager applet ISP_2_DOWN
event track 2 state down
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2.2.2.2
action 4.0 cli command "exit"
action 5.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 6.0 cli command "end"
!
event manager applet ISP_2_UP
event track 2 state up
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2.2.2.2
action 4.0 cli command "exit"
action 5.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 6.0 cli command "end"
In the second scenario, you could use GLBP to load balance. An IP SLA on each router monitors the ISP link,and if the ISP link is down, it will shut down the GLBP enabled interface as well (and clear the NAT translations). If only the GLBP enabled interface is down, an EEM script will clear the NAT translations.
The configs would look like this (again, IP addressing is arbitrary):
R1
track 1 ip sla 1 reachability
!
ip sla 1
icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
timeout 500
threshold 500
frequency 2
!
ip sla schedule 1 start-time now life forever
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description GLBP LAN 1
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
glbp 1 ip 192.168.1.1
glbp 1 timers msec 50 msec 70
glbp 1 priority 110
glbp 1 preempt
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
description Link to ISP
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 GigabitEthernet0/1
!
ip nat inside source list 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 overload
!
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
!
event manager applet GLBP_DOWN
event syslog pattern "Active - Init"
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 3.0 cli command "end"
!
event manager applet ISP_DOWN
event track 1 state down
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "interface GigabitEthernet 0/0"
action 4.0 cli command "shut"
action 5.0 cli command "end"
action 6.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 7.0 cli command "end"
R2
track 1 ip sla 1 reachability
!
ip sla 1
icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
timeout 500
threshold 500
frequency 2
!
ip sla schedule 1 start-time now life forever
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description GLBP LAN 2
ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
glbp 1 ip 192.168.1.1
glbp 1 timers msec 50 msec 70
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
description Link to ISP
ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 GigabitEthernet0/1
!
ip nat inside source list 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 overload
!
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
!
event manager applet GLBP_DOWN
event syslog pattern "Active - Init"
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 3.0 cli command "end"
!
event manager applet ISP_DOWN
event track 1 state down
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "interface GigabitEthernet 0/0"
action 4.0 cli command "shut"
action 5.0 cli command "end"
action 6.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 7.0 cli command "end"
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-28-2020 03:02 AM
Hi there,
Take a look at this document:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/border-gateway-protocol-bgp/13762-40.html
...it covers the dual-homed and multihomed scenarios you have described.
cheers,
Seb.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-28-2020 03:02 AM
Hi @techjoe.2
In the first scenario, the objective can be achieved with IP SLA, traking the interface connected to the main ISP. In the second scenario, the objective can be achieved through HSRP, traking or interface connected to the main ISP.
Regards
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-28-2020 04:33 AM
Thanks for the reply,
As you said,
1. If I use IPSLA it would give me the Failover, but what about Load Balancing ?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-28-2020
04:33 AM
- last edited on
07-27-2023
10:53 PM
by
Translator
![]()
Hello,
in both scenarios, since you have (and pay for) two links, you might as well use them both.
In the first scenario, you would have two static default routes which automatically load balance all traffic. The IP SLAs track the Internet connections and remove the static routes when the respective link is down; it also clears the NAT translations.
The configuration would look like this (IP addresses are arbitrary, obviously):
R1
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description Link to ISP1
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
description Link to ISP2
ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
description LAN
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
!
track 1 ip sla 1 reachability
track 2 ip sla 2 reachability
!
ip sla 1
icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/0
timeout 500
threshold 500
frequency 2
!
ip sla 2
icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
timeout 500
threshold 500
frequency 2
!
ip sla schedule 1 start-time now life forever
ip sla schedule 2 start-time now life forever
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.2
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2.2.2.2
!
ip nat inside source list 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/0 overload
ip nat inside source list 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 overload
!
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
!
event manager applet ISP_1_DOWN
event track 1 state down
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.2
action 4.0 cli command "exit"
action 5.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 6.0 cli command "end"
!
event manager applet ISP_1_UP
event track 1 state up
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.2
action 4.0 cli command "exit"
action 5.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 6.0 cli command "end"
!
event manager applet ISP_2_DOWN
event track 2 state down
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2.2.2.2
action 4.0 cli command "exit"
action 5.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 6.0 cli command "end"
!
event manager applet ISP_2_UP
event track 2 state up
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2.2.2.2
action 4.0 cli command "exit"
action 5.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 6.0 cli command "end"
In the second scenario, you could use GLBP to load balance. An IP SLA on each router monitors the ISP link,and if the ISP link is down, it will shut down the GLBP enabled interface as well (and clear the NAT translations). If only the GLBP enabled interface is down, an EEM script will clear the NAT translations.
The configs would look like this (again, IP addressing is arbitrary):
R1
track 1 ip sla 1 reachability
!
ip sla 1
icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
timeout 500
threshold 500
frequency 2
!
ip sla schedule 1 start-time now life forever
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description GLBP LAN 1
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
glbp 1 ip 192.168.1.1
glbp 1 timers msec 50 msec 70
glbp 1 priority 110
glbp 1 preempt
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
description Link to ISP
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 GigabitEthernet0/1
!
ip nat inside source list 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 overload
!
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
!
event manager applet GLBP_DOWN
event syslog pattern "Active - Init"
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 3.0 cli command "end"
!
event manager applet ISP_DOWN
event track 1 state down
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "interface GigabitEthernet 0/0"
action 4.0 cli command "shut"
action 5.0 cli command "end"
action 6.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 7.0 cli command "end"
R2
track 1 ip sla 1 reachability
!
ip sla 1
icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
timeout 500
threshold 500
frequency 2
!
ip sla schedule 1 start-time now life forever
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description GLBP LAN 2
ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
glbp 1 ip 192.168.1.1
glbp 1 timers msec 50 msec 70
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
description Link to ISP
ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 GigabitEthernet0/1
!
ip nat inside source list 1 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 overload
!
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
!
event manager applet GLBP_DOWN
event syslog pattern "Active - Init"
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 3.0 cli command "end"
!
event manager applet ISP_DOWN
event track 1 state down
action 1.0 cli command "enable"
action 2.0 cli command "conf t"
action 3.0 cli command "interface GigabitEthernet 0/0"
action 4.0 cli command "shut"
action 5.0 cli command "end"
action 6.0 cli command "clear ip nat translation *"
action 7.0 cli command "end"
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-28-2020 05:51 AM
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-28-2020 07:15 AM
Hello,
that would work as well, the difference is that you need to specify which traffic you want to go where, but in essence, it achieves the same thing...
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-17-2021
01:22 PM
- last edited on
07-27-2023
10:56 PM
by
Translator
![]()
In the first scenario, I have a problem. could you please solve this?
In the first scenario for instance, if track 1 goes down (8.8.8.8 unreachable) then the router removes the
default route
from the router by using the event manager. Is it possible that track 1 becomes up without adding manually
default routes (IP route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.1.2)
? Because track1 state up into event manager could not be enabled unless we add
default route
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-17-2021
01:26 PM
- last edited on
07-27-2023
10:56 PM
by
Translator
![]()
Basically, I want to ask you why we are using the event manager for ISP_1_UP. when we have to add a manually
default route
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-28-2020 06:09 AM
Hello
The information provided on your topology isnt clear enough to provide a viable solution at this time.Depending on the below will provide a clearer understanding to what options you have for resiliency and load-balancing
What type of wan connection is being hosted - mpls, internet etc...
What make/model are your wan rtrs, l3 switches, software running on them
What routing EGP/IGP routing protocols if any are you running ( bgp,ospf, eigrp) or static
Are you implementing NAT.
Please rate and mark as an accepted solution if you have found any of the information provided useful.
This then could assist others on these forums to find a valuable answer and broadens the community’s global network.
Kind Regards
Paul
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide
