- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Collaboration
- Collaboration Knowledge Base
- Deploying a VXC 6215 endpoint with UC capabilities
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-08-2012 04:32 AM - edited 03-12-2019 09:47 AM
Introduction
In these days of virtualization, the thin client is reviving more than it ever did before. Problems may arise when people want to use voice and video communications along with it. When you're using a softphone on your desktop in the datacenter, and you call your colleague who may be physically sitting next to you, the RTP will be streamed to the Datacenter, and then back. That is not ideal as this is needlessly stressing/poluting the WAN link unneccesarily. We call this the hairpinning effect.
The VXC 6215 solves this by keeping the audio and video end to end. So not only is the 6215 a device acting as a thin client, it also operate as a phone for the user. The control of the device will come via CUPC or CUCI.
The goal of this document is to provide a single document you can follow as a recipe to deploy a series of VXC 6215's with UC capabilities. It is quite a lot of proza but we hope that because of this, it will be somewhat easier to grasp everything than by going through several technical guides where it's sometimes difficult to find where you would start. We believe this document could be a jumpstart to better understand the entire VXC 6000 series and do more advanced things with them.
If you prefer to skip all the proza and you're just looking for a technical dry run on how to deploy the UC capabilities of the VXC 6215, please go through http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/vxc/english/vxc_6215_1-0/deploy/b_6215_fw8.6_deployment_guide.html .
Restrictions
At the time of writing, the Unified Communications capabilities of the 6215 are only supported with XenDesktop and not with VMWare View.
Please review to the release notes here:
Configuration steps in brief
- Build a VDI setup with a supported Citrix XenDesktop version
- Deploy registry settings to your Virtual Desktops (HVDs)
- Install CUPC on your HVDs
- Add your VXC device(s) in CUCM and associate the user
- Assign your CUCM enduser with CUPC and CUP license capability
- Ensure the desired user is synced to CUP server
- Configure CTI Gateway server for CUPC
- Create CTI Gateway Profile and associate it with CUPC users
- Configure CCMCIP profile for CUPC
- Install UC Add-On to the VXC 6215 if still needed
- Verify
Architecture
As mentioned before, today the VXC UC capabilities on the 6215 will only work with Citrix XenDesktop. The below diagram outlines how all the different pieces are working together.
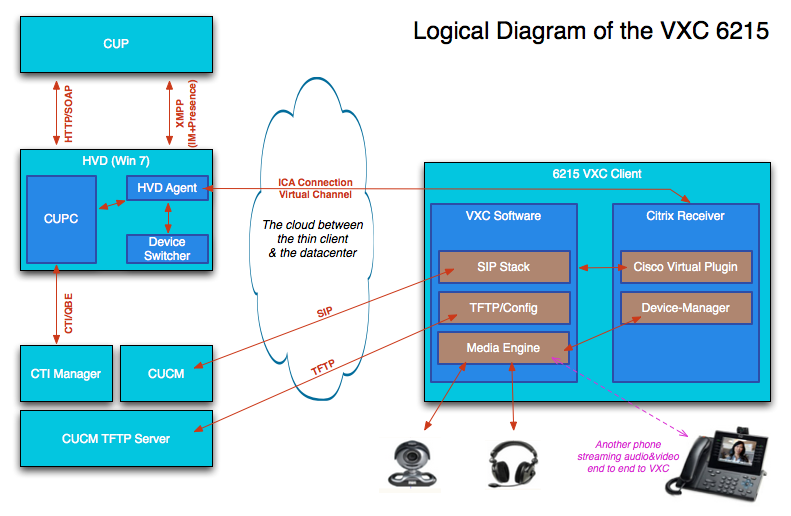
On the Hosted Virtual Desktop (HVD), eg Windows 7, you have CUPC and Citrix HVD agent running. On the thin client there's the Citrix Receiver process (which talks to HVD agent) and the VXC Software component, which talks to CUCM (using SIP). VXC enables the thin client to provide its telephony services and rich media terminiations.
CUPC connects to CUPS via SOAP/HTTPS and CUPS goes via CUCM CCMIP service to retrieve a list of associated devices to the user that is using the HVD. It picks up the VXC device (which is a specific VXC devicetype), and sends the name through the ICA virtual channel, through which the VXC component on the thin client receives it. Then it registers itself to CUCM.
In more detail: CUPC picks up the VXC device name by filtering the VXC devicetype (example: VXCdiscostu), and passes on the device name to the VXC client through the ICA virtual channel, and once the VXC client receives the device name, it registers itself to CUCM with the retrieved device name.
Once the VXC client SIP registration is good, CUCM notifies CUPC via CTIManager that the device is in service, meaning it has its own SIPStationD process on CUCM and is now capable to talk to other processes. In normal speak: it is capable of receiving and sending call setup messages to other devices such as other SIP phones, SCCP or even PSTN destinations.
Due to the nature of it being on a virtualized environment, CUPC will not try to launch itself as true softphone as we want to eliminate the hairpin effect remember. We also don't want to use it to control our deskphone(s) (although we could, but in this document we shall use the UC features on the VXC 6215 instead). If CUPC detected a registry key which tells it it's virtualized, it will try to control the VXC 6215 via CTI Manager. The effective end result is that we shall be doing desk phone control of the VXC 6215 whereas for the user it will look as if it is being used as a softphone.
The control via CTI does mean that the enduser in CUCM must have CTI Enabled rights as well.
If all is good, the user will be able to open the dial-pad and dial a number. A call will be initiated from the VXC device to another destination.
Once the call is established, the media stream goes end to end. In the diagram above, you can see that the media engine will send/receive the media.
In the tasktray at the bottom right you can find the device switcher. There you can see a list of devices attached to the thin client such as a headset or webcam. Please note that in order for the device switcher to properly work, you are required to be logged in on the thin client as 'thinuser'. Sometimes customers log on as 'admin' for quick demo's but keep in mind that you should be logged on as thinuser in order to be able and use the full capabilities this client can give you.
When going through the below configuration steps, or when troubleshooting, please keep the above way of working in mind. It will make a lot more sense then.
Enough chat about how it works, let's now proceed with the real configuration.
Configuration steps worked out
1. Build a VDI setup with a supported Citrix XenDesktop Version
As a first step, you are assumed to have built a basic Windows Guest OS and have it controlled by Citrix XenDesktop.
Once you logged onto the XenDesktop webpage, you are expected to be succesfully launching your virtual desktop. Configuration of Windows and XenDesktop is out of scope of this document.
2. Deploy registry settings to your Virtual Desktops (HVDs)
For this point and the next point you'll need to download some software from Cisco.com.
Download the CUPC installation files from Cisco.com:
You will need:
- cupc-Admin-ffr.8-6-1.zip
- cupc-Install-ffr.8-6-1.zip
One archive has the installation files for CUPC which we'll use in step 3, the other has adm and registry files which we can use to push Group Policy Objects (GPO's) through active directory for our virtual desktop environment.
As mentioned in the architecture section, CUPC will behave differently depending on it being virtualized or not. However, in order for it to know it is virtualized, you need to set a registry key:
- For 32 bit Machines [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Cisco Systems, Inc.\Virtualisation]
"VirtualisationEnabled"="true"
- For 64 bit Machines [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Cisco Systems, Inc.\Virtualisation]
"VirtualisationEnabled"="true”
Since this is a local machine setting, you can go and set this on your golden image and update the machines again, or you can push it through Active Directory (see later).
Besides the local machine setting, you also need to set a few things for the current user as well. This won't be put in your golden image as most likely your endusers will be Active Directory domain users not tied to a specific machine.
Two options exist:
a. If you're using a dedicated desktop for the specific AD user, add these registry settings manually for that specific user:
- Set HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Cisco Systems, Inc.\Client Services Framework\AdminData\DeskphoneStartupMode to 1
- Set HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Cisco Systems, Inc.\Client Services Framework\AdminData\TftpServer1 to <ip_address_of_ucm_tftp>
- Set HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Cisco Systems, Inc.\Client Services Framework\AdminData\CUPServer to <fqdn or ip_address_of_cup>
b. Push the above through AD GPO objects so it is set for every AD authenticated user that logs on to the machine:
- On Windows 2008R2, open Group Policy Management
- Right-click the OU where your HVD users reside
- Select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here...
- Once you've created the GPO object you can see it in the right pane. Right-click it and select Edit.
- Select the User Configuration> Policies > Administrative Templates and right click it to Add/Remove Templates...
- In the dialog window, select Add and fine the adm files which came with 'cupc-Admin-ffr.8-6-1.zip'
- Once you've added these, the Group Policy Management Editor will show you some additional settings under User Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Classic Administrative Templates (ADM) > Cisco Unified Client Services Framework
- Here you can set CUP Server, Deskphone Mode and Virtualization Settings. These items will set the 3 required settings as listed above, though in a different location:
- Set HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Policies\Cisco Systems, Inc.\Client Services Framework\AdminData\DeskphoneStartupMode to 1
- Set HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Policies\Cisco Systems, Inc.\Client Services Framework\AdminData\TftpServer1 to <ip_address_of_ucm_tftp>
- Set HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Policies\Cisco Systems, Inc.\Client Services Framework\AdminData\CUPServer to <fqdn or ip_address_of_cup>
To verify this is working well, logon as a domain user in the OU to an HVD and inspect the registry for above keys. If you do not see them, try and refresh using gpupdate /force .
Special note: The keys in the Policies hive, take precedence over the other ones. This means that if you have at least one of the 3 set in Policies, but not all of them, while having all 3 properly set in the first hive, things won't work. The two locations should be mutually exclusive and you should only use one of them. Not both. If you use both, then realize that the policies settings will take precedence and whatever is in the other one will be completely ignored.
3. Install CUPC on your HVDs
Once the settings in registry are properly set, now it's time to install CUPC. At installation time, it will detect is is going to be virtualized and will install the necessary extra components.
For this document we have used CUPC 8.6(1).
Depending on the CUCM version you're running, you may also have noticed that you are not able to add a VXC6215 device.
'cupc-Admin-ffr.8-6-1.zip' Also contains the COP file that is required to be installed on the CUCM to add support of VXC device type for those CUCM versions which do not come with native support of VXC device type.
Important Note: Please note that it is also required for the CUCM and TFTP servers to be rebooted after the COP file installation! Many customers do not follow this step and for each and everyone of them it has led to not-working setups.
The installation of CUPC by itself is just like any other installation. The magic happens later
If you are using a pooled catalog on XenDesktop, install it on your golden image and then update your machines using that so all of the HVD virtual machines now have CUPC installed.
After the CUPC installation, it will also install the device switcher in the HVD, and make sure that the device switcher at least is able to recognize the default sound device "HDA ATI SB Analog Stereo", this audio device is the default sound device on the VXC 6215.
4. Add your VXC device(s) in CUCM
Now comes the time to add your VXC devices to the CUCM. On CUCM, go to device > phone and click add.
Select the device type "Cisco Virtualization Experience Client (VXC 6215)", and also add minimum one line number to the device
As mentioned in step 2, if you do not have this device type, you will need to install a cop-file followed by a reboot of the CUCM and TFTP server (refer to step 2 to find the cop file).
5. Assign your CUCM enduser with CUPC and CUP license capability
On CUCM, go to System > Licensing > Capabilities Assignments. Find your enduser, and select CUP enabled and CUPC enabled.
6. Ensure the desired users are synced to CUP server
On CUP, go to User Managment > End User. Find your enduser, and make sure you can see them. If not, stop here and troubleshoot your integration. Make sure your sync services are properly started!
7. Configure CTI Gateway server for CUPC
CTI Gateway server for CUPC is to provide the desired CTI Manager server IP address and Port number in the Communications Manager cluster to CUPC for enabling desk phone control, and in this scenario, CUPC will be controlling the VXC device in Communications Manager via the CTI Manager.
On CUP, go to Application > Cisco Jabber > CTI Gateway Server, you may find an automatically created CTI Gateway Server by CUP installation, simlar to "10.67.82.15_cti_tcp_host_synced_000", it is normally your CUCM publisher server, but if this is not your desired CTI Manager server, please add a new CTI Gateway Server in this page, and then proivde the IP address of one of your subscriber servers as your designated CTI Manager for CUPC desk phone control. The port number will be 2748, and then Save. You may also want to add another CTI Gatway server to act as your backup server.
8. Create CTI Gateway Profile and associate it with your CUPC users
On CUP, go to Application > Cisco Jabber > CTI Gateway Profile. You may find an automatically created CTI Gateway Profile by CUP installation, simlar to "Default_cti_tcp_profile_synced_000", feel free to add a new one or change the default one to associate the profile with the primary and backup CTI Gateway server you configured in step 7. Then select the users in concern used earlier, and click on "Add users to profile" to associate the CTI Gateway Profile with your CUPC users.
9. Configure CCMCIP profile for CUPC
CCMCIP (Cisco IP Phone Service) running on CUCM cluster (Normally it is your publisher server) is used by CUPC to retrieve the VXC device name which is associated with the CUPC user in CUCM's end user configuration page. As you may recall from the architectural explanation, the retrieved device name will be then passed on to VXC 6215 thin client for registering the VXC device to CUCM.
On CUP, go to Application > Cisco Jabber > CCMCIP Profile, you will normally find an automatically created CCMCIP profile which is pointing to your CUCM Publisher server. Feel free to change it to your desired CUCM server ip address. Then associate this CCMCIP profile to your CUPC user(s) by selecting the users and clicking "Add users to profile".
10. Install UC Add-On to the VXC 6215 if still needed
Once you've unboxed your new VXC 6215's, they may be nothing more than just a VDI client, depending on the firmware & packages already installed. To unleash the UC capabilities, we need to have the VXC software stack installed on the VXC 6215. This goes by installing a SUSE Linux RPM.
Download the UC Add-On RPM and the update package used by VXCM to push the INI, base image and UC ADD-On RPM to thin client.
In order to push it, you can import the .rsp file into VXC Manager, then you can use the Package Distribution Wizard to deploy it.
If you're using the DHCP options method of managing your VXC devices (DHCP Options 161 and 162), then make sure your WLX.ini contains at least these lines.
Update.Preserve_changes=No
Update.Mode=Both
InstallAddOns=vxc-8.6-567.sletc11sp1.rpm
In order for the VXC client to succeed downloading this RPM and installing it, make sure the rpm is in the ADDONS directory on the fileserver, together with a file called 'directory' (no extension!), which has at least the rpm's full filename on a line by itself.
Information about DHCP Options 161 and 162: Please note that when you're using DHCP Options 161 and 162, the VXC device will pick up that path. If in option 161 you did not specify a protocol, the device will assume protocol FTP. If you would like to use HTTP, then you should prefix the protocol such as "http://". Option 162 will then specify the folder where the VXC devices should fetch their files from. The concatenated path will be used. Say for example we've set 161 to "10.48.37.163" and 162 to "Cisco", then the VXC client will connect to "ftp://10.48.37.163/Cisco/".
However, if you have previously deployed a package through VXC Manager, the VXC's settings will be pointing to the package URL. This would be something like "ftp://<server>/MYWDM/<packagename>/" . It is very important to understand this! We recommend to use 1 approach to manage your devices, else your ini files, add-ons, .. etc will be hard to manage.
To verify whether the VXC client properly installed the rpm, you can also use 2 methods:
- In VXC Manager, select the VXC 6215 device and in the bottom pane, verify "vxc" is listed in the Application Info tab.
- On the VXC 6215 itself, open the Diagnostics Log Viewer and verify you can see VxC logs in the left pane.
Verification
If you've followed all the steps correctly, you should be able to do the following:
- Start your VXC 6215 client
- Login as thinuser (by autologin)
- Browse to the XenDesktop server and login using an Active Directory domain user
- Load up the Desktop the user has access to
- On the loaded HVD, start CUPC and login using your CUCM enduser (possibly sync'd from LDAP)
- See the VXC device being registered in CUCM ccmadmin pages
- Hover the dialpad and see it light up when the mouse is on top of it
- Select it, and dial a number
If something in the above does not work, take a step back and try to find out, what the last part is that works. Move on step by step checking each step it is supposed to do, keeping the architecture in mind. Assure yourself your CUCM enduser is properly associated to the VXC device, that the registry keys are properly set, required services are started, ... etc.
Links
- http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/products/ps11976/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
- http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/products/ps11582/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Original Authors: Jeffrey Zhou (jezhou), Cedric Van Labeke (cvanlabe)
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Very helpful Document, thanks
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
"At the time of writing, the Unified Communications capabilities of the 6215 are only supported with XenDesktop and not with VMWare View." Any update info if the 6215 now support vmware view?
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: