- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Collaboration
- Collaboration Knowledge Base
- Extension Mobility Cross Cluster (EMCC) Configuration Guide
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-14-2017 04:42 PM - edited 03-12-2019 10:27 AM
Hello All,
This document describes the complete step by step configurations of Extension Mobility Cross Cluster (EMCC). This is an extended version of normal Extension Mobility.
The Cisco Extension Mobility Cross Cluster feature allows a user of one CUCM Cluster (Home Cluster) to log into an IP Phone of another CUCM cluster (Visiting Cluster).
Let's get started with the configurations of EMCC!
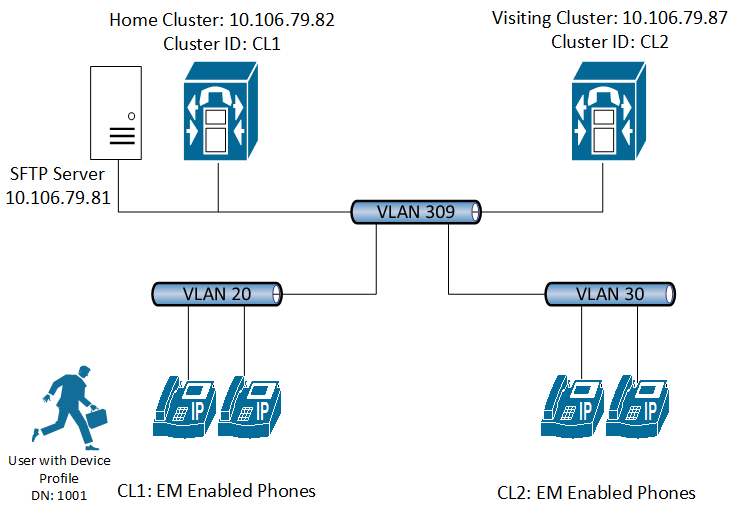
EMCC Lab Setup:
| Home Cluster CUCM IP | CL1 | 10.106.79.82 |
| Visiting Cluster CUCM IP | CL2 | 10.106.79.87 |
Lab Topology for EMCC:
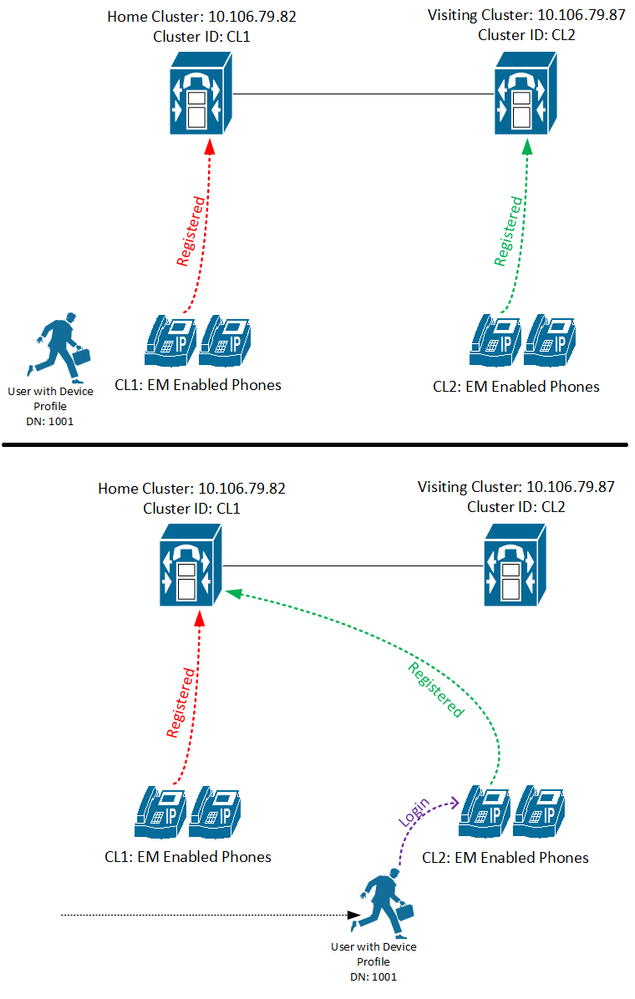
Concept of Extension Mobility Cross Cluster
When home cluster user logs in to visiting cluster phone, the remote phone gets register to home cluster.
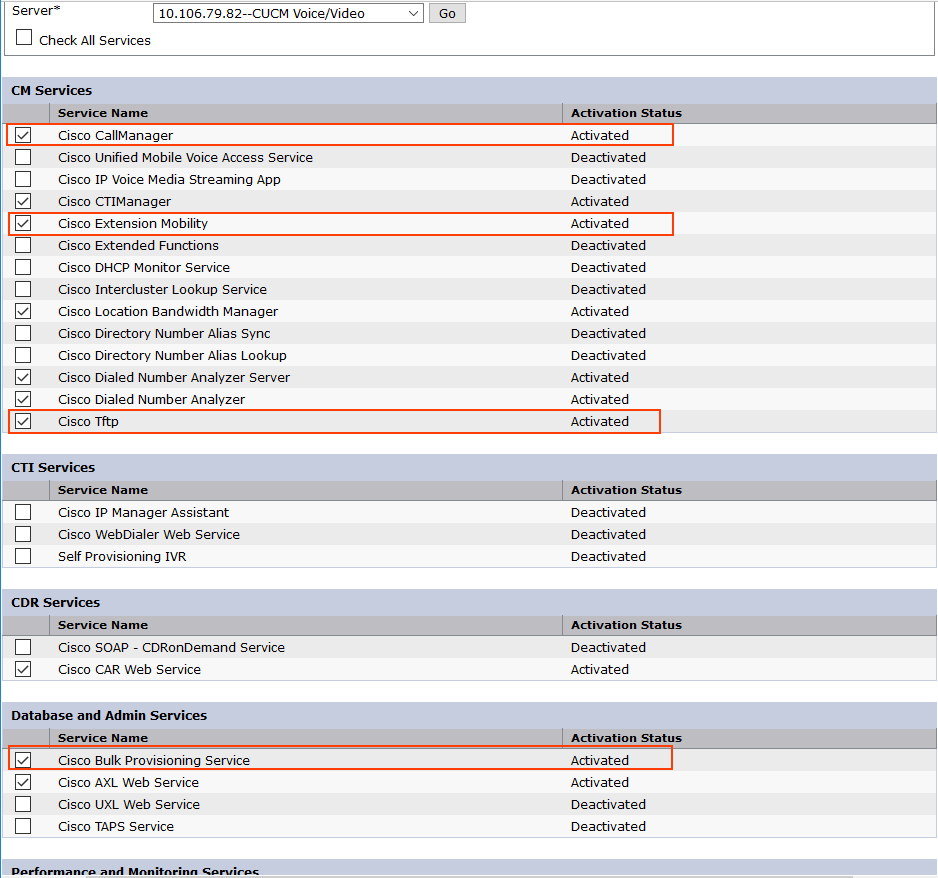
Step 1: Service Activation
Login to the CL1 CUCM Service Ability Page > Tools > Service Activation >>
[✓] Cisco Call Manager
[✓] Cisco Tftp
[✓] Cisco Extension Mobility
[✓] Bulk Provisioning Service
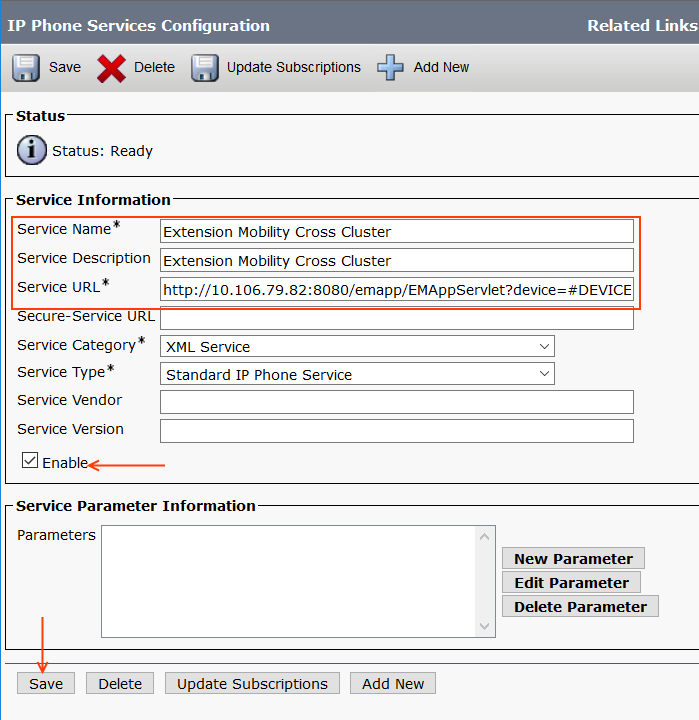
Step 2: Add Extension Mobility Cross Cluster Service
Just like Extension Mobility Service, we will have to create an IP Phone Service for EMCC.
Go to Device > Device Settings > Phone Services > Add new
- Service Name: Extension Mobility Cross Cluster
- Service Description: Extension Mobility Cross Cluster
- Service URL: http://10.106.79.82:8080/emapp/EMAppServlet?device=#DEVICENAME#&EMCC=#EMCC#
- Service Category: XML Service
- Service Type: Standard IP Phone Service
- [✓] Enable
Note: If we check the 'Enterprise Subscription', then the individual phones and device profile subscription not required.
Step 3: Device Profile Configuration
The device profile is a virtual profile which gets updated to the phone when we login via EM or EMCC. If you are running Extension Mobility on our network, this profiles likely to be there already. For the sake of lab, I'm adding a new Device Profile.
Go to Device > Device Settings > Device Profile > Add New
- Device Profile Name: UDP_ABDUL_JASEEM_1001
- Description: UDP_ABDUL_JASEEM_1001
- Phone Button Template: Standard 7962G SCCP
- Softkey Template: Standard User
- Extension Mobility Cross Cluster CSS: EMCC_DEVICE_INTERNAL_CSS
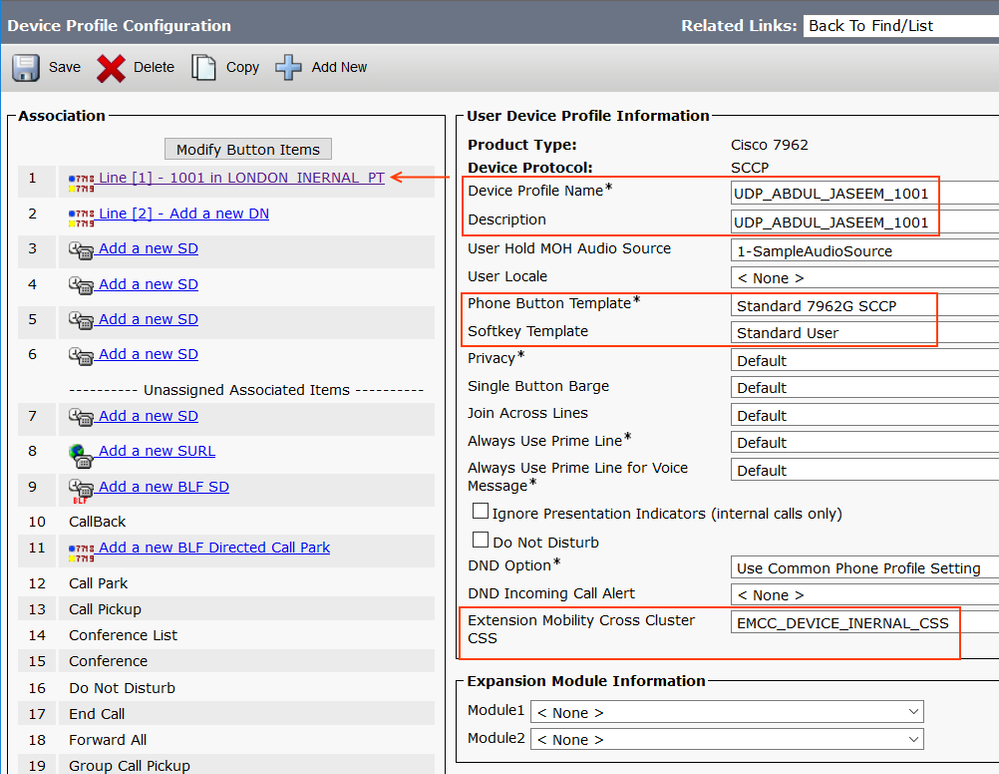
Note: The 'Extension Mobility Cross Cluster CSS' gets used as 'Device CSS' of the remote phone during EMCC login.
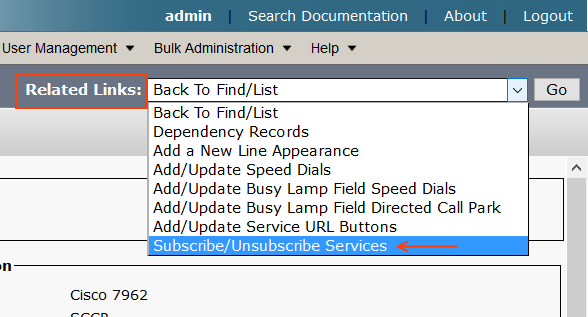
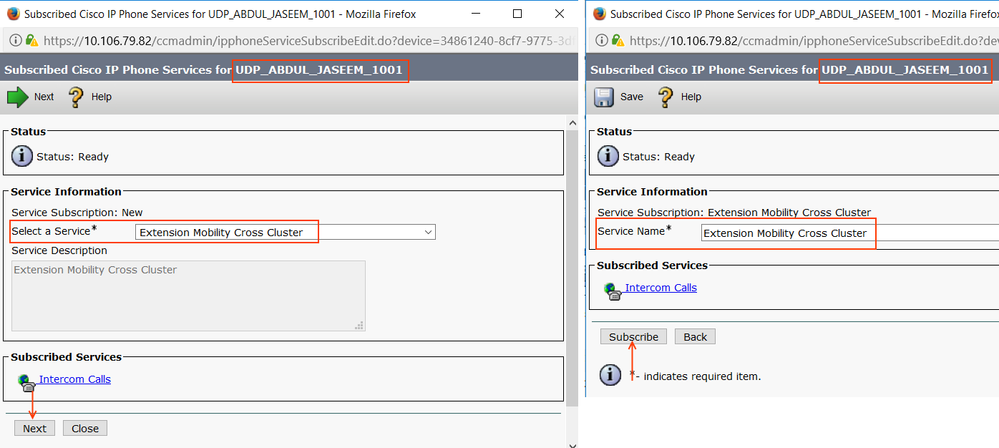
Step 4: Subscribe EMCC Service to Device Profile
Select the Device Profile > Related Links > Subscriber/ Unsubscribe > Go
Go ahead and Subscribe the Extension Mobility Cross Cluster service
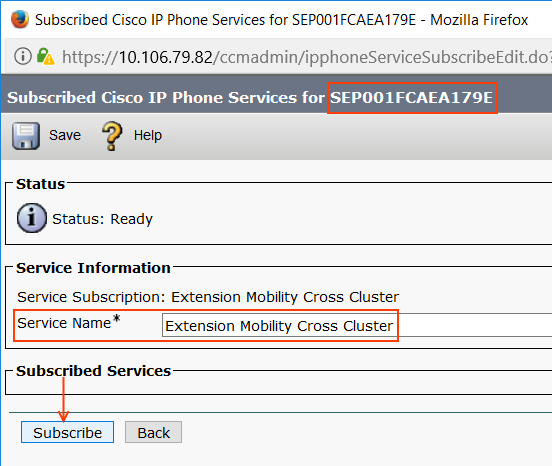
Step 5: Subscribe EMCC Service to Phone and Enable EM
Go to Device > Phone > Related Links > Subscriber/ Unsubscribe > Go
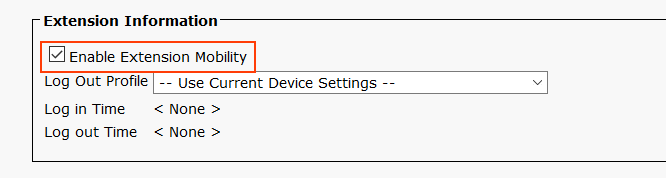
Also, check the 'Enable Extension Mobility' box on the device page.
Note: Using EMCC Service, we are able to login to any phones in the Home Cluster (Just like EM). Try logging in to any available phone in the CL1. This is to make sure the service URL is working fine.
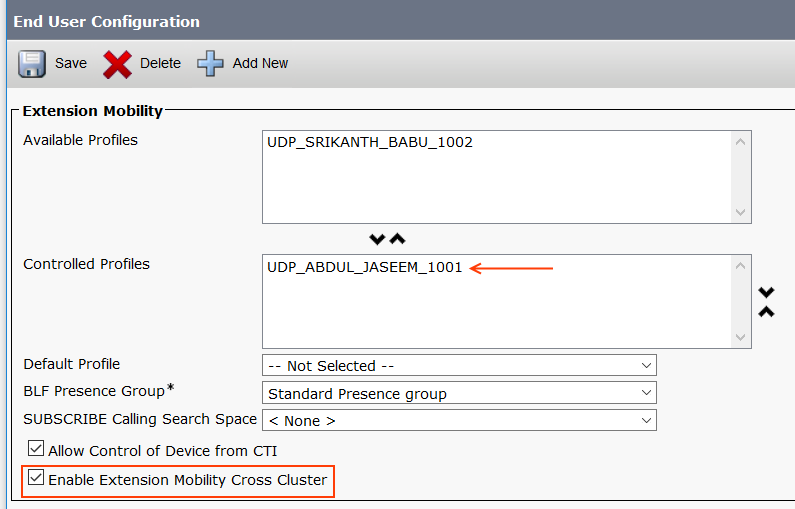
Step 6: End User Configuration
Go to User Management > End User > Find.
Select the user and set a PIN (this PIN will be used to authenticate extension mobility login).
Assign the Extension Mobility Profile to the user. Also, enable Extension Mobility Cross Clsuter check box.
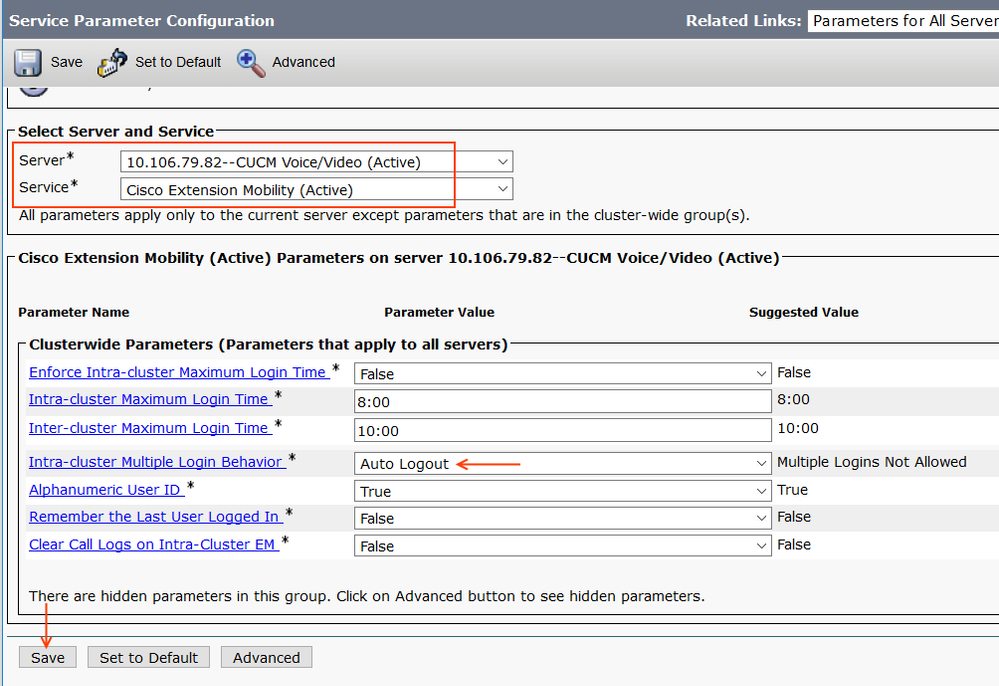
Step 7: Customize Extension Mobility Service (Optional)
Go to System > Service Parameters > Select the Server where you have activated Extension Mobility Service & select service as Cisco Extension Mobility (Active)
Intra-Cluster Multiple Login Behaviour set to Auto Logout
Step 8: Configure Visiting Cluster CL2
Perform the above Steps 1 to 7 in Visiting Cluster - CL2 as well.
