- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Security
- Security Knowledge Base
- iPSK (Identity Pre-Shared-Key) Manager portal server for ISE
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-02-2019 08:40 AM - edited 03-08-2022 03:31 PM
Note: The iPSK Manager is now an open source project! Please go to GitHub iPSK Manager link for up-to-date information. Following page will not be updated:
- Introduction
- iPSK Manager Installation
- iPSK Manager Configuration
- 1. LDAP Servers
- 2. (Optional) Internal Users
- 3. Platform Configuration
- 4. Group
- 5. Authorization Template
- 6. Endpoint Grouping
- 7. Wireless Network SSID
- 8. Portal Group
- 9. Portal
- ISE Configuration
- ODBC
- Authorization profile
- Policy Set
- WLC Configuration
- AireOS Wireless Controller
- Catalyst 9800 Controller
- Meraki MR
- Appendix
- (Experimental) Keeping iPSK Manager up to date
- Notes about Ubuntu 20.04 LTS based installation
- (Experimental) GUI Logging
- Use non-SSL port for admin and end user portal
- FAQ
Introduction
PSK (Pre-Shared-Key) WLAN is widely used for consumer & enterprise IoT onboarding as most of IoT device doesn’t support 802.1X. While PSK WLAN provides easy way to onboard IoT, it also introduces challenge as it doesn’t provide security that many enterprise requires due to limitation of single PSK for the entire WLAN.
Identity PSK allows unique PSK per endpoint or based on policy. For instance groups of like endpoints can share a same PSK value or each of the endpoint can have a unique PSK providing added security compared to a WLAN with single common PSK shared by all endpoints. IPSK on Cisco wireless solution is a great feature to address security for IoT and BYOD. However, main way to leverage IPSK in scale was to extend ISE internal DB to include IPSK value. While this is a good way to leverage IPSK, it required ISE admin to maintain IPSK for the entire deployment.
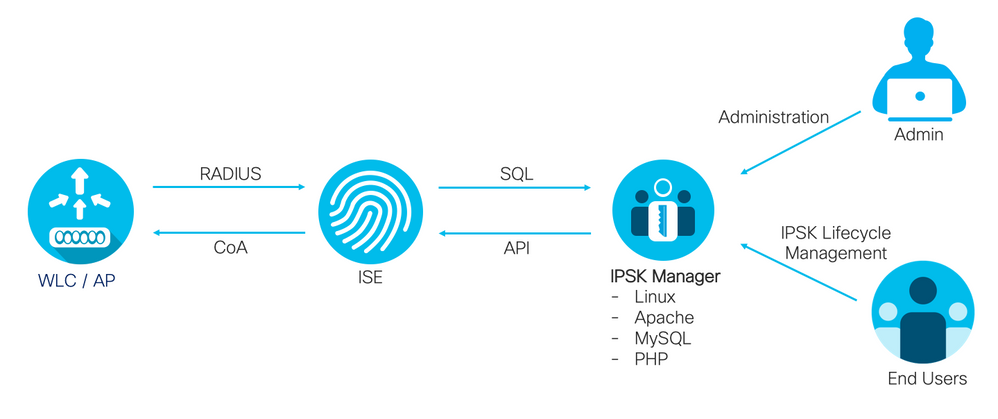
Here I am going to introduce a better way to use IPSK by utilizing external portal + SQL endpoint database for IPSK management, called iPSK Manager. The iPSK Manager portal can be used by end user to register devices on their own as well as manage IPSK string without the help of ISE admin.
There are two different modes of operation when it comes to iPSK feature on Cisco WLC. First mode is where WLC is able to associate with endpoints using individual PSK value. This is supported on all selling wireless products as of 2019. The second mode is where WLC can form a private network for endpoints with common PSK value. This is currently supported with Cisco WLC 8.8 and Catalyst 9800 17.1.1 only. iPSK Manager can leverage both mode of operation. For more information on IPSK on AireOS platform, please read Identity PSK Feature Deployment Guide.
Here is the table that describes IPSK support on different Cisco wireless platforms:
| AireOS | Catalyst 9800 | Mobility Express AP | Meraki MR | Embedded WLC on Catalyst AP | |
| Min. Version | 8.5 | 16.10.1 | 8.8MR2 | 26.5 | 16.12.2 |
| Released Date | July 2017 | November 2018 | March 2019 | October 2019 | November 2019 |
| RADIUS PSK Attribute | Cisco VSA | Cisco VSA | Cisco VSA | RADIUS:Tunnel-Password(69) | Cisco VSA |
| Attribute format | psk=XXXXXXXX | psk=XXXXXXXX | psk=XXXXXXXX | XXXXXXXX | psk=XXXXXXXX |
| IPSK + WPA3/SAE | Yes | No WPA3 | ? | ||
| PSK Caching | Yes | Yes | ? | ||
| IPSK P2P blocking | 8.8 | 17.1.1s | ? | ||
| PSK encrypted in transit | Yes | ||||
| PSK Visible in ISE Live Log | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Default PSK | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
There are three main use cases the iPSK Manager portal supports:
- iPSK IoT portal: The use case for this is where a local site technician will be onboarding multiple IoT devices. Consider a hospital with many PSK enabled medical device needs to be securely connected to the network. Local technician can use this portal to add medical devices with individual PSK or common PSK for like devices. This portal allows importing from CSV file or from ISE via ERS API.
- iPSK personal portal: This is similar to ISE my devices portal. End user can login and perform CRUD operation for MAC/iPSK values. User can either create unique PSK per endpoint or per user. By using single random PSK value for all of one’s endpoint, one can form a private network combined with the WLC supports iPSK p2p blocking feature.
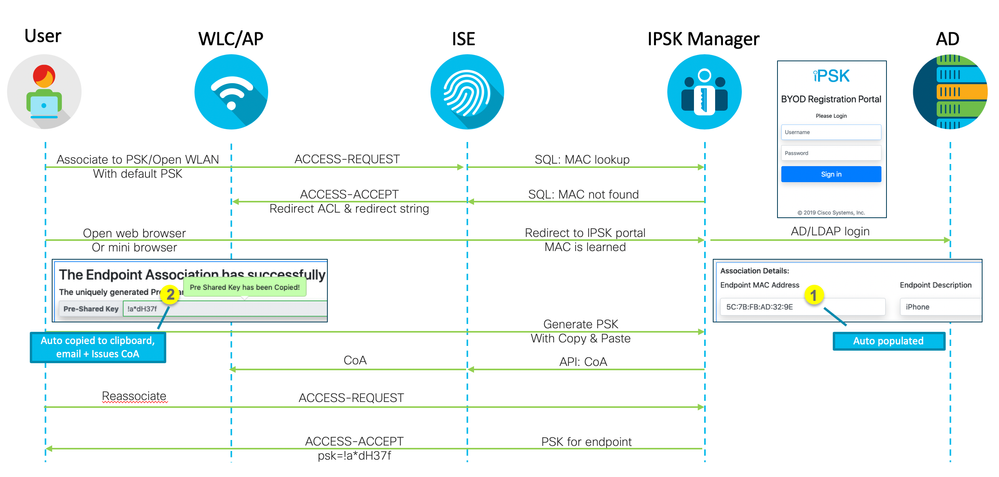
- PSK assisted onboarding: This flow is similar to ISE BYOD onboarding flow where user is redirected to the portal and endpoint is registered and onboarded and eventually gets full network access. Unlike ISE flow, iPSK flow works with any devices that has a functioning web browser which includes mobile phones, tablets, laptops as well as some devices with screen and keyboard (Virtual or physical). The benefit of PSK assisted onboarding is that the enduser does not have to manually enter MAC address nor the PSK value. It also leverages settings most users are already familar with.
iPSK Manager Installation
Before proceeding with the download and install please note the license of this application and this document you are reading:
|
Copyright (c) 2019 Cisco and/or its affiliates. This software is licensed to you under the terms of the Cisco Sample Code License, Version 1.1 (the "License"). You may obtain a copy of the License at https://developer.cisco.com/docs/licenses All use of the material herein must be in accordance with the terms of the License. All rights not expressly granted by the License are reserved. Unless required by applicable law or agreed to separately in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either expressed or implied. |
0. Install Linux. Most distribution should work, but following steps are based on Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS
1. After installing Ubuntu OS, make sure the system is up-to-date:admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get update
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get upgrade
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install php apache2 mysql-server php-mysqlnd php-ldap php-curl php-mbstring php-xml
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo a2enmod rewrite
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo a2enmod ssl
4. Download iPSK Manager from GitHub
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo git clone https://github.com/CiscoSE/iPSK-Manager.git /var/www/iPSK-Manager
[sudo] password for admin:
Cloning into '/var/www/iPSK-Manager'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 13, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (13/13), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (13/13), done.
remote: Total 261 (delta 6), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 248
Receiving objects: 100% (261/261), 311.44 KiB | 2.29 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (141/141), done.
admin@ubuntu:~$
5. (Recommended) Run post installation script for MySQL
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo mysql_secure_installation utility
Note: For more information on the MySQL secure installation utility, please review: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/mysql-secure-installation.html
6. (Recommended) Instead of using MySQL root account, a temporary 'install' account can be created to install the iPSK Manager then removed once completed
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo mysql -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 1080
Server version: 5.7.27-0ubuntu0.18.04.1 (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> CREATE USER 'install'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '{SOME PASSWORD}'
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'install'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION;
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
mysql> exit
7. Change owner of the iPSK-Manager directory (Showing example of Ubuntu distribution which uses www-data user and group for the apache process)
admin@ubuntu:~$ cd /var/www
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo chown www-data:www-data -R iPSK-Manager
8. It is recommended to use SSL for security and subsequent section describes how to enable SSL. However, if no certificate is available,follow the instructions in the Appendix on how to use non-SSL port for the portals
9. (Recommended) Create self-signed certificate using OpenSSL or external tools. You will need private key, signed certificate, and CA chain if applicable
10a. (Recommended) Enable SSL for admin portal. There are sample apache configuration files for the admin portal and end user portal located at the root of the install directory called 'portal-ssl.sample.conf' file. There are 3 sections in the file for admin portal and also for enabling port 8443 & 8445 for SSL. You can simply copy each section in to separate files and place them in '/etc/apache2/sites-enabled' to get it enabled. Aside from that you need to make sure to update the path and file names for the certificate. First for admin portal create a file called '443-ssl.conf' with following content:
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerAdmin webmaster@ipskmanager
DocumentRoot /var/www/iPSK-Manager/adminportal
<Directory /var/www/iPSK-Manager/adminportal>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/admin-error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/admin-access.log combined
# SSL Engine Switch:
# Enable/Disable SSL for this virtual host.
SSLEngine on
# A self-signed (snakeoil) certificate can be created by installing
# the ssl-cert package. See
# /usr/share/doc/apache2/README.Debian.gz for more info.
# If both key and certificate are stored in the same file, only the
# SSLCertificateFile directive is needed.
SSLCertificateFile /path/to/my/ssl.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /path/to/my/ssl.key
# Server Certificate Chain:
# Point SSLCertificateChainFile at a file containing the
# concatenation of PEM encoded CA certificates which form the
# certificate chain for the server certificate. Alternatively
# the referenced file can be the same as SSLCertificateFile
# when the CA certificates are directly appended to the server
# certificate for convinience.
SSLCertificateChainFile /path/to/my/ssl.chain
<FilesMatch "\.(cgi|shtml|phtml|php)$">
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars
</FilesMatch>
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
Note: Make sure to modify the path and file name for the certificate, private key, and the certificate chain
10b. (Recommended) Enable SSL for end user portal port. Next for end user portal create a file called '8443-ssl.conf' with following content:
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
Listen 8443
<VirtualHost *:8443>
ServerAdmin webmaster@ipskmanager
DocumentRoot /var/www/iPSK-Manager/portals
<Directory /var/www/iPSK-Manager/portals>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/portal-8443-error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/portal-8443-access.log combined
# SSL Engine Switch:
# Enable/Disable SSL for this virtual host.
SSLEngine on
# A self-signed (snakeoil) certificate can be created by installing
# the ssl-cert package. See
# /usr/share/doc/apache2/README.Debian.gz for more info.
# If both key and certificate are stored in the same file, only the
# SSLCertificateFile directive is needed.
SSLCertificateFile /path/to/my/ssl.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /path/to/my/ssl.key
# Server Certificate Chain:
# Point SSLCertificateChainFile at a file containing the
# concatenation of PEM encoded CA certificates which form the
# certificate chain for the server certificate. Alternatively
# the referenced file can be the same as SSLCertificateFile
# when the CA certificates are directly appended to the server
# certificate for convinience.
SSLCertificateChainFile /path/to/my/ssl.chain
<FilesMatch "\.(cgi|shtml|phtml|php)$">
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars
</FilesMatch>
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
11. (Recommended) Once SSL is enabled restart apache. This time you will be asked to enter password to access the private key file:
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo service apache2 restart
Enter passphrase for SSL/TLS keys for 127.0.1.1:443 (RSA): *********
admin@ubuntu:~$
12. Run setup via browser. Open web browser from any machine and go to the IP or hostname (If DNS is already setup) of the IPSK Manager host: https://portal.authc.net or https://192.168.201.90/
13. You will be greeted with setup screen, click Next and accept the license agreement page and click Next to continue with setup
14. Installer will also make sure that required PHP modules are installed, if any of the modules are missing go back to the CLI and make sure they are installed and rerun the Installer
15. Accept default values or change values as needed
| Field Name | Sample Entry | Note |
| mySQL Server IP/FQDN | 127.0.0.1 | |
| iPSK Database Username | ipsk-db-user | A random password will be generated at the end of installation process |
| Cisco ISE ODBC Username | ipsk-ise-user | This is the username ISE will use for SQL connection. A random password will be generated at the end of installation process |
| iPSK Database Name | ipsk | |
| MySQL Admin/Root Username | install | If using temporary MySQL install account, if not use root account |
| MySQL Admin/Root Password | ******** | If using temporary MySQL install account, if not use root password |
16. You will also be asked to create local GUI administrator account password
17. If the install fails, please make sure to go through the steps above to see any of the steps were missed
18. At the end of setup process, it will automatically download a txt file called 'DONOTDELETE-iPSKMANAGER-Install.txt' which contains the database details including username & password needed for ISE communication such as following:
#Copyright (c) 2019 Cisco and/or its affiliates.
#
#This software is licensed to you under the terms of the Cisco Sample
#Code License, Version 1.1 (the "License"). You may obtain a copy of the
#License at
#
# https://developer.cisco.com/docs/licenses
#
#All use of the material herein must be in accordance with the terms of
#the License. All rights not expressly granted by the License are
#reserved. Unless required by applicable law or agreed to separately in
#writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS
#IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express
#or implied.
########################################################
## iPSK Manager
## DO NOT DELETE THIS DATA - STORE IN A SECURE LOCATION
## THIS FILE CONTAINS DETAILS ABOUT YOUR INSTALLATION
########################################################
#Organization SID for iPSK Manager
#---------------------------------
Organization (System) SID Value = S-1-9-1569991369-1569991369-1
#Encryption Key for Encrypting MySQL Sensitive Data
#--------------------------------------------------
Encryption Key = AipsBSIhIJ+TnwsYkLlw1fTPSXc/siDQoP8YaTWZNpY=
#iPSKManager Database Credentials
#--------------------------------
Host = 127.0.0.1
Username = ipsk-db-user
Password = t@DKrkNyZhvXnUTd
Database = ipsk
#Cisco ISE MySQL Credentials
#---------------------------
Username = ipsk-ise-user
Password = e1YV3JefcDQut8g
Database = ipsk
#Cisco ISE Stored Procedures Names
#---------------------------------
iPSK_AttributeFetch
iPSK_AuthMACPlain
iPSK_FetchGroups
iPSK_FetchPasswordForMAC
iPSK_MACLookup
###OPTIONAL### Cisco ISE Replacement Stored Procedures for returning only Non-Expired Endpoints Contained within the iPSK Database
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
iPSK_AuthMACPlainNonExpired
iPSK_FetchPasswordForMACNonExpired
iPSK_MACLookupNonExpired
Note: Keep this file safe in case iPSK Manager needs to be restored or new ISE / iPSK Manager integration is needed
19. You should be redirected to the iPSK Manager login page where you can enter the credential (default GUI admin username is "administrator") created during the setup to login to proceed with iPSK Manager configuration
20. Allow SQL connection from other hosts, by editing the '/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf' file. Find the line 'bind-address = 127.0.0.1' and add '#' at the front to remark it
Note: Please make sure to utilize MySQL security best practices such as FW rules and limiting mySQL user to specific hosts as above allows SQL access from all hosts
21. Restart MySQL service by running "sudo service mysql restart"
22. (Optional) If temporary MySQL account was created in previous step, run the following to remove the 'install' account
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo mysql -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 1080
Server version: 5.7.27-0ubuntu0.18.04.1 (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES, GRANT OPTION FROM 'install'@'%';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
mysql> DROP USER 'install'@'%';
iPSK Manager Configuration
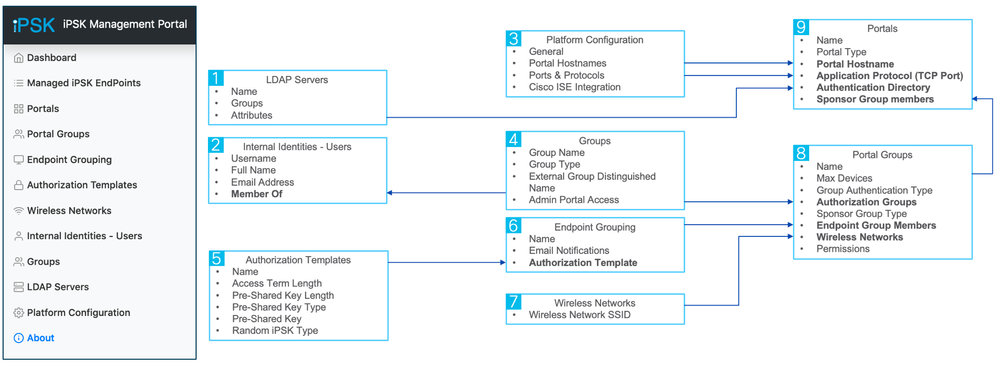
iPSK Manager GUI provides extensible options to provide multiple use cases to different user groups. This document steps through creating simple use cases for a small hospital. Here, we will start out by creating 3 endpoint grouping:
- Personal Device: Added by employee users to onboard BYOD, will be limited to 1 year
- Heart Monitoring: Added by IT staff, PSK will be valid indefinitely
- Ultra Sound: Added by IT staff, PSK will be valid indefinitely
We will create two separate portals that will utilize port 8443
- BYOD Registration Portal: For employee users to register personal devices
- IoT Registration Portal: For IT Staff to register medical devices; Heart Monitoring & Ultra Sound
Use following diagram as guideline to the iPSK Manager configuration. It dipicts how each elements feed into each other to build the portals:
Information used in the document:
| Host | IP Address | Host Name |
| ISE | 192.168.201.93 | ise24.authc.net |
| iPSK Manager | 192.168.201.90 | portal.authc.net |
| LDAP / DNS | 192.168.201.71 |
1. LDAP Servers
In general it is best to utilize existing authentication directory for iPSK Manager so the end user does not have to manage separate account for managing iPSK for endpoints.
Click on LDAP Servers > Click Add LDAP Server
Enter relevant information that are applicable to your site:
| Field name | Sample entry | Note |
| Connection Name | authc.net | Name of LDAP server that can be identified within iPSK Manager Admin console |
| Domain | authc.net | AD domain name |
| Server | 192.168.201.71 | AD server IP or hostname |
| Search Base DN | DC=authc,DC=net | Base DN for searching users and groups |
| Username | admin | User that can bind via LDAP. Does not need to be administrative account. |
| Password | ******** |
Click Update
Once back to LDAP Servers screen, click Test icon to confirm LDAP server is configured properly
Note: If Full Name and Email address field is populated in the AD, IPSK Manager will pull the information when binding MAC address to the PSK. It can also use email address to send binding information to the user
2. (Optional) Internal Users
For general users, it is recommended to utilize existing directory. However if local user account is preferred, they can be created in this section. Note that there is pre-enabled local administrator user.
Click on Internal Identities - Users > Click Add User
| Field name | Sample entry | Note |
| Username | ||
| Full Name | ||
| Description | ||
| Email Address | If provided, iPSK manager can send MAC to iPSK mapping to the user's email address | |
| Password |
Once groups are defined in the next step, clicking Groups icon for the user will allow internal groups to be mapped to the user
3. Platform Configuration
Settings in this section are global settings which includes ISE integration for API, LDAP for external authentication, SMTP for sending iPSK instructions to the end user
1. Click on Platform Configuration > Portal Hostnames
2. Click Add New Hostname to create FQDN to auto redirect to specific portal page. This option allows admin to provide user with easy to remember URL. If using digital certificate, make sure CN or SAN of the certificate has corresponding DNS entries to avoid any certificate errors on the browser. At minimum add IP address of the server as the value is needed when creating the end user portals
3. Click on Ports & Protocols
4. Click Add Protocol/Port to add any HTTP or HTTPS ports to be used for the portals. Note that same port can be used by multiple end user portals but admin portal port cannot be shared with end user portals
5. Click on Cisco ISE Integration
6. Cisco ISE ERS Integration settings allows iPSK Manager to bulk import endpoint group from ISE and author ISE Authorization Profile for Assisted iPSK BYOD flow
7. Cisco ISE Monitoring Integration settings allow iPSK portal to send CoA for Assisted iPSK BYOD flow
8. SMTP Configuration Settings allow SMTP related settings so iPSK Manager can send email notification for new IPSK to MAC binding
9. Advanced Settings allow end user to change the PSK value and enabling logging
4. Group
Click on Internal Identities - Groups > Add Group
| Field name | Sample entry | Sample entry | Note |
| Group Name | Employees | IT Staff | Limited to 25 characters |
| Group Type | External | External | |
| External Group Distinguished Name | CN=Employees,CN=Users,DC=authc,DC=net | CN=IT Staff,CN=Users,DC=authc,DC=net | It is recommended to create non-primary group instead due to LDAP limitation. Users with primary group may not authenticate properly. These groups need to be pre-created on AD for external group mapping to work. |
Click Update
5. Authorization Template
This controls length of access, iPSK type (Random or static), and whether random PSK is per endpoint or per user
Click on Authorization Template > Add Authorization Template
| Field name | Sample entry | Sample entry | Sample entry | Note |
| Name | Personal Device | Heart Monitoring | Ultra Sound | |
| Access Term Length | 1 year | No Expiration | No Expiration | Choose between 1 day - 5 years, or No Expiration |
| Pre-Shared Key Length | 16 | 12 | 12 | 8 - 64 |
| Pre-Shared Key Type | Random PSK | Common PSK | Common PSK | Common PSK allows admin to scribe the PSK while Random PSK will be generated per user or per device upon registration |
| Pre-Shared Key | Value of PSK. If common PSK is selected above, admin user can click on randomizer button to generate random password within the template | |||
| Random iPSK Type | Unique PSK per User | Controls whether enduser will own single PSK for all endpoints one owns or can generate PSK per endpoint. If p2p blocking feature is to be used, Unique PSK per User should be selected |
Click Update
6. Endpoint Grouping
This is logical container to map Authorization templates to portal group. Also controls whether email notification will be sent upon PSK mapping is created
Click on Endpoint Grouping > Add Endpoint Group
| Field name | Sample entry | Sample entry | Sample entry | Note |
| Name | Personal Device | Heart Monitoring | Ultra Sound | Limited to 25 characters |
| Email Notification | Checked | Recommended for personal devices | ||
| Authorization Template | Personal Device | Heart Monitoring | Ultra Sound | Select one from previous step |
7. Wireless Network SSID
List of SSIDs that will be mapped to Sponsor groups and used in email instructions sent to enduser
Click on Wireless Networks > Add Wireless Network
| Field name | Sample entry | Note |
| Name | IPSK-SSID | This is for informational purpose. By providing SSID name, SSID name can be provided to the user such as via email notification. |
Click Update
8. Portal Group
Each sponsor includes settings for max # of endpoints, endpoint groups that can be assigned, SSID names, and mapping to user identity group to internal/external identity store, and various iPSK permissions
Click on Portal Groups > Add Portal Group
| Field name | Sample entry | Sample entry | Note |
| Name | Employee | IT Staff | |
| Max Devices | 5 | 1000 | |
| Group Authentication Type | External Authentication | External Authentication | External for AD |
| Authorization Groups | Employees | IT Staff | |
| Sponsor Group Type | Non-Sponsored Group | Sponsor Group | Sponsor Group is for users that are going to be multiple types of devices for onboarding non-personal IoT devices with PSK. This user type will be able to select multiple endpoint groups |
| Endpoint Group Members | Personal Devices | Heart Monitoring, Ultra Sound | |
| Wireless Networks | IPSK-SSID | IPSK-SSID | |
| View Permissions | Only Endpoints owned by the user | Only Members of the Endpoint group | For the View permissions, since this is a IoT portal to co-manage IoT endpoints, selecting Only Member of the Endpoint group will allow any user with portal access to view endpoints member of Endpoint Group selected above |
| Allow Viewing of Pre-Shared Keys | Checked | Checked | |
| Permissions |
|
|
Select additional permissions to control user access |
Click Update
9. Portal
Portal setting allows admin to create multiple portals. Each portal can be configured with unique virtual host, port, and sponsor group access control.
Click on Portals > Add Portals
| Field name | Sample entry | Sample entry | Sample entry | Note |
| Name | BYOD Registration Portal | IoT Registration Portal | IPSK Assisted Onboarding | Limited to 25 characters |
| Portal Type | Sponsor Portal | Sponsor Portal | Captive Portal | |
| Portal Hostname | portal.authc.net or 192.168.201.90 | portal.authc.net or 192.168.201.90 | portal.authc.net or 192.168.201.90 | |
| Application Protocol (TCP Port) | HTTPS (8443) | HTTPS (8443) | HTTPS (8443) | |
| Authentication Directory | authc.net | authc.net | authc.net | |
| Sponsor Group members | Employees | IT Staff | Employees |
Click Update
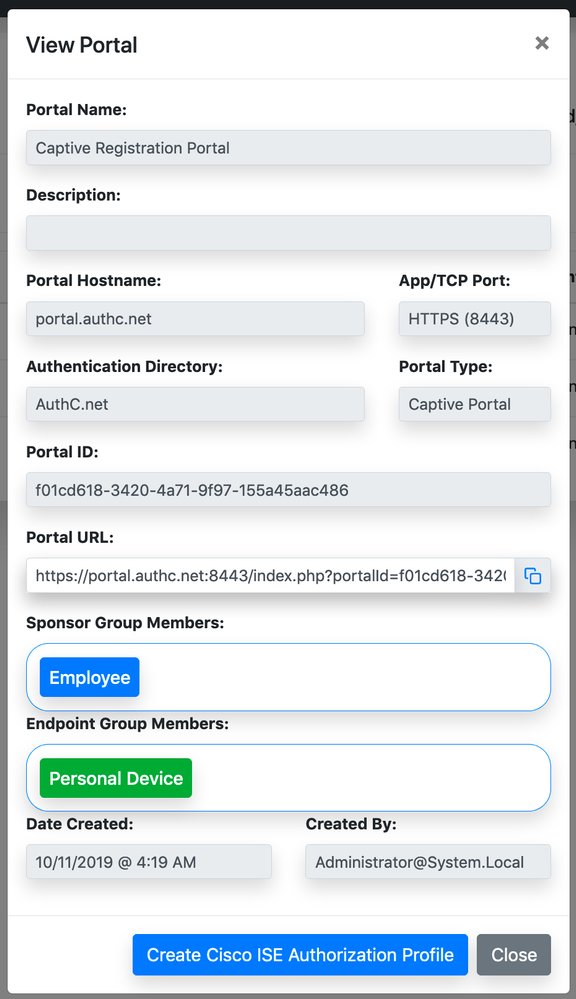
By clicking View Portal and clicking on Copy & Paste icon for the Portal URL, you can find out the portal URL generated by the system. Once copied to clipboard, you can paste into browser URL bar to login as end user.
ISE Configuration
ODBC
Primary integration between ISE and iPSK manager is via ODBC to the SQL database. Follow the instruction below to create the ODBC identity store on ISE.
1. Go to Administration > Identity Management > External Identity Sources
2. On LHS > Click ODBC
3. Click Add
4. Provide Name and Description (Using iPSK as the name in this document)
5. Click on Connection tab and enter following information
| Field name | Sample entry | Note |
| Hostname/IP[port] | 192.168.201.90 | |
| Database name | ipsk | This is the database name used during installation step |
| Admin username | ipsk-ise-user | This is the username created during installation step |
| Admin password | e1YV3JefcDQut8g | This is the password that was created after the installation step via txt file |
| Database type | MySQL |
Click on Stored Procedures tab and enter following info
| Field name | Sample entry | Note |
| Stored procedure type | Returns recordset | |
| Plain text password authentication | iPSK_AuthMACPlainNonExpired | Alternatively, iPSK_AuthMACPlain can be used to ignore iPSK Manager expiry feature |
| Plain text password fetching | iPSK_FetchPasswordForMACNonExpired | Alternatively, iPSK_FetchPasswordForMAC can be used to ignore iPSK Manager expiry feature |
| Check username or machine exists | iPSK_MACLookupNonExpired | Alternatively, iPSK_MACLookup can be used to ignore iPSK Manager expiry feature |
| Fetch groups | iPSK_FetchGroups | |
| Fetch attributes | iPSK_AttributeFetch | |
| Search for MAC address in format | xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx |
6. Click on Connection tab Click Test Connection (Due to permissions on certain version of mySQL, the stored procedure may not be found but this error can be ignored)
Note: If using Ubuntu 20.04 LTS or later and running into issues with the MySQL authentication, see appendix for more information
7. Click on Attributes tab and click on Add > Select Attributes From ODBC
8. Enter * in the Sample User or Machine and click Retrieve Attributes
9. Select attributes to retrieve during authentication as shown below
| Field Name | Type | Name in ISE | Note |
| fullName | String | fullName | Optional |
| emailAddress | String | emailAddress | Optional |
| createdBy | String | createdBy | Optional |
| expirationDate | String | expirationDate | Recommended |
| accountExpired | String | accountExpired | Recommended |
| pskValue | String | pskValue | Required for AireOS & C9800 deployment. It prefixes PSK values with 'psk=' |
| pskValuePlain | String | pskValuePlain | Required for Meraki deployment. There is no prefix to the PSK value |
10. Click on Groups tab and click Add > Add Group
11. Enter * in the Sample User of Machine and click Retrieve Groups
12. Select Groups to retrieve during authentication as show below (Note: When new groups are created on the iPSK Manager, repeat this step to retrieve newly created groups)
| Field name | Sample entry | Sample entry | Sample entry | Note |
| Name | Personal Devices | Heart Monitoring | Ultra Sound | |
| Name in ISE | Personal Devices | Heart Monitoring | Ultra Sound |
10. Click Save
Authorization profile
1. Go to Policy > Policy Elements
2. On LHS > Click Authorization > Authorization Profiles
3. Click Add
| Field name | Sample entry | Sample entry | Note |
| Name | iPSK-AuthZ | iPSK-CaptivePortal-AuthZ | If ERS API was configured between ISE and iPSK Manager, iPSK Manager can create matching authorization profile for the ISPK assisted flow. See next section for how to achieve this. |
| Common Tasks | dACL = IPSK-ACL |
Only relevant for Catalyst 9800 Platform. The content of IPSK-ACL dACL should allow DNS and access to end user portal port: permit udp any host 192.168.201.71 eq domain |
|
| Advanced Attribute Settings | Cisco:cisco-av-pair=psk-mode=ascii | Cisco:cisco-av-pair=url-redirect-acl=ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT | 'Cisco:cisco-av-pair=psk-mode=ascii' is not needed for Meraki IPSK |
| Cisco:cisco-av-pair=iPSK-ODBC:pskValue | Cisco:cisco-av-pair=url-redirect=https://portal.authc.net:8443/index.php?portalId=b3a8fd37-eddb-4a2f-bf75-af255340c8fb&SessionIdValue&client_mac=ClientMacValue |
For Meraki IPSK, use "Radius:Tunnel-Password=iPSK-ODBC:pskValuePlain". For CaptivePortal the redirect URL value copied from the captive portal setting above within the iPSK Manager. Make sure to append "&SessionIdValue&client_mac=ClientMacValue" |
4. Click Save
Using iPSK Manager to create authorization profile for IPSK assisted onboarding flow
1. Login to iPSK Manager GUI
2. Go to Portals and click on View icon for thr assisted onboarding flow portal
3. Click on 'Cisco ISE Authorization Profile' button
4. Enter in Authorization profile name that is not currently used in ISE
5. Click 'Create Cisco ISE Authorization Profile' button
6. Go back to ISE Authorization Profile screen to confirm a new authroization profile has been created
7. Add redirect ACL Cisco VSA and dACL as noted in the previous section
Note: Above flow requires a valid ERS admin/operator user has been configured on both ISE and the iPSK Manager. Currently due to defect ISE 2.6 and above does not support assisted flow including the creation of authorization profile noted here. This is fixed with ISE 2.7p2 and 2.6p7.
Policy Set
1. Go to Policy > Policy Sets
2. Click on the ‘+’ in the upper left corner to create new policy set
| Field name | Sample entry | Note |
| Name | IPSK-Rule | |
| Condition | RADIUS:Called-Station-ID ENDS_WITH IPSK-SSID | This is to match on an SSID named 'IPSK-SSID'. If the SSID name is different, change it to the proper SSID name |
| Allowed Protocols / Server Sequence | Default Network Access |
3. Click Save
4. Click > for newly created IPSK policy set
5. Click > next to Authentication Policy
6. For the Default authentication rule select Internal Endpoints
7. Click > next to Options
8. For if User not found, Select CONTINUE
9. Click > next to Authorization Policy
| Field name | Sample entry | Sample entry | Sample entry | Note |
| Rule Name | Personal devices | Medical devices | Default | |
| Conditions | iPSK-ODBC:ExternalGroups EQUALS Personal Devices | iPSK-ODBC:ExternalGroups EQUALS Heart Monitoring or iPSK:ExternalGroups EQUALS Ultra Sound | ||
| Results - Profiles | iPSK-AuthZ | iPSK-AuthZ | iPSK-CaptivePortal-AuthZ |
10. Click Save
WLC Configuration
AireOS Wireless Controller
AireOS wireless controller supports regular iPSK mode as well as p2p blocking (Peer to peer blocking feature). There is no setting to enable iPSK on a PSK WLAN aside from enabling AAA Override. ISE-RADIUS (Or NAC-RADIUS) feature can be enabled for PSK assisted onborading. Following configuration snippet provides instructions on WLAN with iPSK enabled. The sample configures iPSK WLAN called IPSK-SSID with WLAN-ID of 1. This requires AireOS 8.5+.
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan create 1 IPSK-SSID IPSK-SSID
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan interface 1 ACCESS
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan mac-filtering enable 1
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan security wpa akm 802.1x disable 1
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan security wpa akm psk enable 1
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan security wpa akm psk set-key ascii Cisco123
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan aaa-override enable 1
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan nac radius enable 1
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan profiling radius all enable 1
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan enable 1
In the case of IPSK assisted flow, create redirect ACL
(Cisco Controller) >config acl create ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule add ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule action ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1 permit
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule protocol ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1 6
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule source port range ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1 0 65535
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule destination address ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1 192.168.201.90 255.255.255.255
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule destination port range ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1 8443 8443
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule add ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule action ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1 permit
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule protocol ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1 6
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule source address ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1 192.168.201.90 255.255.255.255
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule source port range ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1 8443 8443
(Cisco Controller) >config acl rule destination port range ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT 1 0 65535
(Cisco Controller) >config acl apply ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT
To enable iPSK p2p blocking (Peer to peer blocking feature) with AireOS version 8.8+
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan disable 1
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan peer-blocking allow-private-group 1
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan enable 1
For more information on AireOS WLC configuration please read AireOS WLC configuration for ISE
Catalyst 9800 Controller
C9800 (Catalyst 9800) controller supports regular iPSK mode. There is no setting to enable iPSK on a policy profile aside from enabling AAA Override. NAC feature can be enabled for PSK assisted onborading. Following configuration snippet provides instructions on WLAN with iPSK enabled. The sample configures iPSK WLAN called IPSK-SSID with WLAN-ID of 1. This sample leverages default policy profile ' default-policy-profile'. If using non default profile, make sure to create tag mapping and apply it to the AP or AP list. This requires IOS-XE 16.10+.
C9800-CL(config)#wlan IPSK-SSID 1 IPSK-SSID
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#mac-filtering default
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#security wpa psk set-key ascii 0 Cisco123
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#no security wpa akm dot1x
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#security wpa akm psk
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#security dot1x authentication-list default
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#no shutdown
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#exit
C9800-CL(config)#wireless profile policy default-policy-profile
C9800-CL(config-wireless-policy)#shutdown
C9800-CL(config-wireless-policy)#aaa-override
C9800-CL(config-wireless-policy)#accounting-list default
C9800-CL(config-wireless-policy)#dhcp-tlv-caching
C9800-CL(config-wireless-policy)#http-tlv-caching
C9800-CL(config-wireless-policy)#nac
C9800-CL(config-wireless-policy)#radius-profiling
C9800-CL(config-wireless-policy)#vlan VLAN0080
C9800-CL(config-wireless-policy)#no shutdown
C9800-CL(config-wireless-policy)#exit
C9800-CL(config)#
In the case of IPSK assisted flow, create redirect ACL
C9800-CL(config)#ip access-list extended ACL_IPSK_REDIRECT
C9800-CL(config-ext-nacl)#10 deny udp any any
C9800-CL(config-ext-nacl)#20 permit tcp any any eq www
C9800-CL(config-ext-nacl)#30 permit tcp any any eq 443
C9800-CL(config-ext-nacl)#exit
C9800-CL(config)#
Note: In the case of Catalyst 9800, it is recommended to combine the redirect ACL with dACL such as following to limit access during redirected state. Create dACL with following ACE on ISE and apply it to the redirect authorization profile:
| permit udp any host 192.168.201.71 eq domain permit tcp any host 192.168.201.90 eq 8443 deny ip any any |
To enable iPSK p2p blocking (Peer to peer blocking feature) with 17.1.1s
C9800-CL(config)#wlan IPSK-SSID 1 IPSK-SSID
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#shutdown
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#peer-blocking allow-private-group
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#no shutdown
C9800-CL(config-wlan)#exit
For more information on Catalyst 9800 configuration please read ISE and Catalyst 9800 Series Integration Guide
Meraki MR
For more information on Meraki IPSK, please read Meraki IPSK with RADIUS Authentication
Appendix
(Experimental) Keeping iPSK Manager up to date
When there is an update to the Git repository, local iPSK Manager deployment can be updated without reinstallation
1. Make sure to make backups of the install directory and the database, and also the config.php file should be backed up
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo cp /var/www/iPSK-Manager/supportfiles/include/config.php /some/backup/directory/
2. Go to iPSK Manager install directory
admin@ubuntu:~$ cd /var/www/iPSK-Manager
3. Pull repository
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo git pull
Notes about Ubuntu 20.04 LTS based installation
Perform the following steps after the IPSK Manager setup:
Update the MySQL Configuration located in ‘/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf’ and add the following line below.
default_authentication_plugin=mysql_native_password
Then restart the MySQL Service or Reboot the system.
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo service mysql restart
Then update the ISE MySQL credential with mysql_native_password to make it compatibe with ISE
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo mysql -p
mysql> ALTER USER 'ipsk-ise-user'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '{PASSWORD}';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
(Experimental) GUI Logging
Logging via GUI can be enabled by editing the 'additionalmenus.json' file in /var/www/iPSK-Manager/supportfiles/adminportals/modules/ directory. Change the "menuEnabled" flag at the end to 1 (default is 0) as shown below and refresh admin GUI and you will see 'System Logging' option visible just below 'About' settings. Note that logging view currently lacks few features to make it useable beyond basic troubleshooting.
{"0":{"id":"menuLogging","module":"logging","data-feather":"flag","menuText":"System Logging"},"menuItems":1,"menuEnabled":1}
Note: Rest of the logging settings are under Platform Configuration > Advanced Settings and Logging Settings
Use non-SSL port for admin and end user portal
It is recommended to use SSL for security and main section of the document describes how to enable SSL. However, if no certificate is available, port 80 request to admin portal can be used by creating a file called '80.conf' with following content and placed in '/etc/apache2/sites-enabled' directory:
<VirtualHost *:80>
# The ServerName directive sets the request scheme, hostname and port that
# the server uses to identify itself. This is used when creating
# redirection URLs. In the context of virtual hosts, the ServerName
# specifies what hostname must appear in the request's Host: header to
# match this virtual host. For the default virtual host (this file) this
# value is not decisive as it is used as a last resort host regardless.
# However, you must set it for any further virtual host explicitly.
#ServerName www.example.com
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/www/iPSK-Manager/adminportal
<Directory /var/www/iPSK-Manager/adminportal>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
# Available loglevels: trace8, ..., trace1, debug, info, notice, warn,
# error, crit, alert, emerg.
# It is also possible to configure the loglevel for particular
# modules, e.g.
#LogLevel info ssl:warn
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
# For most configuration files from conf-available/, which are
# enabled or disabled at a global level, it is possible to
# include a line for only one particular virtual host. For example the
# following line enables the CGI configuration for this host only
# after it has been globally disabled with "a2disconf".
#Include conf-available/serve-cgi-bin.conf
</VirtualHost>
Note: May need to remove default config file in the '/etc/apache2/sites-enabled' directory
Next, point port 8080 request to end user portal by creating a file called '8080.conf' with following content and place it in '/etc/apache2/sites-enabled' directory:
Listen 8080
<VirtualHost *:8080>
# The ServerName directive sets the request scheme, hostname and port that
# the server uses to identify itself. This is used when creating
# redirection URLs. In the context of virtual hosts, the ServerName
# specifies what hostname must appear in the request's Host: header to
# match this virtual host. For the default virtual host (this file) this
# value is not decisive as it is used as a last resort host regardless.
# However, you must set it for any further virtual host explicitly.
#ServerName www.example.com
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/www/iPSK-Manager/portals
<Directory /var/www/iPSK-Manager/portals>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
# Available loglevels: trace8, ..., trace1, debug, info, notice, warn,
# error, crit, alert, emerg.
# It is also possible to configure the loglevel for particular
# modules, e.g.
#LogLevel info ssl:warn
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
# For most configuration files from conf-available/, which are
# enabled or disabled at a global level, it is possible to
# include a line for only one particular virtual host. For example the
# following line enables the CGI configuration for this host only
# after it has been globally disabled with "a2disconf".
#Include conf-available/serve-cgi-bin.conf
</VirtualHost>
Note: Within iPSK manager admin portal, go to Portals and make sure the end user portals are configured with port 8080
Lastly, restart apache service:
admin@ubuntu:~$ sudo service apache2 restart
FAQ
Support
As iPSK Manager is provided as a sample code, there is no support available for it. However, you can post iPSK manager related questions in the ISE forum and other community members who are already using the iPSK Manager may be able to provide guidance:
Redundancy
Since iPSK Manager is a ODBC identity source from ISE, either LB (For IP) or GLB (For hostname) can be used to provide rendancy. iPSK database can be replicated between multiple nodes with native features on the DB.
What does API integration with ISE provide
- Integration with ERS API with ISE admin node:
- Provides creation of Authorization Profile for the PSK Assisted Onboarding flow. However note that you still need to add redirect ACL and possibly dACL manually to the authorization profile.
- Provides import of MAC addresses in ISE endpoint group into iPSK Manager database
- Integration with session API with ISE MnT node:
- Provides CoA for the PSK Assisted Onboarding flow. It is helpful when single-SSID PSK onboarding is used, so initial session with default PSK is dropped and the user is forced to re-enter assigned PSK.
What is the maximum PSK mapping supported
The table is capped at 4,294,967,295 entries. But responses may be impacted on a large database.
Can't make Assisted flow work
There is an open defect with ISE 2.6+ that does not allow custom redirect string in the authorization profile. This is fixed with ISE 2.7p2 and 2.6p7.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Are there minimum / recommended hardware requirements for this deployment?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
2 - cpu
4 gb ram
100 gb hdd.
Im running these in a vm so if I need to add resources it's not a big deal. Hope that helps.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I can't get this to work.
It fails on 19.
The installation seemed to work fine, and I was able to download the DONOTDELETE file, but I'm not redirected to the portal web page.
Instead I get an error: This page isn't working. HTTP ERROR 500
After som digging, I see some errors in /var/log/apache2/admin-error.log:
[Wed Mar 03 12:39:45.708525 2021] [php7:error] [pid 1791] [client 1.5.1.50:61781] PHP Fatal error: Uncaught Error: Call to a member function query() on null in /var/www/iPSK-Manager/supportfiles/include/iPSKManagerDatabase.php:215\nStack trace:\n#0 /var/www/iPSK-Manager/adminportal/index.php(54): iPSKManagerDatabase->getGlobalClassSetting()\n#1 {main}\n thrown in /var/www/iPSK-Manager/supportfiles/include/iPSKManagerDatabase.php on line 215
gkadmin@GK-iPSK-Portal:/var/log/apache2$
Thanks
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Are you setting this up with a single server or HA? Does the “user” your user your using for sql have “install” rights? I had issues with it once and had to cancel setup, go into mysql delete the ipsk db and the db users and start over. It worked after that.
Just a suggestion.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
It could be related to default user authentication in mysql. You may find more logs in /var/log/mysqld.log.
Log into mysql as root.
# mysql -u root -p
Check user host and authentication (it should be set to mysql_native_password, but is auth_socket by default. Host should be %).
# select User, host, plugin from mysql.user;
Change the authentication method
# ALTER USER 'ipsk-ise-user'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'enter_password_here';
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi. Thanks for answering.
I did alter the user, but it's still not working.
I see this:
mysql> select User, host, plugin from mysql.user;
+------------------+-----------+-----------------------+
| User | host | plugin |
+------------------+-----------+-----------------------+
| install | % | caching_sha2_password |
| ipsk-db-user | % | caching_sha2_password |
| ipsk-ise-user | % | mysql_native_password |
| debian-sys-maint | localhost | caching_sha2_password |
| mysql.infoschema | localhost | caching_sha2_password |
| mysql.session | localhost | caching_sha2_password |
| mysql.sys | localhost | caching_sha2_password |
| root | localhost | auth_socket |
+------------------+-----------+-----------------------+
Does that look correct?
Are you sure this is mysql related? I still see the same PHP error when I try to access the web page.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Try altering ipsk-db-user as well. The PHP script is making a database call which is failing.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
No, didn't work.
I threw in a reboot of the (VM) host as well for good measure, but no.
The OS is Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Check /var/log/php-fpm for PHP related logs.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
/var/log/php-fpm failed: No such file or directory
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi
I tried serval time to build iPSK Manager VM and failed to get it up n running. I hope someone can post an OVA file for lab tests. iPSK Manager or a self-provisioning portal feature should be natively built into ISE. I don't know why Cisco ISE doesn't have this fundamental feature for IoT or dormitory devices. I hope the new version of Cisco ISE should have this iPSK Manager natively supported, it makes BYOD or temporary access to the network much simpler.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Can you provide details about your problem, including where in the step it is failing. Also, details on the linux, mysql, etc. would help as well. Also, for suggestion on having the IPSK feature on ISE, I recommend providing that via ISE feedback tool by logging into ISE, select on gear icon on the top right corner and select 'Make a wish'. On older versions, you can select 'About ISE' and select 'Provide Feedback'
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Also: the ODBC connection from ISE fails as well.
I enter the credentials, and press the Test Connection button. And it says:
Connection failed
Stored procedures could not be checked
as connection with DB failed
When I try the exact same credentials from my PC using MYSQL Workbench, it works just fine.
Update:
When using mysql_native_password as plugin, the /var/log/mysql/query.log says:
Connect Access denied for user 'ipsk-ise-user'@'radius.somedomain.local' (using password: YES)
When using the caching_sha2_password as plugin, the log says:
Connect Access denied for user 'ipsk-ise-user'@'radius.somedomain.local' (using password: NO)
This is when i press the Test Connection button from within ISE. None of them works of course.
Both methods works from MySQL Workbench from my PC
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Like others I ran into the same issue with install failure once the GUI wizard is run with this spun up on Ubuntu 20.x; reinstalled it on 18.04 and no issues. This is a great frontend for iPSK, hope to see it part of ISE natively or at least TAC-supported one day.
- « Previous
-
- 1
- 2
- Next »
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: