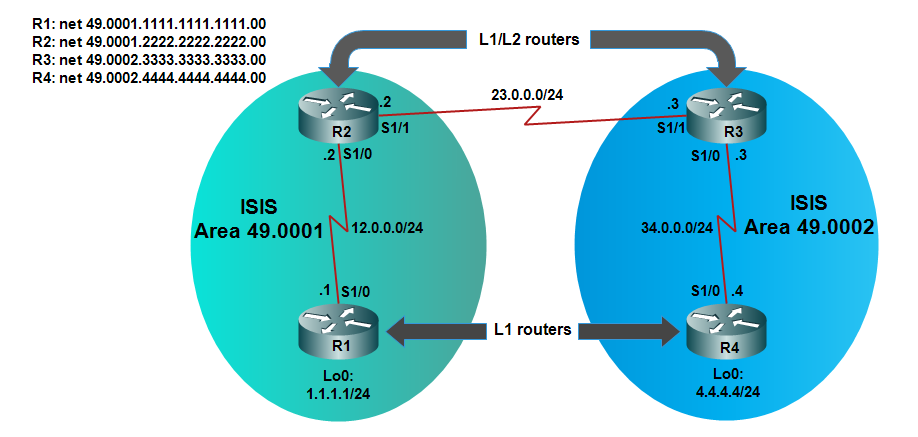
Basic configuration of all routers:
R1:
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 12.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
R2:
interface Serial1/0
ip address 12.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
!
interface Serial1/1
ip address 23.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
R3:
interface Serial1/0
ip address 34.0.0.3 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
!
interface Serial1/1
ip address 23.0.0.3 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
R4:
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 34.0.0.4 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
Let's configure ISIS:
R1 and R4 should be a L1 routers using the is-type level-1 command.
R2 and R3 will be a L1/L2 routers which the default ISIS state.
R1:
router isis
net 49.0001.1111.1111.1111.00
is-type level-1
R2:
router isis
net 49.0001.2222.2222.2222.00
R3:
router isis
net 49.0002.3333.3333.3333.00
R4:
router isis
net 49.0002.4444.4444.4444.00
is-type level-1
let's enable ISIS on all interfaces:
The neighbor relationship ISIS between R1 and R2 should be in level 1.
The neighbor relationship ISIS between R3 and R4 should be in level 1.
The neighbor relationship ISIS between R2 and R3 should be in level 2.
R1:
interface Loopback0
ip router isis
!
interface Serial1/0
ip router isis
R2:
interface Serial1/0
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-1
!
interface Serial1/1
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2
R3:
interface Serial1/0
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-1
!
interface Serial1/1
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2
R4:
interface Loopback0
ip router isis
!
interface Serial1/0
ip router isis
Let's verify the adjacencies:
As expected R2 built a L1 adjacencies with R1 and a L2 adjacencies with R3.
R2#show isis neighbors
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id
R1 L1 Se1/0 12.0.0.1 UP 29 01
R3 L2 Se1/1 23.0.0.3 UP 22 01
R2#
As expected R3 built a L1 adjacencies with R4 and a L2 adjacencies with R2:
R3#show isis neighbors
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id
R2 L2 Se1/1 23.0.0.2 UP 23 01
R4 L1 Se1/0 34.0.0.4 UP 24 01
R3#
Because R2 and R3 are configured as a L1/L2 routers, they have two Link State Databases for L1 and L2:
R2#show isis database
IS-IS Level-1 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R1.00-00 0x00000004 0x1B17 869 0/0/0
R2.00-00 * 0x00000005 0x0AAC 882 1/0/0
IS-IS Level-2 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R2.00-00 * 0x00000004 0xCA49 876 0/0/0
R3.00-00 0x00000005 0xB33D 890 0/0/0
R2#
R3#show isis database
IS-IS Level-1 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R3.00-00 * 0x00000003 0x36B9 826 1/0/0
R4.00-00 0x00000004 0x85E3 824 0/0/0
IS-IS Level-2 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R2.00-00 0x00000004 0xCA49 810 0/0/0
R3.00-00 * 0x00000005 0xB33D 828 0/0/0
R3#
Because R1 and R4 are a L1 routers only, they have one Link State Database for the L1:
Notice that R2 and R3 set the Attached Bit (ATT) in their LSPs advertised to R1 and R4 respectively and as a result they will use a default route to reach the routes learned outside their area 1 and 2 respectively:
R1#show isis database
IS-IS Level-1 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R1.00-00 * 0x00000004 0x1B17 786 0/0/0
R2.00-00 0x00000005 0x0AAC 795 1/0/0
R1#
R4#show isis database
IS-IS Level-1 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R3.00-00 0x00000003 0x36B9 741 1/0/0
R4.00-00 * 0x00000004 0x85E3 743 0/0/0
R4#
Let's check the routing tables of R1 and R4:
Both R1 and R4 are receiving a default route because the attached bit from R2 and R3 respectively and this route is installed as L1 route because they are configured as L1 routers.
R1#show ip route isis
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is 12.0.0.2 to network 0.0.0.0
i*L1 0.0.0.0/0 [115/10] via 12.0.0.2, 00:10:11, Serial1/0
R1#
R4#show ip route isis
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is 34.0.0.3 to network 0.0.0.0
i*L1 0.0.0.0/0 [115/10] via 34.0.0.3, 00:10:23, Serial1/0
R4#
Now let's verify the routing tables of the L1/L2 routers R2 and R3:
R2 learns a L1 route from R1 and two L2 routes from R3:
R2#show ip route isis
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L1 1.1.1.0 [115/20] via 12.0.0.1, 00:11:33, Serial1/0
4.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L2 4.4.4.0 [115/30] via 23.0.0.3, 00:11:15, Serial1/1
34.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L2 34.0.0.0 [115/20] via 23.0.0.3, 00:11:27, Serial1/1
R2#
R3 learns a L1 route from R4 and two L2 routes from R2:
R3#show ip route isis
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L2 1.1.1.0 [115/30] via 23.0.0.2, 00:11:37, Serial1/1
4.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L1 4.4.4.0 [115/20] via 34.0.0.4, 00:11:32, Serial1/0
12.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L2 12.0.0.0 [115/20] via 23.0.0.2, 00:11:37, Serial1/1
R3#
Let's verify the connectivity between the loopback networks:
R1#ping 4.4.4.4 source 1.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 4.4.4.4, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 1.1.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 84/108/140 ms
R1#
R4#ping 1.1.1.1 source 4.4.4.4
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 1.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 4.4.4.4
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 68/80/108 ms
R4#