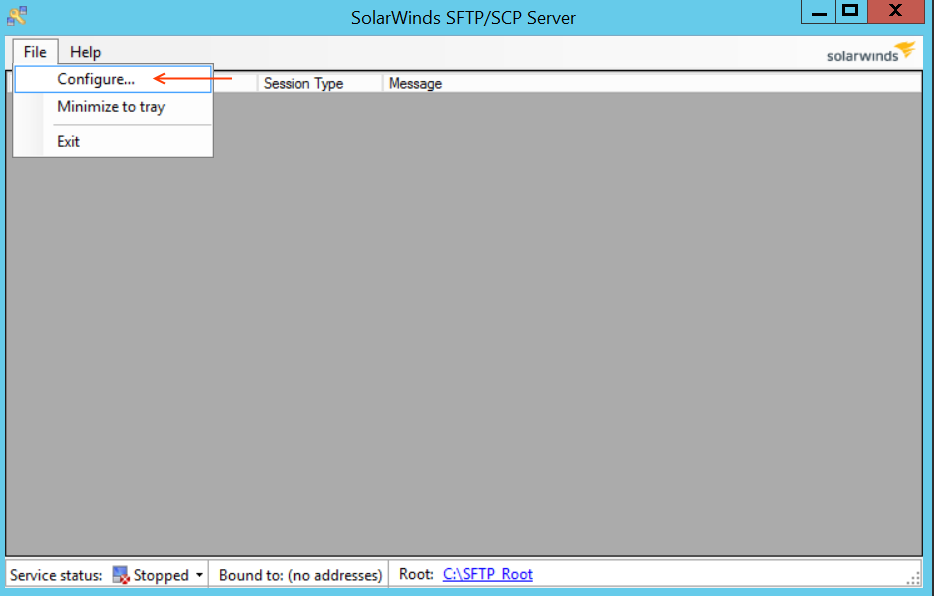
Step 9: Setup SFTP For Certificate Management
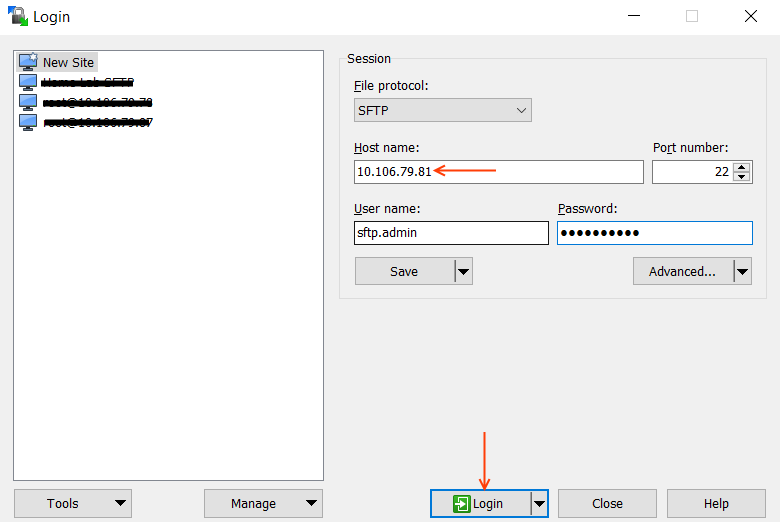
Install SolarWinds SFTP SCP Server on a Windows Machine. If you have already an SFTP Server running on your network, go ahead and use that. Please make sure this SFTP Server should be reachable from Home & Visiting Cluster.
- Download SolarWinds SFTP Server:
After installing the software, launch the application.
File > Configure
Select 'Users' tab and 'New User'. Set a username and password as shown below.
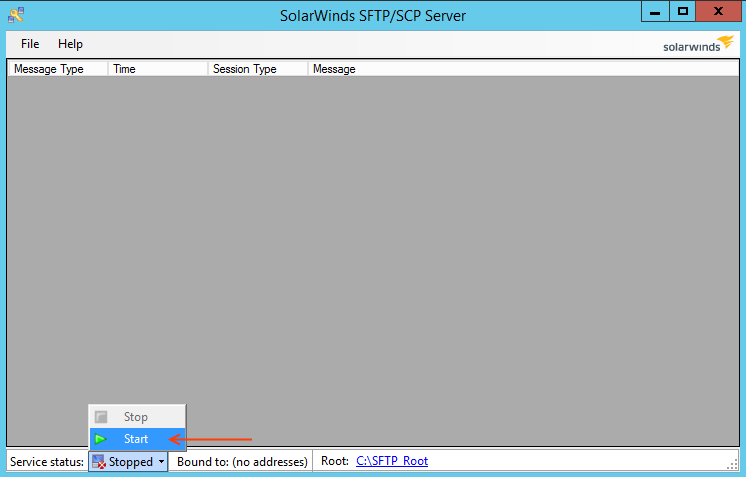
Apply Changes > OK
Go to the status bar of the application and Start the service.
Now, this is completed, in order to test the SFTP Server, use WinSCP or FileZilla and connect to the IP address of the machine where we have installed SFTP Server application.
I have used WinSCP software and I can connect successfully to the server.
Once this is ready, let's move to the Certificate Management section of EMCC configuration.
Step 10: Consolidate and Import Certificates
Trust Certificates for both clusters must be signed by a common set of security tokens in order to EMCC feature to operate.
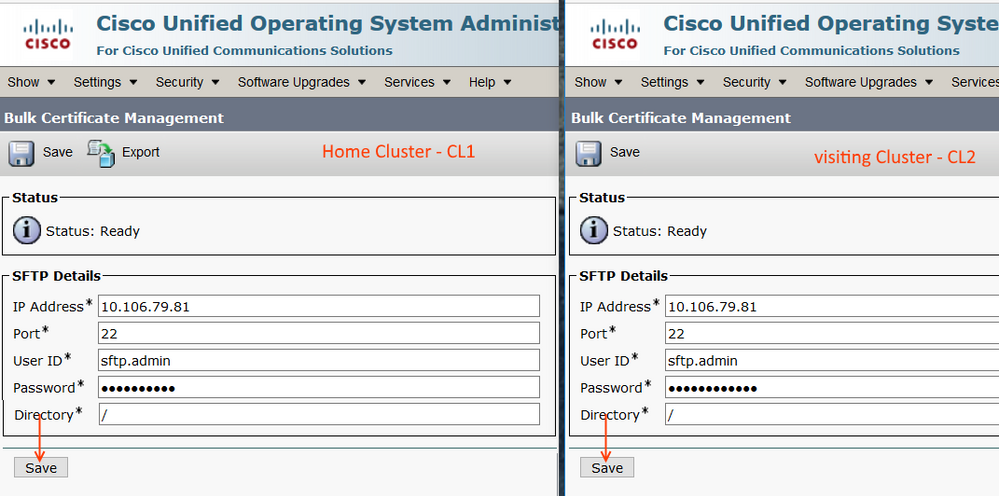
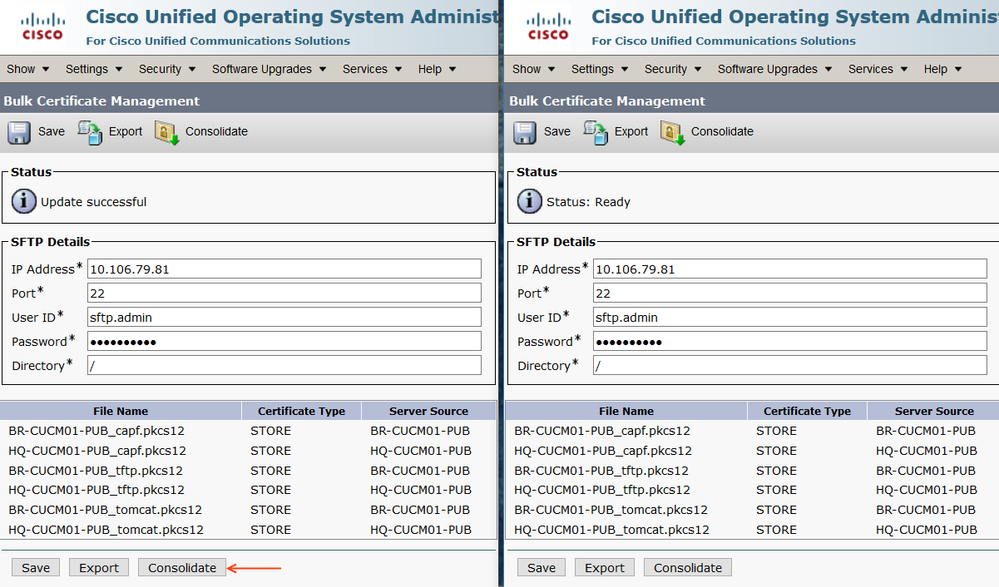
Login to OS Administration Page of Home Cluster (CL1) and Visiting cluster (CL2).
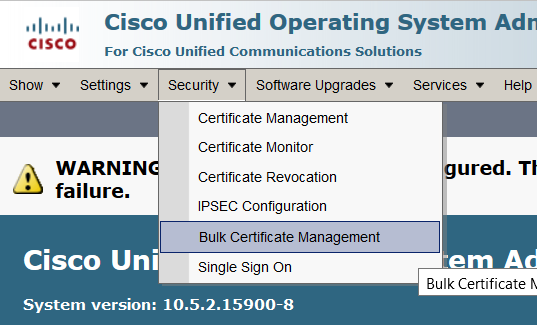
Navigate to Security > Bulk Certificate Management
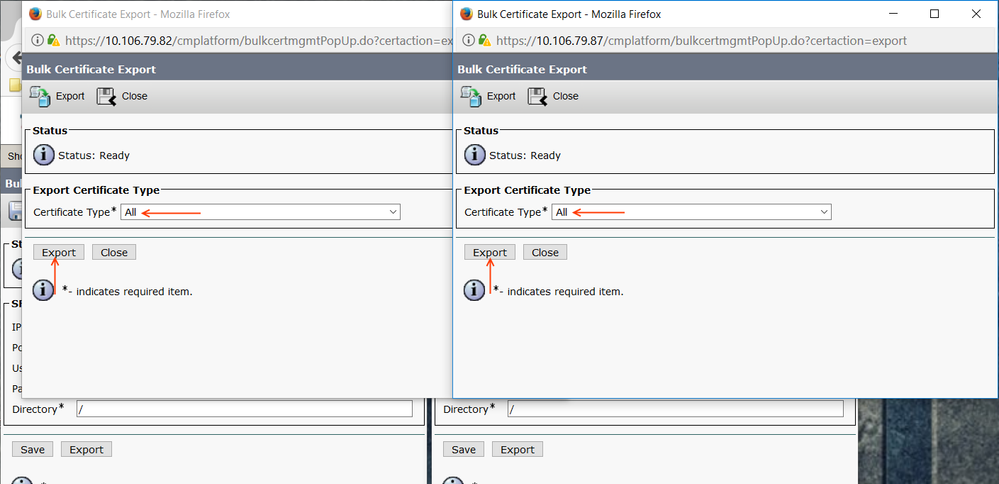
Provide the SFTP Server information (IP, user ID, Password) as shown below and Save
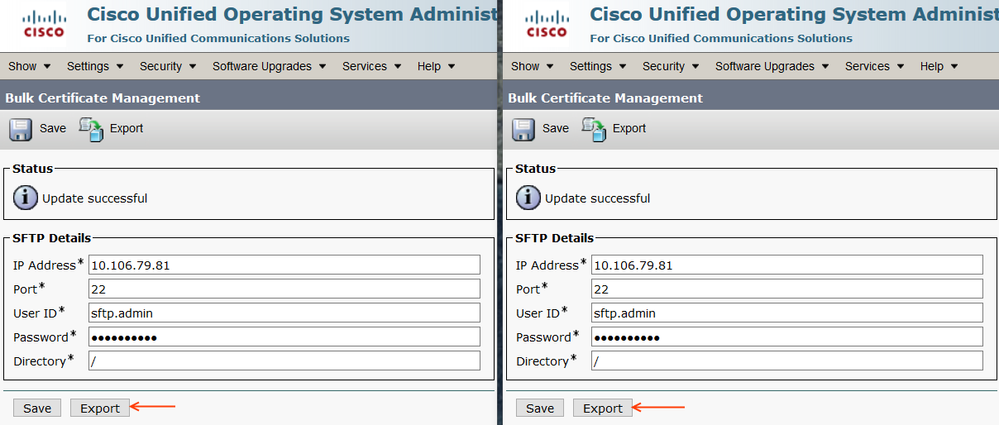
Click Export from CL1 and CL2
Certificate Type: All and proceed with Export.
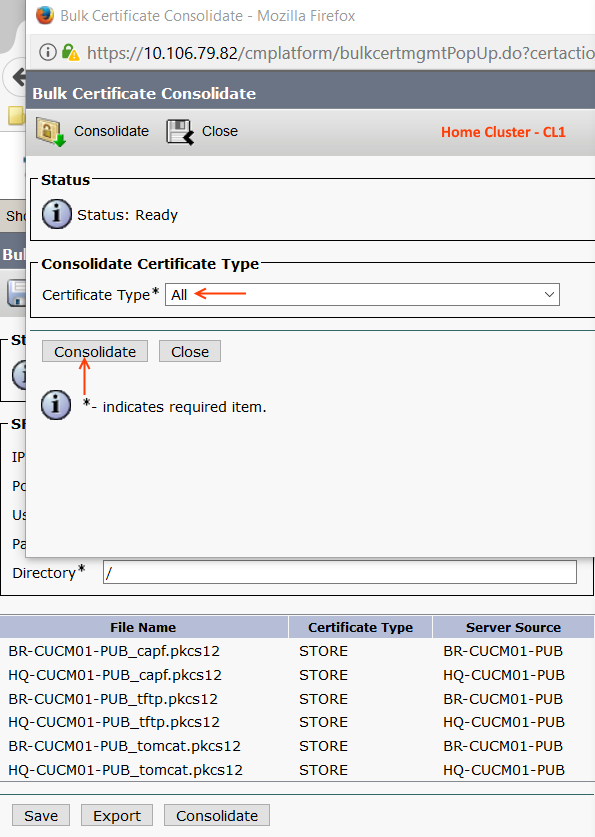
Now we have to Consolidate the certificates. (You need to perform the consolidate the certificate from any of the Cluster, no need to do it from both)
Now we have to Import the new consolidated certificate. Importing must be performed on both nodes.
Now we have successfully Imported the certificate to both clusters.!
Note: You can go to Security > Certificate Management to view the newly imported certificates.
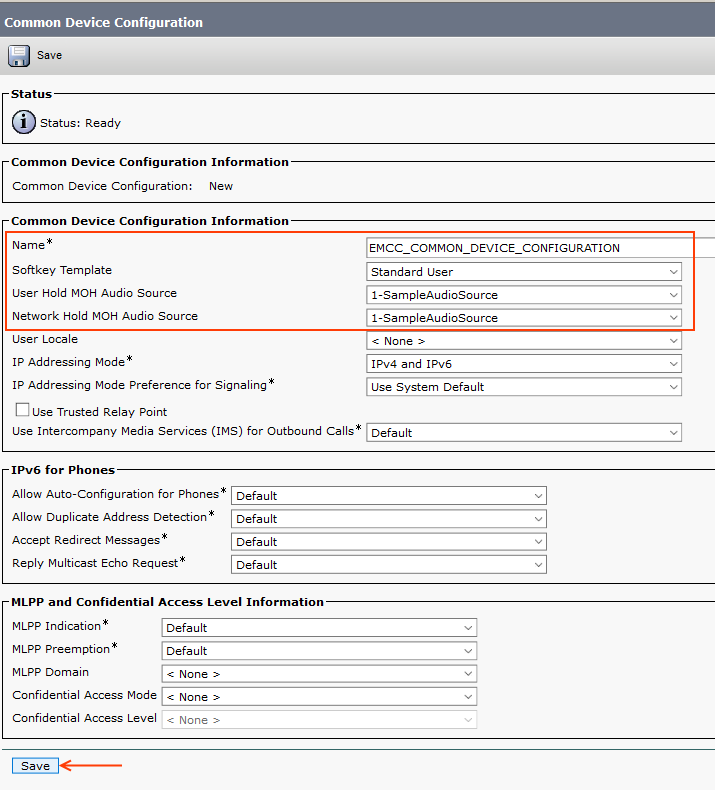
Step 11: EMCC Common Device Configuration
Common Device Configuration provides common settings for EMCC phones such as Softkey Template, MoH Audio Source, etc.
Go to Device > Device Settings > Common Device Configurations > Add New, then configure it as follows.
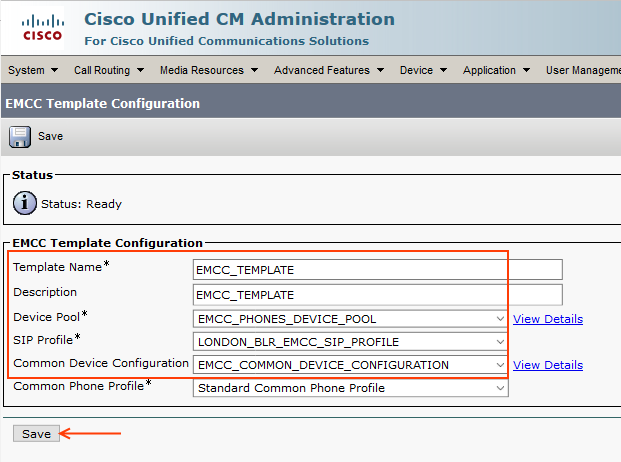
Step 12: Add EMCC Template
EMCC Template plays the role of assigning Device Pool to visiting phones.
Read my another article which describes the EMCC Device Pool Selection Mechanism
Go to Bulk Administration > EMCC > EMCC Template > Add New
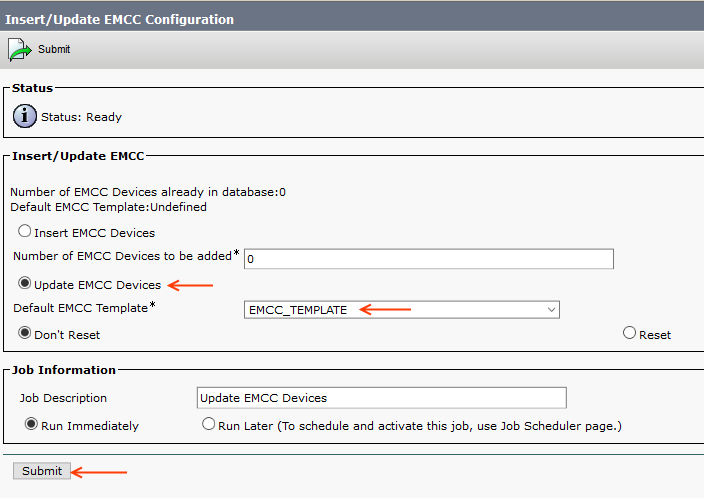
Step 13: Update EMCC
We need to update EMCC devices with the EMCC Template.
Go to Bulk Administration > EMCC > Insert/Update EMCC
Select the Update EMCC Devices radio button and EMCC Template created in Step 12, then run the job.
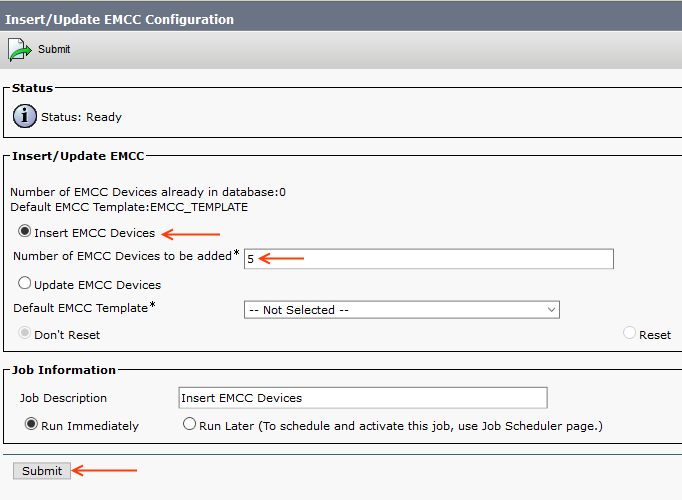
Step 14: Insert EMCC
Now we are going to insert the EMCC Virtual Devices. For this example, I'm adding 5 EMCC Devices.
Go to Bulk Administration > EMCC > Insert/Update EMCC
Select the Insert EMCC Devices radio button and enter the number of EMCC Devices, then run the BAT job.
Step 15: Configure Visiting Cluster CL2
Perform the Steps 11 - 14 in Visiting Cluster - CL2
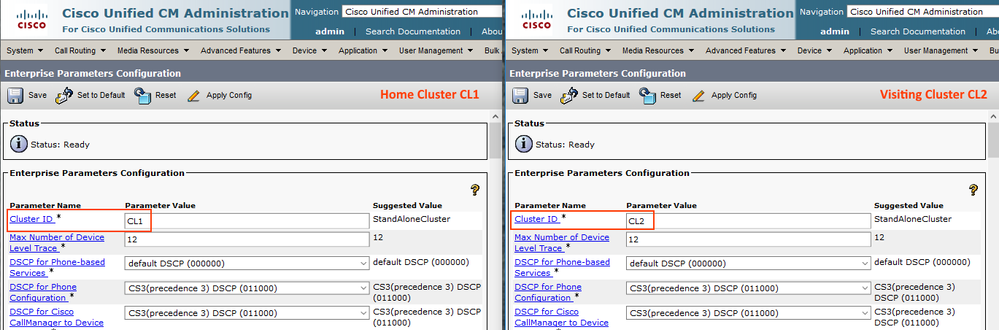
Step 16: Configure Cluster ID on both Clusters
This parameter provides a unique identifier to the cluster.
Go to System > Enterprise Parameters
Set cluster ID for both Home and Visiting clusters.
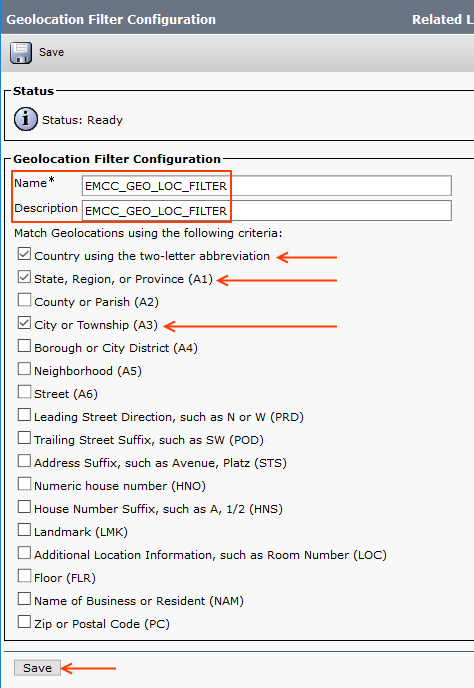
Step 17: Add Geolocation Filter
Home Cluster will consider the Geolocation of the Visiting phone using the Geolocation filter specified in the EMCC Feature Configuration. Then match the Geolocation information from the home cluster to assign specific device pool.
When this parameter is set to None, EMCC will not function correctly; phones that attempt to login but cannot be assigned to a roaming device pool will fail to log in.
Note: Since I planned to put all the visiting phones in dedicated EMCC Device Pool (Based on the EMCC Template), I haven't configured any Geolocation for the visiting phone. But Geolocation filter is mandatory to configure EMCC
Read my another article which describes the EMCC Device Pool Selection Mechanism
Go to System > Geolocation Filter > Add New, configure it as follows.
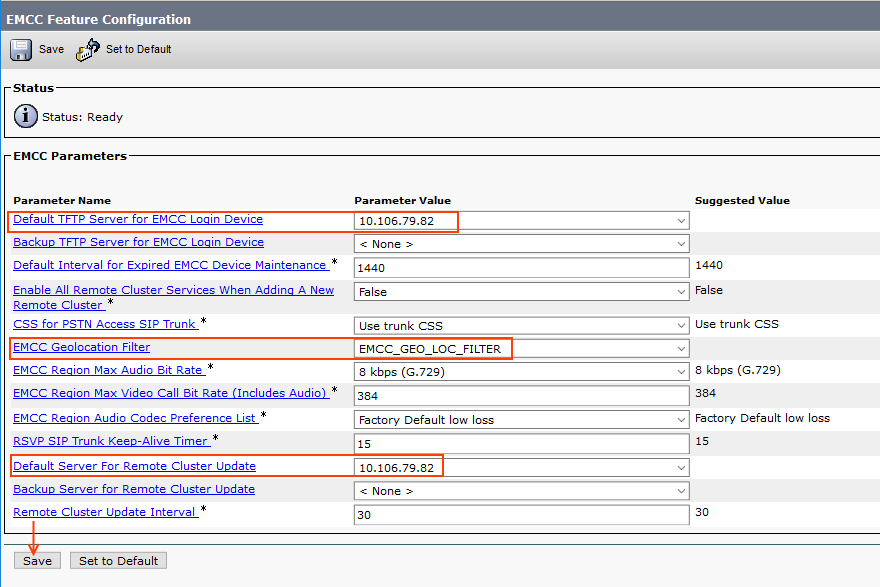
Step 18: EMCC Feature Configuration
These are the set of configurations used by EMCC.
Go to Advanced Services > EMCC > EMCC Feature Configuration
- Default TFTP Server for EMCC Login Device: [Select TFTP Server]
This should be used by the phones logging in to EMCC from a remote cluster.
- EMCC Geo Location Filter: [Select the filter created in Step 17]
- Default Server For Remote Cluster Update: [Select a node where EM Service running]
Choose the default server name or IP address of the primary Cisco Unified CM server in this local cluster that has the Cisco Extension Mobility service activated. The remote cluster will access this server to get information about this local cluster.
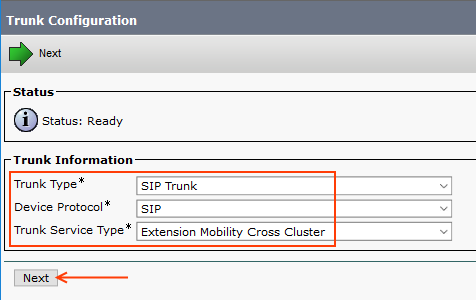
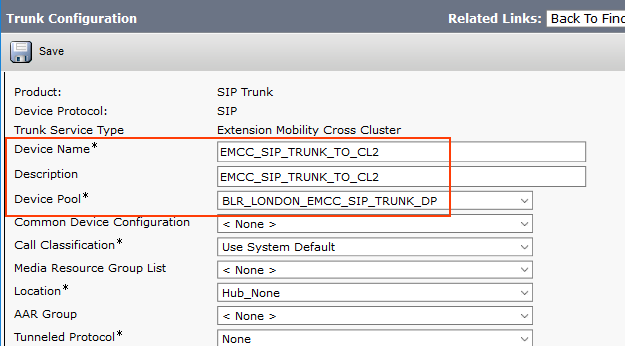
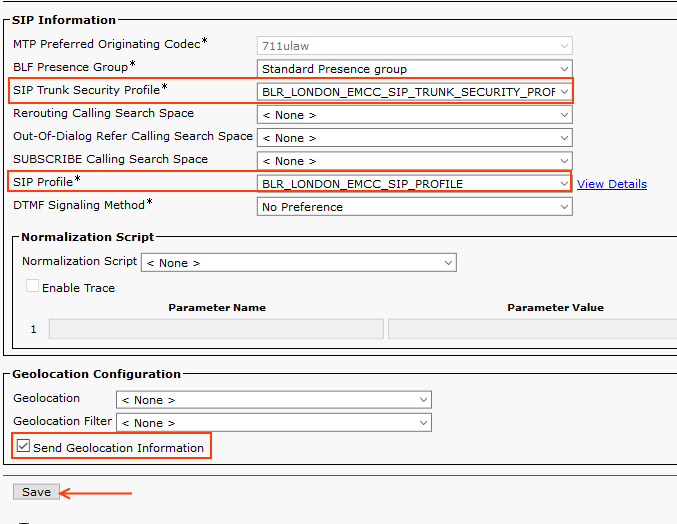
Step 19: EMCC SIP Trunk
This is used Visiting Cluster PSTN Access for emergency dialling.
Go to Device > Trunk > Add New >
> Next
configure the trunk parameters as given below,
Please reset the SIP Trunk after saving.
Note: EMCC SIP Trunk doesn't have any destination IP Address!
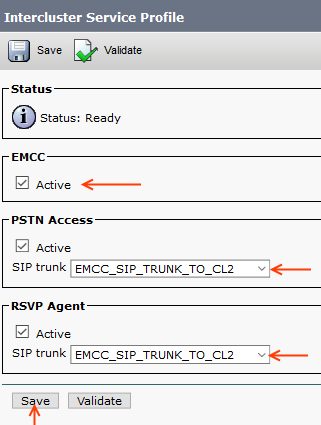
Step 20: EMCC Intercluster Service Profile
We have to enable EMCC feature in this step. Also, specify the SIP trunk for PSTN access.
Advanced Features > EMCC > Inter Cluster Service Profile > Add new
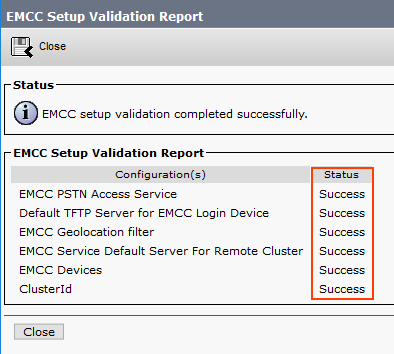
You can click Validate to see the status.
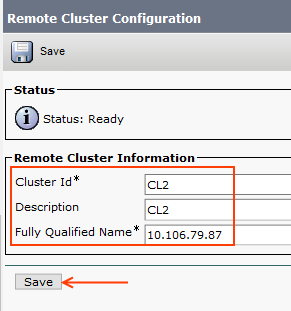
Step 21: Add Remote Cluster
At this step, we specify the remote cluster where home cluster contacts for EMCC login.
Advanced Features > Cluster View > Add New
Step 22: Configure Visiting Cluster CL2
Perform Steps 17 - 21 on Visiting Cluster CL2
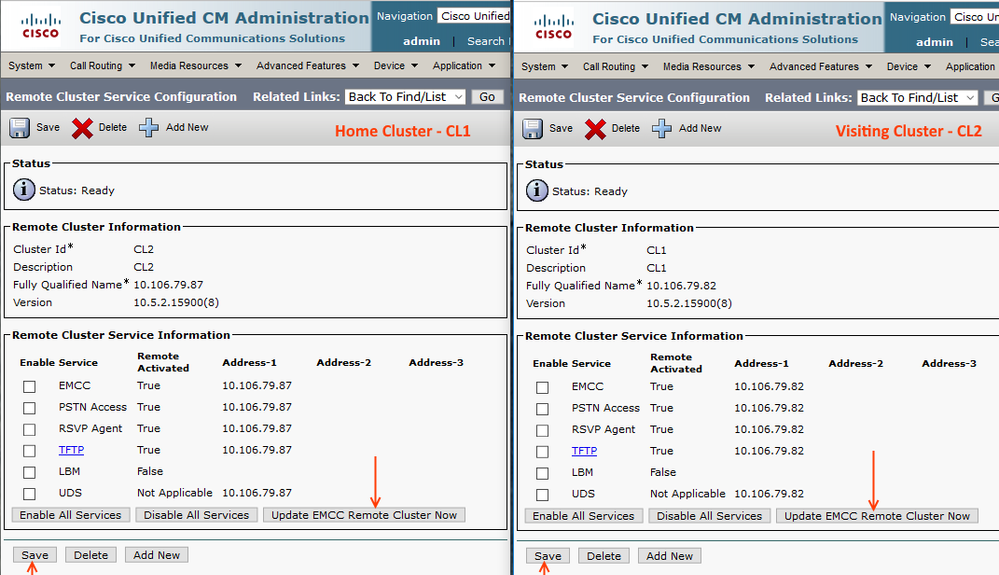
Step 23: Update EMCC Remote Cluster on both
Make sure home cluster and visiting cluster discover each other.
Advanced Features > Cluster View > Select the Remote Cluster
Perform the same on CL2
Great! We have done the EMCC Configurations successfully! Its time to test and understand the EMCC Registration.
Verify EMCC Login
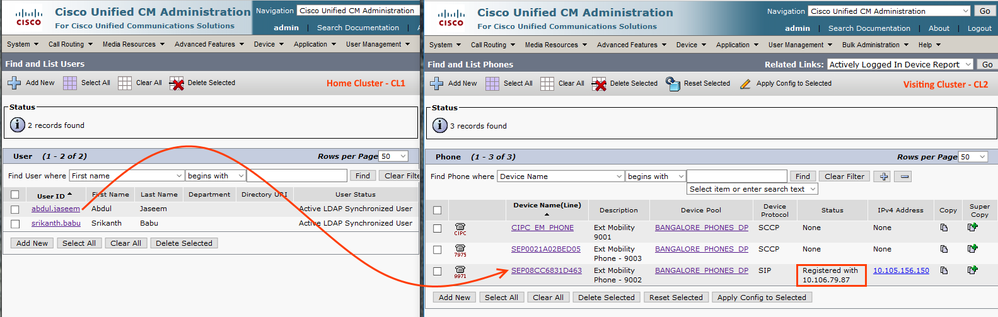
Select any of the phones in Visiting Cluster CL2.
- Press Service Button and select "Extension Mobility Cross Cluster" service. Enter the User ID and Password of the Home Cluster user.
- Enter the User ID and Password of the Home Cluster user.
[img]
- I have a home cluster user 'abdul.jaseem' trying to login to remote cluster phone which is highlighted below.
- The device on the Visiting Cluster CL2 will unregister and the same device remotely registers with Home Cluster CL1.
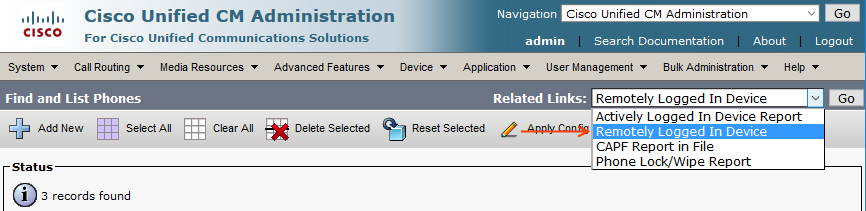
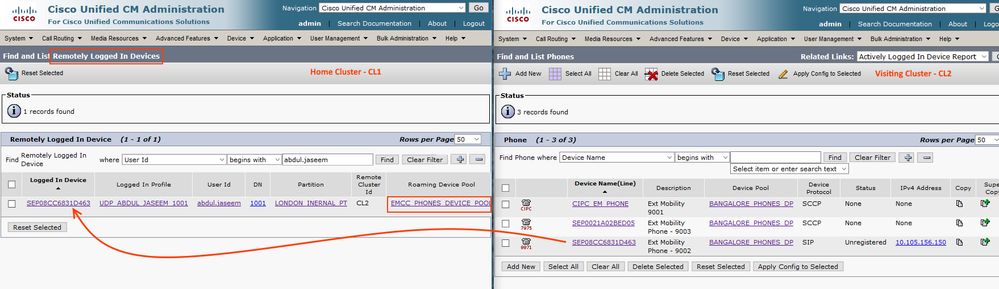
- Go to home cluster Device > Phones > Remotely Logged in Devices
- You can see that the visiting cluster phone unregister from CL2 and register to CL1
That all about Extension Mobility Cross Cluster Configuration. I will be covering detailed information about the Call Routing In EMCC Login in my next article.
You find more information about EMCC Call Routing and EMCC Error codes for troubleshooting in the below links.
Link 1: More on EMCC Call Routing
Link 2: EMCC Error Codes
Please share your thoughts here and feel free to ask doubts.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Can a jabber for windows client control users phone profile if it exists in the visiting cluster?
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hey
Nice, brief explanation.
Alex
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi there,
We have 2 clusters with multiple country/region presence in each. For example, we have a cluster that supports sites in the US and Australia (call it CL1), and another that Supports EMEA region and Bangalore (call it CL2). For this scenario, would we need to configure an EMCC SIP trunk for US to CL2, and another for Australia to CL2 so that the trunks are able to have the correct regions Device Pools (and SLRG's) configured, as per step 19?
Thanks for the above configuration guide, its been very helpful.
Regards, Sharon
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Nice detailed explanation Abdul. Thanks.
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks for this article, though it needs 1 more update.
At step 23, we need to enable the services as well.
Find answers to your questions by entering keywords or phrases in the Search bar above. New here? Use these resources to familiarize yourself with the community: