- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Collaboration
- Collaboration Blogs
- Implementing PSTN Gateways in CUCM
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
[toc:faq]
Introduction
Recently there were few discussions in CSC on Implementing PSTN gateways in CUCM with queries related to configuration and troubleshooting. To help the users, I have decided to write this blog and provide configuration and troubleshooting steps to make the gateway implementation easy in the Service Provider (SP) network. Also I have been trying to capture all the day to day issues we face in the SP network and address the common issues in implementing the PSTN gateways in CUCM.
I have created this blog based on my work experience in implementing PSTN Gateways in the Service Providers (SP) network and I will cover the Basics, Configuration and Troubleshooting part.
Pl share your inputs and the issues you have faced in your network in the comments section and also let us know if you are looking for any further information or solution related to this topic.
To help all types of readers I will start from Basics and then I will cover the Network design, Configuration and Troubleshooting part.
PSTN Gateways in CUCM
To place external calls, Cisco Unified Communications Network (CUCM) deployment needs a connection the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). PSTN connections are provided through Gateways, which connect traditional time-division-multiplexing (TDM) telephony interface (digital T1/E1 or analog FXO port) and VOIP domains.
Gateways can be integrated in CUCM by using different protocols such as Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP), H.323 or Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for signaling on VOIP call legs.
Gateway Protocol functions for CUCM Integration
Three main signaling protocols - MGCP, H.323 and SIP provides different feature support. There are Pros and Cons in each protocol.
MGCP: Centralized dial plan configuration and Centralized gateway configuration hence it will be easy to implement in a large SP network.
H.323: Dial plan configured directly on the gateway. More specific call routing and it support third-party integration on SP network.
SIP: Dial plan configured directly on the gateway. It supports third-party telephony integration and end devices.
MGCP Gateway Considerations
A constant logical IP session (connection) must be present between the Cisco IOS MGCP gateway and CUCM. If the connection between CUCM and the MGCP gateway isunavailable, the following can happen:
- If the gateway was configured for failover (by using the ccm-manager fallback-mgcp command), the MGCP gateway can fail over to local call control mode. All active calls are dropped (no call survivability/call preservation), and a complete local dial plan must be present. Fallback-MGCP functionality is normally enabled on branch gateway routers configured with SRST in centralized call-processing architectures.Fallback-MGCP can be configured on headquarters routers as well, but this functionality is normally not present because the MGCP gateway’s CUCM group defined in the gateway’s device pool can include up to three CUCM servers to register the MGCP gateway to. Local MGCP registration failovers will not result in disconnected calls at the headquarters because of the graceful switchover feature that enables call survivability. No softkey features will be available during the duration of the survived calls, and new inbound and/or outbound calls will not work until the gateway reregisters with a CUCM server.
- If no failover configuration is present, all calls are dropped, and the PRI interface goes down.
Gateway Integration with CUCM
In this blog I will be discussing the following Gateway integration.
1) Integrating MGCP gateways with CUCM
2) Integrating H.323 gateways with CUCM
3) Integrating SIP gateways with CUCM
A gateway is a device that can translate between different types of signaling and media. One type of gateway is a voice gateway. Voice gateways are used anytime that a Cisco IP Phone communicates with TDM interface. For example, PSTN, traditional PBX, Analog phone, fax and so on.
1) Integrating MGCP gateways with CUCM
- MGCP is a plain-text protocol that call-control devices use to manage the IP telephony gateways.
- MGCP is a client/server protocol that allows the call agent (CA) to take control of a specific gateway endpoint (port).
- MGCP has the advantage of centralized gateway administration in the CUCM. CUCM controls the state of each port on the gateway endpoint .
- MGCP gateway can be controlled on a per endpoint (TDM port) level but H.323 and SIP cannot.
Note: MGCP gateway must be supported in CUCM. Use the Cisco software advisor Tool to make sure that the platform and version of Cisco IOS software or Cisco Catalyst Operating system is compatible with MGCP for CUCM.
MGCP Gateway Support:
MGCP support in CUCM includes a wide range of analog and digital interfaces that can be used ton several Cisco router and switch platforms. FXO, FXS, T1-CAS, T1-PRI, E1-CAS, E1-PRI but some voice ports are not supported by MGCP say, E&M voice ports. CUCM pushes the Cisco IOS MGCP gateway configuration from the Cisco TFTP server to the gateway when automatic configuration is configured.
CUCM also supports Q.931 backhaul. Q.931 backhaul is only supported on ISDN voice ports. MGCP backhaul allows CUCM to process the Q.931 messaging from the ISDN circuit. The gateway router encapsulates the Q.931 signaling from the gateway over TCP port 2727.
MGCP Call flow:
MGCP communication is used between the CUCM and the MGCP Gateway.
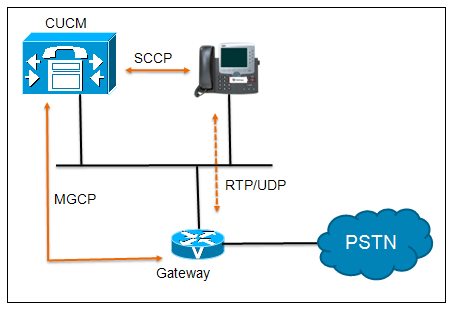
MGCP Configuration Server:
Configuration Server feature allows all MGCP configurations to be administered through the GUI in CUCM. Cisco IOS commands are downloaded automatically from the TFTP server to the MGCP gateway. Figure shows the MGCP configuration sever communication.
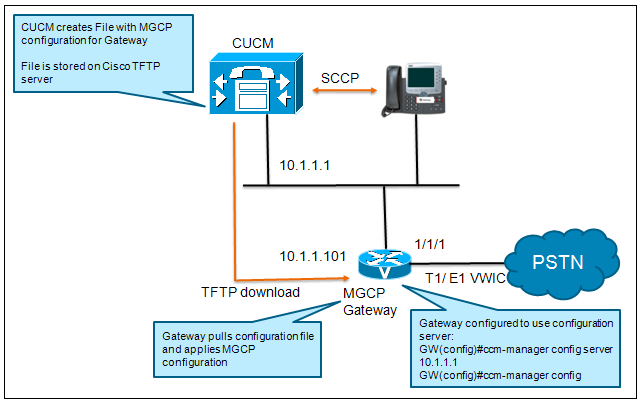
Q.931 Backhaul:
Q.931 backhaul is a reliable TCP transport layer TCP/IP connection between CUCM and Cisco MGCP gateway. Q.931 backhaul is an encapsulation of the Q.931 signaling in the D channel of the ISDN TDM interface. Q.931 backhaul carries the raw Q.931 signaling to CUCM to be processed natively. The Gateway is still responsible for the termination of the Layer 2 Q.921 Link Access Protocol D-Channel (LAPD) signaling, but all ISDN layer 3 call setup/call tear down signaling (Q.931) is sent to CUCM for processing.
1.1) MGCP Gateway Configuration: CUCM
Add an MGCP Gateway to CUCM
Step1: In CUCM Administration, Choose Device > Gateway.
Step2: Click the Add New button.
Step3: Choose the Appropriate MGCP gateway by gateway or router name
[ Gateway Type * - Cisco IAD2400/Cisco 1751/Cisco 1760/Cisco 1861/Cisco 269x/Cisco 26xx/Cisco 2801/Cisco 2811/Cisco 2821/Cisco 2821/Cisco 2851/Cisco 2901/Cisco 2811/Cisco 2821/Cisco 2851/Cisco 2901/Cisco 2911/Cisco 2921/Cisco 2951/Cisco 362x/Cisco 364x/Cisco 366x/Cisco 3725/Cisco 3745 etc)
Say in this case, Gateway Type: Cisco 2811
Step4: Click Next.
Step5: Choose MGCP from the protocol drop-down menu and click Next
| MGCP Gateway Configuration |
|---|
Sample MGCP gateway configuration displayed on the CUCM Page: Select the type of gateway you would like to add: Gateway Type Cisco 2811 Protocol * - options are MGCP / SCCP In this case for MGCP gateway, select MGCP as the Protocol |
For the detailed MGCP Gateway Configuration on CUCM with the step-by-step procedure, refer the document which I have created seperately to associate with this blog,
https://supportforums.cisco.com/docs/DOC-22421
Note: To make this blog easy to read and understand, I'vecovered all the detailed procedures in seperate document for better clarity. All the key configuration and verification procedures are covered in this blog. I've captured all the below given information from my LAB CUCM and MGCP gateway.
| Detailed MGCP Gateway Configuration |
|---|
Sample MGCP gateway configuration display from the CUCM Administration Page: Gateway Details Product: Cisco 2811 Protocol: MGCP Domain Name * : HQ-1 Description: HQ-1 headquarters MGCP gateway Cisco Unified Communications Manager Group*: Default Configured slots, VICs and Endpoints Module in Slot 0 Module in Slot 1 (To add modules refer the next section “Endpoint module configuration” Product specific configuration layout Global ISDN Switch type: 4ESS Switchback Timing* Graceful Type of DTMF Relay* Current GW config Modem Passthrough* Enable |
| MGCP Endpoint configuration |
|---|
Sample MGCP Endpoint configuration, from the CUCM administration page Device Information Product: Cisco MGCP E1 Port Gateway: HQ-1 Device Protocol: Digital Access PRI End Port Name* S0/SU1/DS1-0@HQ-1 Description S0/SU1/DS1-0@HQ-1 Device Pool* Default Location Hub_None Enable : PSTN Access Interface information PRI Protocol Type* PRI EURO QSIG Variant* No changes Protocol side* User Channel selection order* Bottom up PCM Type* A-law |
1.2) MGCP Gateway Configuration: Cisco IOS Configuration
Only the two following commands are required to configure an MGCP gateway. Assume the TFTP server IP address is 192.168.1.200
# ccm-manager config
# ccm-manager config server 192.168.1.200
| Configuring MGCP Gateway Registration |
|---|
Controller E1 0/3/0 framing crc4 linecode hdb3 pri-group timeslots 1-31 service mgcp ! Interface serial0/3/0:15 isdn switch-type primary-4ess isdn incoming-voice voice isdn bind-13 ccm-manager ! ccm-manager mgcp ccm-manager music-on-hold ! mgcp mgcp call-agent 10.1.1.1 2427 service-type mgcp version 0.1 mgcp rtp unreachable timeout 1000 action notify mgcp modem passthrough voice mode nse mgcp package-capability rtp-package mgcp package-capability sst-package mgcp package-capability pre-package no mgcp package-capability res-package no mgcp package-capability fxr-package no mgcp timer receive-rtcp mgcp sdp simple mgcp rtp payload-type g726r16 static ! |
1.3) MGCP Gateway: Registration Verification
| Verifying MGCP Gateway Registration |
|---|
Router# show ccm-manager MGCP domain name : Router Priority Status Host Primary Registered 10.16.240.124 First Backup None Second Backup None Current active Call Manager: 10.16.240.124 Backhaul/Redundant link port: 2428 Failover Interval: 30 seconds Keepalive Interval: 15 seconds Last keepalive sent: 00:45:31 (elapsed time: 00:00:04) Last MGCP traffic time: 00:45:31 (elapsed time: 00:00:04) Last failover time: None Switchback mode: Graceful MGCP fallback mode: Not selected Last MGCP Fallback start time: 00:00:00 Last MGCP Fallback end time: 00:00:00 PRI Backhaul Link info Link Protocol: TCP Remote Port Number: 2428 Remote IP Address: 10.16.240.124 Current Link State: OPEN Statistics: Packets recvd: 32 Recv failures: 0 Packets xmitted: 32 Xmit failures: 0 PRI Ports being backhauled: Slot 1, port 0 ! Configuration Auto-Download information No configurations downloaded Current State: Automatic Configuration Download feature is disabled Configuration Error History: FAX mode: cisco |
1.4) Verifying MGCP Endpoint Registration
| Verifying Endpoint Registration |
|---|
Router# show mgcp endpoints Interface T1 1/0 ! ENDPOINT-NAME V-PORT SIG-TYPE ADMIN S1/ds1-0/1@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/2@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/3@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/4@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/5@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/6@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/7@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/8@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/9@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/10@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/11@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/12@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/13@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/14@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/15@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/16@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/17@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/18@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/19@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/20@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/21@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/22@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP S1/ds1-0/23@AV-2620-4 1/0:23 none UP |
1.5) Fractional T1/E1 Configuration on MGCP Gateway
In some situations, not all time slots of a T1 or E1 connection will be used. This type of PRI is called a fractional T1 or E1, depending on what part of the world you’re in. You can specify the number of usable B channels in Cisco Unified Communications Manager by setting the Cisco CallManager service parameter Change B-Channel Maintenance Status for the individual B channels on the ISDN PRI. Five PRI endpoints can be configured to have B channels in maintenance status. The B-Channel Maintenance Status setting has no effect on the XML configuration file that is received through the MGCP configuration server. The PRI group on the Cisco IOS MGCP gateway will always allocate the maximum number of B channels that are available for a specific controller type, but CUCM will never route a phone call to one of the configured B channels because the CUCM configuration indicates that certain B channels are out of service. To configure fractional T1 or E1 on the Cisco IOS gateway, a manual gateway configuration would need to be performed that only specified the number of active time slots in the respective ds0-group (T1/E1 CAS) or pri-group (T1/E1 PRI) Cisco IOS commands.
The configuration server functionality can be disabled in the router, and the preexisting MGCP configuration received from the TFTP server will be maintained. The fractional PRI group on the corresponding T1 or E1 controller is then configured. Anytime that Cisco IOS or CUCM versions are upgraded, I recommend testing the ccm-manager config server commands in a lab environment to see whether the new versions enabled any
new MGCP commands (MGCP package capabilities and so on) that might be required for the new version of Cisco IOS and CUCM to communicate properly. It’s always best to use the automatic configuration commands unless there’s a requirement for a fractional T1 or E1. Fractional circuits are not very common anymore in North America and other technically advanced countries because of dropping circuit costs.
Note:- The maximum number of PRI group B channels that can be supported in the gateway router depends on the number of installed voice interfaces and digital signal processors (DSP). T1 and E1 interfaces share DSP resources with hardware media resources configured in CUCM (transcoding, conferencing, and media termination point).
1.6) Fractional T1/E1 Configuration on CUCM
To put specific time slots of an MGCP T1 or E1 PRI into the maintenance state, you need to retrieve the MGCP endpoint ID, example : S0/SU1/DS1-0@HQ-1 and select the Enable status Poll check box in the interface information configuration section on the MGCP endpoint configuration page.
From the CUCM Administration, choose System > Service Parameter and then choose the Cisco Call Manager Service from the Service drop-down menu. Click the Advanced button at the top of the configuration page to view hidden advanced configuration options on the MGCP gateway that are required to change the B-Channel Maintenance status parameter.
This parameter allows CUCM to change the individual B-Channel maintenance state for the time slots on the T1/E1 interface.
The following is an example of a fractional T1 interface that has four active channels with top-down channel selection order:
0000 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
1.7) Verifying T1/E1 Controller Status
Rourter # show controller e1
- E1 status should be UP.
- E1 should be Channelized E1 – balanced , 120 ohms
- No Alarms Detected.
| Verifying T1/E1 Controller status |
|---|
HQ-1 ## show controller e1
E1 7/0 is up. Applique type is Channelized E1 - balanced Description: E1 from Idea No alarms detected. alarm-trigger is not set Version info of slot 7: HW: 1032, PLD Rev: 7 Framer Version: 0x9 Manufacture Cookie Info: EEPROM Type 0x0001, EEPROM Version 0x01, Board ID 0x03, Board Hardware Version 4.8, Item Number 73-3996-05, Board Revision A1, Serial Number JAE1125M7VQ, PLD/ISP Version <unset>, Manufacture Date 24-Jun-2007. Framing is NO-CRC4, Line Code is HDB3, Clock Source is Line. Data in current interval (770 seconds elapsed): 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs Data in Interval 1: 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs Data in Interval 2: 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs Data in Interval 3: 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs Data in Interval 4: 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs Data in Interval 5: 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs |
1.8) Verifying T1/E1 Interface status
An easy way to check the operation of an MGCP controlled T1/E1 ISDN PRI interface is by using the
# show isdn-status command and checking the Layer1 and Layer2 status as demonstrated here.
| Verifying T1/E1 Interface status |
|---|
Router# show isdn status
HQ-1 # show isdn-status Global ISDN Switchtype = primary-net5 ISDN Serial 0/1/0:15 interface ds1 0, interface ISDN Switchtype = primary-net5 Layer 1 Status: ACTIVE Layer 2 Status: TEI = 0, Ces = 1, SAPI = 0, State = MULTIPLE_FRAME_ESTABLISHED Layer 3 Status: 0 Active Layer 3 Call(s) Active dsl 0 CCBs = 0 The Free Channel Mask: 0xFFFF7FFF Number of L2 Discards = 746, L2 Session ID = 4 Total Allocated ISDN CCBs = 0 |
Keep visiting the page for more updates on configuration procedures and troubleshooting steps.
Comments? Questions?
Please post your comments, feedbacks and questions to this blog post. Also if you would like to see any other article, Please feel free to share.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: