- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Routing
- RIB,FIB,LIB,LFIB
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-31-2019 08:45 AM
Hi!
Can anyone briefly describe the difference between RIB,FIB,LIB,LFIB. How CEF comes into action and building adjacency tables.
It would be really helpful if you could share a document on them as well.
Thank is advance.
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
Routing Protocols
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
09-01-2019 06:56 AM
Hello tiger.ibra123,
CEF builds a separate table called Adjacency table to store detailed forwarding information about the next-hops.
The FIB for each FEC entry contains a pointer to one or more entries in the Adjacency table.
This separation provides efficiency, as the number of next-hops is quite lower compared to the number of IP prefixes.
The packet rewrite information contained for each next-hop is so low level that also MPLS next-hops should be supported including MPLS IGP label (or external label).
I don't think that exist an IP Adjacency table and an MPLS Adjacency table.
Warning : a router is not able to distinguish between two equal cost paths one via an IP only path and one via an MPLS enabled network.
To avoid issues with MPLS L3 VPN connectivity that requires to use MPLS enabled paths , IP only paths can be used but should have an higher IGP cost so that they are not used and not in competition with MPLS enabled links.
This known limitation should confirm that the ADj table is only one.
Hope to help
Giuseppe
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-31-2019 09:15 AM
Hi @network_geek ,
I think this discussion can help you:
https://community.cisco.com/t5/mpls/relationship-between-lib-fib-and-lfib/td-p/782307
Regards
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-31-2019 10:42 AM
Although the discussion is quite healthy but it does not clarify the difference between all.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-31-2019 05:45 PM
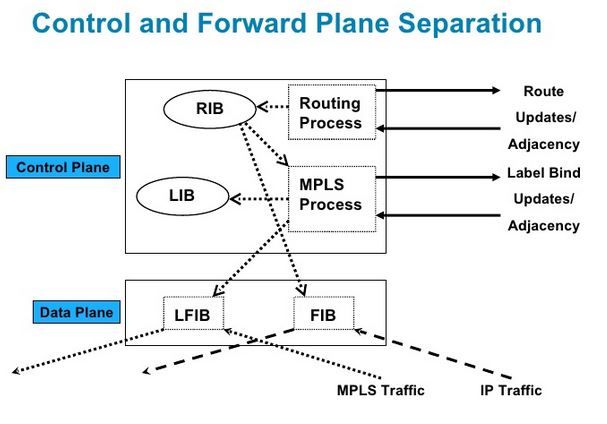
RIB - Routing Information Base
This is the route table. ( seperate case with VRF- Each VRF have their own).
FIB – Forwarding Information Base
The FIB is an optimised version of the RIB. Or more correctly it’s the table a router looks at when deciding where to actually forward traffic. In Cisco land, the CEF table is a FIB.
MPLS
LIB – Label Information Base
The LIB is an MPLS table. This is the place where the router will keep all known MPLS labels.
LFIB – Label Forwarding Instance Base
The LFIB is another MPLS table. This is the table that the router uses to forward labelled packets going through the network. LIB uses the LFIB to forward traffic.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
09-01-2019 06:32 AM
Can I say that the FIB maintains all outgoing interfaces for a specific destination and the MAC address of the next hop as well?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
09-01-2019 06:56 AM
Hello tiger.ibra123,
CEF builds a separate table called Adjacency table to store detailed forwarding information about the next-hops.
The FIB for each FEC entry contains a pointer to one or more entries in the Adjacency table.
This separation provides efficiency, as the number of next-hops is quite lower compared to the number of IP prefixes.
The packet rewrite information contained for each next-hop is so low level that also MPLS next-hops should be supported including MPLS IGP label (or external label).
I don't think that exist an IP Adjacency table and an MPLS Adjacency table.
Warning : a router is not able to distinguish between two equal cost paths one via an IP only path and one via an MPLS enabled network.
To avoid issues with MPLS L3 VPN connectivity that requires to use MPLS enabled paths , IP only paths can be used but should have an higher IGP cost so that they are not used and not in competition with MPLS enabled links.
This known limitation should confirm that the ADj table is only one.
Hope to help
Giuseppe
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide