- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Switching
- Re: arp vs flooding
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-03-2018 09:47 AM - edited 03-08-2019 02:06 PM
i confuse what the diffrenrt between arp to flooding
for my understanding arp is layer 3 that use the distenation target with the ip address 255.255.255.255
and floding is layer 2 and he just flood the unicast message with destination mac address ff:ff:ff:ff
if pc or router create arp message and athe arp message get in the switch,the arp message "force" the switch to do flooding if he dont know the destination mac address or just transferor the arp message without reading it because this brodcast ?
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Labels:
-
Other Switching
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-03-2018 08:50 PM
thanks you,but i want to understand deeply for mt first question arp and flooding its diffrent think
i read when switch do flooding ,the flooding stop when he get the mac address and when arp do brodcast this message get for all the deveice in tne broadcast domain , this true ?
according to what u answered me on the secondary question when pc create arp message he send the message with destination of 255.255.255.255 to all the network the switch can not read this because he pass to all his port (except the port that get the message) and this message moved the second switch and to switch after.. until the message get all the deviece in the broadcast domain
but, if the switch do flooding ,the flooding can be stop on the second switch ( if he know the mac addres) brodcast send one message for all the deveice in one time ,flooding send messgae by steps.
according to this the arp and flooding is diffrent think .arp is protocol and flooding is operation on the switch, i write ?
thanks you :)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-03-2018 10:43 PM - edited 03-03-2018 10:54 PM
Broadcast traffic is as it is already established previously sending traffic to MAC address ffff.ffff.ffff (L2 broadcast) or to IP address 255.255.255.255 (L3 broadcast) or to subnet broadcast address (for example 192.168.0.255 for subnet 192.168.0.0/24 if default broadcast address is not changed).
In Windows hosts (I removed extra routes for simplicity):
C:\>route print
IPv4 Route Table
===========================================================================
Active Routes:
Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric
192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 On-link 192.168.1.6 291
192.168.1.6 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.6 291
192.168.1.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.6 291
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 192.168.1.6 291
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.6 291
===========================================================================
Unicast flooding is happening in situation when switch receives frame with unknown destination MAC address (switch has no MAC address present in MAC address table (CAM table) on any port). Since switch has no idea where end host with specific MAC address is located frame will be sent to all ports in the same broadcast domain except the port where the frame is received. If switch receives return traffic from host that is receiver of traffic on any of its ports switch will learn direction in which host is located and unicast flooding will stop. From that moment all traffic destined to that host will be forwarded only to the port where destination MAC address is present in CAM table.
Typical scenarios that will cause unicast flooding can be found in article below.
For more details, please read article - Unicast Flooding in Switched Campus Networks
according to this the arp and flooding is diffrent think .arp is protocol and flooding is operation on the switch, i write ?
Correct.
ARP is protocol used to resolve binding between known L3 address to its unknown L2 address.
Flooding is process typically performed by switch in which frames/packet are being sent to all ports (except the port where traffic was received) since destination host MAC address is currently not present in CAM table (for whatever the reason).
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-03-2018 09:55 AM
arp is the thing that establishes the relationship between the IP address and the mac address associated with that IP address. flooding has to do with sending something to lots of destinations.
So I would say that the difference is that arp is how you look for something and flooding is how you send something.
HTH
Rick
Rick
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-03-2018 10:29 AM
I want just underatand that when the pc create arp message and rhis message get in to the switch ,the switch do flooding or do brodcast message to all his ports
And another question
If i have pc1---sw---pc2
The two pc arp table clean
The cam table of the switch know pc 1 and pc2. Pc1 do ping to pc2 ,pc1 create arp message because his arp table his clean,the arp get in the switch ,the switch do flooding or just pass the arp message to the port that connect the pc2 because he know in his cam table who is pc2 and what his mac addres ?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-03-2018 03:22 PM
I think it may be helpful to clarify that we are talking about traditional switching which is the behavior of layer 2 switches (and of layer 3 switches when ip routing is not enabled). A layer 3 switch with routing enabled would act differently because it can act based on the layer 3 information in the frame .
When the PC creates an arp request it is sent as a local broadcast (the destination mac address is a broadcast address). When that arp request gets to the switch then the switch sends a copy of the frame to every port in the local vlan/local subnet (except for the port on which it was received).
In your second question the switch can not just forward the frame to pc 2. The switch does know the mac address of pc 2. But the switch does not know the IP address of pc 2 and therefore does not know that pc 2 is the one that should receive the arp request. Also remember that the arp request from pc 1 does not have pc 2 as the destination address. An arp request is addressed to every host in the local vlan.
HTH
Rick
Rick
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-03-2018 08:50 PM
thanks you,but i want to understand deeply for mt first question arp and flooding its diffrent think
i read when switch do flooding ,the flooding stop when he get the mac address and when arp do brodcast this message get for all the deveice in tne broadcast domain , this true ?
according to what u answered me on the secondary question when pc create arp message he send the message with destination of 255.255.255.255 to all the network the switch can not read this because he pass to all his port (except the port that get the message) and this message moved the second switch and to switch after.. until the message get all the deviece in the broadcast domain
but, if the switch do flooding ,the flooding can be stop on the second switch ( if he know the mac addres) brodcast send one message for all the deveice in one time ,flooding send messgae by steps.
according to this the arp and flooding is diffrent think .arp is protocol and flooding is operation on the switch, i write ?
thanks you :)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-03-2018 10:43 PM - edited 03-03-2018 10:54 PM
Broadcast traffic is as it is already established previously sending traffic to MAC address ffff.ffff.ffff (L2 broadcast) or to IP address 255.255.255.255 (L3 broadcast) or to subnet broadcast address (for example 192.168.0.255 for subnet 192.168.0.0/24 if default broadcast address is not changed).
In Windows hosts (I removed extra routes for simplicity):
C:\>route print
IPv4 Route Table
===========================================================================
Active Routes:
Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric
192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 On-link 192.168.1.6 291
192.168.1.6 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.6 291
192.168.1.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.6 291
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 192.168.1.6 291
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.6 291
===========================================================================
Unicast flooding is happening in situation when switch receives frame with unknown destination MAC address (switch has no MAC address present in MAC address table (CAM table) on any port). Since switch has no idea where end host with specific MAC address is located frame will be sent to all ports in the same broadcast domain except the port where the frame is received. If switch receives return traffic from host that is receiver of traffic on any of its ports switch will learn direction in which host is located and unicast flooding will stop. From that moment all traffic destined to that host will be forwarded only to the port where destination MAC address is present in CAM table.
Typical scenarios that will cause unicast flooding can be found in article below.
For more details, please read article - Unicast Flooding in Switched Campus Networks
according to this the arp and flooding is diffrent think .arp is protocol and flooding is operation on the switch, i write ?
Correct.
ARP is protocol used to resolve binding between known L3 address to its unknown L2 address.
Flooding is process typically performed by switch in which frames/packet are being sent to all ports (except the port where traffic was received) since destination host MAC address is currently not present in CAM table (for whatever the reason).
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-04-2018 05:23 AM
I like several things in the response from Predrag and would like to emphasize them. I hope it is helpful to recognize that broadcast messages can be layer 3 broadcast or layer 2 broadcast (which is the focus in this discussion). It is also important to recognize that with broadcast we are dealing with something where we are intentionally sending something to every device in the broadcast domain. The destination address is ALL devices. In flooding we are dealing with a unicast destination address where the destination is really a single device. If the switch receives a frame with a unicast destination it will attempt to forward to that device. Only if there is not a matching address in the mac address table will the switch flood the frame to all ports in the vlan.
So the important distinction is whether the destination address is unicast or broadcast.
HTH
Rick
Rick
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-03-2018 11:28 PM
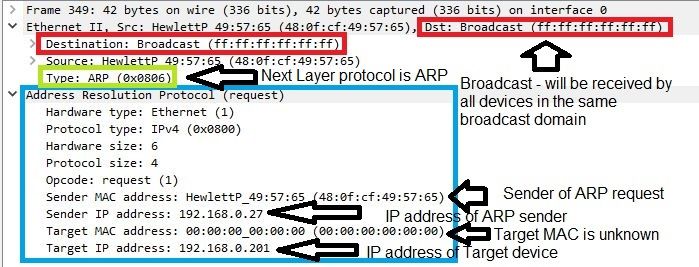
according to what u answered me on the secondary question when pc create arp message he send the message with destination of 255.255.255.255
There is no L3 header in ARP request message.
ARP message is broadcasted to L2 br0adcast address of all Fs.
Source and Destination IP addresses are present only in ARP message (as it ca be seen in capture below), but IP addresses present in ARP request are from source and destination IP addresses of devices involved in process.
Every device in broadcast domain will receive ARP and check if its IP address matches Target IP address in ARP request. Only device that matches target IP address in broadcast domain will respond to ARP message and send ARP reply informing requester about its MAC address.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-05-2018 05:13 AM
Broadcasts flood, which is what both your L3 and L2 addresses do.
PIM-DM "floods" and then prunes. Unicast flooding is what happens when a switch doesh't have a unicast MAC in its MAC table. The reason I mention these two, both don't use a broadcast address.
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: