- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Service Providers
- Service Providers Knowledge Base
- ASR9000/XR: Understanding SNMP and troubleshooting
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on 03-25-2013 09:43 AM
Introduction
In this document we'll be discussing the SNMP architecture as it is implemented in IOS-XR. As you can read in the IOS to XR migration guide (A starting point), some of the high level differences between IOS and XR are already being highlighted.
As IOS-XR is a highly distributed operating system and is using hardware forwarding, the way that SNMP retrieves counts and responds to requests is a bit different then what you might be used to and in this article we deep dive into the architecture of stats collection, how it operates and what show commands you can use to verify the performance of your SNMP in regards to IOS-XR and specifically for the ASR9000 (though this article also applies to CRS and GSR running IOS-XR).
XR routers are highly distributed. Increasing capacity by distribution and replication does come at a cost. In any scaled design where replication or multiplication of the processing devices is used, a critical additional component is the design is the inter process communication path between the processing components
The nature for this article originated from the fact that some of our customers have seen SNMP timeouts in XR 4.2.3 and has raised a lot of questions in regards to caching, stats collection and the way SNMP operates. Hopefully with this technote we can clear up some of the confusion.
SNMP architecture in IOS-XR
This section describes the symptoms of the problem and the main issue the document resolves.
SNMP Packet flow inside the system
Depending on your configuration SNMP packets can be received in band or out of band (as per MPP definitions, see article on LPTS and MPP for more info) and after intial reception and punting to the control plane (RSP), they are handed over to NETIO. NETIO is sort of an IP INPUT process in IOS that deals with process level switching.
IF the SNMP requests are "for me" they are handed over to the SNMP-D process for evaluation of the request and dispatch to the next layer of processing.
XR SNMP Specifics
- Informs supported as of 4.1 (Inform proxy not supported)
- Full AES Encryption support in 4.1 (V3 related)
- Full IPv6 support In 4.2 (snmp engine transport)
- VRF-aware support in 3.3 (snmp engine, some MIBs already available)
- Across Cisco capability files not well supprtoed, ASR9K MIB guide developed to improve situation
- Event/expression MIB support for extendibility as in IOS
- Warm standby on snmp agent
- Management plane protection (mpp) / snmp overload control to limit impact of snmp on device
- Standards based MIB support (IETF & IEEE)
ENTITY-MIB
IF-MIB
IP MIBs support
Routing MIBs support (BGP, OSPF, ISIS, etc)
MPLS, Pseudowire, VPLS MIBs support
IEEE 802x (LAG, CFM, OAM)
SNMP performance improvements
- Asynchronous request processing / multithreading (4.2)
- Bulk processing (dedicated processing path for bulking) (4.2)
- Data Collection Manager – bulk MIB data collection and file push (4.2.0 & 4.2.1)
- Additional IPv6 / VRF aware MIB support (4.2 and after)
- Additional improvements with Async IPC and SysDB Backend infra (4.1)
- Overload Control Integration (4.0)
SNMP request processing blocked during critical event periods (i.e. OSPF convergence)
Debugability:
- Additional PDU performance monitoring support (4.2)
- MIB guide update (4.2)
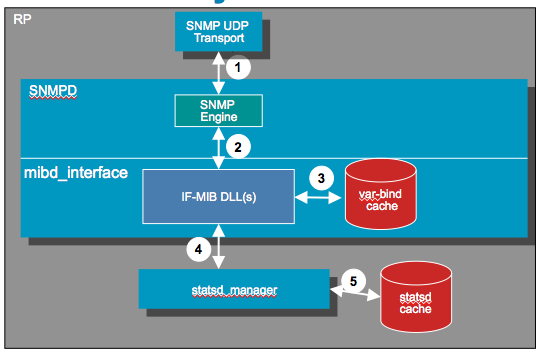
Caching
Caching is an integral part of IOS XR SNMP processing allowing it to perform at best performance while maintaining the most accurate stats possible.
There are various levels of caching and some of them are configurable, some of them are not. The reason why we cache is also to alleviate the hardware from the burden of getting continuous requests, especially in WALK scenarios retrieving many requests for eg interface stats counters.
There is a process called STATS-D which is a proc running on the linecard that periodically scrapes statistics of the linecards hardware and updates the interface counters and MIB stats.
This means that if you poll within the stats-D update time, you'd realistically see the same counter being returned twice.
Show interface commands (depending on release) will force a direct update read from hardware to get the most accurate reading, but the IF-MIB stats are cached.
Visualizing caching differently:
Two caching mechanisms:
- Statsd caching
- Lookahead caching
1: Statsd caching:
Used for interface related statistics (IF-MIB, IF-EXTENSON-MIB, etc.)
Statsd caching is configurable (via CLI).
2: Lookahead caching:
Conceptually a varbind cache.
Not configurable.
Not all MIBs leverage/use this cache.
Statsd cache:
System maintains look ahead cache:
***Data for up to 500 interfaces kept in cache
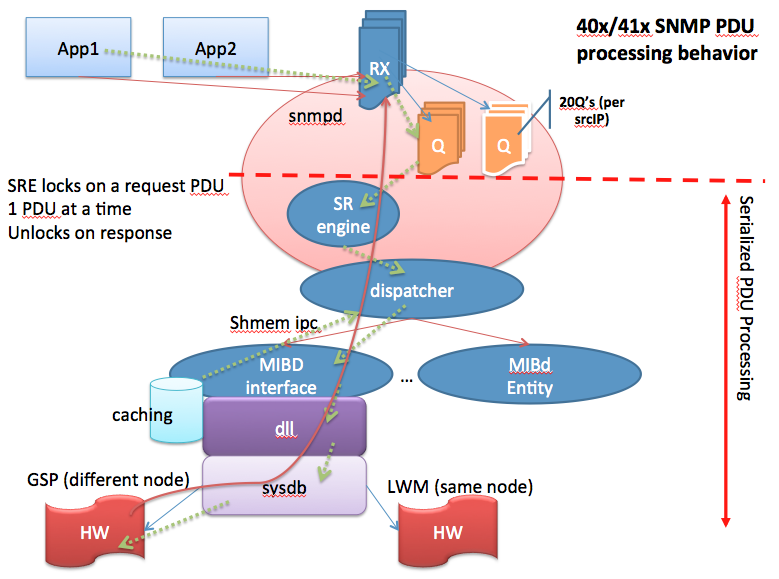
Parallel vs Serialized processing
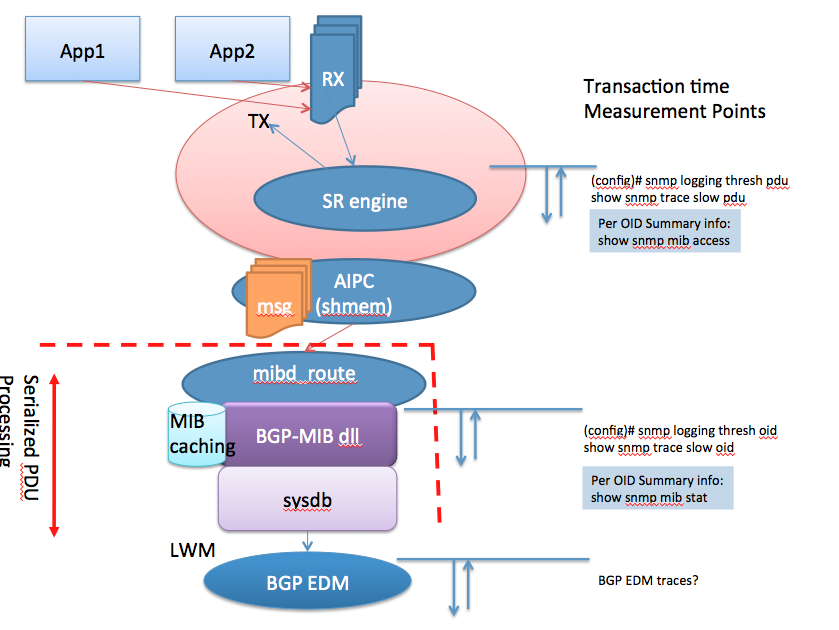
The following picture tries to explain what the serialized processing means:
When an SNMP request is being received they are handled in a sequential manner. If one request currently in progress is "slow", subsequent requests are waiting to be handled and may time out.
The NMS station may resend its SNMP request building up the request queue potentially causing more trouble.
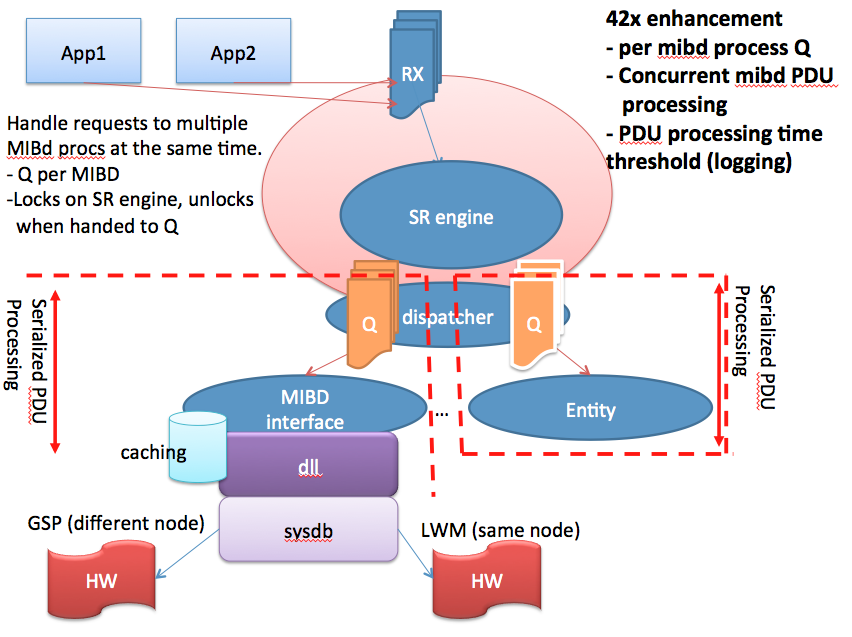
Now the good news is in 431 we have the ability to detect duplicate requests and throw them out of the queue making sure we're dealing only with "NEW" requests.
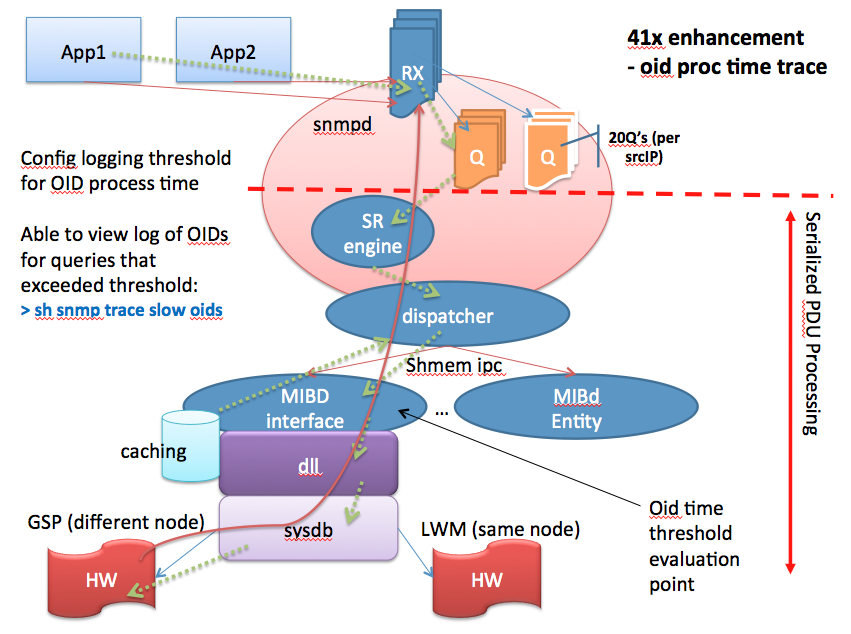
Enhancements in XR 4.1
Enhancements in XR 4.2
Example (performance) trace point logging
SNMP process architecture
- All management interfaces (SNMP, XML, CLI) utilize the same core processing architecture [sysdb].
- The SNMP processing architecture serializes PDU processing (pre-4.2).
- Request PDUs for all pollers effect the response rate seen for a single poller.
- The SNMP per-OID polling rate is very MIB specific (each MIB’s underlying data model dictates the performance of MIB’s OID access)
- MIB request processing commonly involves the GSP IPC mechanism, sysDB (data store) and statsd in some cases.
- In band and out of band SNMP requests are treated the same within SNMP.
- (In band means that the SNMP request can be received on an interface that is also transporting customer/user traffic. Out of band interfaces, such as the MGMT interfaces on the RSP are dedicated for management and carry management traffic only).
- The current SNMP architecture has an SNMP daemon enqueue requests and separate MIB daemons process requests (requests are enqueued from transport layer receive fairly quickly)
- There are multiple MIB-specific caching mechanisms in place to improve performance which also complicate the polling rate calculations.
- There is no queue size limit for SNMP requests (grows with memory).
XR processes referenced
StatsD is a process that collects statistics from various places (eg hardware) and updates tables on the LC shared memory.
IPC is an inter process call or communication that is used by processes to talk to each other to request data or send commands.
GSP is group services protocol, which is a process in IOS-XR that allows for one process to communicate with multiple "nodes" at the same time (like a sort of multicast way that the RSP can use to talk to multiple linecards, for instance to update a FIB route).
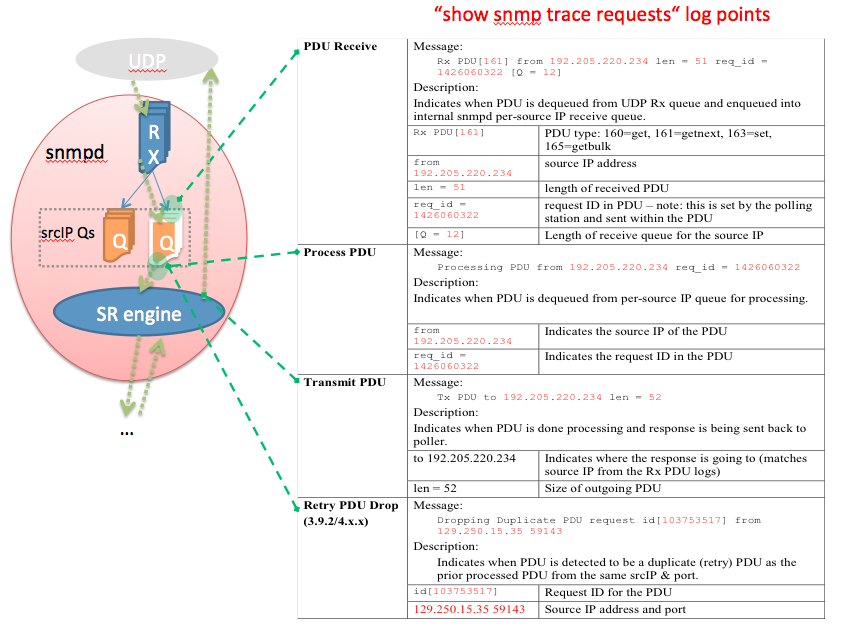
SNMP tracepoints
XR MIB implementation specifics
Troubleshooting commands and what they do
The following show and debug commands are very powerful to verify and track SNMP.
show snmp | Global agent counters—incoming, outgoing (request and trap), & error PDUs Technique: - Periodically collect output to determine overall PDU response rate and identify error rate. |
show snmp trace requests | Log of high level PDU processing tracepoints—Rx, Proc Start, Tx time Technique: Periodically collect this log. Decode and use the data to determine the following per-PDU data: 1.Source IPs of pollers 2.Queue lengths of per-source IP PDU queues 3.Types of request PDUs being used 4.Timestamp when PDUs are enqueued into the queues for the source IPs 5.Duration of the PDU enqueued & waiting to be processed 6.Processing time of PDUs from pollers |
show snmp mib access | Per-OID counters indicating the number of times an operation was done on that OID, ie. GET, GETN, SET. Technique: Periodically collecting & diff will indicate what was polled during the time periods. |
show snmp mib access time |
Per-OID timestamp of the last operation on the OID. Technique: Periodically collecting & diff will indicate if any polling on the OID was done in the time period. |
debug snmp request (careful!!!) | Enable to log every OID being processed by every PDU to syslog. Need to enable “debug snmp packet” as well to identify source of PDUs. NOTE: Disable “logging trap debug” if “snmp trap syslog” is configured!!! |
debug snmp packet (careful!!!) | Enable to log same data as “sh snmp trace requests” to syslog. NOTE: Disable “logging trap debug” if “snmp trap syslog” is configured!!! |
Show commands that are new to XR 4.2 onwards
show snmp mib statistics | Per-OID statistics summarizing transaction times within the mibd level—count + min/max/avg . Technique: Collect to determine if specific MIB objects are averaging high processing times and/or large variance (low min, high avg & max). |
show snmp queue rx | Indicates the min/max/avg queue sizes for the PDU receive and pending queues. Real-time and 5min views. |
show snmp queue trap | Indicates the min/max/avg queue sizes for the internal trap PDU queue |
(config)# snmp logging thresh oid show snmp trace slow oid | Allows configuring a duration threshold for logging per-OID transactions exceeding the time threshold. This is measured within the mibd process beginning with the call to the MIB specific handler for the OID and ending with the response from the same. |
(config)# snmp logging thresh pdu show snmp trace slow pdu |
Allows configuring a duration threshold for logging per-PDU transactions exceeding the time threshold. When logging all OIDs within the PDU are also logged to this buffer. This is measured within the snmpd process beginning with the dequeue of the PDU from the receive queue and ending when all the OIDs in the PDU have been processed and the response is ready to be sent. |
Troubleshooting PDU performance issues
Some MIBs dont have accelerated processing or dont have caching and because in certain releases SNMP is processed serially, it could happen that you'll see timeouts on OID requests that are normally operating perfectly fine. An example of a slow MIB is the SONET MIB. Because this mib needs to talk from the SNMP process all the way down to the SPA of the SIP-700 linecard (on the ASR9000), the response may not be provided in a timely manner. At the same time new requests for other OID's may be in the holding or pending queue causing timeouts and retries.
Retries to an already under performing MIB may exacerbate the overal issue.
The vast majority of PDU performance issues are related to a poller polling a specific MIB which is slow to process its OIDs.
This causes all other pollers to see some of their PDUs slowed due to queueing delays (waiting on slow MIB)
Troubleshooting Goal:
Workarounds
Use SNMP View Access Control to block access to the slow MIB tables / objects
snmp-server view MyPollView <slow MIB OID> excluded
Use ACLs to permit only “known” NMS devices/applications . In this case “known” is referring to content of requests issued from the app
Determining Internal Timeout of a MIBd
snmpd will timeout a mibd process if it has not received a response to a request for an OID/s within 10s by default.
Once in timeout state, snmpd will continue processing requests BUT it will mark the mibd as unavailable until it responds to the timed-out request.
- Getnext operations to any OIDs for MIBs in the timed out mibd will skip to the lexi-next OID owned by a different mibd process.
- Get/Set operations to any OIDs for MIBs in the timed out mibd will be responded to with a PDU error-code of “resourceUnavailable”.
Troubleshooting
(in addition to normal “slow OID” techniques):
Examples and Recommendations
For the purpose of clarification the following is an example of an snmp table. The columns (vertical) represent the instance or entity, and the rows represent the objects. In this case we have 3 instances 1, 2 and 3, and each instance has 3 objects, ifName, ifInOctets and ifMtu.
ifIndex | ifName | ifInOctets | ifMtu |
1 | Ethernet1/0 | 1234 | 1500 |
2 | POS2/0 | 512 | 500 |
3 | Serial3/0 | 235 | 600 |
The customers current snmp design is using snmpwalk. Snmpwalk works by performing a sequence of get-nexts, but on a column by column basis if the column object is specified as the starting point.
An example of a column walk specifying the ifDescr from IF-MIB
[no-sense-1 68] ~ > snmpwalk -c public 10.66.70.87 IF-MIB::ifDescr
IF-MIB::ifDescr.1 = STRING: Loopback0
IF-MIB::ifDescr.2 = STRING: Bundle-POS1
IF-MIB::ifDescr.3 = STRING: Bundle-Ether1
IF-MIB::ifDescr.4 = STRING: TenGigE1/2/0/0
IF-MIB::ifDescr.5 = STRING: TenGigE1/2/0/1
IF-MIB::ifDescr.6 = STRING: SONET0/2/0/0
IF-MIB::ifDescr.7 = STRING: SONET0/2/0/1
IF-MIB::ifDescr.8 = STRING: SONET0/2/0/2
IF-MIB::ifDescr.9 = STRING: SONET0/2/0/3
IF-MIB::ifDescr.10 = STRING: SONET0/2/0/4
<cut>
Snmpwalk can also be used to get a single object only, for instance, the object IF-MIB::ifDescr.9. It does not support the ability to specify any more than 1 object in its request. The example below shows two objects being requested, but only the first returned.
[no-sense-1 69] ~ > snmpwalk -c public 10.66.70.87 IF-MIB::ifDescr.9
IF-MIB::ifDescr.9 = STRING: SONET0/2/0/3
[12:18 - 0.31]
[no-sense-1 70] ~ > snmpwalk -c public 10.66.70.87 IF-MIB::ifDescr.9 IF-MIB::ifDescr.10
IF-MIB::ifDescr.9 = STRING: SONET0/2/0/3
[12:18 - 0.36]
For efficiency row traversal is preferred, with multiple objects requested in a single snmp transaction. This reduces unnecessary overhead on the XR system. For this reason snmpwalk is not recommended.
Examples of row traversal
The customer is currently requesting via snmpwalk the following IF-MIB objects
ifDescr
ifHCInOctets
ifHCOutOctets
ifHCInUcastPkts
ifHCOutUcastPkts
ifInNUcastPkts
ifOutNUcastPkts
ifInOctets
ifOutOctets
ifInUcastPkts
ifOutUcastPkts
The preferred method is to specify all the objects required from an instance/entity in a single command such as get-next or bulk-get. An example follows using snmpbulkget
[no-sense-1 115] ~ > snmpbulkget -v 2c -c public 10.66.70.87 IF-MIB::ifDescr IF-MIB::ifHCInOctets IF-MIB::ifHCOutOctets IF-MIB::ifHCInUcastPkts IF-MIB::ifHCOutUcastPkts IF-MIB::ifInNUcastPkts IF-MIB::ifOutNUcastPkts IF-MIB::ifInOctets IF-MIB::ifOutOctets IF-MIB::ifInUcastPkts IF-MIB::ifOutUcastPkts
IF-MIB::ifDescr.1 = STRING: Loopback0
IF-MIB::ifHCInOctets.2 = Counter64: 0
IF-MIB::ifHCOutOctets.2 = Counter64: 7116596
IF-MIB::ifHCInUcastPkts.2 = Counter64: 0
IF-MIB::ifHCOutUcastPkts.2 = Counter64: 99611
IF-MIB::ifInDiscards.2 = Counter32: 0
IF-MIB::ifOutDiscards.2 = Counter32: 0
IF-MIB::ifInOctets.2 = Counter32: 0
IF-MIB::ifOutOctets.2 = Counter32: 7116596
IF-MIB::ifInUcastPkts.2 = Counter32: 0
IF-MIB::ifOutUcastPkts.2 = Counter32: 99611
IF-MIB::ifDescr.2 = STRING: Bundle-POS1
IF-MIB::ifHCInOctets.3 = Counter64: 38796828
IF-MIB::ifHCOutOctets.3 = Counter64: 66076323
IF-MIB::ifHCInUcastPkts.3 = Counter64: 331833
IF-MIB::ifHCOutUcastPkts.3 = Counter64: 402546
IF-MIB::ifInDiscards.3 = Counter32: 0
IF-MIB::ifOutDiscards.3 = Counter32: 0
IF-MIB::ifInOctets.3 = Counter32: 38796828
IF-MIB::ifOutOctets.3 = Counter32: 66076323
IF-MIB::ifInUcastPkts.3 = Counter32: 331833
IF-MIB::ifOutUcastPkts.3 = Counter32: 402546
IF-MIB::ifDescr.3 = STRING: Bundle-Ether1
<snip>
Note above that all the objects in a row for all instances (columns) are obtained with one command. The same can be done with a get-next, however the added overhead of including the instance must be used for each instance present.
[no-sense-1 120] ~ > snmpgetnext -v 2c -c public 10.66.70.87 IF-MIB::ifDescr.1 IF-MIB::ifHCInOctets.1 IF-MIB::ifHCOutOctets.1 IF-MIB::ifHCInUcastPkts.1 IF-MIB::ifHCOutUcastPkts.1 IF-MIB::ifInNUcastPkts.1 IF-MIB::ifInOctets.1 IF-MIB::ifOutOctets.1 IF-MIB::ifInUcastPkts.1 IF-MIB::ifOutUcastPkts.1
IF-MIB::ifDescr.2 = STRING: Bundle-POS1
IF-MIB::ifHCInOctets.2 = Counter64: 0
IF-MIB::ifHCOutOctets.2 = Counter64: 7116596
IF-MIB::ifHCInUcastPkts.2 = Counter64: 0
IF-MIB::ifHCOutUcastPkts.2 = Counter64: 99611
IF-MIB::ifInDiscards.2 = Counter32: 0
IF-MIB::ifInOctets.2 = Counter32: 0
IF-MIB::ifOutOctets.2 = Counter32: 7116596
IF-MIB::ifInUcastPkts.2 = Counter32: 0
IF-MIB::ifOutUcastPkts.2 = Counter32: 99611
[13:03 - 0.35]
Although the examples are specific to IF-MIB, the same concept is relevant to all MIBs.
Timeout and Retry Setting on NMS
Timeout recommenations:
- use dynamic timeout when available
- if dynamic timeout is not available, increase timeout if more management applications are simultaneously polling the SNMP agent on asr9k. Multiply the default timeout by the number of applications that are simultaneously polling the SNMP agent on asr9k.
Retry recommendations:
- use dynamic retry when available
- if dynamic retry is not available, establish number of retries based on testing
For more details refer to IOS XR SNMP Best Practices.
Related Information
- Monitoring power supplies via SNMP, technote https://supportforums.cisco.com/docs/DOC-21667
Special thanks to the XR SNMP dev team for some of the amazing content used in this article, most notably Timothy Swanson and Leon Zachary
Xander Thuijs CCIE #6775
Principal Engineer, ASR9000
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Once again on the 'sh snmp mib statistics' COUNT field. Per Xander's reply below, "its indicative of the number of queries it had received on that mibD:". In the most simple way, what I am wondering is whether that count increments even tho there are now OIDs being excluded via "snmp-server view view_name...".
My follow up question (as I assume the answer is yes): Is there a way to determine ONLY what OIDs are actually replying to requests? After applying a quite lengthy list of OID excludes it would be nice to have some sort of verification that things are working as expected from the router POV.
Thanks again!
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Alexander
first of all, thanks for all good materials you share accross this forum.
I have a question regarding informs on XR 5.3.4 (ASR 9006)
You wrote :
XR SNMP Specifics
- Informs supported as of 4.1 (Inform proxy not supported)
but in the following link, we can see informs are not supported :
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/asr9000/software/asr9k_r5-3/sysman/configuration/guide/b-sysman-cg-53xasr9k/b-sysman-cg-53xasr9k_chapter_010011.html#con_1095024
Last point, i was able to configure this on my device
snmp-server host X.X.X.X informs version 2c public
What is the status for that ?
Thanks for your help
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
hey jerome!! thank you! :) its fun to do!
hmm that is funky and annoying, contradicting info :) I can confirm that informs are supported xr41 onwards.
funnily enough while I was checking how or why, there was a ddts request to update the documentation. which happened as seen in this doc, but it seems like your reference was not updated to reflect the proper status. I'll have it corrected.
cheers!
xander
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Xander,
In IOS-XR 5.3.x on the ASR9K, is it possible to obtain a list of all the possible traps that could get generated by enabling the various traps under "snmp-server traps x"?
I know I can obtain all the MIBs which are supported in IOS-XR and on the ASR9K - and this is a huge list, but, for example, if I was to enable the command "snmp-server traps vpls status" - how could I determine what traps that could generate?
I could probably do this myself if there was an easy way to map each of the "snmp-server traps" to a specific MIB, but it isn't always obvious which MIB a specific trap command refers to. I am trying to generate a list of all potential traps based on our configuration to allow us to review them so we can categorize them from a priority and severity perspective within our OSS system.
Thanks,
Chris
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
yikes, good question, but that is not easily available... :(
Most of the individual options under the snmp traps directly related to the respective mibs, hence it would be all the trap OID;s part of the notification section of that mib.
To be honest, I think it is always best to enable all traps and filter them out in the mgmt station those that you are not interested in. In that regard it is always best to receive too much information than too little and use the mgmt station that receives it to classify what is important for your network/services.
having said that, I am going to see if we can produce a list of items that show what traps are associated with what sub option with a bit more guidance than what it gives today.
regards
xander
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks Xander. I must admit after having spent the last few days trying to work this out, that the CLI does help in some instances, but it is inconsistent.
The following example shows the actual MIBs involved:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:Router(config)#snmp-server traps ?
bgp Enable BGP4-MIB and CISCO-BGP4-MIB traps
entity-redundancy Enable SNMP CISCO-ENTITY-REDUNDANCY-MIB traps
If only they were all like that! The ISIS option is very good indeed and allows you to enable each trap individually.
Thanks
Chris
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
yeah yeah precise that command I meant as it gives direction for some but not all.
I am checking with a few folks if we can produce a list, I'll post it out when we have got something.
cheers!
xander
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi
We're having a problem in getting values from an interface , it happened suddenly after a link flap .
When i try to get values from our snmp cacti server i got :
snmpwalk -v 2c -c xxxxxxxx <ip-address> .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.16.38
IF-MIB::ifOutOctets.38 = No Such Instance currently exists at this OID
while a week ago it was ok, we got an integer as expected.
If i run "sh snmp trace mib ifmib | inc 0_2_0_25 " having the interface Gigabitethernet 0/2/0/25 index 38 , i get :
Feb 9 10:30:12.512 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3786831# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:30:12.512 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3531706# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:30:12.512 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3776111# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:30:12.512 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3842558# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:30:12.512 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3600321# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:30:12.512 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3756815# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:30:12.919 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3694663# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:30:12.919 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3690374# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:30:26.642 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3638937# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:30:58.942 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3782601# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:35:12.994 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3754791# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:35:12.994 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3759080# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:35:12.994 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3696910# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:35:12.994 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3827674# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:35:12.994 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3788032# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:35:12.994 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3790176# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:35:13.348 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3850214# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
Feb 9 10:35:13.348 snmp/mib/ifmib/notify/error_wr 0/RSP0/CPU0 3836263# t9 TP1071: Failed to retrive counters for ifname GigabitEthernet0_2_0_25 rc: 1087180290
The data became unavalilable, but i can't figure out why.
Any hint?
thanks
Regards
Antonello
UPDATE 31/05/2018:
process restart mibd_interface location 0/RSP0/CPU0 solved the problem !
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi Xander,
I have a router with IOS-XR version 4.0.3 running. We've applied the command 'snmp-server ifmib stats cache' on it and after a while de router started to crash, I don't know if the cause of the crashing was the SNMP, but after removing the command the failure stoped and the router started running normally again.
Do you know if there is any bug's related to SNMP or caching functions on the IOS XR version 4.0.3?
Also, is there any way for me to confirm that the statistics are being collected from the cache and not real time?
I saw that all the show command's to snmp ifmib cache were implemented only on version 5.2.2, so I don't know if there is any type of consult I can make on older versions?
Thanks,
Michelle
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi xander,
SNMP v3 is not working with node ASR9K_01. CU were doing NMS migration from SNMPv2 to SNMPv3. Out of 26 router, 25 router is working fine with SNMPv3. But not this router ASR9K_01.
- Its observed that the moment we change the settings ( Migrating ) from SNMP V2 to V3 in NMS ( Ip address 192.168.15.100) end, graph is dropping down from 100% . From graph perspective, this node is down.
- At the same time, parallely, manual SNMP V3 full walk was initiated from the same NMS server CLI. It was observed that ASR9K_01 was responding without any issue. This V3 walk was running for more than 45 minutes without any drop. But during same time, GUI on same NMS graph continued to show drop.
- It appears, ASR9K_01 is functioning properly considering the above.
Do we have a conditional based debug only to debug the packet for SNMP poll,
Chassis:- 9010
Version :- 5.3.4
Thanks,
Arun
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Running IOS-XR 5.3.3. Was being polled by Solarwinds and cacti and all was fine.
We added Zabbix (to replace cacti) and the ASR9000 stopped answering everyone - cacti and solarwinds (stops answering after an hour or so).
We believe this is related to CSCve04643 since a 'process restart snmpd' fixes the problem.
What we are unable to determine is what MIB is causing it. The bug report states
"In order to understand which MIBD got blocked, "show processes blocked" and follow process of that MIBD process would help." Can someone explain how one can follow a process of what MIB is causing the issue so we can stop Zabbix from polling that MIB?
Thanks!
- « Previous
- Next »
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: