- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Service Providers
- Service Providers Knowledge Base
- ASR9000/XR: BNG and Dual-stack ipv4 and ipv6 sessions
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on 01-14-2014 05:36 AM
Introduction
This document provides an overview for dual stack sessions for ASR9000 BNG, running ipv4 and ipv6 address stacks next to each other for subscriber sessions.
Dual Stack
Dual stack refers to the concept of running a subsciber session with an IPv4 address as well as an IPv6 address.
Deployment models and general concept
Address Assignment
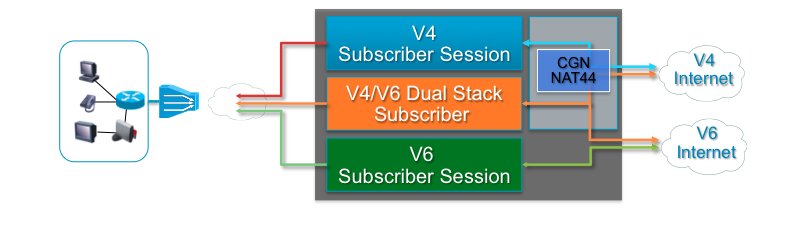
To unravle the complex terminology associated with address assignment in particular to IPv6 this picture below shows the various address assignment options available.
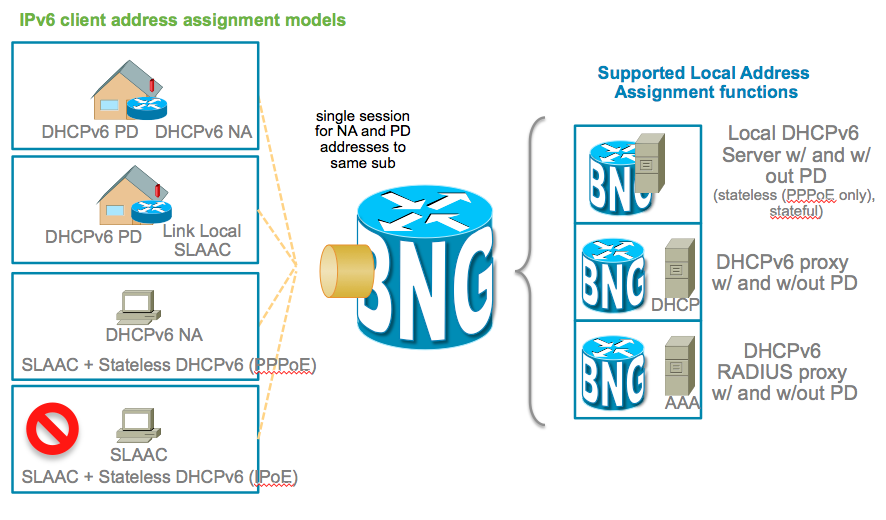
You can also use the framed-ipv6-address radius attribute to provide an address to the subscriber from radius which then will be advertised
via SLAAC (NA/ND) for both PPPoE and IPoE sessions.
The additional attribute ipv6:ipv6-default-gateway VSA can be used to provide the default router in case no dhcpv6 is used for IPoE sessions.
IPv6 Addressing
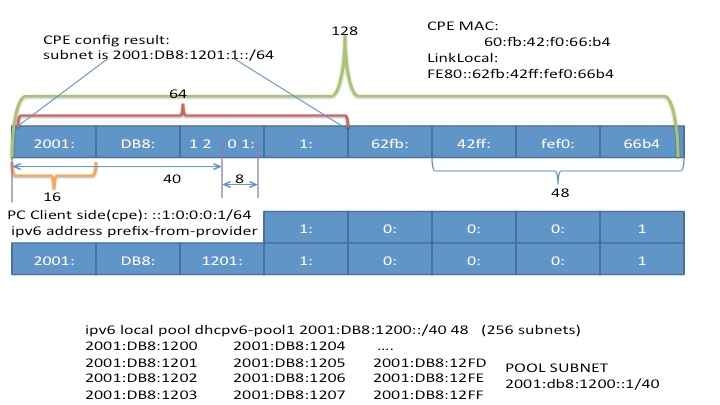
When it comes to "prefix delegation" that is having a large IPv6 like subnet that is shared between subscribers who get a subnet from that subnet sort of speak the following addressing example hopefully visualizes how it all ties together
Addressing mapping
Configuration CPE
The following 2 secions provide the configuration for the client side and the WAN side of the CPE
PC client side of the CPE
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
description to switch fa0/15
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no ip unreachables
ip nat inside
ip virtual-reassembly
duplex full
speed 100
media-type rj45
negotiation auto
ipv6 address prefix-from-provider ::1:0:0:0:1/64
WAN side of the CPE
interface FastEthernet2/0.50
encapsulation dot1Q 50
ipv6 address autoconfig default
ipv6 enable
ipv6 dhcp client pd prefix-from-provider
In these examples we are expanding the delegated prefix with a :1/64 and we perceive ourselves to be the ".1" and default gateway.
Configuration DHCPv6 Server
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 dhcp pool dhcpv6
prefix-delegation pool dhcpv6-pool1 lifetime 6000 2000
ipv6 route 2001:60:45:28::/64 2005::1
ipv6 route 2001:DB8:1200::/40 2005::1
ipv6 route 200B::/64 2005::1
ipv6 route 2600:80A::9/128 4000::1
ipv6 local pool dhcpv6-pool1 2001:DB8:1200::/40 48
More info on IOS dhcpv6 server:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk872/technologies_configuration_example09186a0080b8a116.shtml
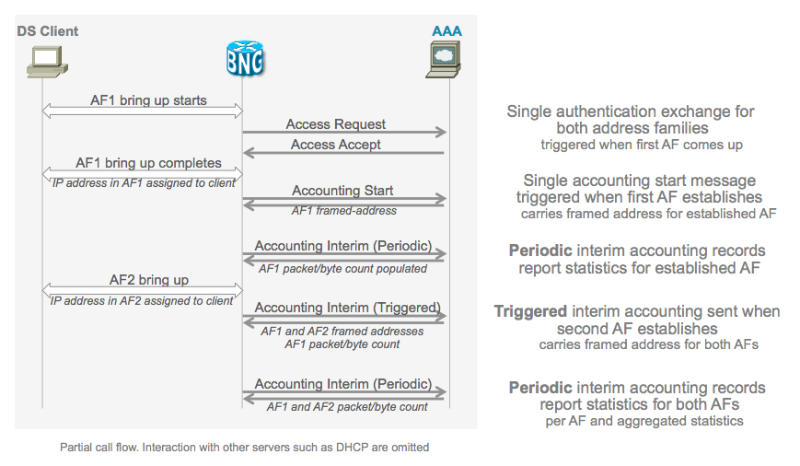
Operation and Call Flow
Because ASR9000 treats the 2 stacks as a single subscriber, and hence ONE access request and a SINGLE accounting record are generated for both stacks, differences of desired operation exist when it comes to when for isntance to generate an accounting request.
There are 2 key things to consider and of importance:
- When the first AF comes up, an access-request is generated, the access-accept should contain BOTH ipv4 and ipv6 information for the session although there is no second request for the other AF maybe yet
- An accounting-start can be generated as soon as the first AF comes up, we can wait for a determined period of time and generate a single accounting start record for BOTH AF's, or we can do a triggered interim accounting record when the second AF comes up.
Call Flows
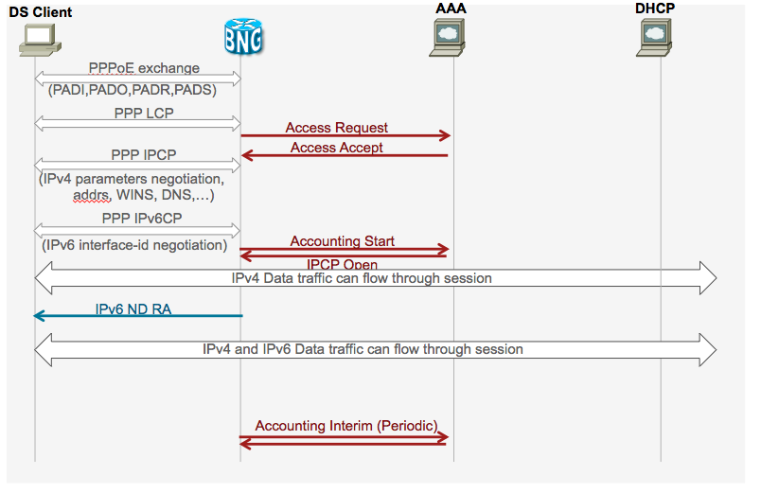
Dual stack generic call flow
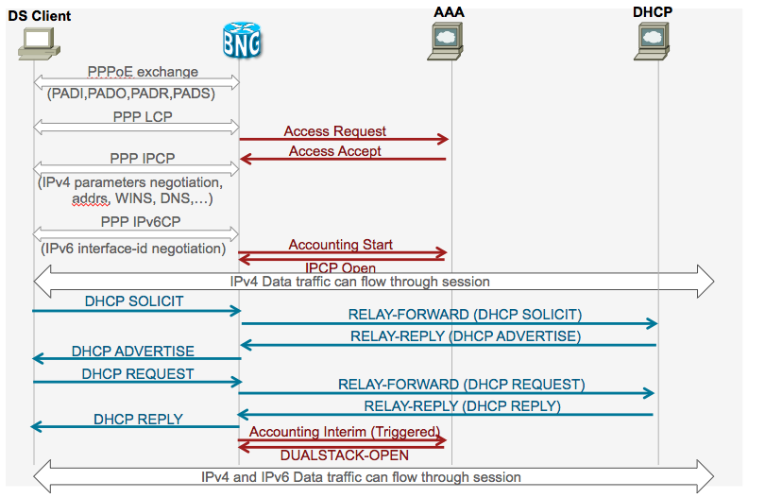
PPPoE DS detailed call flow SLAAC based address assignment
PPPoE DS detailed call flow DHCPv6 based address assignment
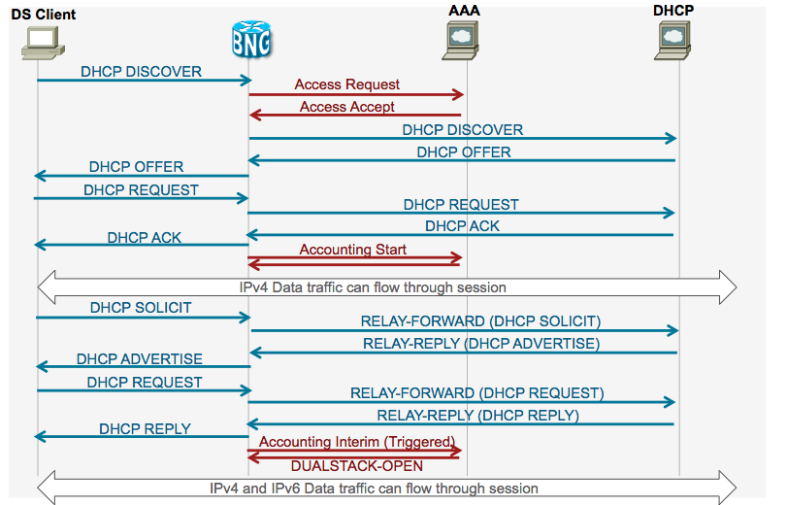
IPoE DS detailed callflow IPv4 AF starts first
IPoE DS detailed callflow IPv6 AF starts first
Sample Scenario
Sample Topology for the configuration example

Configuration
hostname bng logging console debugging |
Radius server configuration.
Radius server is listening on 5.5.5.2 with auth-port on 1645 and accounting-port on 1646
radius-server host 5.5.5.2 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 key 7 010107000A5955 ! |
COA server or policy-server with ip-address 5.5.5.2 is running
aaa server radius dynamic-author client 5.5.5.2 vrf default server-key 7 03165A0F575D72 ! aaa group server radius RADIUS server 5.5.5.2 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 ! aaa accounting service default group radius aaa accounting subscriber default group radius aaa authorization subscriber default group radius aaa authentication subscriber default group radius line console stopbits 1 ! |
DHCPv6 address pool is defined locally within BNG box and local pool is used for ipv6 address assignment to IPv6 BNG clients
pool vrf default ipv6 ipv6_address_pool address-range 2001::2 2001::7dff ! |
DHCPv4 server with ip address 20.20.20.2 is deployed externally and this ipv4 address should be reachable from BNG device. Routing protocols should take care of reachability of 20.20.20.2 from BNG device. DHCPv4 proxy is configured as follows.
dhcp ipv4 profile IPoEv4 proxy helper-address vrf default 20.20.20.2 giaddr 10.10.10.1 ! |
DHCPv4 proxy is enabled on bundle sub-interface
interface Bundle-Ether1.10 proxy profile IPoEv4 ! |
DHCPv6 server is configured and already configured DHCPv6 address pool is referred within DHCPv6 server configuration. DHCPv6 profile is configured as follows with address pool.
dhcp ipv6 profile IPoEv6 server address-pool ipv6_address_pool ! |
DHCPv6 address pool is referred on bundle sub-interface.
interface Bundle-Ether1.10 server profile IPoEv6 ! interface Bundle-Ether1 bundle maximum-active links 1 ! |
Bundle sub-interface with dot1q encapsulation configured with single tag. Subscriber traffic from
CPE should come with single dot1q tag and this vlan tag should match with vlan id 10 configured under bundle sub-interface. In dual-stack IPoE configuration, “initiator dhcp” is configured ipv4/ipv6 l2 connect mode.
Policy-map type control’s name is referred with service-policy
interface Bundle-Ether1.10 ipv4 point-to-point ipv4 unnumbered Loopback1 ipv6 enable service-policy type control subscriber pm-src-mac encapsulation dot1q 10 ipsubscriber ipv4 l2-connected initiator dhcp ! ipsubscriber ipv6 l2-connected initiator dhcp ! ! |
Ipv4 address 10.10.10.1 is default-gateway ip address for pool of ipv4 address allocated to dual-stack BNG clients
interface Loopback1 ipv4 address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 enable ! interface MgmtEth0/RSP0/CPU0/0 ipv4 address 9.22.11.3 255.255.0.0 ! interface MgmtEth0/RSP0/CPU0/1 shutdown ! |
Physical interface gigabit0/0/0/0 is configured as bundle interface.
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 bundle id 1 mode on negotiation auto transceiver permit pid all ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 ipv4 address 20.20.20.1 255.255.255.0 transceiver permit pid all ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/5 ipv4 address 5.5.5.1 255.255.255.0 ! |
Dual-stack dynamic-template is configured for dual-stack initiation. “ipv6 enabled” under dual-stack template and ipv4 unnumbered
address, ipv4 urpf configured.
dynamic-template type ipsubscriber Dual_stack_IPoE accounting aaa list default type session periodic-interval 5 ipv4 verify unicast source reachable-via rx ipv4 unnumbered Loopback1 ipv6 enable ! ! |
Class-map configured for dual-stack scenario to match DHCPv6 – SOLICIT and DHCPv4 DISCOVER as sign of life packet
class-map type control subscriber match-any dual_stack_class_map match protocol dhcpv4 dhcpv6 end-class-map |
Class-map “Dual_stack_class_map “ is referred within policy-map. Even session-start is hit based on DHCPv4/DHCPv6 FSOL, template “Dual_stack_IPoE” is activated. Subscriber mac-address is used as subscriber identification and it is authorized with AAA server
policy-map type control subscriber pm-src-mac event session-start match-all class type control subscriber dual_stack_class_map do-all 1 activate dynamic-template Dual_stack_IPoE 2 authorize aaa list default identifier source-address-mac password cisco ! ! end-policy-map ! end |
Verification example
”show subscriber session all” command shows ipv4/ipv6 clients session active
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:bng#show subscriber session all Tue Jan 29 12:49:25.237 UTC Codes: IN - Initialize, CN - Connecting, CD - Connected, AC - Activated, ID - Idle, DN - Disconnecting, ED - End Type Interface State Subscriber IP Addr / Prefix LNS Address (Vrf) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- IP:DHCP BE1.10.ip22 AC 10.10.10.10 (default) 2001::2 (default)
|
Command “show subscriber session all detail” should show ipv4/ipv6 clients details detailly.
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:bng#show subscriber session all deta Tue Jan 29 12:49:27.752 UTC Interface: Bundle-Ether1.10.ip22 Circuit ID: Unknown Remote ID: Unknown Type: IP: DHCP-trigger IPv4 State: Up, Tue Jan 29 12:46:32 2013 IPv4 Address: 10.10.10.10, VRF: default IPv6 State: Up, Tue Jan 29 12:46:42 2013 IPv6 Address: 2001::2, VRF: default IPv6 Interface ID: ..d..... (02 00 64 ff fe 01 01 02) Mac Address: 0000.6401.0102 Account-Session Id: 0000001c Nas-Port: Unknown User name: 0000.6401.0102 Outer VLAN ID: 10 Subscriber Label: 0x00000055 Created: Tue Jan 29 12:46:32 2013 State: Activated Authentication: unauthenticated Access-interface: Bundle-Ether1.10 Policy Executed: policy-map type control subscriber pm-src-mac event Session-Start match-all [at Tue Jan 29 12:46:32 2013] class type control subscriber dual_stack_class_map do-all [Succeeded] 1 activate dynamic-template Dual_stack_IPoE [Succeeded] 2 authorize aaa list default [Succeeded] Session Accounting: Acct-Session-Id: 0000001c Method-list: default Accounting started: Tue Jan 29 12:46:32 2013 Interim accounting: On, interval 1 mins Last successful update: Tue Jan 29 12:48:34 2013 Next update in: 00:00:06 (dhms) Last COA request received: unavailable |
”show dhcp ipv4 proxy binding” command is going to show ipoev4 clients created with ip-address and mac-address, interface on which it is created, vrf-name etc
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:bng#show dhcp ipv4 proxy binding Tue Jan 29 12:49:42.955 UTC
Lease
MAC Address IP Address State Remaining Interface VRF Sublabel -------------- -------------- --------- --------- ------------------- --------- ----------
0000.6401.0102 10.10.10.10 BOUND 3409 BE1.10 default 0x55 |
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:bng#show dhcp ipv4 proxy binding de Tue Jan 29 12:49:49.498 UTC MAC Address: 0000.6401.0102 VRF: default Server VRF: default IP Address: 10.10.10.10 Giaddr from client: 0.0.0.0 Giaddr to server: 10.10.10.1 Server IP Address: 20.20.20.2 Server IP Address to client: 10.10.10.1 ReceivedCircuit ID: - InsertedCircuit ID: - ReceivedRemote ID: - InsertedRemote ID: - ReceivedVSISO: - InsertedVSISO: - Auth. on received relay info:FALSE Profile: IPoEv4 State: BOUND Proxy lease: 3600 secs (01:00:00) Proxy lease remaining: 3403 secs (00:56:43) Client ID: 0x00-0x00-0x64-0x01-0x01-0x02 Access Interface: Bundle-Ether1.10 Access VRF: default VLAN Id: 10 Subscriber Label: 0x55 Subscriber Interface: Bundle-Ether1.10.ip22 |
“show dhcp ipv6 server binding” is going to show ipv6 address allocated from DHCPv6 local pool
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:bng#show dhcp ipv6 server binding Tue Jan 29 12:50:04.560 UTC Summary: Total number of clients: 1 DUID : 00030001000064010102 MAC Address: 0000.6401.0102 Client Link Local: fe80::200:64ff:fe01:102 Sublabel: 0x55 IA ID: 0x0 STATE: BOUND IPv6 Address: 2001::2 (Bundle-Ether1.10) lifetime : 600 secs (00:10:00) expiration: 399 secs (00:06:39) RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:bng# |
Related Information
Configuration example and verification provided by Narendiran Rajaram
Xander Thuijs CCIE #6775
Principal Engineer ASR9000, IOS-XR and NCS6000
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
cheers that helps! it wants to send an icmp unreach with the link local address, that doesnt help, the egress ifh is available, we could morph it such that the icmpv6 will take that address instead of the ingress ifh which only has LL.
I filed CSCva77593 to fix that up.
xander
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Xander,
We're looking at rolling out a dual stack setup using the 5.3.x release. We do not control the access network (DSL/Fibre) which is provided by a 3rd party. We offer both PPPoE and IPoE setup (depending on customer type/size and the product we offer).
While investigating our options when it comes to IPv6 we've identified the following requirements:
1. We need to support both PPPoE and IPoE (we must be able to replace PPPoE (older setup) with IPoE and retain the same IP addressing)
2. We need to allocate static prefixes to subscribers (/56, /60 etc, depending on the product and subscriber type).
3. Some CPEs will require a public /128 for the "WAN" link
We use an external DHCP server for IPv4 and intend to use an external DHCPv6 server as well.
In IPv4 world in order to identify the subscribers we use the DSLAM/OLT capability to insert subscriber specific information into either PPP or DHCP packets. This all works fine for IPv4. For IPv6 it turned out to be more problematic. Since we want to use DHCPv6 we use both
ipv6 nd other-config-flag
ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
on the dynamic template. That forces the CPE to use DHCP for global link addressing and prefix delegation.
Our providers DSLAM/OLTs are not all exactly the same and some can not insert option37 into DHCPv6, what's more none of them can insert option37 when the underlying session is a PPPoE session. That poses an interesting challenge for us - DHCPv6 solicit packets that arrive from those devices have no options that would allow us to identify which subscriber they actually belong to which makes static allocation impossible.
We had a look at the number of things:
1. DHCP ipv6 proxy allows to insert remote-id or interface-id but neither of those are specific to a subscriber so we can't use them (obviously we can't use the remote one either, since it's not there)
2. Framed-Interface-Id in radius accounting is an interesting option (since the proxied DHCPv6 is sources from the same link-local address on the CPE) but it looks like that option is only added to the accounting packet (in interim-update) after the IPv6 addressing has been successfully negotiated, so we can't use it either.
3. DUID - even though it shouldn't be done we tried to extract the MAC address from the DUID to compare it with the MAC address in Access-Request, the issue here is not all CPEs use the 'WAN' MAC address and some use the type 2 DUID that is not MAC address based.
What we need is an ability to add something subscriber specific to the proxied DHCPv6 packet. In fact anything that's visible in Access-Request or Accouting-Request (if it's a start packet) would do. Since we use 'encapsulation ambiguous dot1ad any dot1q any' on the interfaces and the SVID/CVID is unique per subscriber we could use that as well.
At this stage we're willing to look at any option that would allow us to id the DHCPv6 solicit packets. I hope you can point me to something that's going to work for us.
kind regards
Pshem
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Answering my own question :-)
It's possible to correlate the DHCPv6 and radius information. The proxied packet contains the 'interface id' option (18). After looking at that value I realised it contains hex-encoded details: interface number, SVID and CVID. I've asked TAC to confirm the details and this is what they replied:
Double tagged case:
Type - SVLAN value 4 [1 byte]
Length - 6 [1 byte]
Slot [1 byte]
Port [1 byte]
outer_vlan [2 bytes]
inner_vlan [2 bytes]
Single tagged case:
Type - CVLAN value 0 [1 byte]
Length - 4 [1 byte]
vlan_id [2bytes]
slot [1 byte]
port [1 byte]
So in my case the following interface id value "040600ca0002000a" translates to
04 - double tagged
06 - length of the rest of the option
00 - slot
ca - port 202 (in our case PW-Eth202)
0002 - outer vlan 2
000a - inner vlan 10
I wouldn't mind if this was in slightly more third-party friendly format (preferably configurable in a similar fashion to the aaa options), but even encoded like this it will work. It looks like this option is added by default, but for completeness the snipped below makes sure it stays there (works for both IPoE and PPPoE):
On radius side we already use NAS-Port-Id formatted this way:
aaa attribute format NAS-PORT-ID format-string length 128 "%s-%s-%s" physical-port outer-vlan-id inner-vlan-id
so the information can be matched and I can reconstruct the original details from the PPP or DHCPv4 request.
kind regards
Pshem
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
hi phsem, very nice :)
also deepak from the bng team mentioned the following could be used also:
added support for copying the remote-id, circuit-id and username to dhcpv6 options for proxied packets. Mac-address also can be set in dhcpv6 options
#relay option remote-id pppoe -> remote-id
#relay option interface-id insert pppoe -> circuit-id
#relay option subscriber-id pppoe -> username
#relay option link-layer-address set -> mac address
Another possibility is that you can download from radius some dhcp parameters like vendor class. You could take from the access request the nas-port or some other user identifier and insert it back into the vendor class attribute on your radius server to pass some learnt subscriber info back to dhcp before it gets proxied.
xander
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
What software version allows for those options to be inserted? On our (5.3.4 pre-release) I only get this:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:mdr-tdv-b(config-dhcpv6-proxy-profile)#relay option ?
interface-id Interface Id option
remote-id Enter remote-id value
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:mdr-tdv-b(config-dhcpv6-proxy-profile)#relay option interface-id insert ?
local Insert locally generated/configured Interface ID value
received Insert received Interface ID value
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:mdr-tdv-b(config-dhcpv6-proxy-profile)#relay option remote-id ?
WORD Remote ID
Typing pppoe gives me exactly that (ie. string pppoe) as the remote-id option.
How would one add the vendor class based on radius into DHCPv6 proxy?
kind regards
Pshem
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
hi pshem, oh sorry yeah this is recent XR6 development so you wont see it in xr534.
to send a vendor class from radius you can use:
ip:dhcpv6-class=CLASSNAME
or
Cisco-Avpair += "dhcp-class=dhcpclass
xander
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
I have some issues with IPoE and IPv6 sessions. ICMPv6 from BNG to CPE (Windows 7 and Ubuntu) is working, but not in the opposite direction.
Under "show ipv6 neighbors" I can find the neighbor.
This is the debug output:
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ip_icmp_lib_io: pulse code 0 received
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ip_icmp_lib_ipv6_netio_input: code 0
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ip_icmp_lib_ipv6_netio_input: v6: Input event: code: 0
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: Async_icmp: ddc7846b
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: <ip_lib_icmpv6_send_error_msg> enter type: <1> code <0
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: ip_lib_icmp6_c_generate_error
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: Error to be generated. Recvd pak: v(60000007)/t(e0800016) src=fe80::4a35:10bb:2a39:9c92 dst=fe80::a96:adff:fe31:2774 ifh_in=8120 ifh_out=5e0
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: NxtHdr(58)
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: Trigger is an ICMPv6
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: DETERMINE_SRC ifh_in: <<CH8120>>, ifh_out: <<CH5E0>>, dst: <fe80::4a35:10bb:2a39:9c92>, vrf: <0x60000007>, tbl: <0xe0800016>type: <1>, code: <0>
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: ip_lib_icmpv6_pak_construct
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: fe80::4a35:10bb:2a39:9c92 is the target, type: <1>
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: Sending ICMP Destination Unreachable to fe80::4a35:10bb:2a39:9c92
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.861 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6-Info: Sending ICMP Destination Unreachable message (type: <1>, code: <0>, params: <0> vrf: 0x60000007, tblid: 0xe0800016) from <fe80::a96:adff:fe31:2774> to <fe80::4a35:10bb:2a39:9c92>
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.862 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: reg_intf: <1>
LC/0/0/CPU0:Mar 29 10:53:24.862 : ipv6_io[249]: ICMP6: Transmitting ipv6 packet to ingress node for ICMP unreachable generation, input ifh Bundle-Ether10.996.ip7
Config:
dhcp ipv6
profile IPoE_IPv6 server
lease 0 8 0
dns-server 2a02:27b0:3:a::abcd 2a02:27b0:3:b::abcd
address-pool IPoE_IPv6
interface Bundle-Ether10.996 server profile IPoE_IPv6
accounting aaa list BNG_SUBSCRIBER type session dual-stack-delay 30
ipv4 unnumbered Loopback10075
ipv6 nd other-config-flag
ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
ipv6 enable
ipv6 unreachables disable
dhcpv6 address-pool IPoE_IPv6
interface Bundle-Ether10.996
ipv4 point-to-point
ipv4 unnumbered Loopback10075
arp learning disable
ipv6 nd suppress-
ipv6 nd other-config-flag
ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
ipv6 address fe80::5678 link-local
ipv6 enable
service-policy type control subscriber PMAP_IPOE
encapsulation dot1q 996
initiator
initiator unclassified-source
!
initiator
IPv6 connectivity to ipv6.google.com is OK but I wonder why I am not able to ping the BNG from CPE.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
hi smail, I have the suspicion that this may be related to CSCuy17477 ASR9K/513 Windows dual stack PPPoE IPv6 layer 3 connectivity broke
if you can also capture the icmpv6 debugging to see the incoming icmp message, it may be that the ifhandles for input and or dest are not set correctly.
if you can check the incoming echo request and decode the ifhandles via
show im database ifhandle 0x40 brief (replace 40 with whatever ifhandle we are seeing) to get the intf name.
regards!
xander
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks for the info.
Based on the bug info it's related in a way.
We are running 6.1.3, so it should be fixed in our version.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
yeah if you have 613 you should be covered indeed. can you see if you can get the debug icmpv6 logs to see the incoming request and the handling thereof? I am sure this is an issue with the way the request is getting punted, not able to be processed by NETIO/icmpv6 correctly due to some interface handling. xander
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Dear all
I've configured following configuration on ASR9K:
* DS over PPPoE (+DHCPv6-PD)
* IPOE(+DHCPV6-PD)
the BNG provide 1 IPv4 and Ipv6/56 pool.
CPE is GW for IPV4 address.
CPE is using one IPv6/56 (ex: 2001::aa) from IPv6-PD provided By BNG, and any customer use one IPv6/56 (ex: 2001::ab and 2001::ac) from same IPv6 pool.
This configuration work well.
BTW, Telco, provide only one MAC@ per PPPoE/DHCP session over FTTH.
I have then few questions regarding number of MAC@ authorized:
* does CPE act as GW for IPv6 (or as a switch) or does BNG see each customer "directly" connected (seen on debug with their own IPv6 address) ?
* does each customer use their own MAC to connect to network (and not using CPE WAN MAC@):
=> for DS PPPoE: IPV4/DHCPv6
=> for DS IPOE: DHCPv4 and DHCPv6
globally, does number of MAC address configured on ONT/OLT by Telco limit number of users behind CPE?
Thanks for any answers
jp
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi,
you said that the CPE is the GW for IPv4. This means that the CPE is in routed mode and the BNG will see only one session, ergo one MAC address (from the WAN interface). Same is for IPv6.
You could use the CPE in bridge mode and with this method every user behind the CPE will have a session on the BNG. This method will use up your license and HW resources really fast but you/ISP have more control and the possibility to offer better services (e.g. more speed for admin, web filtering for the kids etc).
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
say stupid question maybe, but the address that you're pinging is reacahble in that vrf right?
also what does Loopback10075 config look like?
I think this may be a vrf case situation...
if you can see maybe remove all vrf config and see if this works in global to eliminate that aspect.
xander
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: